- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
-
Head muscles
- Extraocular muscles
-
Facial muscles
- Occipitofrontalis
- Corrugator supercilii
- Depressor supercilii
- Orbicularis oculi
- Malaris
- Buccinator
- Orbicularis oris
- Mentalis
- Depressor anguli oris
- Depressor labii inferioris
- Levator anguli oris
- Levator labii superioris
- Risorius
- Zygomaticus major
- Zygomaticus minor
- Levator labii superioris alaeque nasi
- Nasalis
- Procerus
- Depressor septi nasi
- Compressor narium minor
- Dilator naris anterior
- Muscles of mastication
- Neck muscles
- Muscles of upper limb
- Thoracic muscles
- Muscles of back
- Muscles of lower limb
-
Head muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
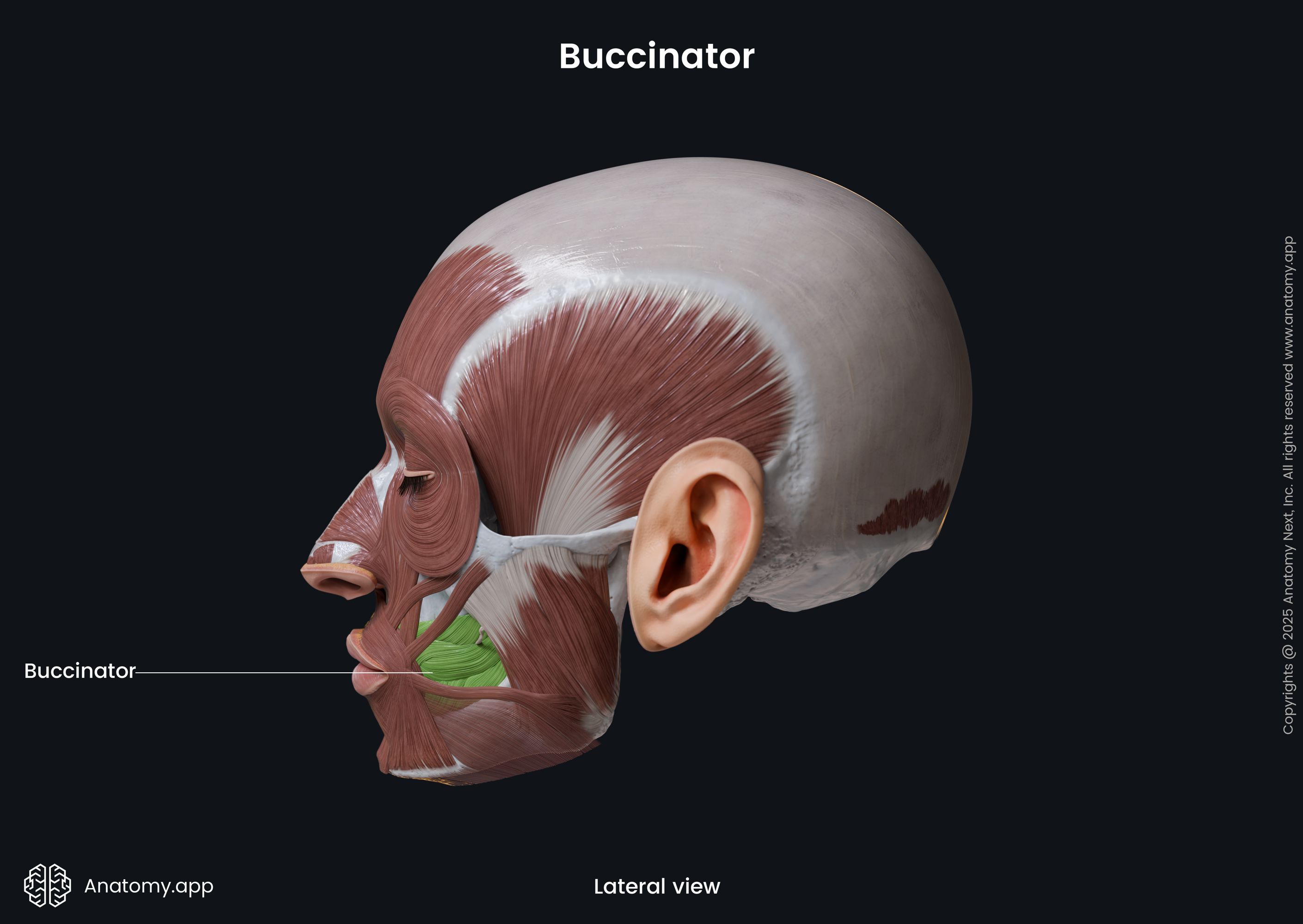
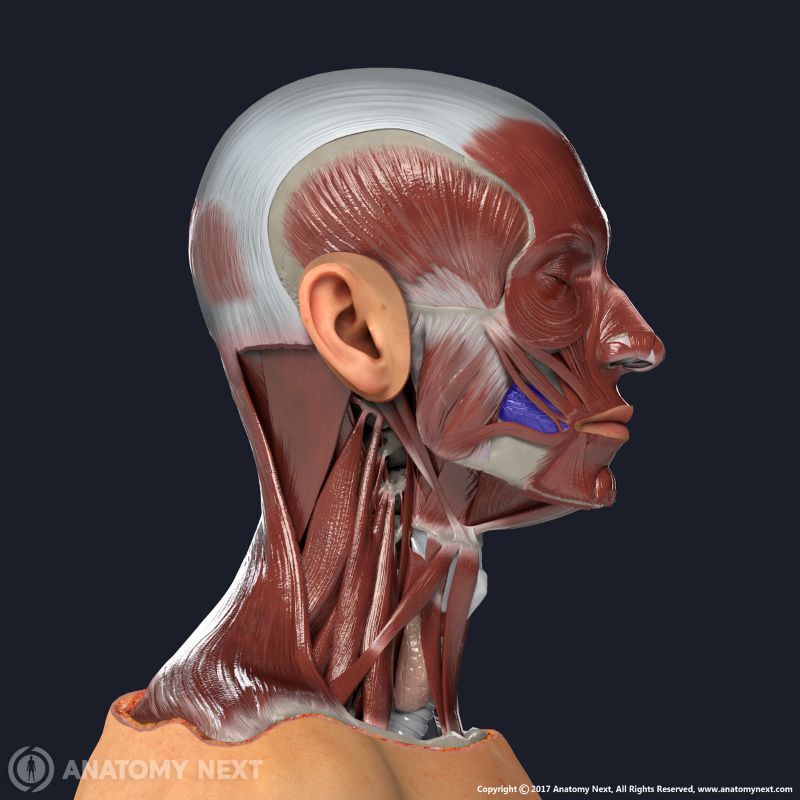
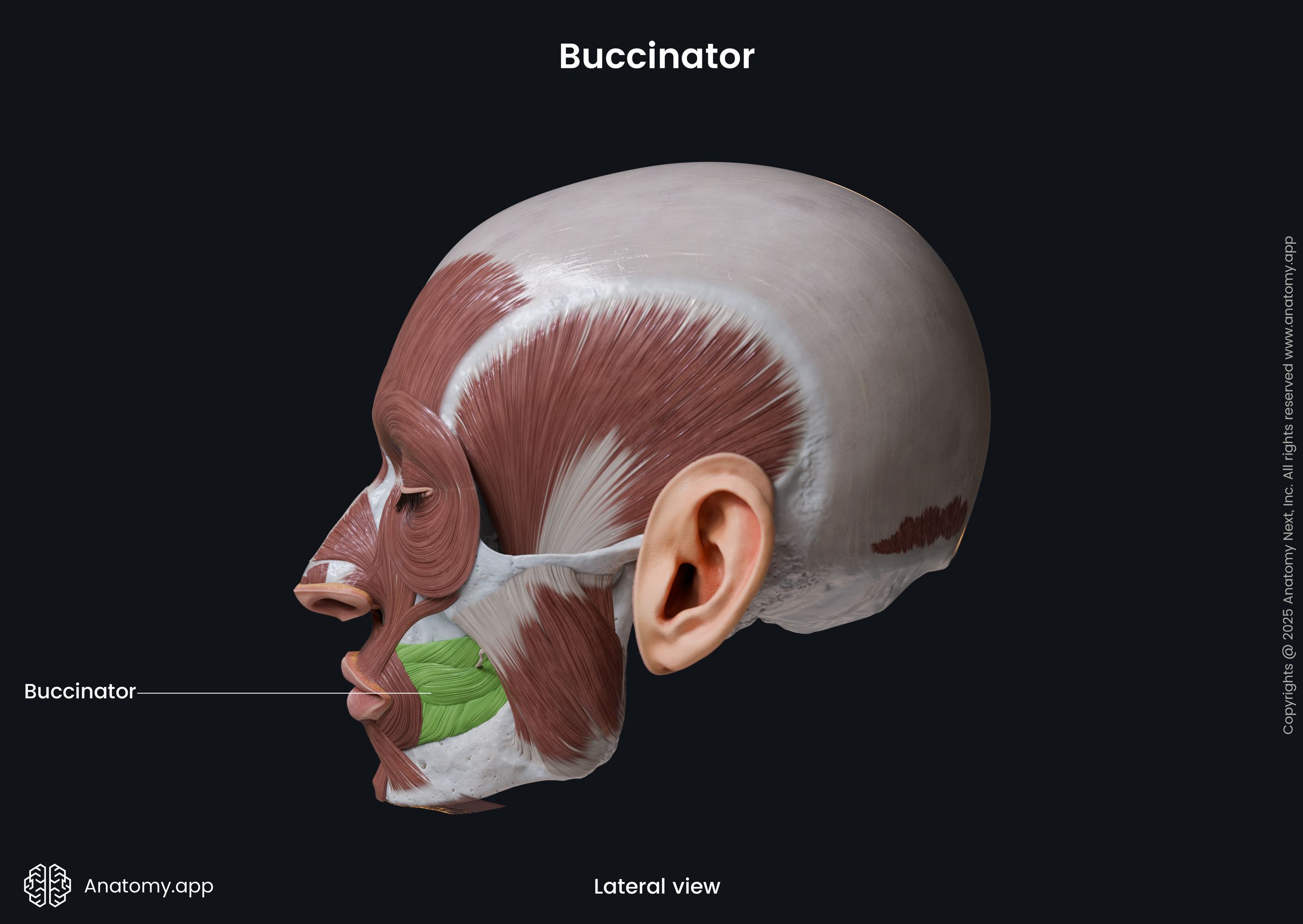
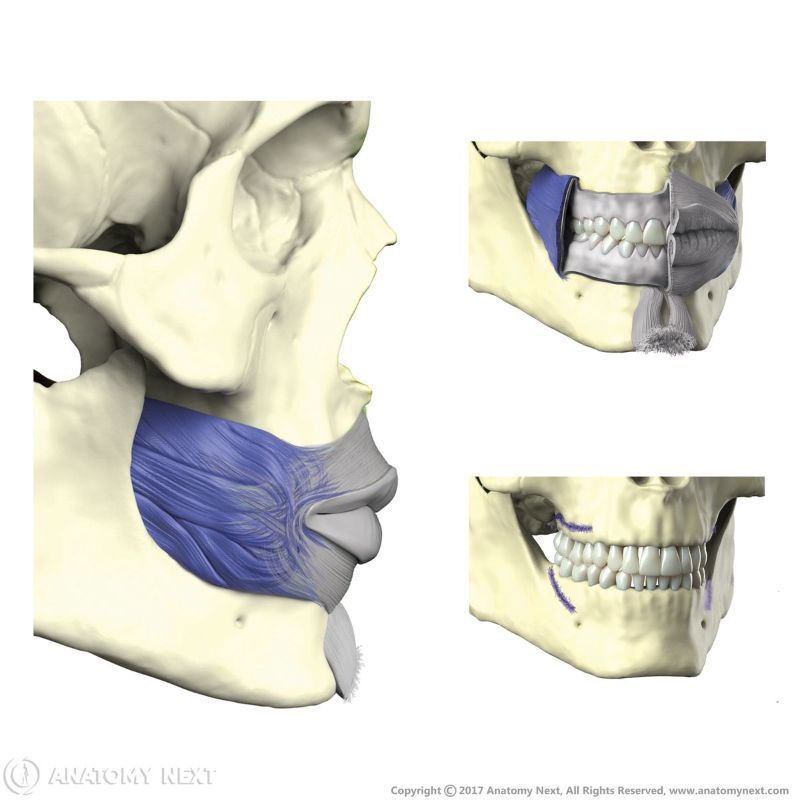
Buccinator
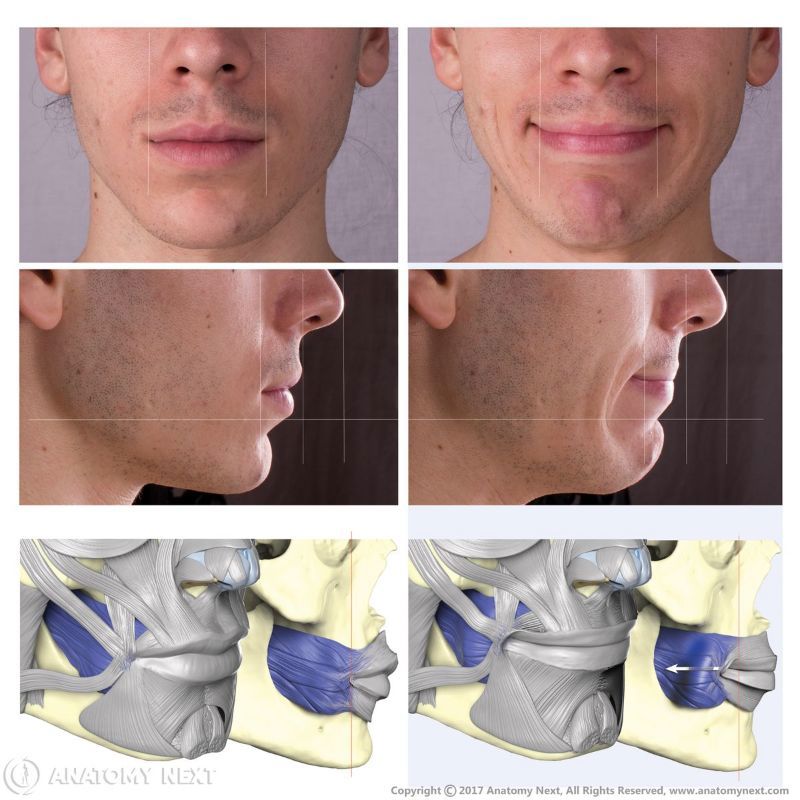
The buccinator (Latin: musculus buccinator) is a facial muscle that participates in forming the anterior part of the cheek and lateral wall of the oral vestibule. It is classified as the buccolabial facial muscle.
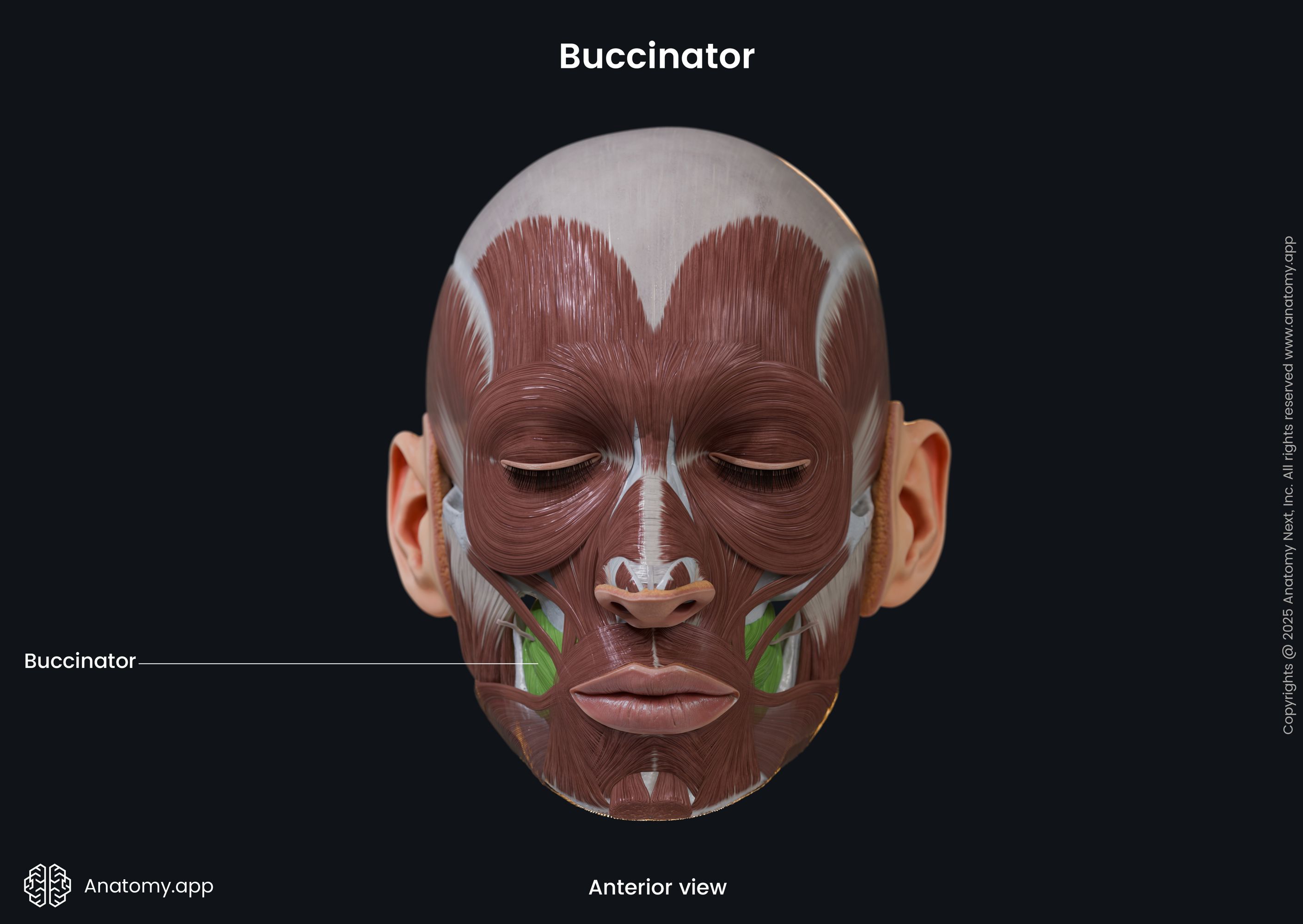
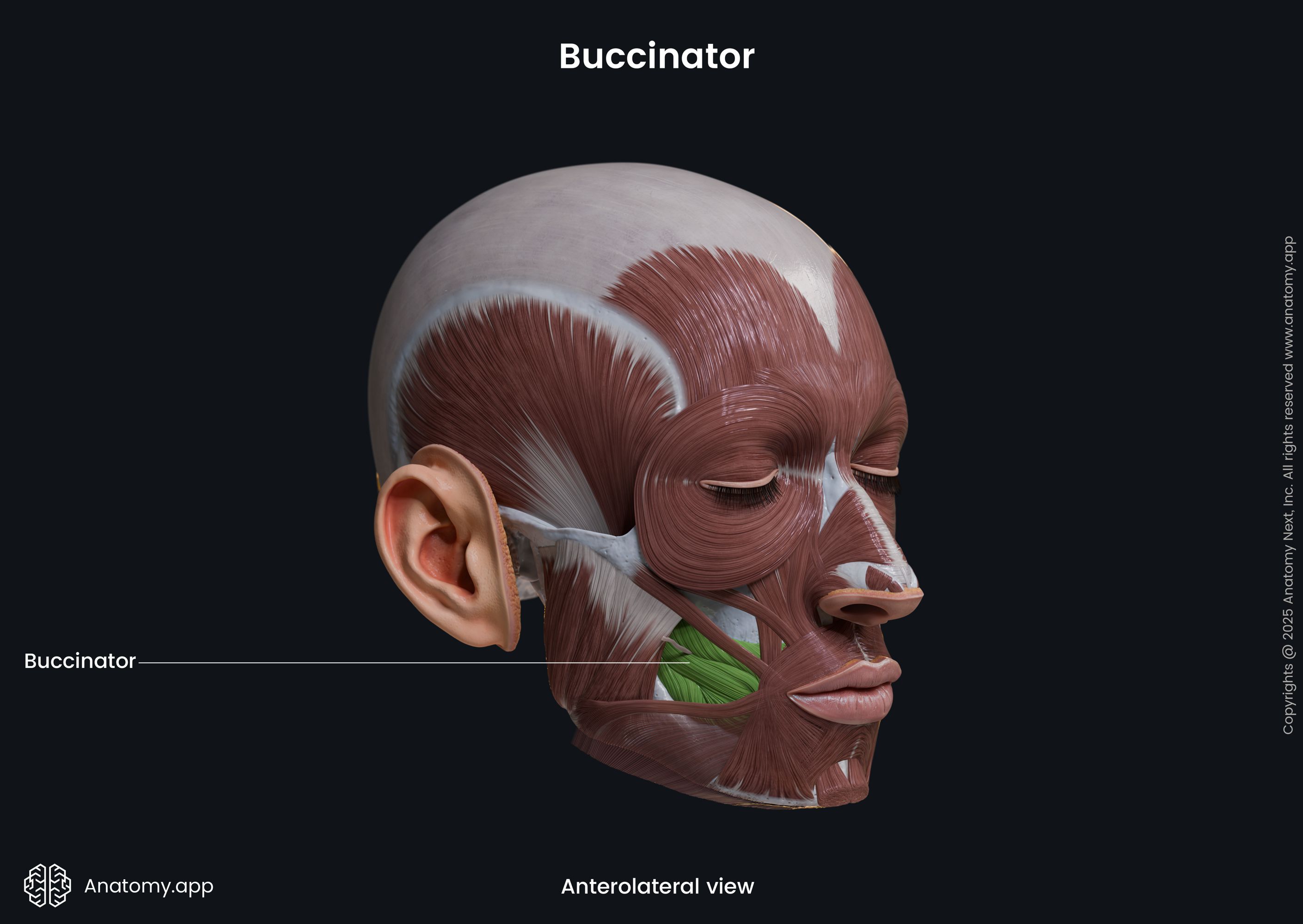
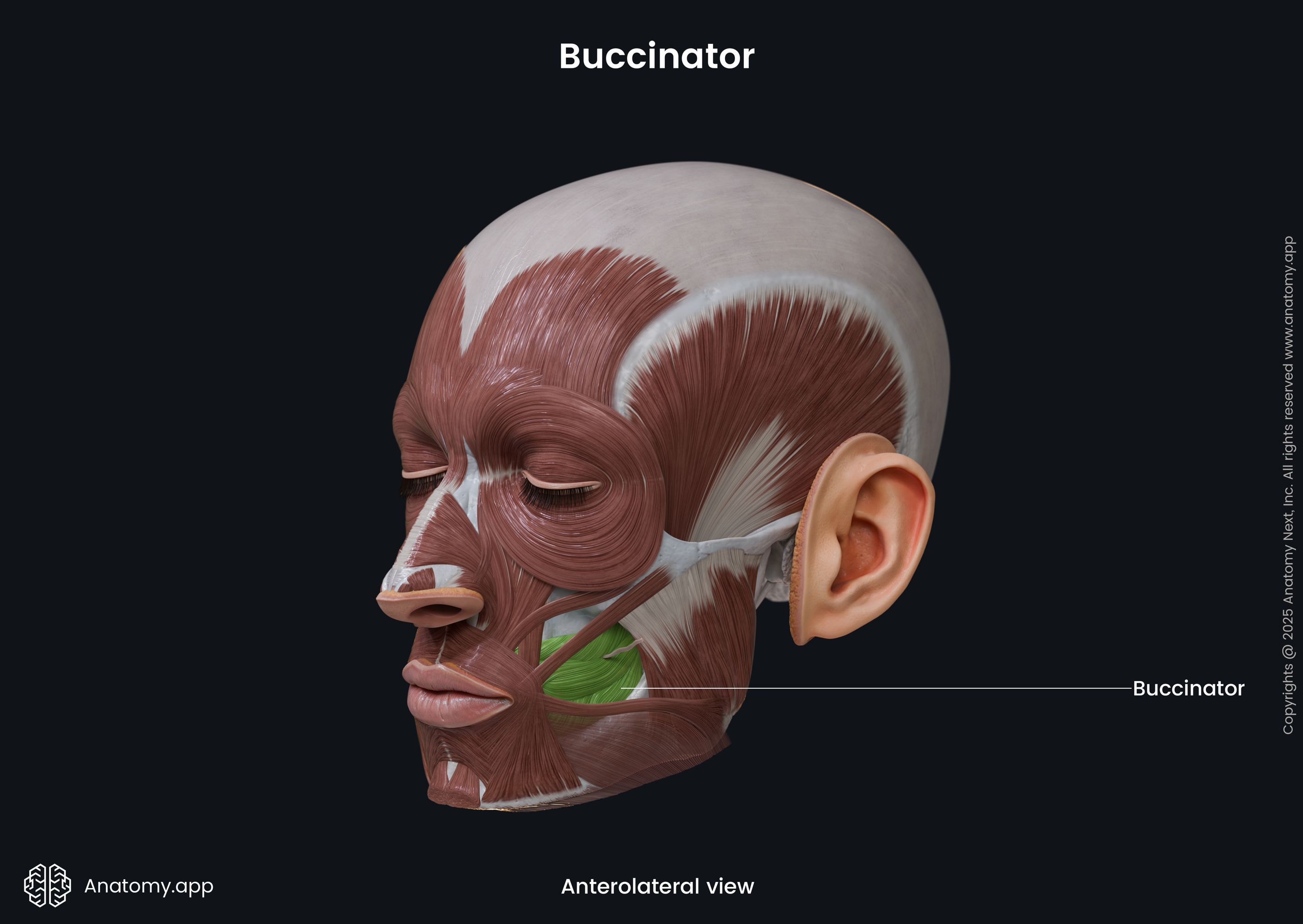
The buccinator is a thin quadrilateral-shaped muscle occupying the interval between the maxilla and mandible. It is the only facial muscle that is covered by the fascia known as the buccopharyngeal fascia.
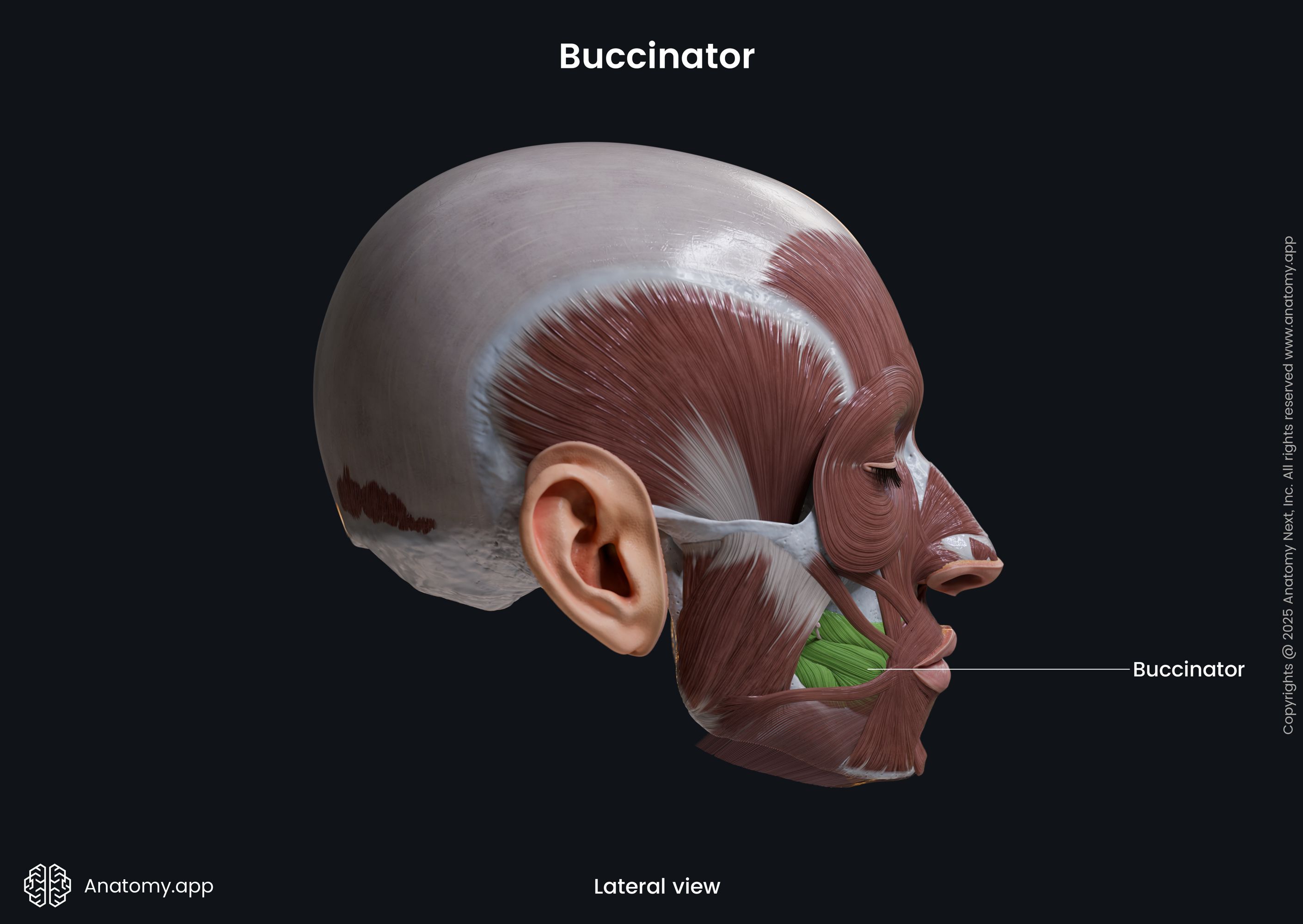
| Buccinator | |
| Origin | Alveolar processes of maxilla and mandible, pterygomandibular raphe |
| Insertion | Angle of mouth, modiolus, blends with orbicularis oris muscle fibers |
| Action | Pulls angle of mouth laterally, presses cheeks to teeth, decreases size of oral vestibule |
| Innervation | Buccal branch of facial nerve (CN VII) |
| Blood supply | Branches of facial artery, buccal branch of maxillary artery |
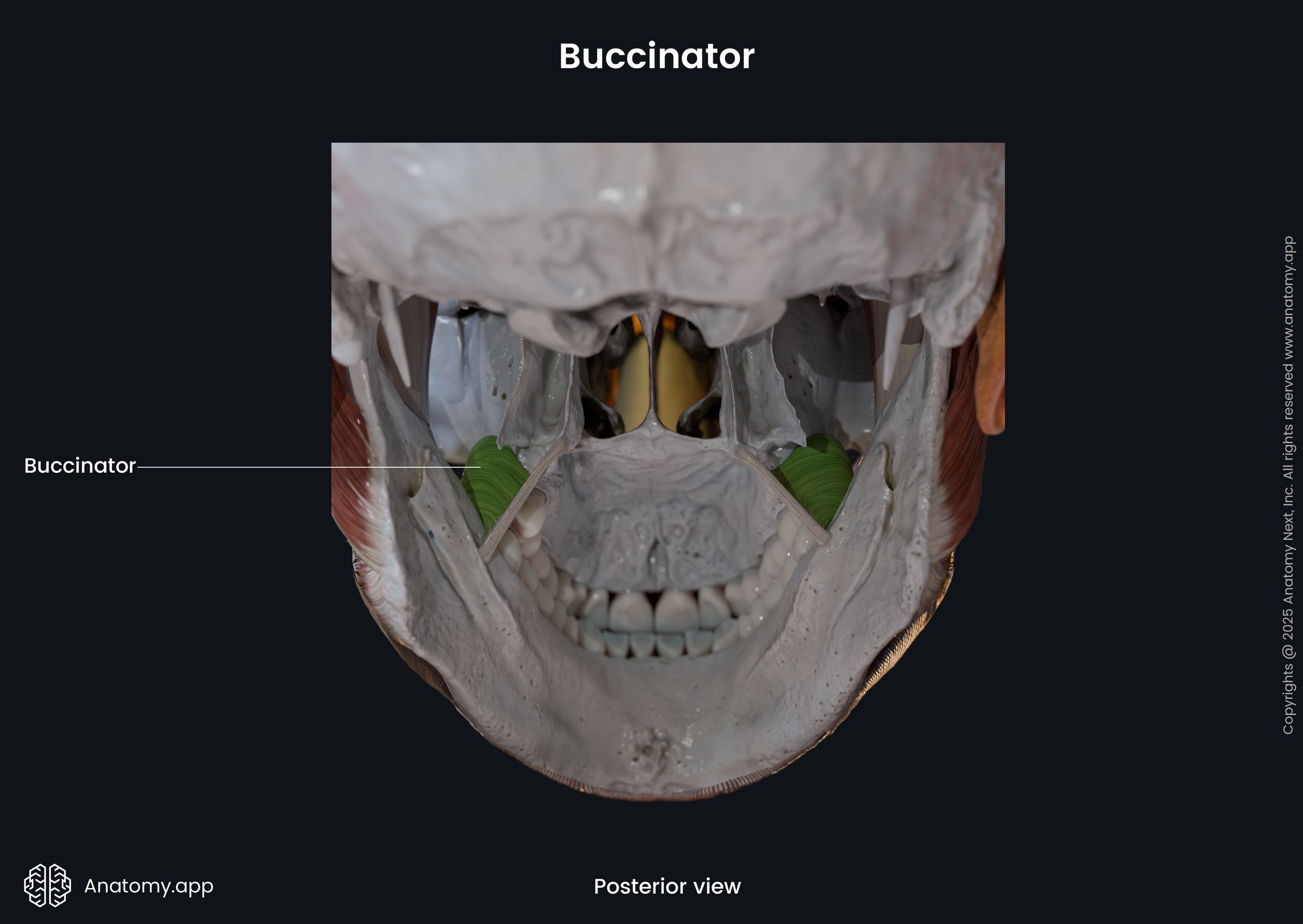
Origin
The fibers of the buccinator arise from the pterygomandibular raphe and alveolar processes of the maxilla and mandible at the region of the first and second molar teeth.

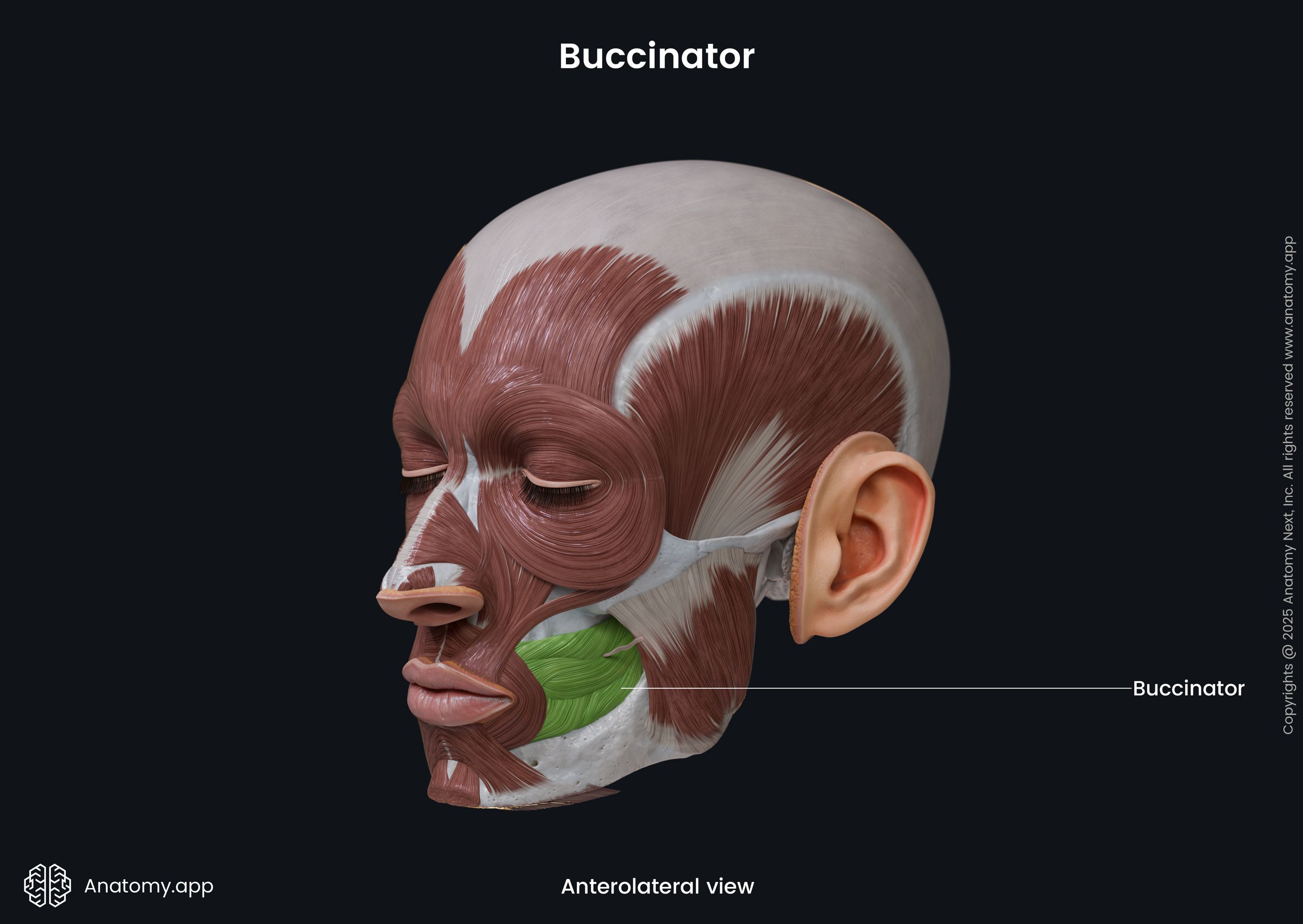
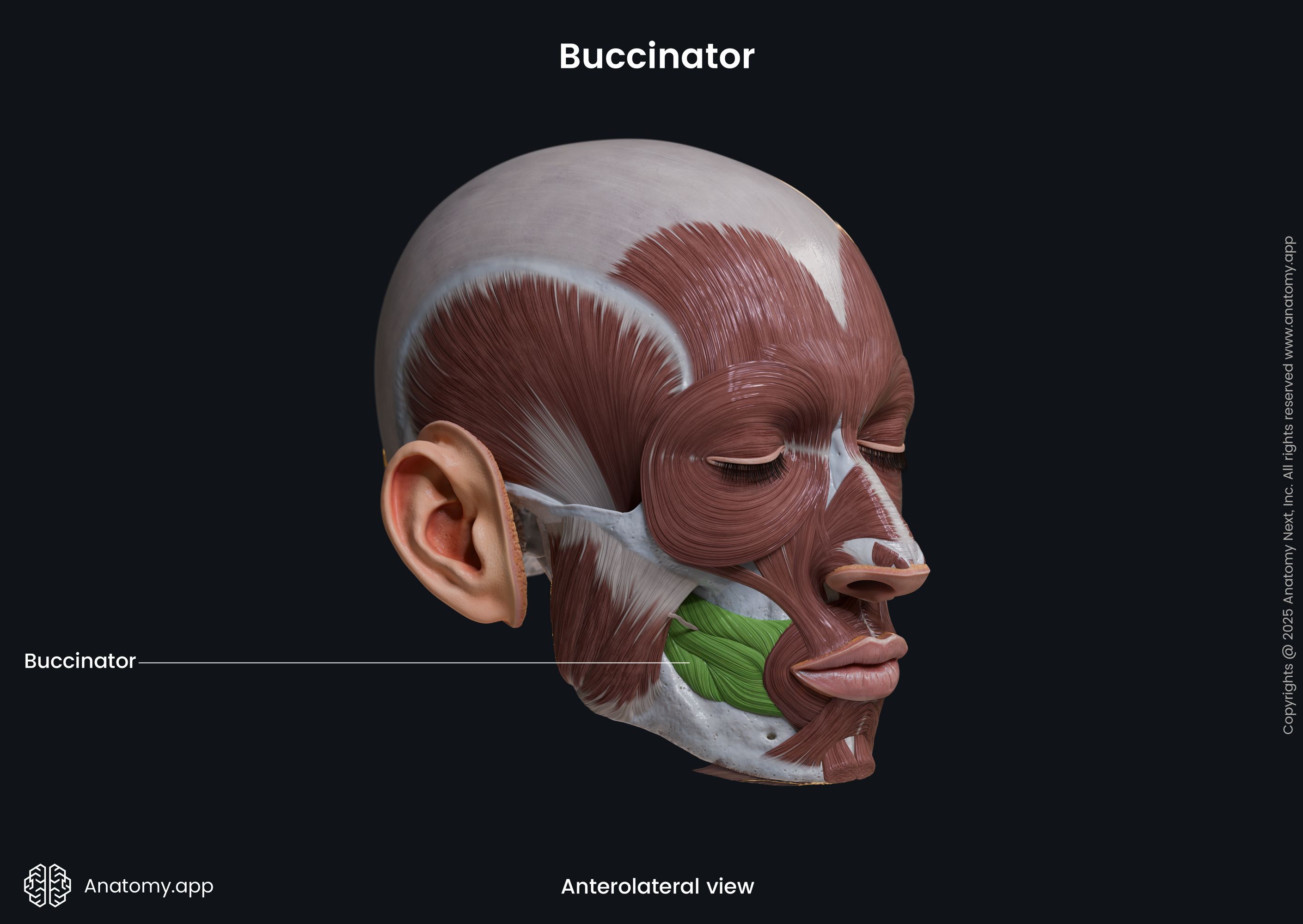
Insertion
The buccinator inserts into the angle of the mouth and modiolus, radiating into the fibers of the orbicularis oris muscle.
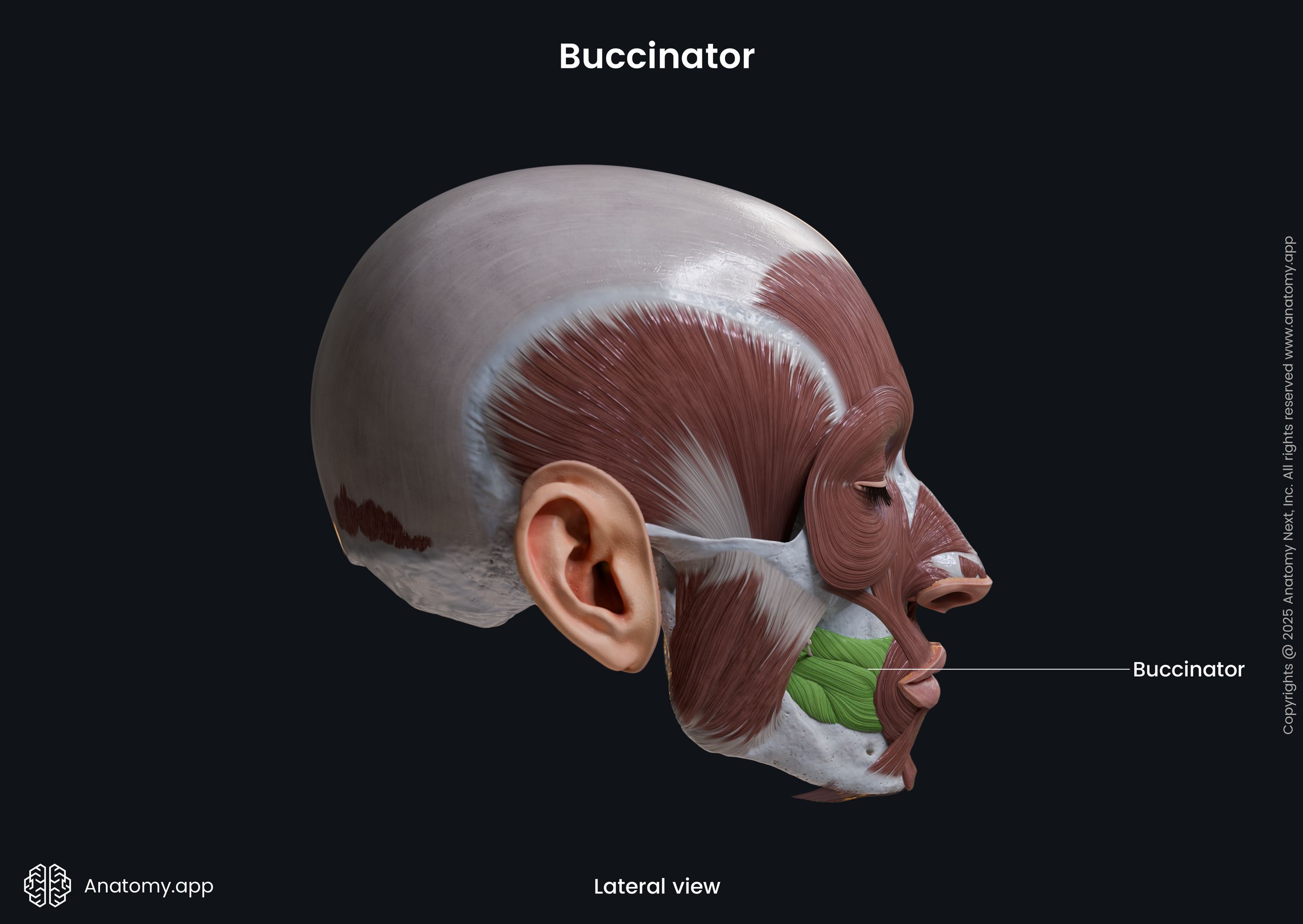
Action
Upon contractions, the buccinator pulls the angle of the mouth laterally and presses the cheeks to the teeth, thus decreasing the oral vestibule. Contractions of this muscle produce facial expressions presenting satisfaction, laughing and crying.
Innervation
The buccinator is innervated by the buccal branch of the facial nerve (CN VII).
Blood supply
The buccinator is supplied by branches of the facial artery and the buccal branch of the maxillary artery.