- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Skeleton of trunk
- Skull
- Skeleton of upper limb
- Skeleton of lower limb
- Joints
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
Sphenoidal sinus
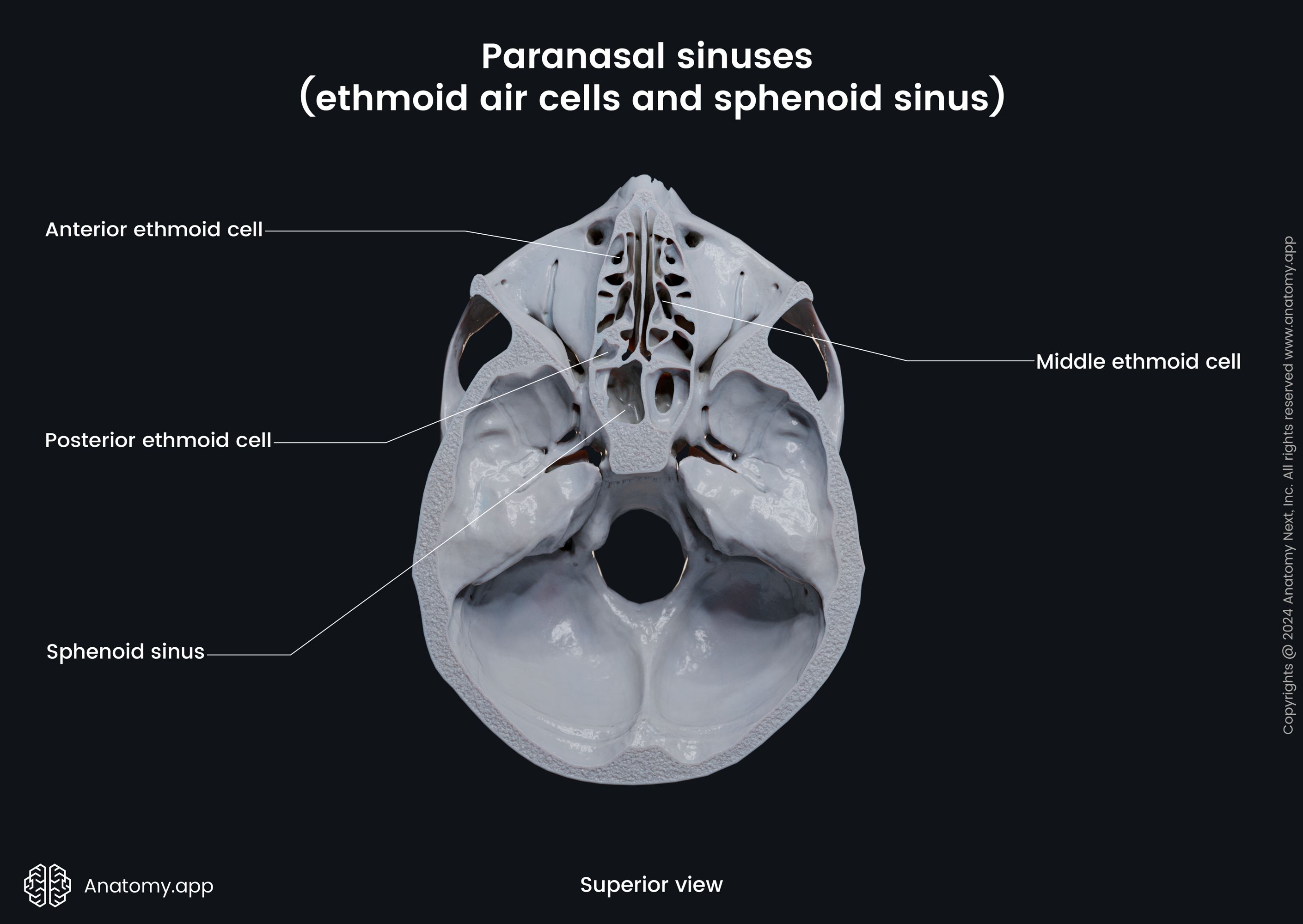
The sphenoidal sinus (Latin: sinus sphenoidalis) is a paired air-filled cavity located within the body of the sphenoid bone. It is one of the four paired paranasal sinuses located within the bones of the skull. The sphenoid sinus is located relatively posterior to the upper aspect of the nasal cavity. The paired sphenoidal sinuses vary in size and shape, and due to physiological lateral deviation of the nasal septum, they are rarely symmetrical.
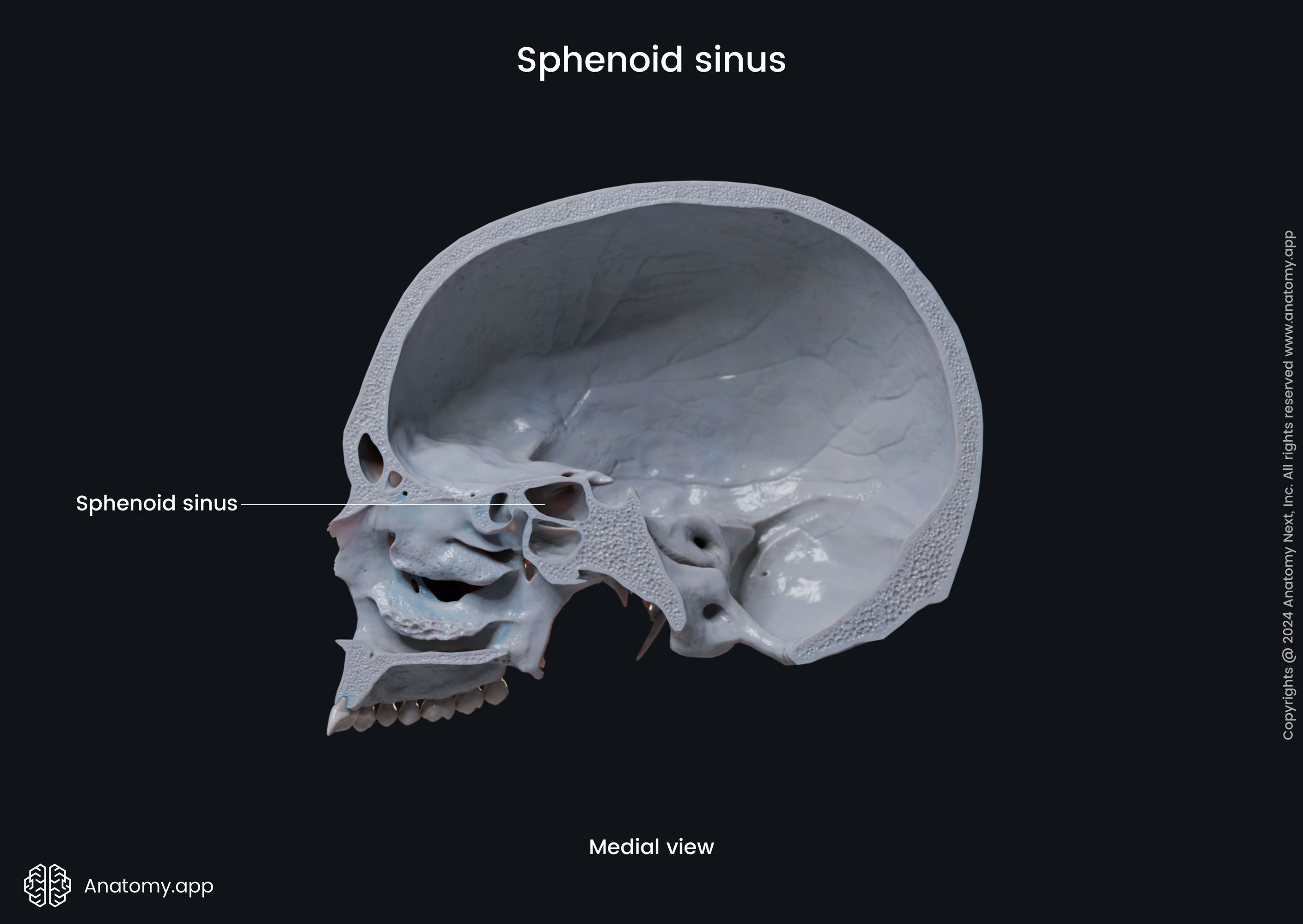
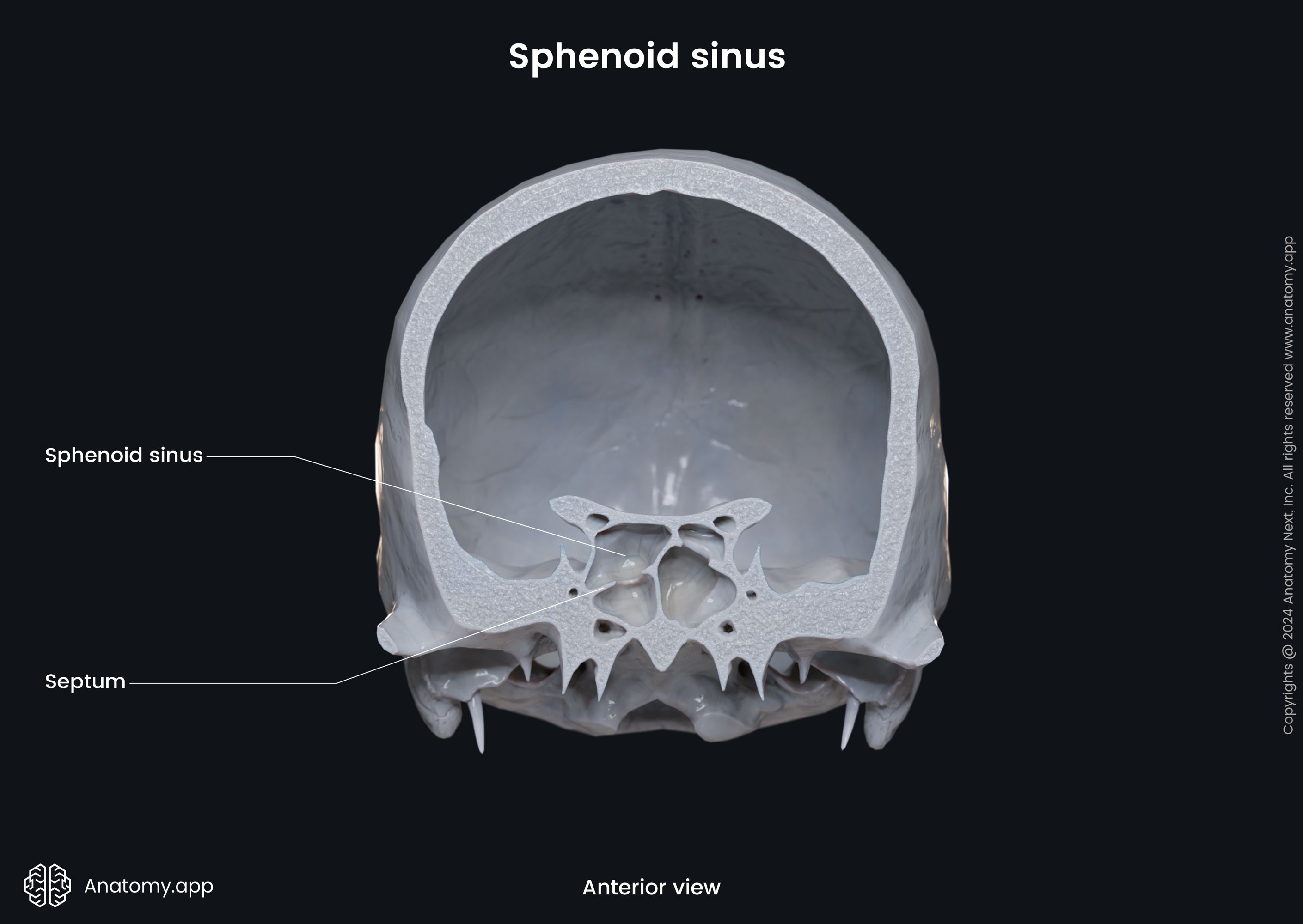
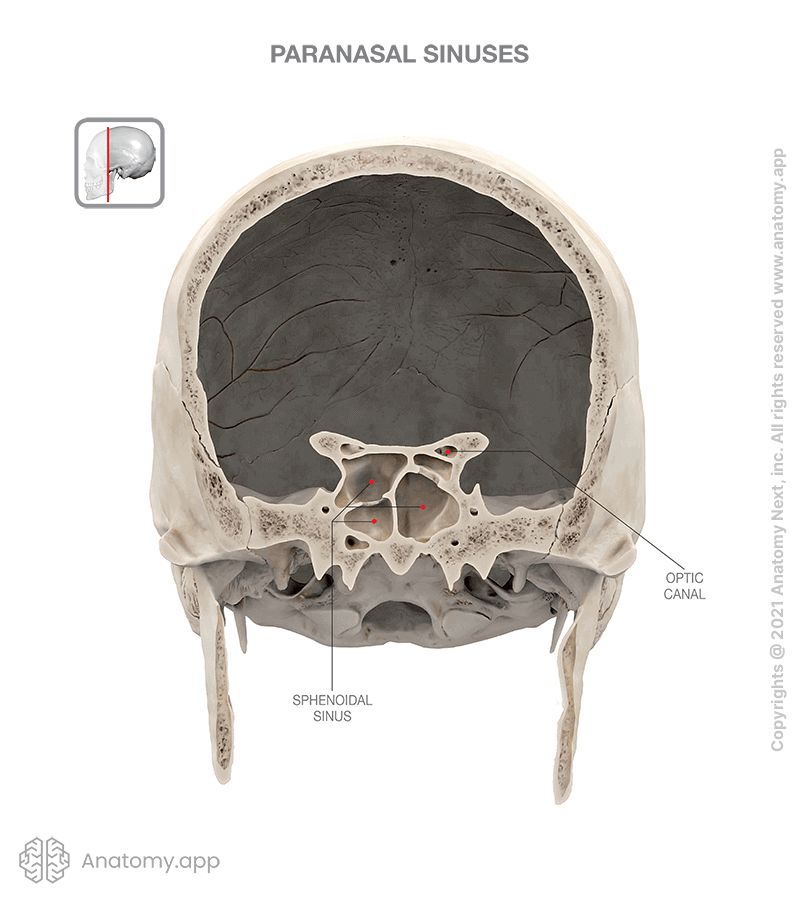
Each sphenoidal sinus opens into the nasal cavity via the opening located on the anterior wall of the sphenoidal body. This opening connects the sphenoidal sinus with the sphenoethmoidal recess located in the superior nasal meatus. The sphenoethmoidal recess is a small space situated posterior and superior to the superior nasal concha. The recess drains not only the sphenoidal sinus but also the posterior ethmoidal air cells.
Blood supply of sphenoidal sinus
The arterial blood supply to the sphenoidal sinus is provided by the following arterial blood vessels:
- Posterior ethmoidal branches of the ophthalmic arteries
- Nasal branches of the sphenopalatine arteries
The venous blood is drained via the posterior ethmoidal veins that carry the blood further to the superior ophthalmic veins.
Nerve supply of sphenoidal sinus
The mucosa of the sphenoidal sinus receives sensory innervation from the following nerves:
- Posterior ethmoidal branches of the ophthalmic nerve (CN V1)
- Orbital branches of the pterygopalatine ganglion