- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Skeleton of trunk
- Skull
- Skeleton of upper limb
- Skeleton of lower limb
- Joints
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
Maxillary sinus
The maxillary sinus (Latin: sinus maxillaris) is a paired air-filled cavity located within the body of the maxilla. It is the most significant paranasal sinus and appears pyramidal in shape. Both maxillary sinuses are located lateral to the nasal cavities and under the orbits.
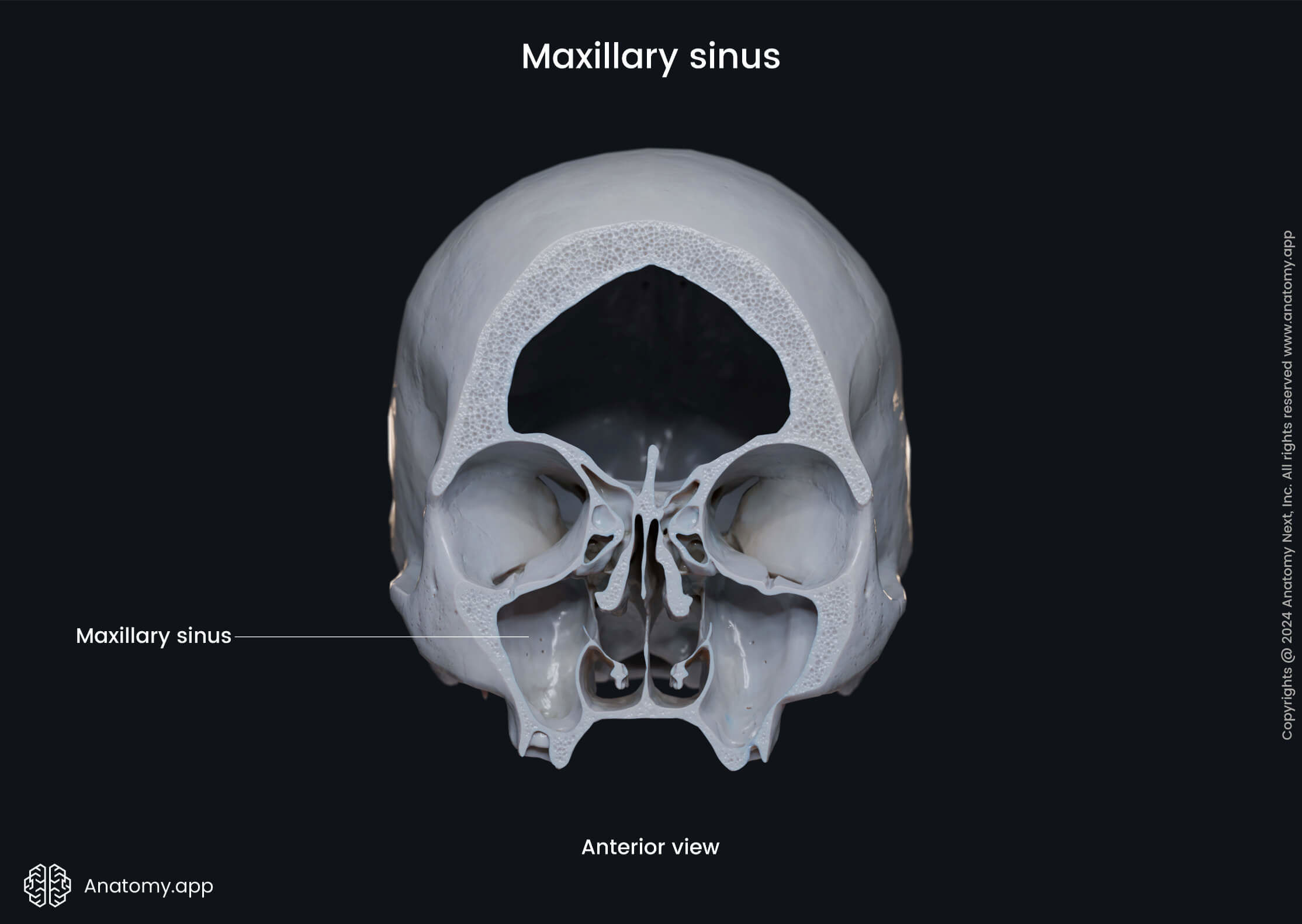
Each maxillary sinus opens into the nasal cavity via the opening located on the nasal surface of the maxilla called the maxillary hiatus. The maxillary sinus drains into the middle nasal meatus of the nasal cavity.
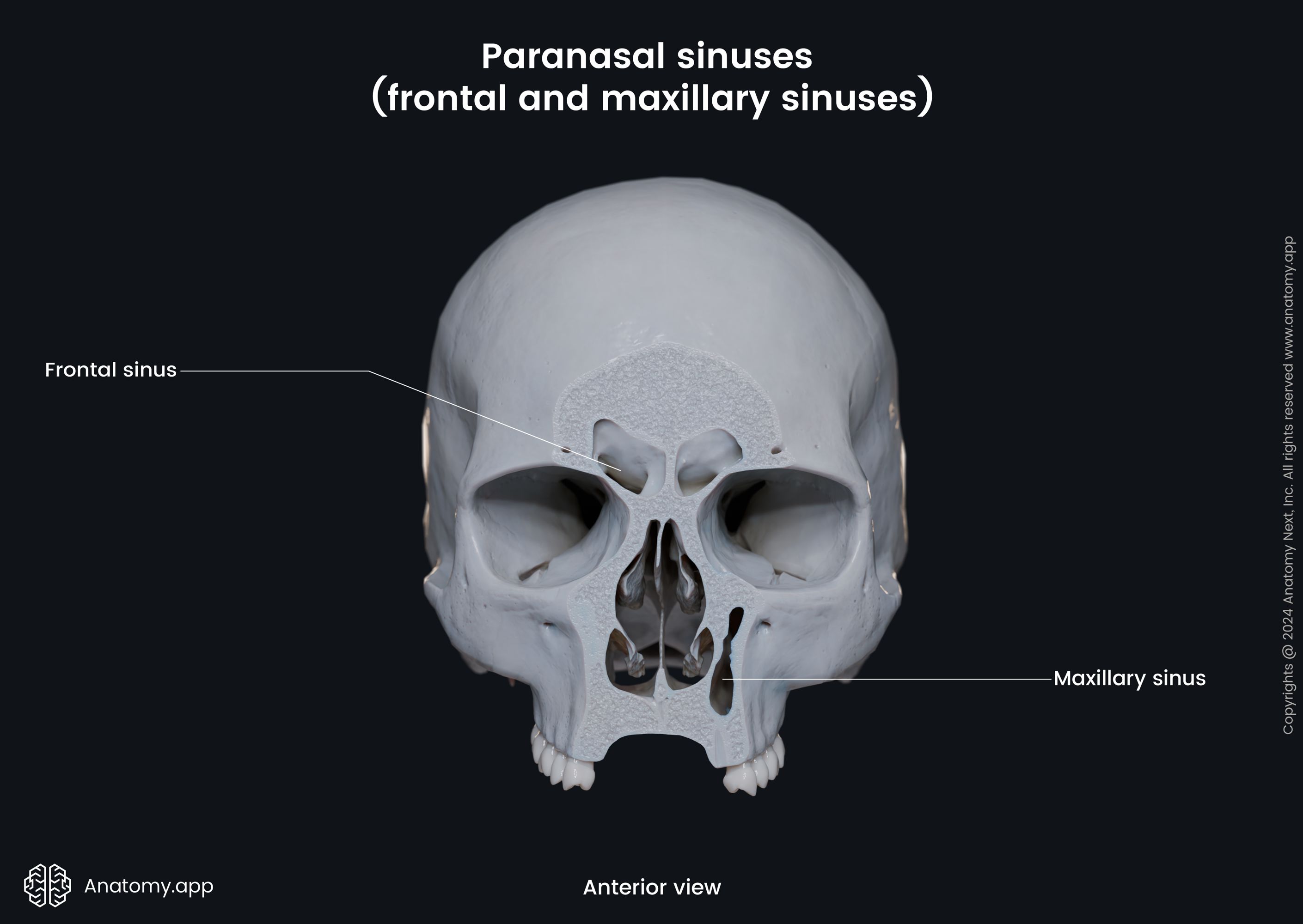
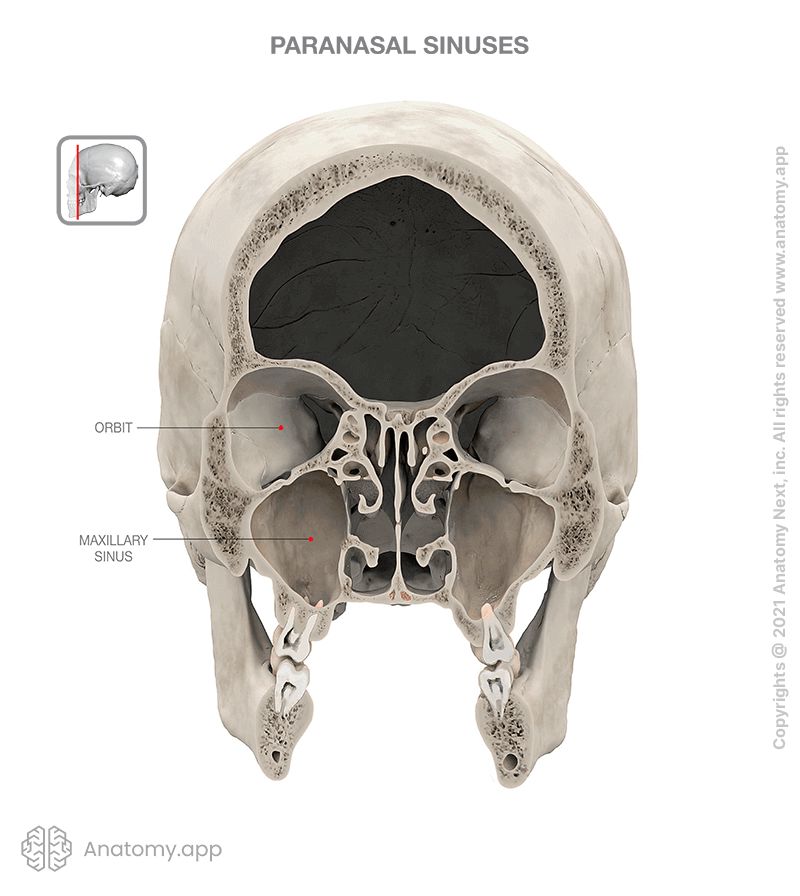
Walls of maxillary sinus
As the maxillary sinus is located within the maxilla, its walls are formed by the anatomical landmarks of the maxilla. The walls of the maxilla are as follows:
- Medial - nasal surface of the body;
- Lateral - zygomatic process of the maxilla;
- Inferior - alveolar process and part of the palatine process of the maxilla;
- Superior - orbital surface of the body;
- Anterior - anterior surface of the body;
- Posterior - infratemporal surface of the body.
Blood supply of maxillary sinus
The arterial blood supply to the maxillary sinus is provided by several arteries, including:
- Anterior, middle and posterior superior alveolar arteries
- Infraorbital artery
- Greater palatine artery
Nerve supply of maxillary sinus
The sensory innervation of the mucosa is provided by the following nerves: