- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
-
Head muscles
- Extraocular muscles
-
Facial muscles
- Occipitofrontalis
- Corrugator supercilii
- Depressor supercilii
- Orbicularis oculi
- Malaris
- Buccinator
- Orbicularis oris
- Mentalis
- Depressor anguli oris
- Depressor labii inferioris
- Levator anguli oris
- Levator labii superioris
- Risorius
- Zygomaticus major
- Zygomaticus minor
- Levator labii superioris alaeque nasi
- Nasalis
- Procerus
- Depressor septi nasi
- Compressor narium minor
- Dilator naris anterior
- Muscles of mastication
- Neck muscles
- Muscles of upper limb
- Thoracic muscles
- Muscles of back
- Muscles of lower limb
-
Head muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
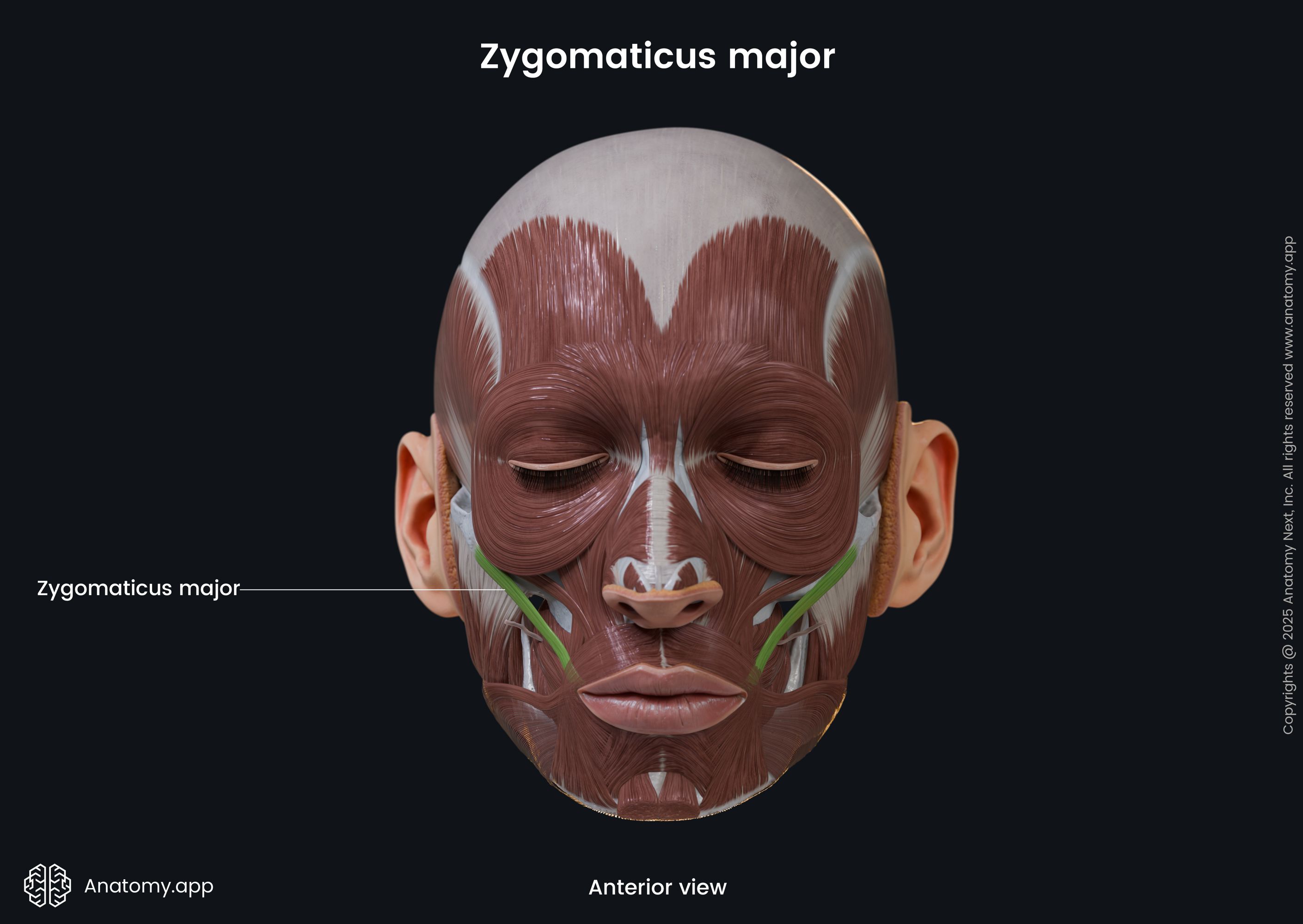
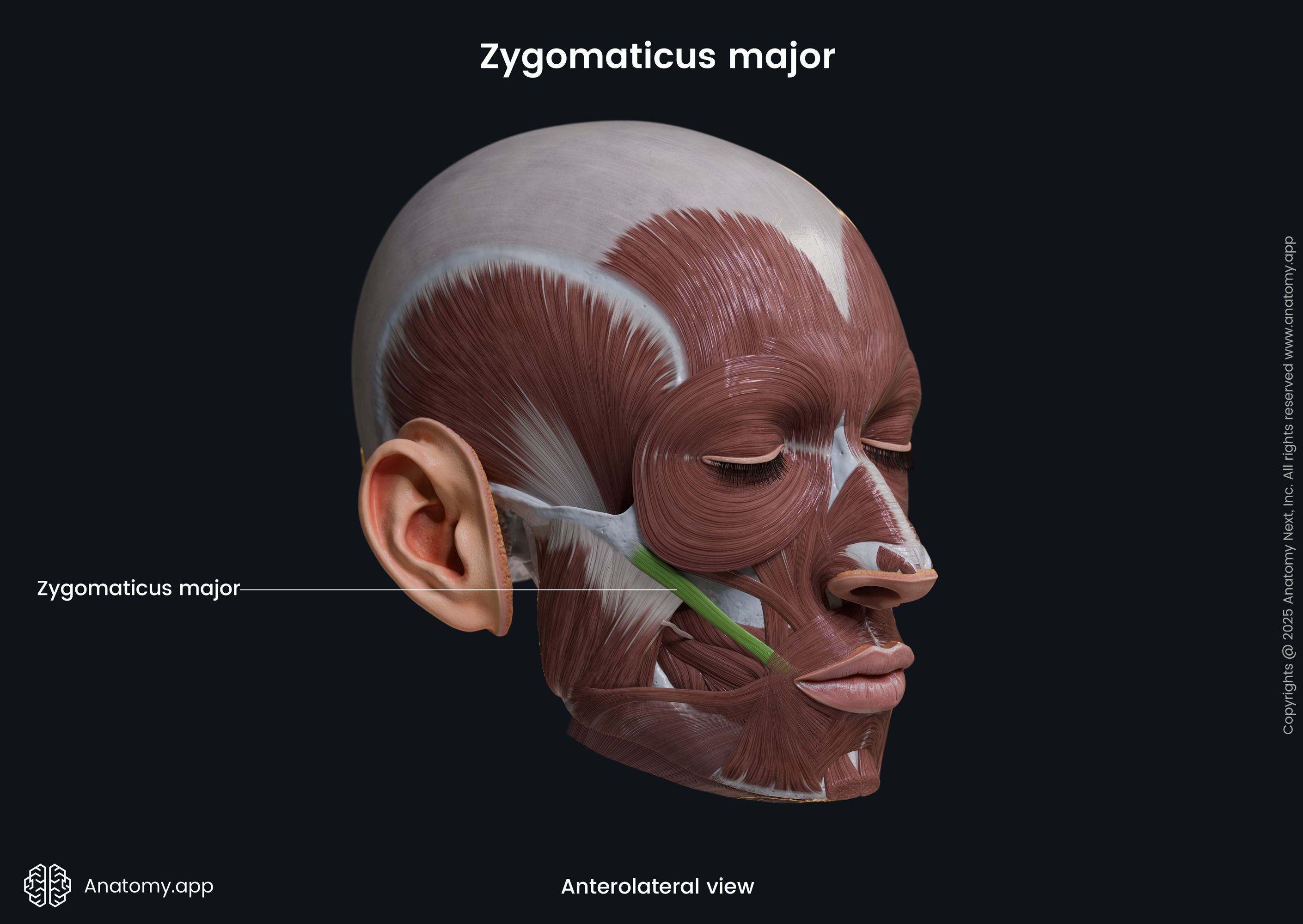
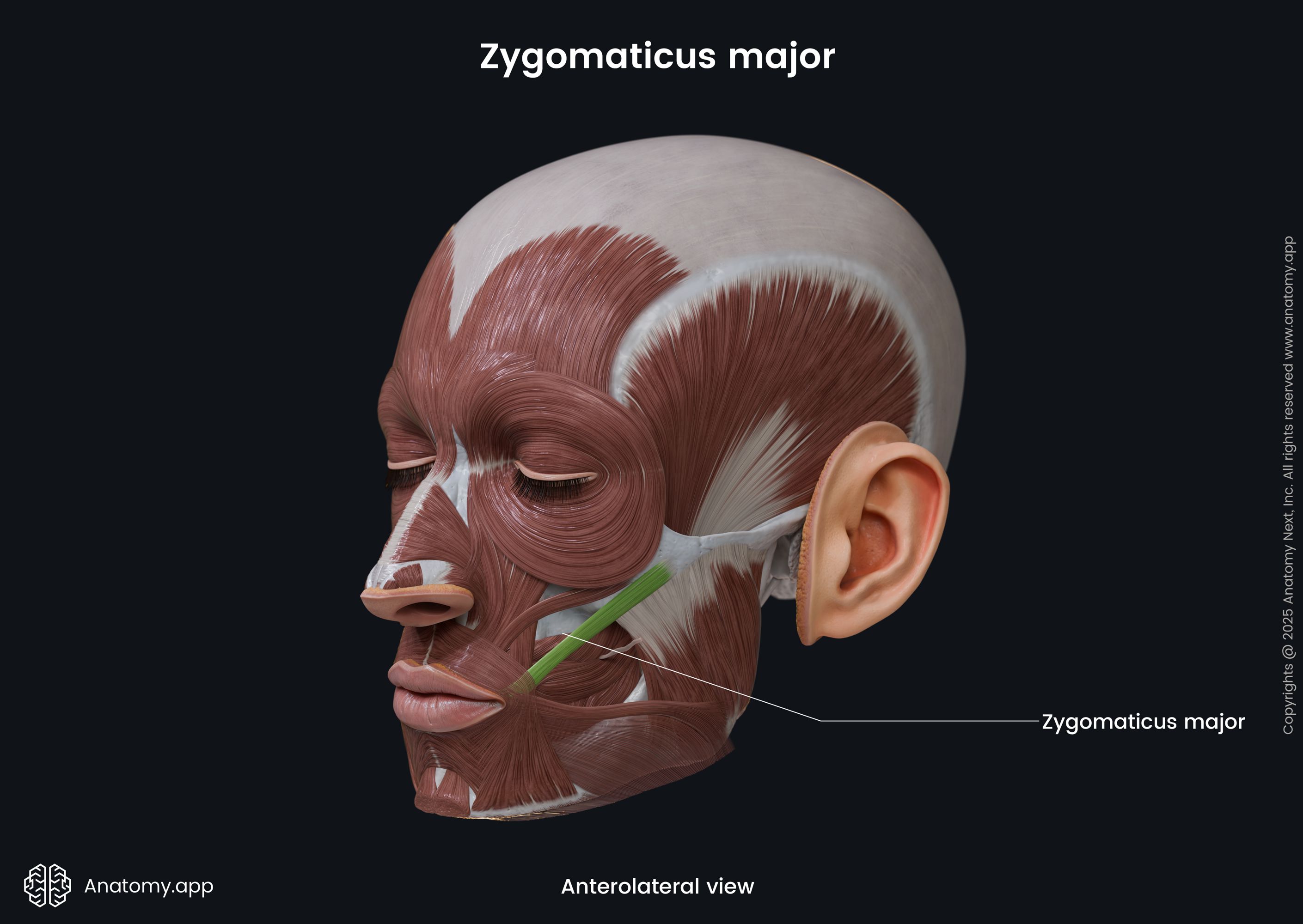
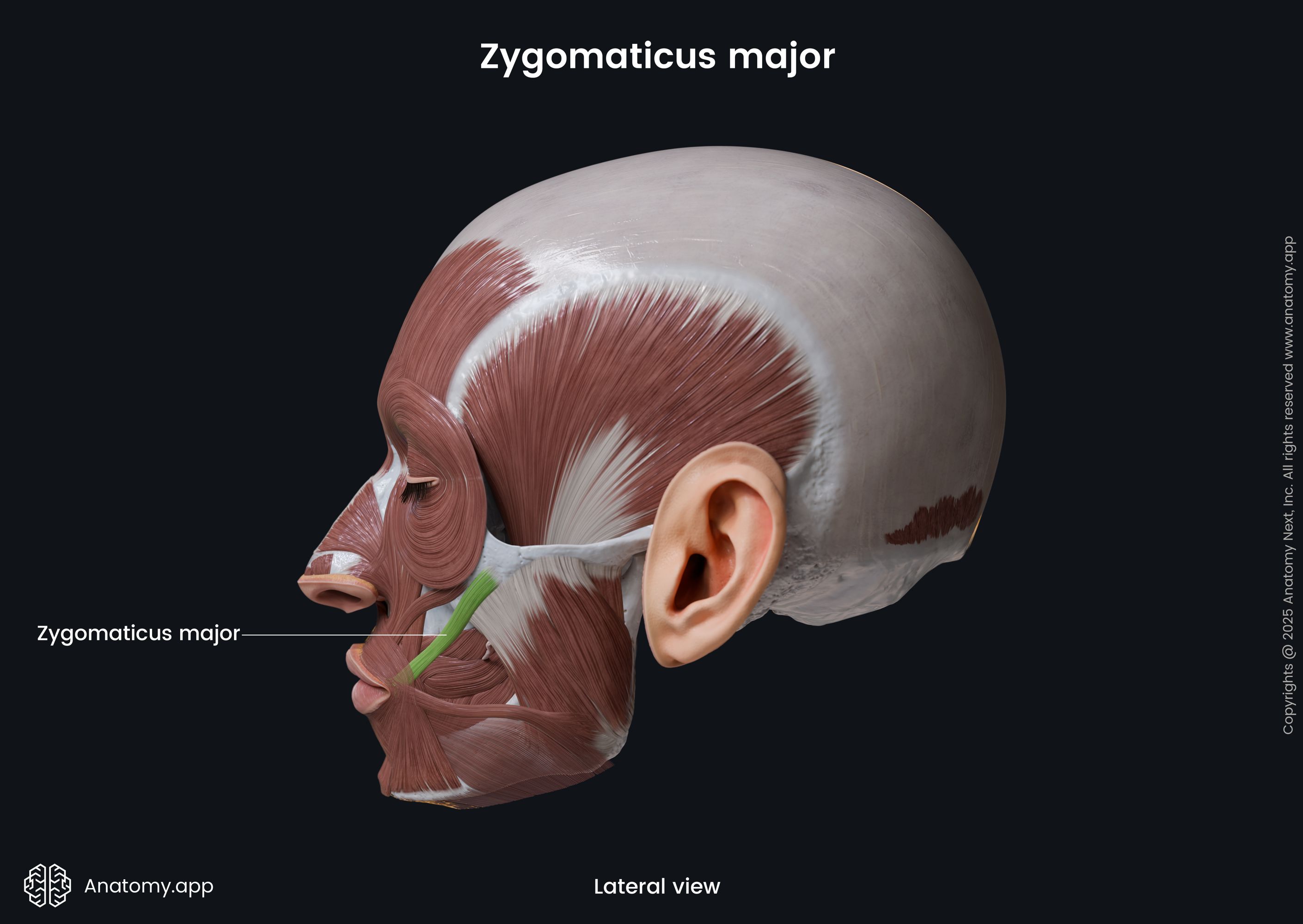
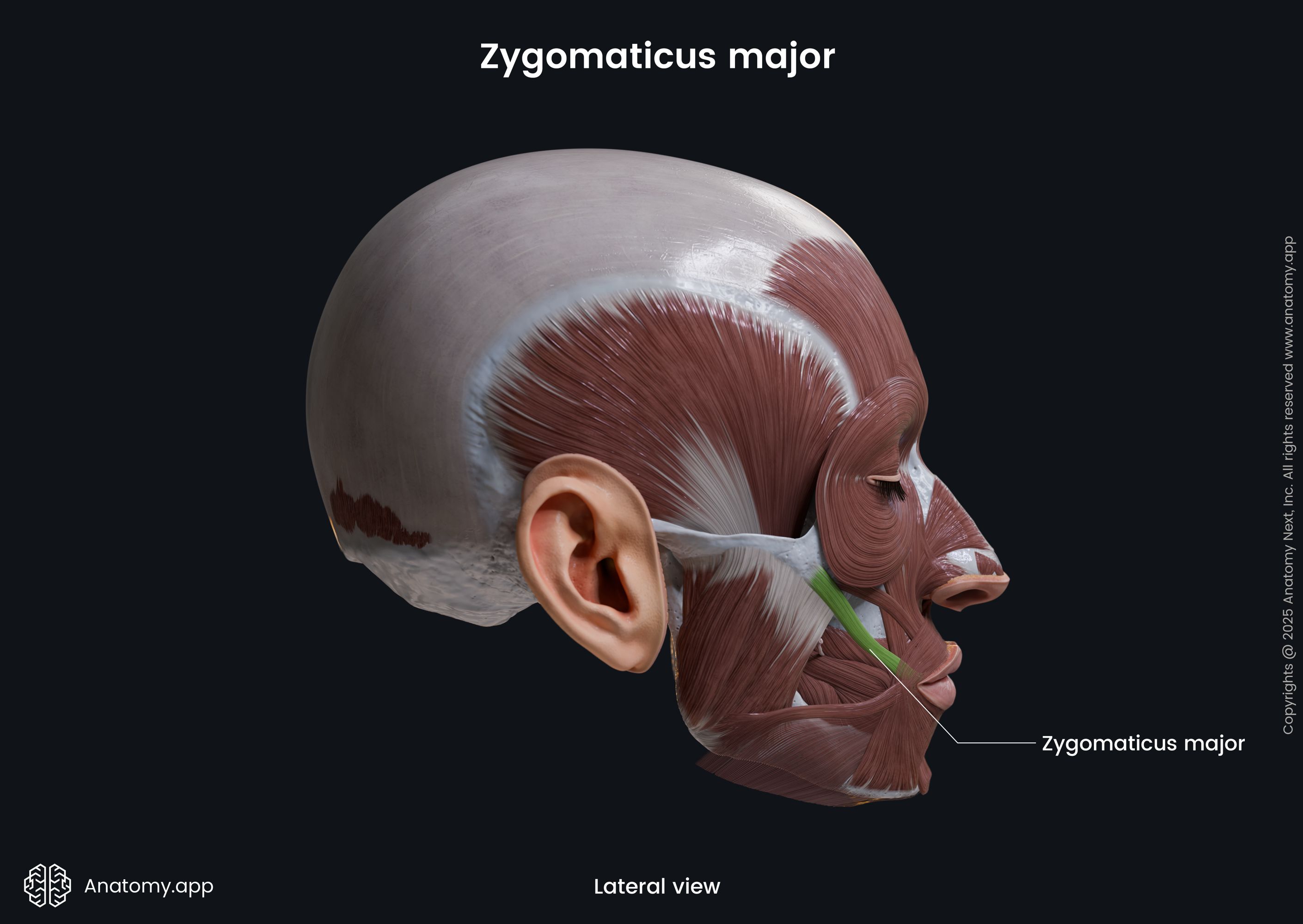
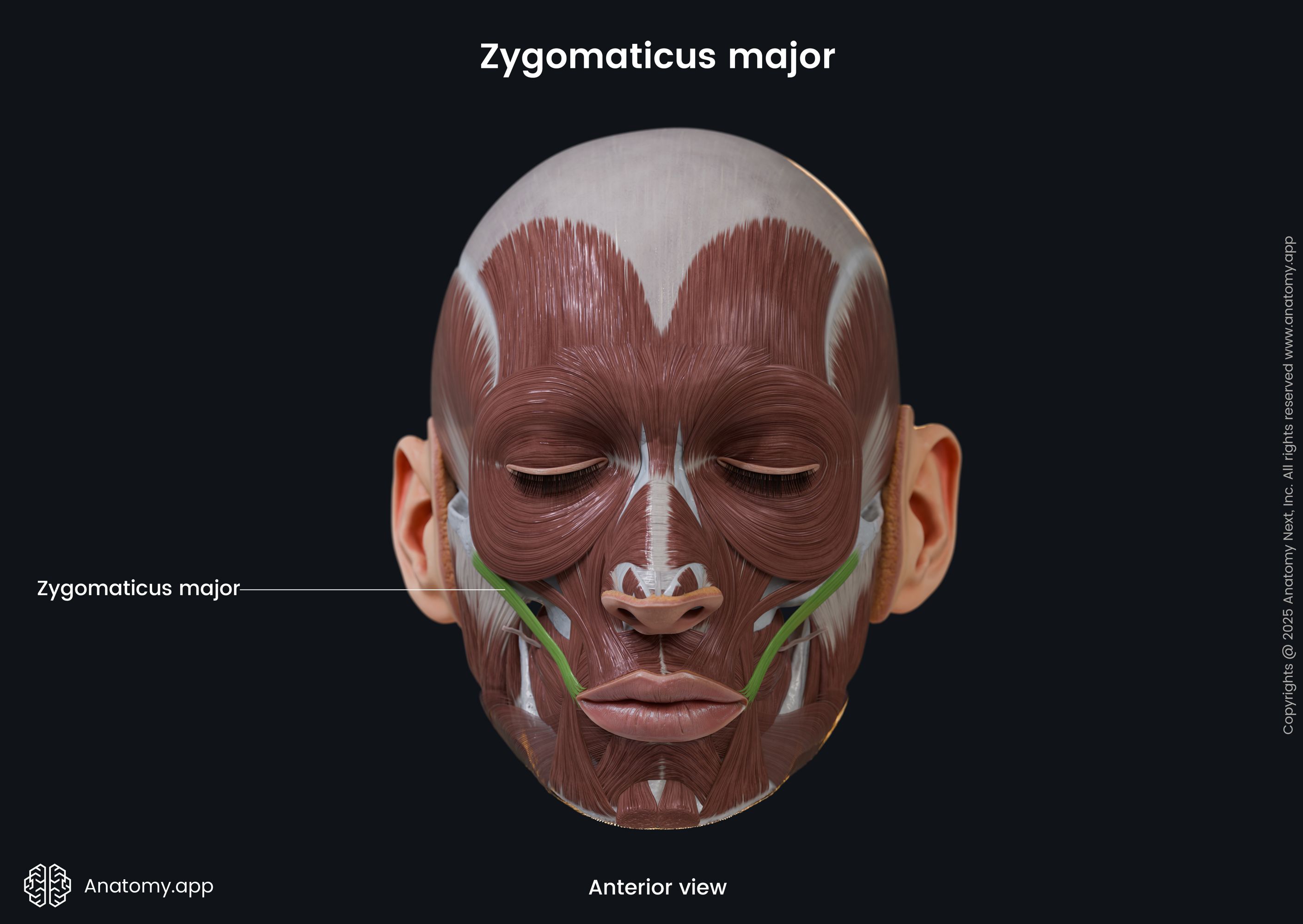
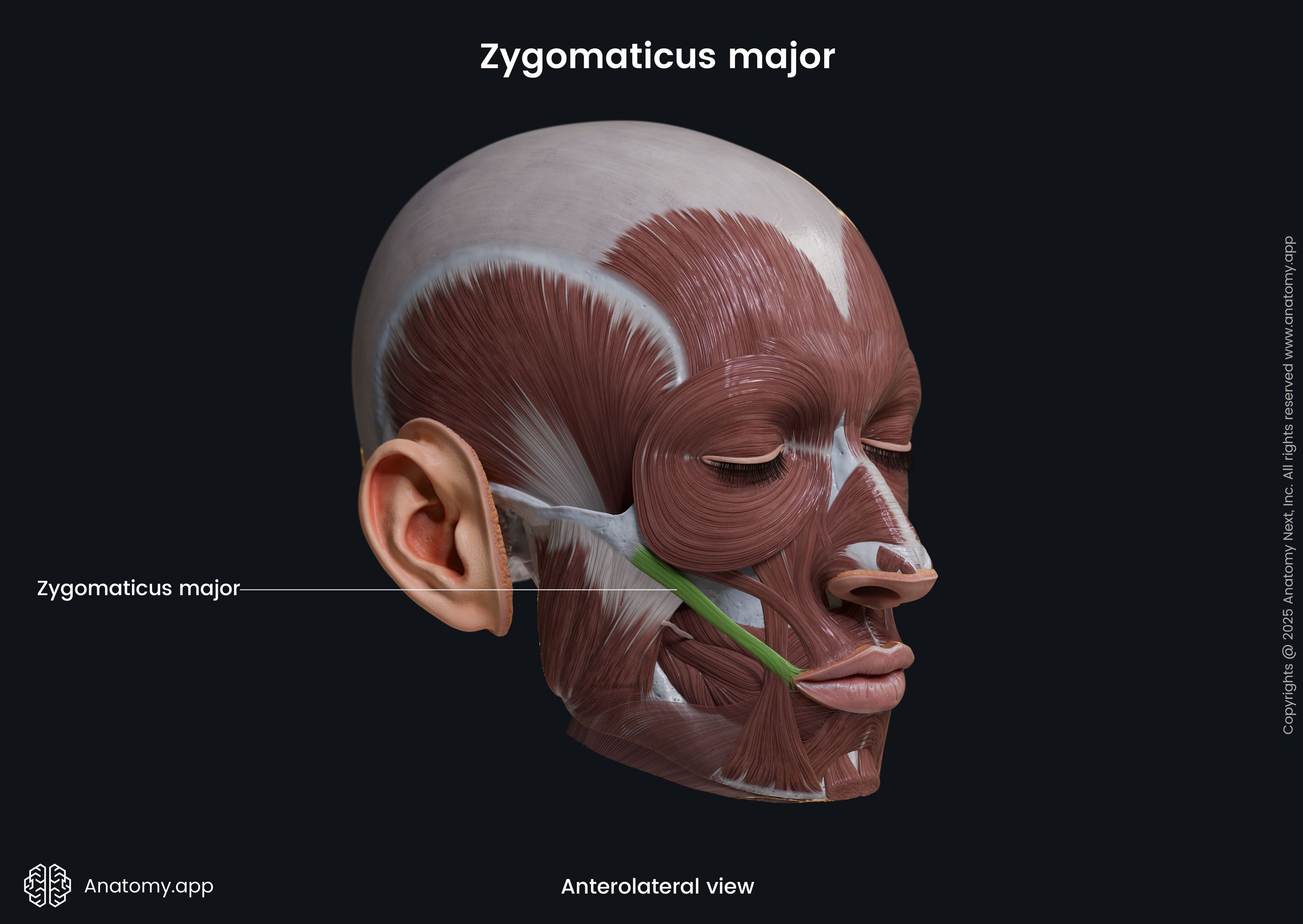
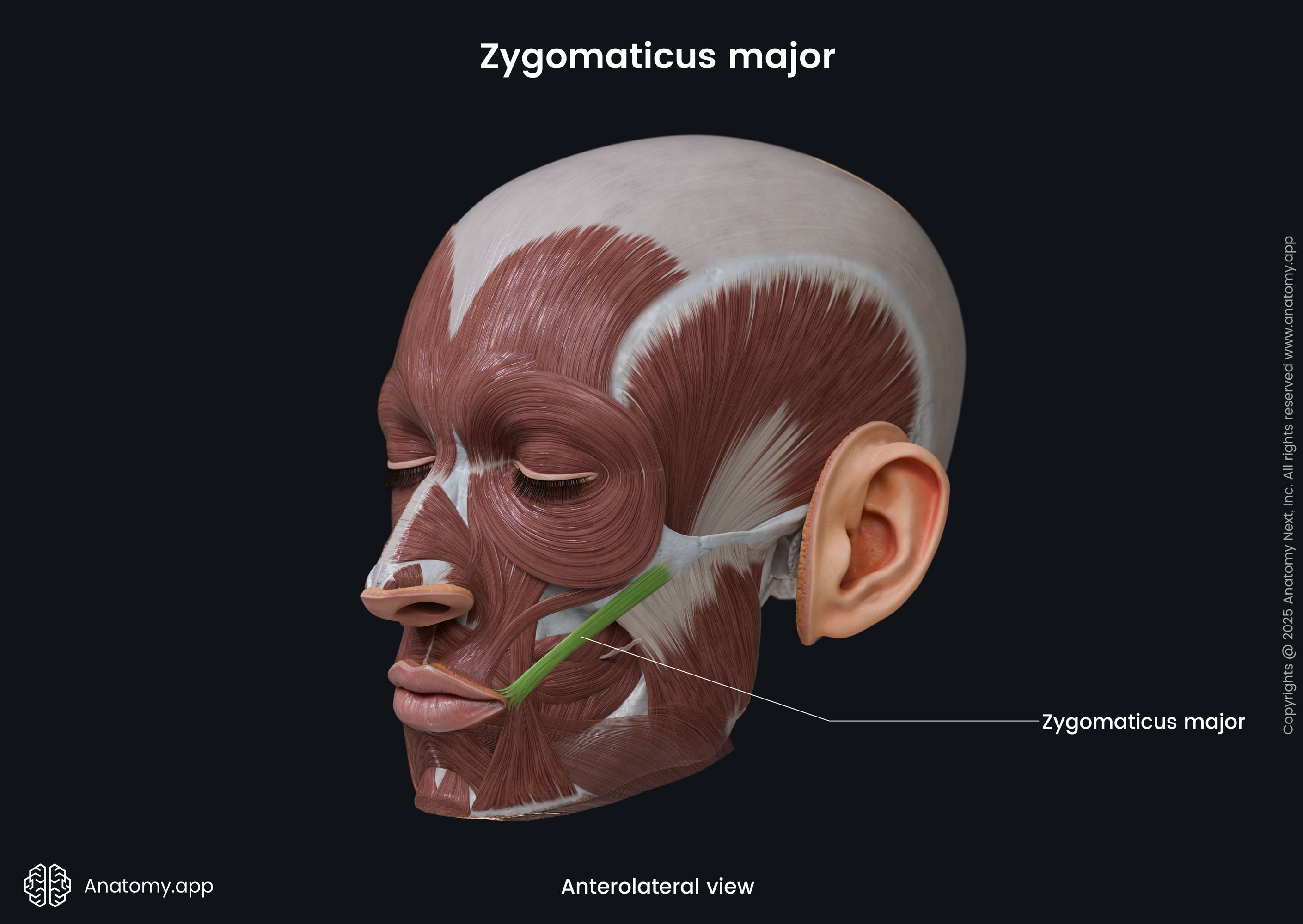
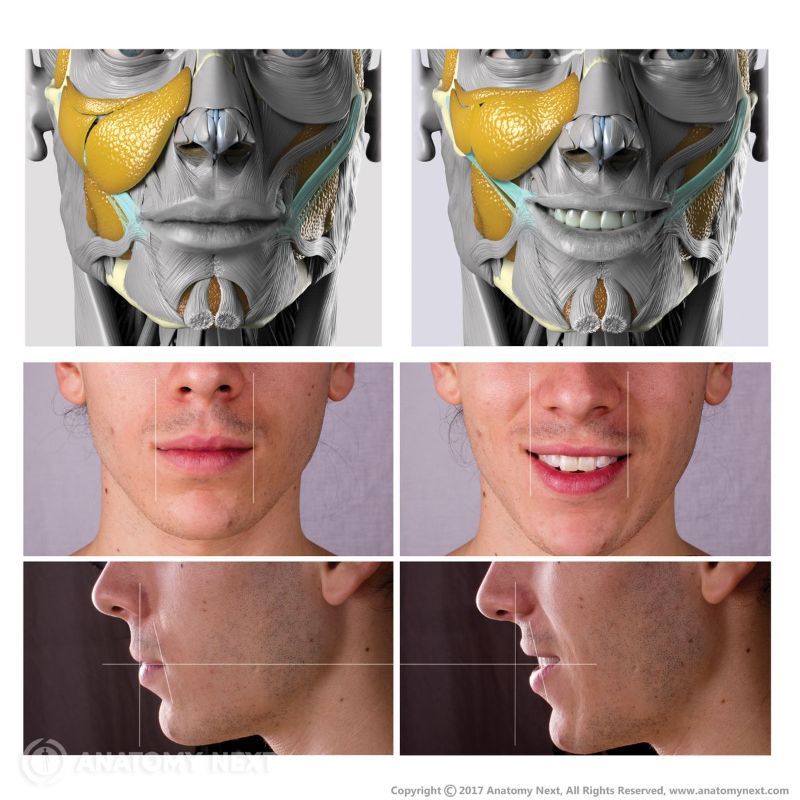
Zygomaticus major
The zygomaticus major muscle (Latin: musculus zygomaticus major) is a paired facial muscle that extends between the zygomatic bone and the angle of the mouth. It is one of two zygomatic muscles, and the other is known as the zygomaticus minor. Both muscles lie next to each other in the cheek area. The zygomaticus major muscle is classified as the buccolabial muscle. When activated, the muscle is involved in creating a facial expression known as the smile.
| Zygomaticus major | |
| Origin | Lateral surface of zygomatic bone |
| Insertion | Skin at angle of mouth |
| Action | Elevates angle of mouth upward and laterally |
| Innervation | Zygomatic and buccal branches of facial nerve (CN VII) |
| Blood supply | Superior labial artery of facial artery |
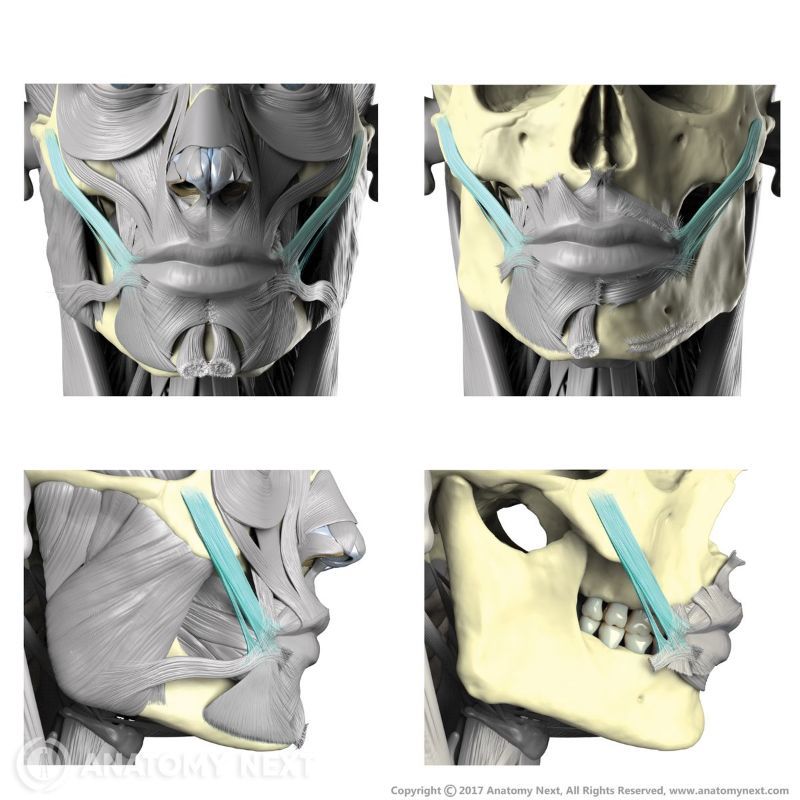
Origin
The zygomaticus major muscle arises from the lateral surface of the zygomatic bone. Its origin site is located anterior to the zygomaticotemporal suture and lateral to the origin site of the zygomaticus minor muscle.
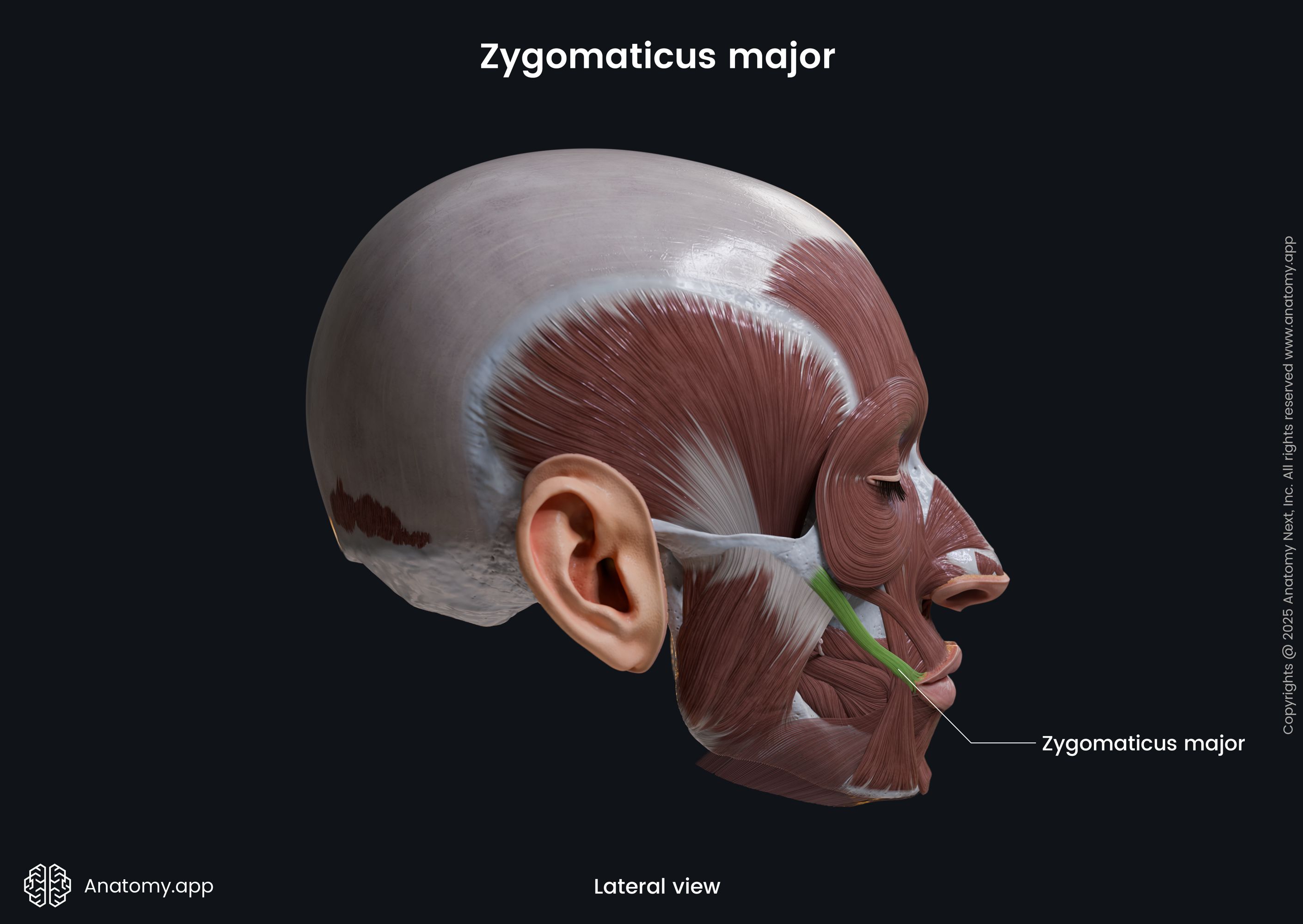
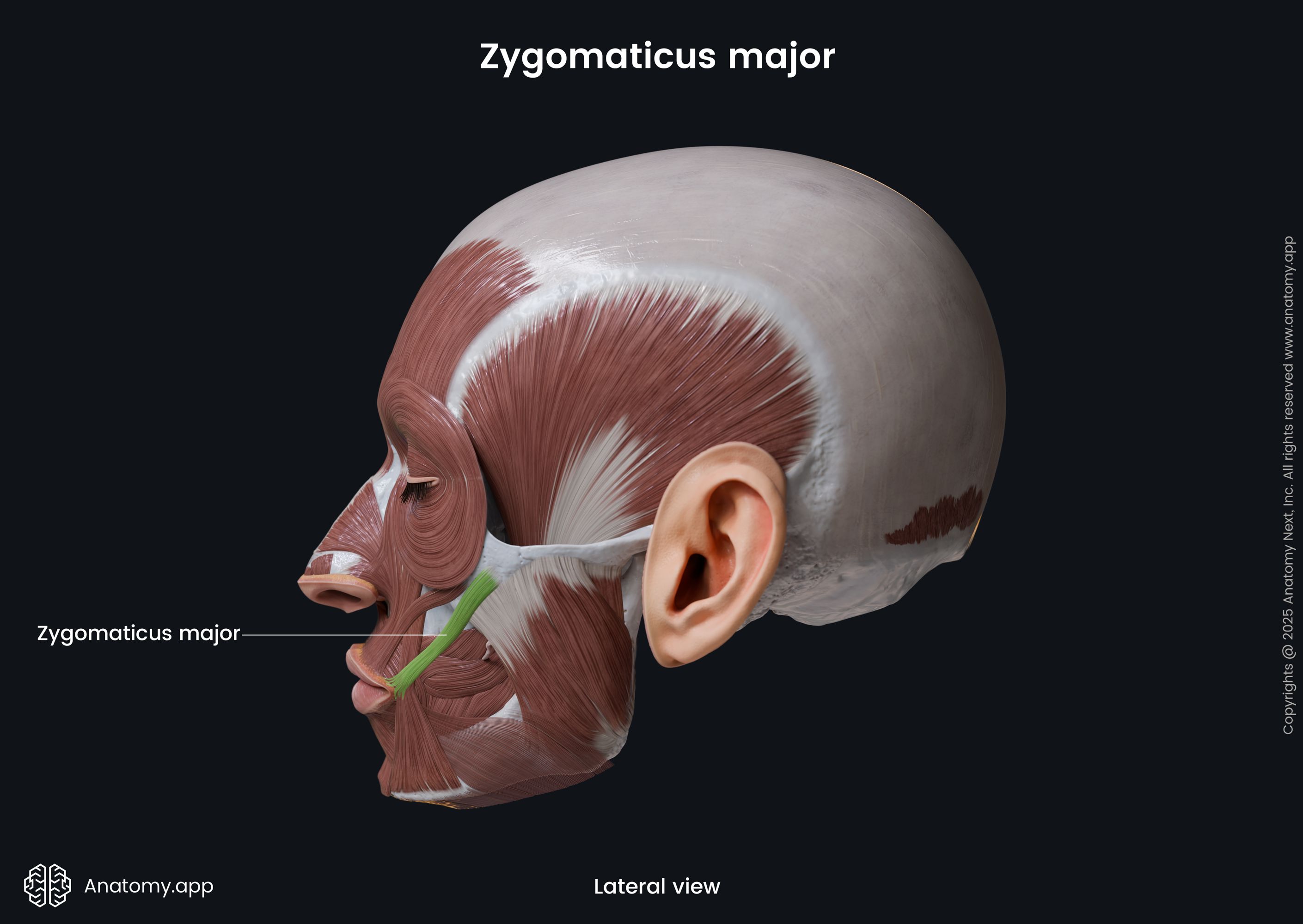
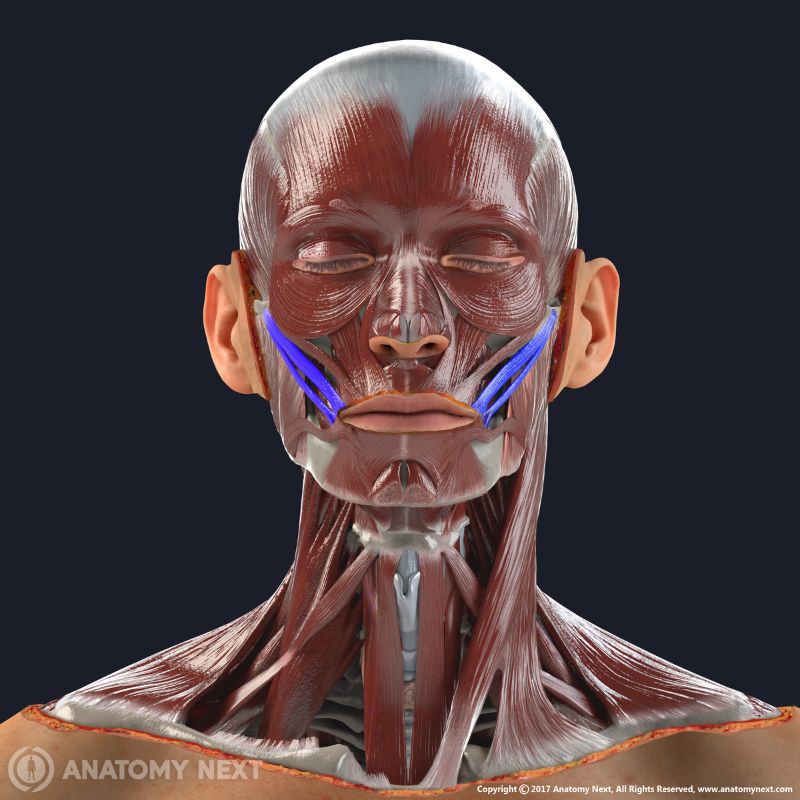
Insertion
The zygomaticus major inserts into the skin at the angle of the mouth, blending with the fibers of the levator anguli oris, orbicularis oris and more deeply placed muscles.
Action
The main action provided by the zygomaticus major muscle is the elevation of the angle of the mouth in the upward and lateral directions. Contractions of this muscle produce facial expressions of pleasure or laughter.
Innervation
The nerve supply of the zygomaticus major is provided by the zygomatic and buccal branches of the facial nerve (CN VII).
Blood supply
The zygomaticus major is supplied with arterial blood by the facial artery and its superior labial branch.
Cheek dimples
The zygomaticus major muscle is associated with the formation of cheek dimples in some individuals. Cheek dimples happen due to different variations of the zygomaticus major muscle. People, who have cheek dimples, usually have separated zygomaticus major muscles.
Before inserting into the connective tissue of the mouth corner, the zygomaticus major muscle sometimes divides into two parts, forming two separate bundles. The split is known as the duplication or bifurcation of zygomaticus major. Skin movements over the split result in dimples, for example, when smiling.
Zygomaticus major muscle stretches from the zygomatic bone to the angle of the mouth. In the case of a separated zygomatic major, the superior bundle inserts slightly lateral and superior at the angle of the mouth, while the inferior bundle inserts slightly lateral and inferior.