- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
-
Head muscles
- Extraocular muscles
-
Facial muscles
- Occipitofrontalis
- Corrugator supercilii
- Depressor supercilii
- Orbicularis oculi
- Malaris
- Buccinator
- Orbicularis oris
- Mentalis
- Depressor anguli oris
- Depressor labii inferioris
- Levator anguli oris
- Levator labii superioris
- Risorius
- Zygomaticus major
- Zygomaticus minor
- Levator labii superioris alaeque nasi
- Nasalis
- Procerus
- Depressor septi nasi
- Compressor narium minor
- Dilator naris anterior
- Muscles of mastication
- Neck muscles
- Muscles of upper limb
- Thoracic muscles
- Muscles of back
- Muscles of lower limb
-
Head muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
Occipitofrontalis
The occipitofrontalis (Latin: musculus occipitofrontalis), also known as the epicranius muscle, is a facial muscle of the calvaria region. It is classified as the epicranial group muscle that covers the upper parts of the skull.
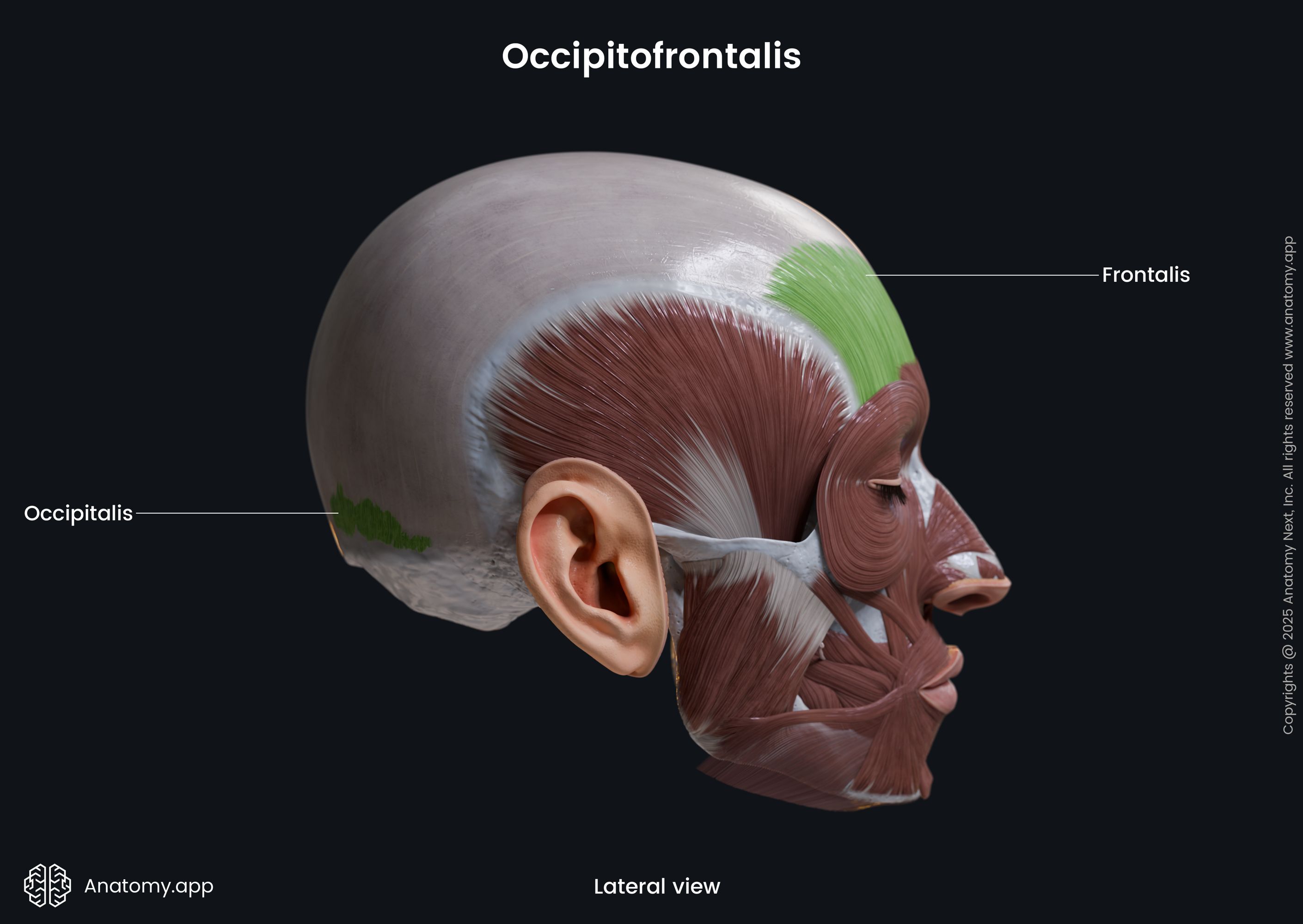
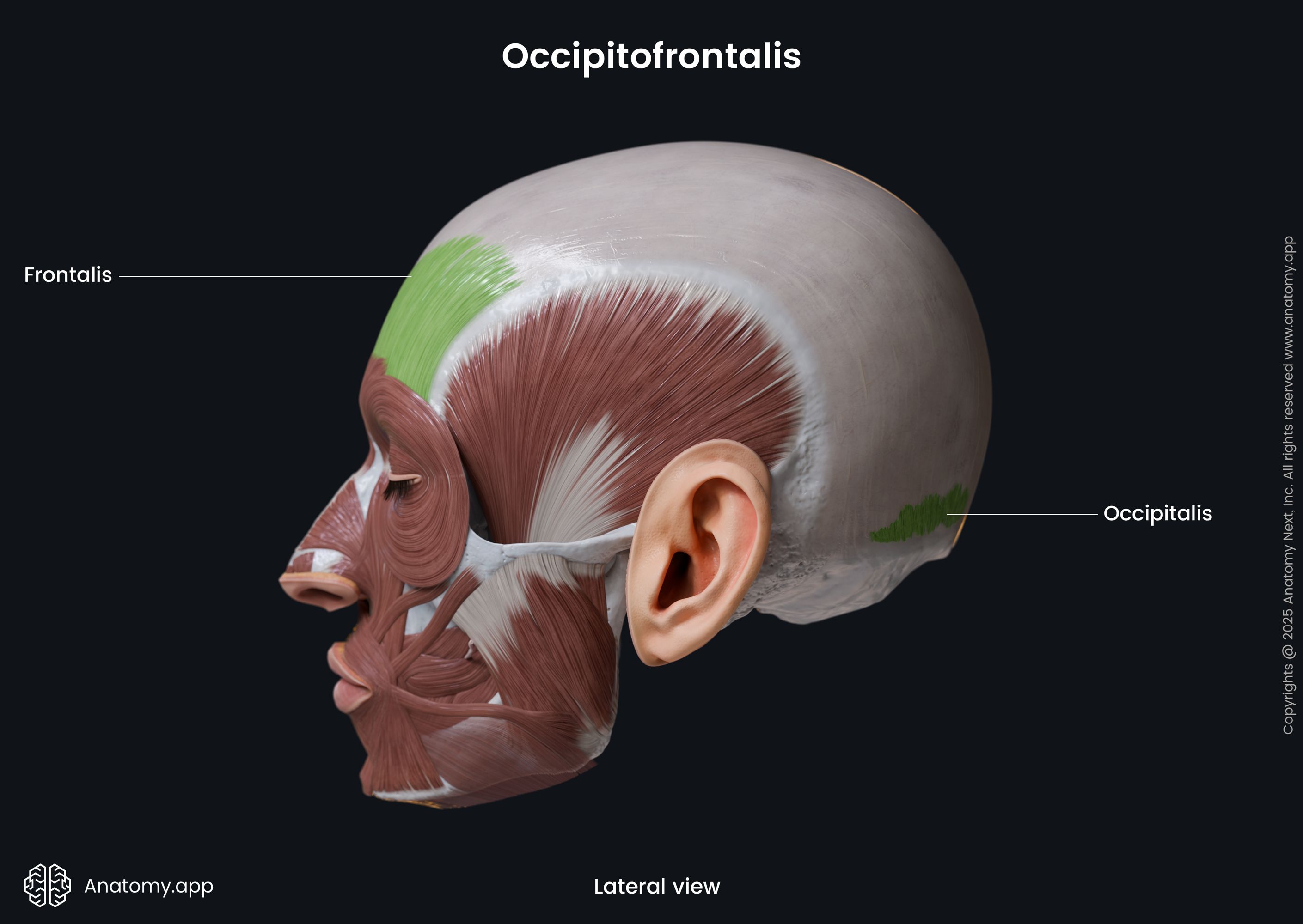
The occipitofrontalis is composed of two parts - occipital belly and frontal belly. Both bellies are connected with epicranial aponeurosis. The occipitofrontalis muscle usually is very loosely bound to the bones but very firmly to the rest parts of the scalp.
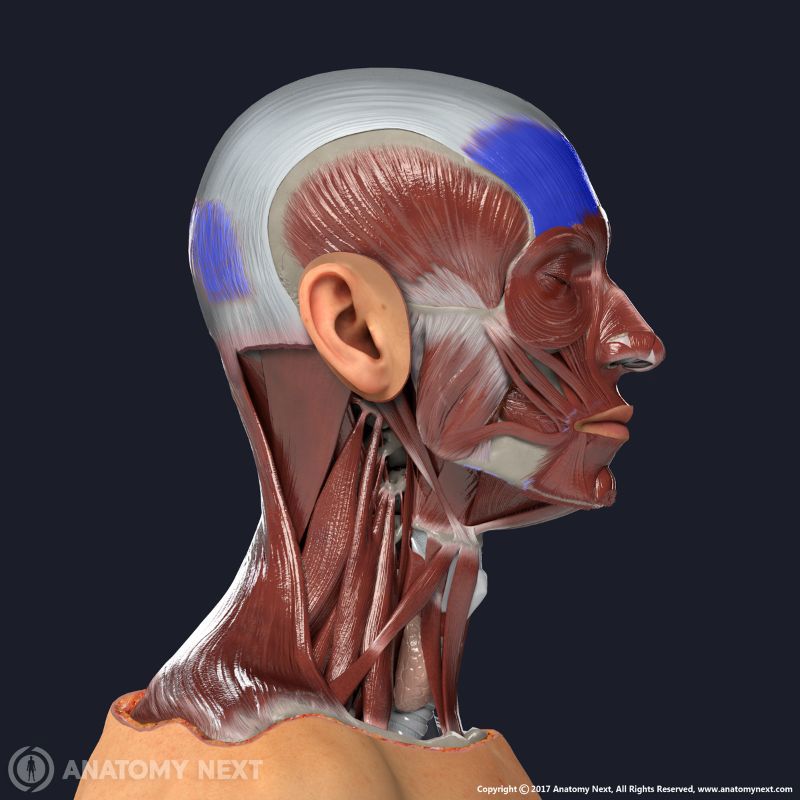
Both bellies of the occipitofrontalis are innervated by branches of the facial nerve (CN VII). The temporal branch innervates the frontal belly, while the occipital belly receives nerve supply from the posterior auricular nerve. The arterial blood supply of the occipitofrontalis muscle is provided by the branches of the following arteries: