- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
Nervous system
The nervous system is a complex network of neurons and supporting cells that transmit information between the brain and spinal cord and different parts of the body.
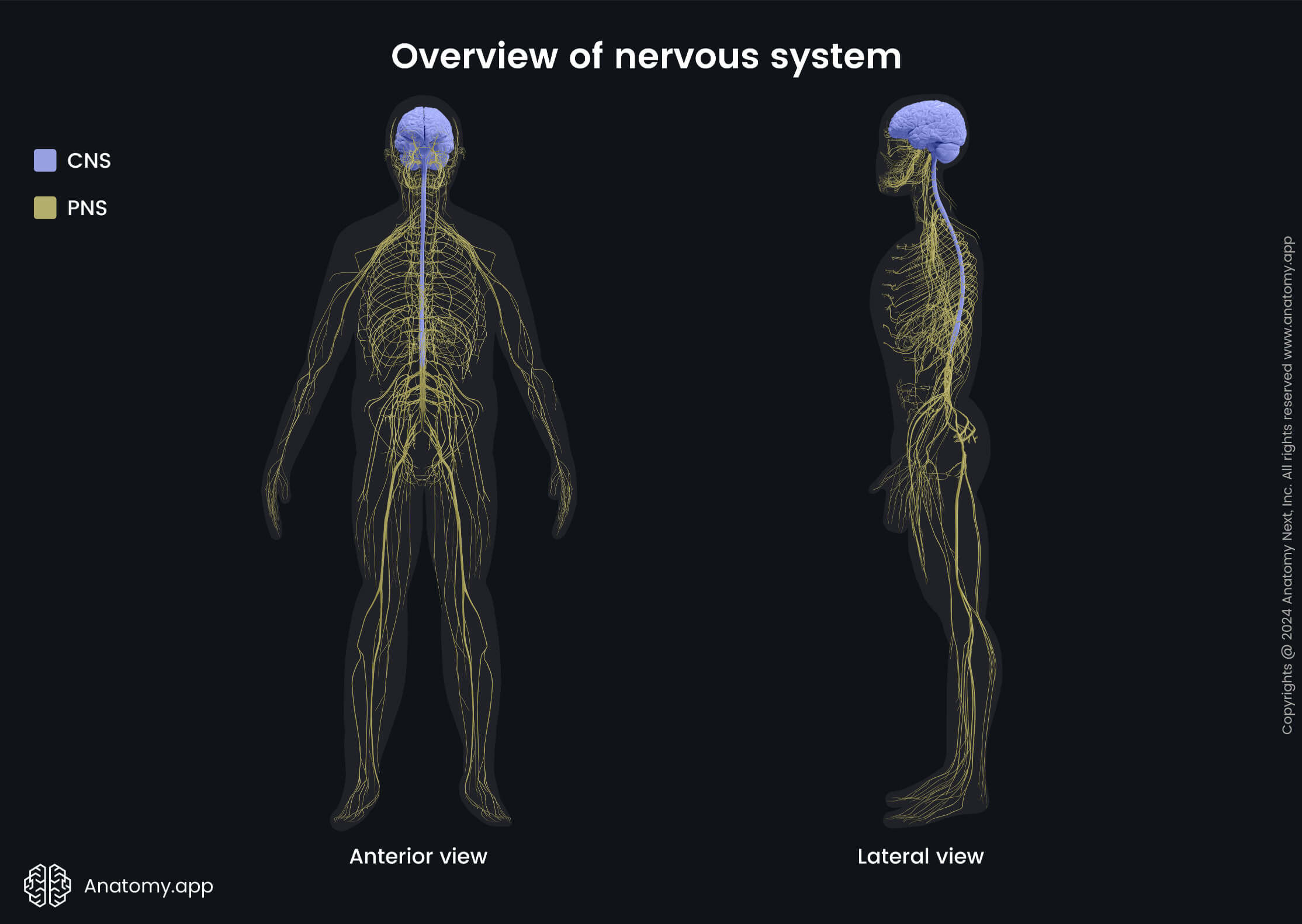
The nervous system consists of the brain, spinal cord, sensory organs and nerves connecting these organs with the rest of the organism. This system is responsible for the control and coordination of the body, as well as communication among its parts. The nervous system has three main functions: sensory, integration, and motor functions.
There are two main parts of the nervous system: central nervous system (CNS) consisting of the brain and spinal cord, and the peripheral nervous system (PNS) formed by nerves and ganglia outside the central nervous system. The PNS is further classified into somatic and autonomic nervous systems. The autonomic nervous system consists of sympathetic and parasympathetic parts.
References:
- Crossman, A. R., & Neary, D. (2019). Neuroanatomy: an Illustrated Colour Text (6th ed.). Elsevier.
- Vanderah, T. W., & Gould, D. J. (2020). Nolte’s The Human Brain (8th ed.). Elsevier.