- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Skeleton of trunk
- Skull
- Skeleton of upper limb
- Skeleton of lower limb
- Joints
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
Ethmoidal air cells
The ethmoidal air cells (Latin: cellulae ethmoidales) are multiple thin-walled cavities located within the ethmoidal labyrinth of the ethmoid bone. The ethmoidal air cells together with three sinuses (frontal, sphenoidal and maxillary) are classified as paranasal sinuses. The ethmoidal air cells are positioned between the upper aspect of the nasal cavity and the orbit. The orbital plate of the ethmoid separates the ethmoidal air cells from the orbit.
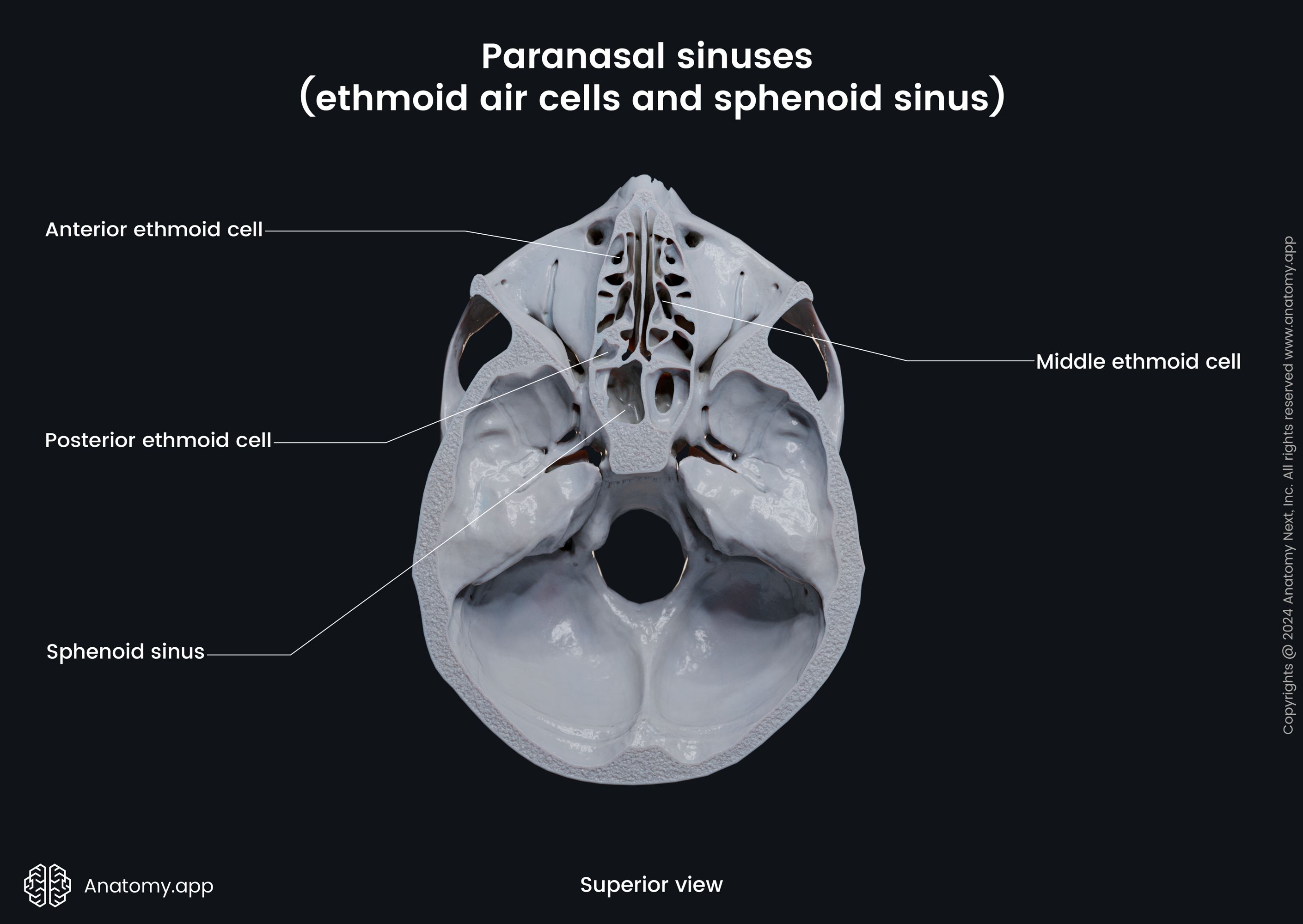
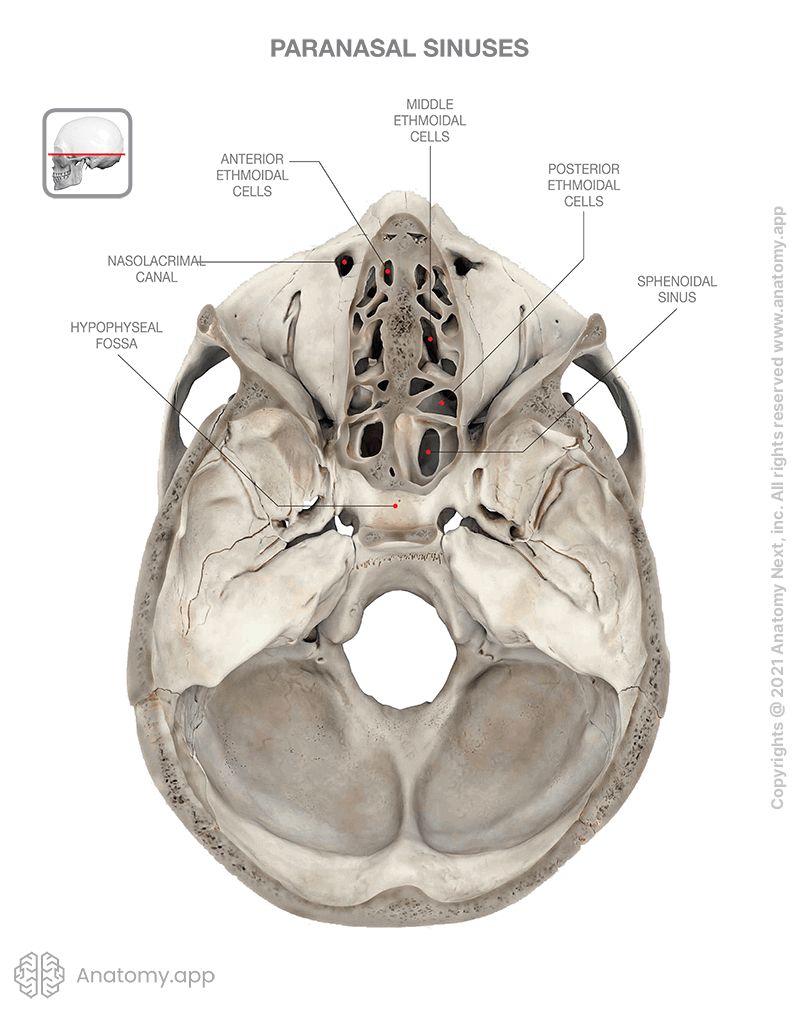
The ethmoidal air cells are subdivided into three smaller groups depending on their location within the ethmoid bone. All groups are located on either side of the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid bone, and they include the following:
- Anterior ethmoidal air cells - drain into the middle nasal meatus via the nasofrontal duct;
- Middle ethmoidal air cells - drain into the middle nasal meatus;
- Posterior ethmoidal air cells - drain into the superior nasal meatus together with the sphenoid sinus via the sphenoethmoidal recess.
Blood supply of ethmoidal air cells
The arterial blood is supplied to the ethmoidal air cells via the following arterial blood vessels:
- Nasal branches of the sphenopalatine artery
- Anterior and posterior ethmoidal branches of the ophthalmic artery
The venous drainage of the ethmoidal air cells is provided by the sphenopalatine and ophthalmic veins.
Nerve supply of ethmoidal air cells
The sensory innervation to the mucosa that lines the ethmoidal air cells is provided by the following nerves:
- Anterior and posterior ethmoidal branches of the ophthalmic nerve (CN V1)
- Orbital branches of the pterygopalatine ganglion