- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Head muscles
- Neck muscles
- Muscles of upper limb
- Thoracic muscles
- Muscles of back
- Muscles of lower limb
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
-
Eye
- Accessory structures of eye
- Ear
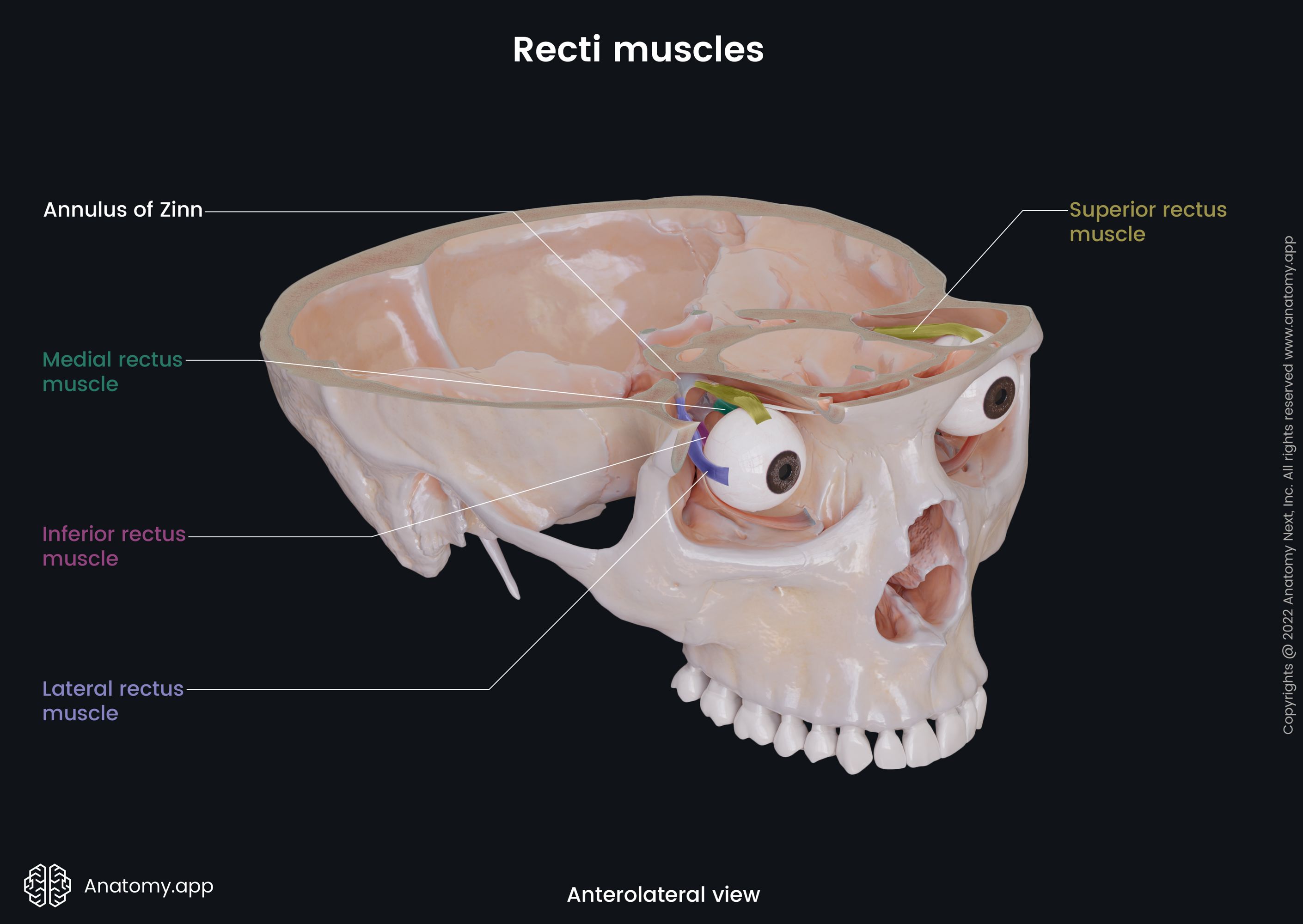
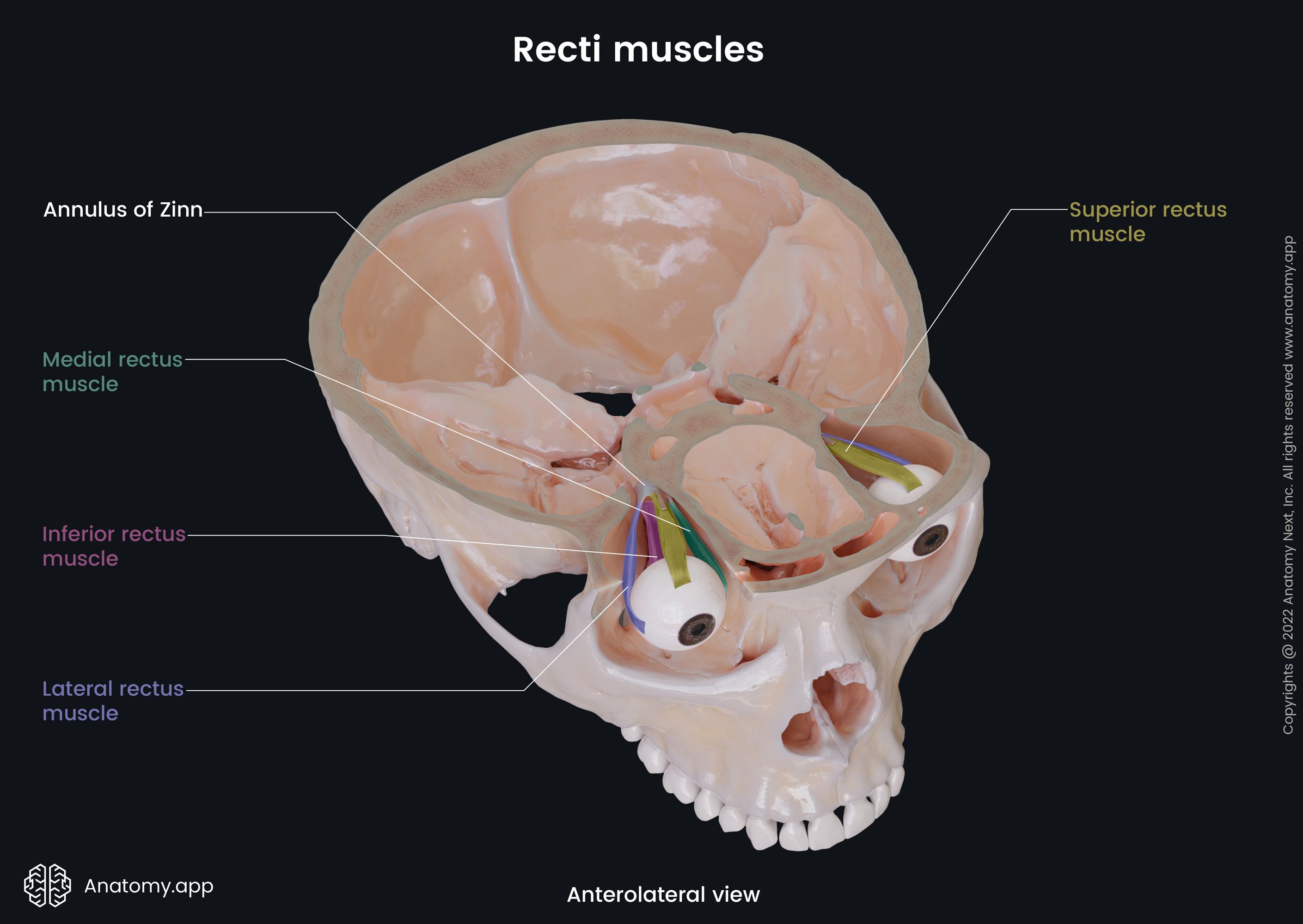
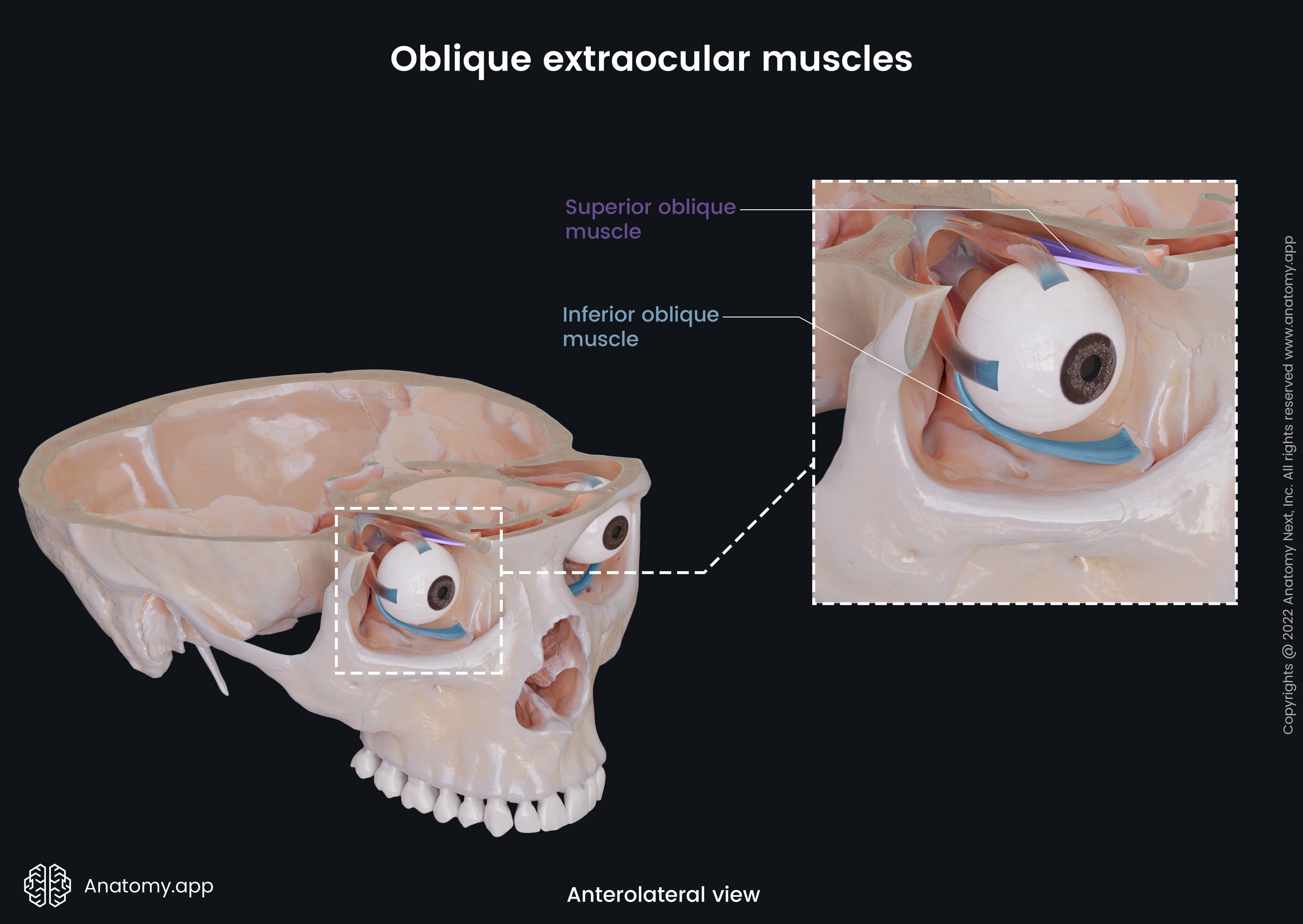
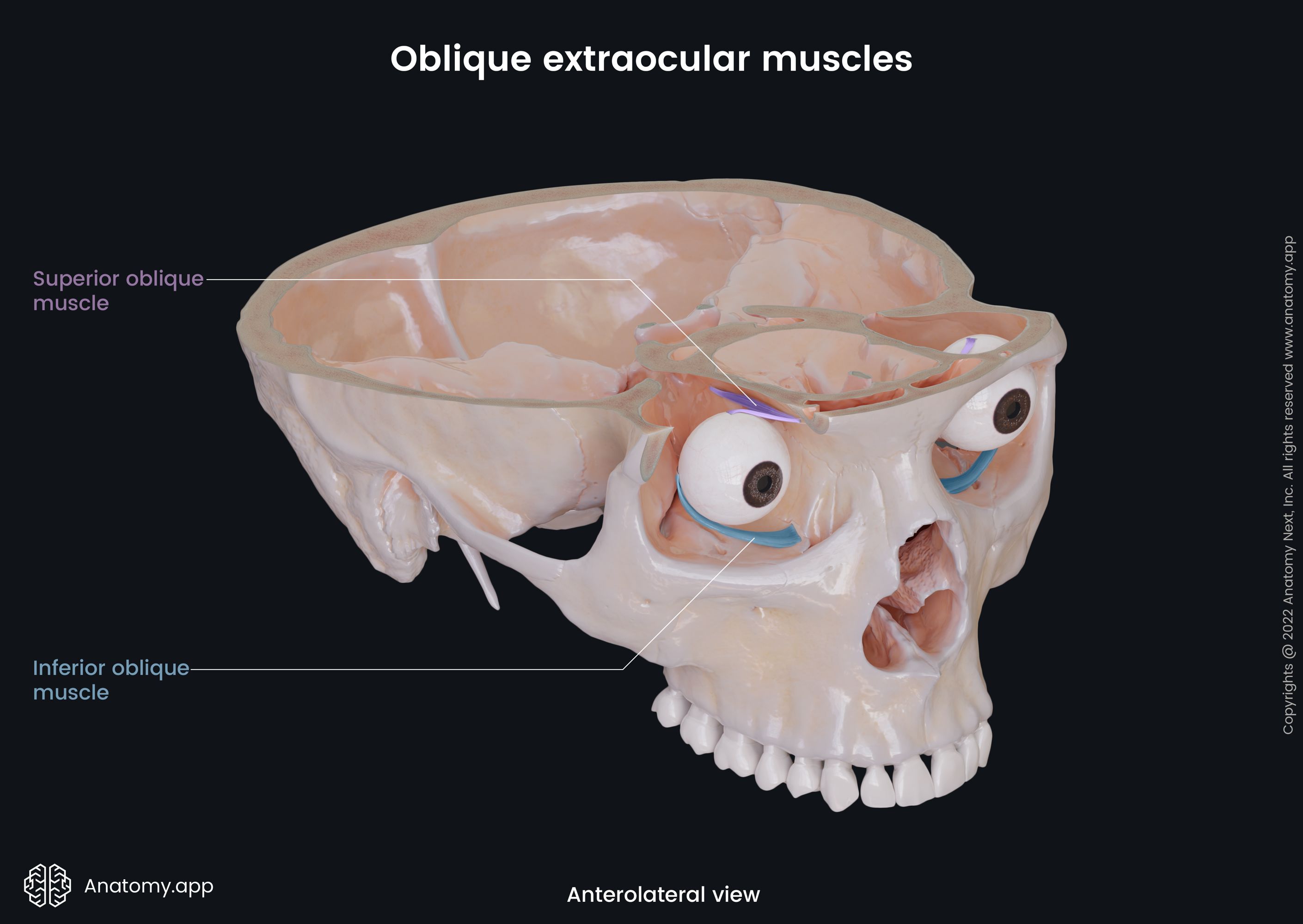
Extraocular muscles
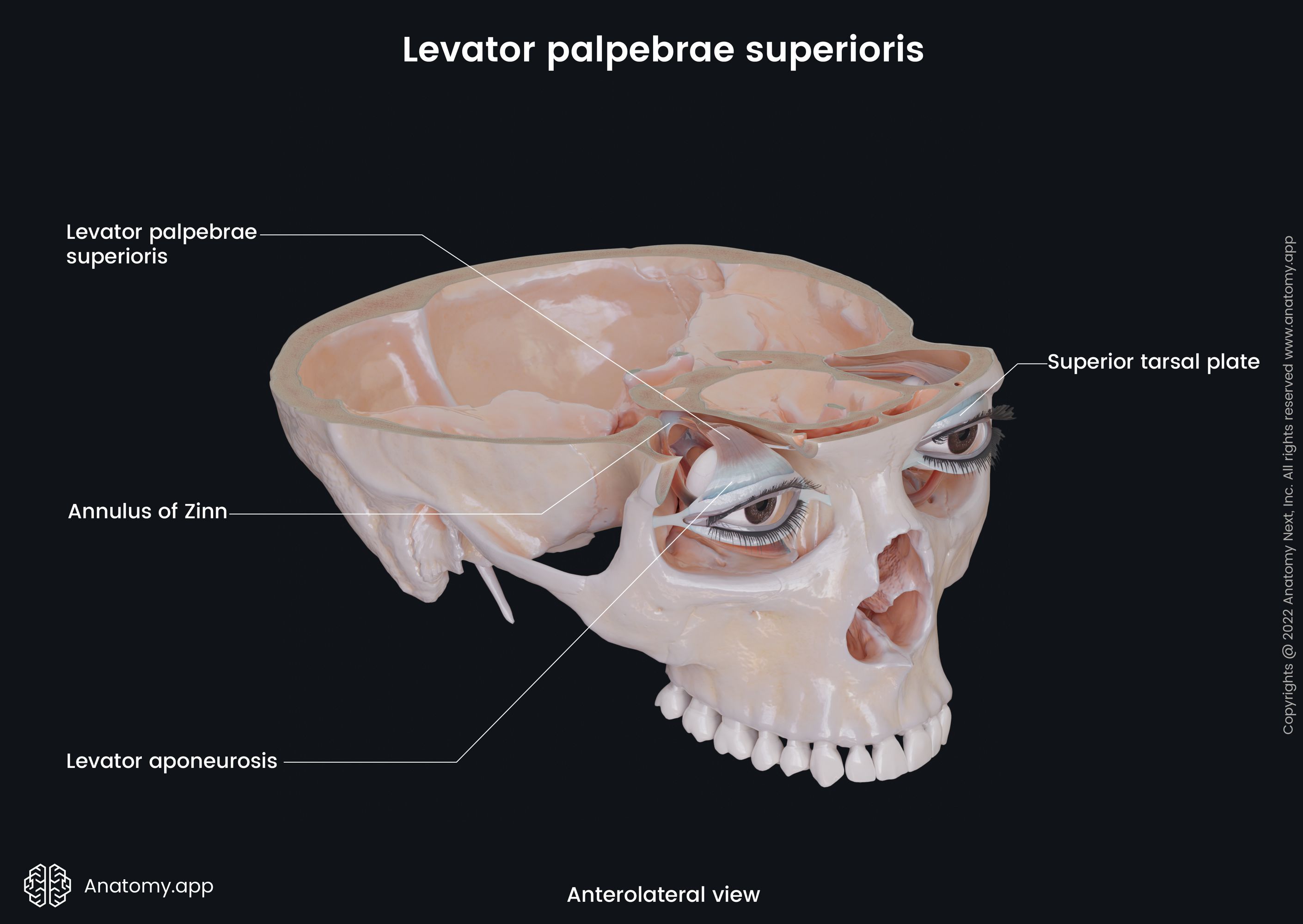
The extraocular muscles (Latin: musculi externi bulbi oculi), also known as the extrinsic muscles of eyeball, are a set of seven muscles located within each orbit and connected with the eyeball. There are six extraocular muscles responsible for eye movements and one providing elevation of the upper eyelid.
The six muscles controlling the eye movements include four recti muscles - superior rectus, inferior rectus, medial rectus, lateral rectus, and two oblique muscles - superior oblique and inferior oblique. There is the seventh extraocular muscle that provides the elevation of the upper eyelid, and that is the levator palpebrae superioris. The main actions provided by each extraocular muscle are as follows:
- Superior rectus - elevation and adduction of the eyeball, and medial rotation of the eyeball;
- Inferior rectus - depression and lateral rotation of the eyeball;
- Medial rectus - turning the eyeball medially;
- Lateral rectus - turning the eyeball laterally;
- Superior oblique - intorsion (internal rotation), depression, and abduction of the eyeball;
- Inferior oblique - extortion (external rotation), elevation, and abduction of the eye;
- Levator palpebrae superioris - elevation of the upper eyelid.
The motor innervation of the extraocular muscles is provided by three cranial nerves: oculomotor (CN III), trochlear (CN IV) and abducens (CN VI). The oculomotor nerve (CN III) supplies five extraocular muscles: three out of the four recti muscles (superior, inferior, medial), inferior oblique muscle, and levator palpebrae superioris muscle. The trochlear nerve (CN IV) innervates only the superior oblique, while the abducens nerve (CN VI) supplies the lateral rectus muscle.