- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Aorta
- Blood vessels of head and neck
- Arteries of head and neck
- Veins of head and neck
- Blood vessels of upper limb
- Blood vessels of thorax
- Blood vessels of abdomen
- Blood vessels of pelvis and lower limb
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
Maxillary artery
The maxillary artery (Latin: arteria maxillaris) is the largest terminal branch of the external carotid artery that arises posterior to the neck of the mandible. It supplies deep structures of the face, such as the mandible, maxilla, teeth, muscles of mastication, palate, nose, and part of the cranial dura mater.
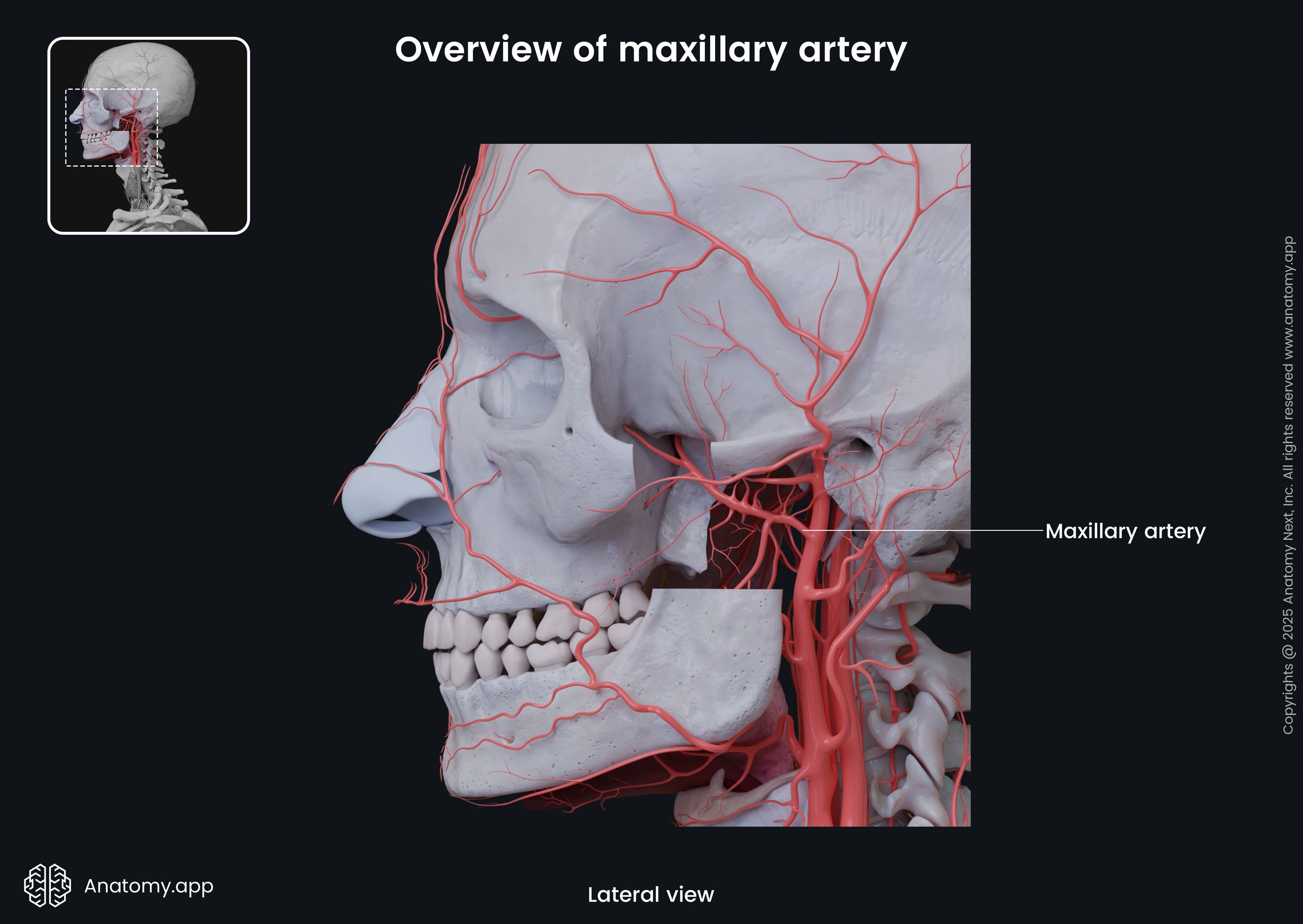
Course and parts of maxillary artery
At its origin, the maxillary artery is embedded in the parotid gland. After exiting the gland, it runs through the infratemporal fossa and enters the pterygopalatine fossa via the pterygomaxillary fissure. While passing through the pterygopalatine fossa, the maxillary artery divides into four branches, and gives off several side branches. Topographically the maxillary artery can be divided into three portions:
Branches of maxillary artery
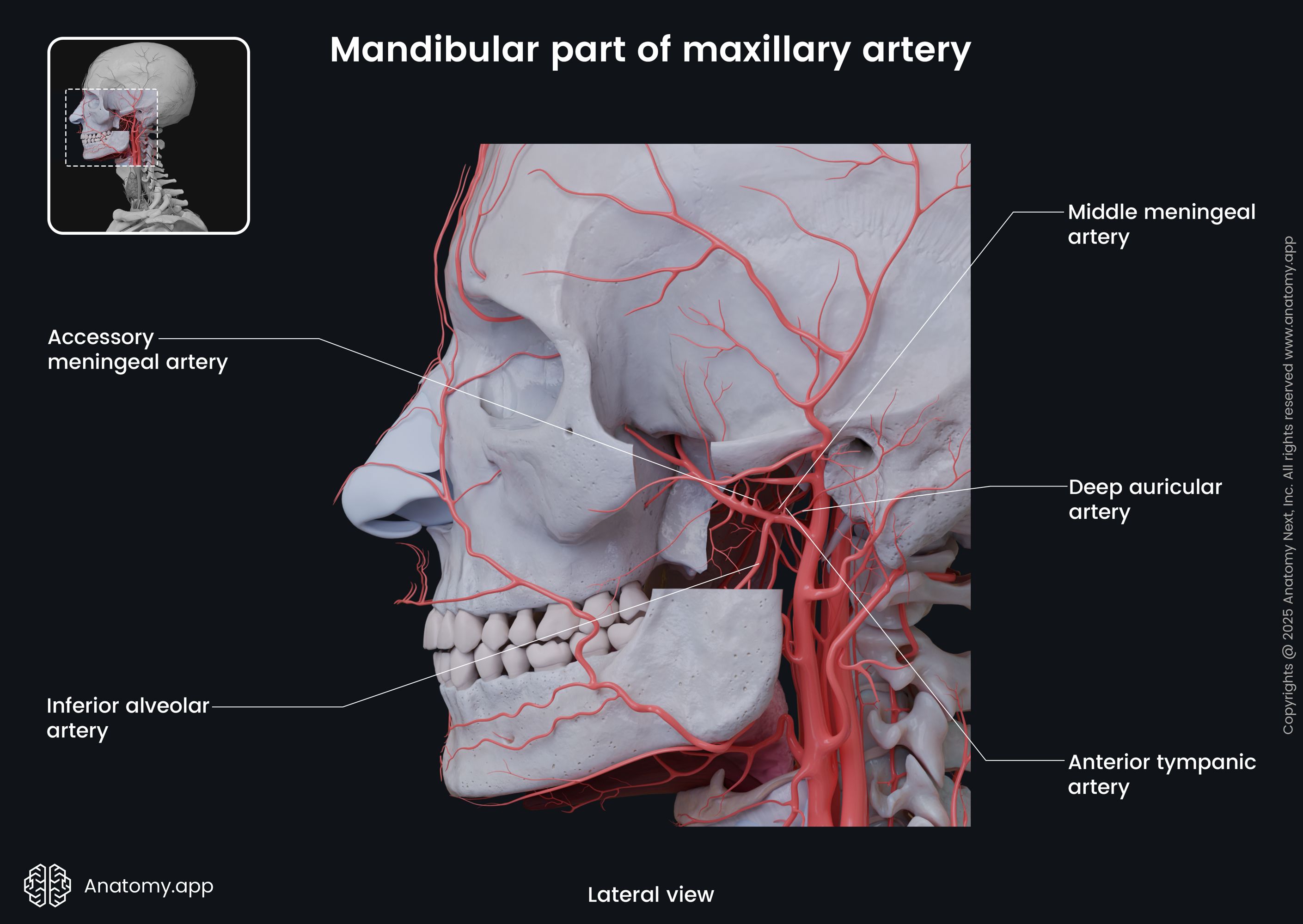
From the mandibular part, the maxillary artery gives off five branches that enter the skull and supply bones of the skull. These branches are:
- Deep auricular artery
- Anterior tympanic artery
- Middle meningeal artery
- Accessory meningeal artery
- Inferior alveolar artery
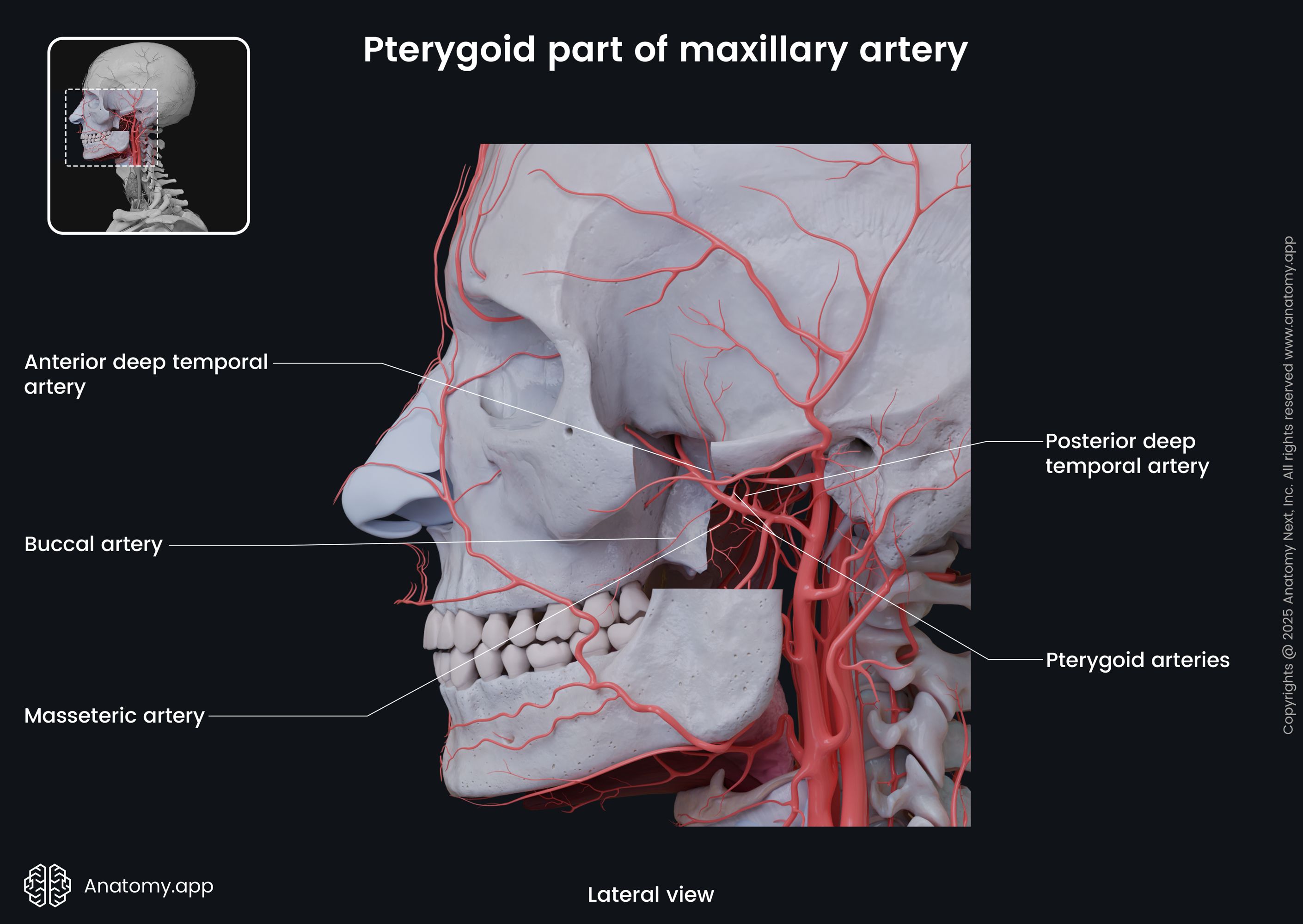
The pterygoid part of the maxillary artery gives off the following four branches that supply the corresponding muscles:
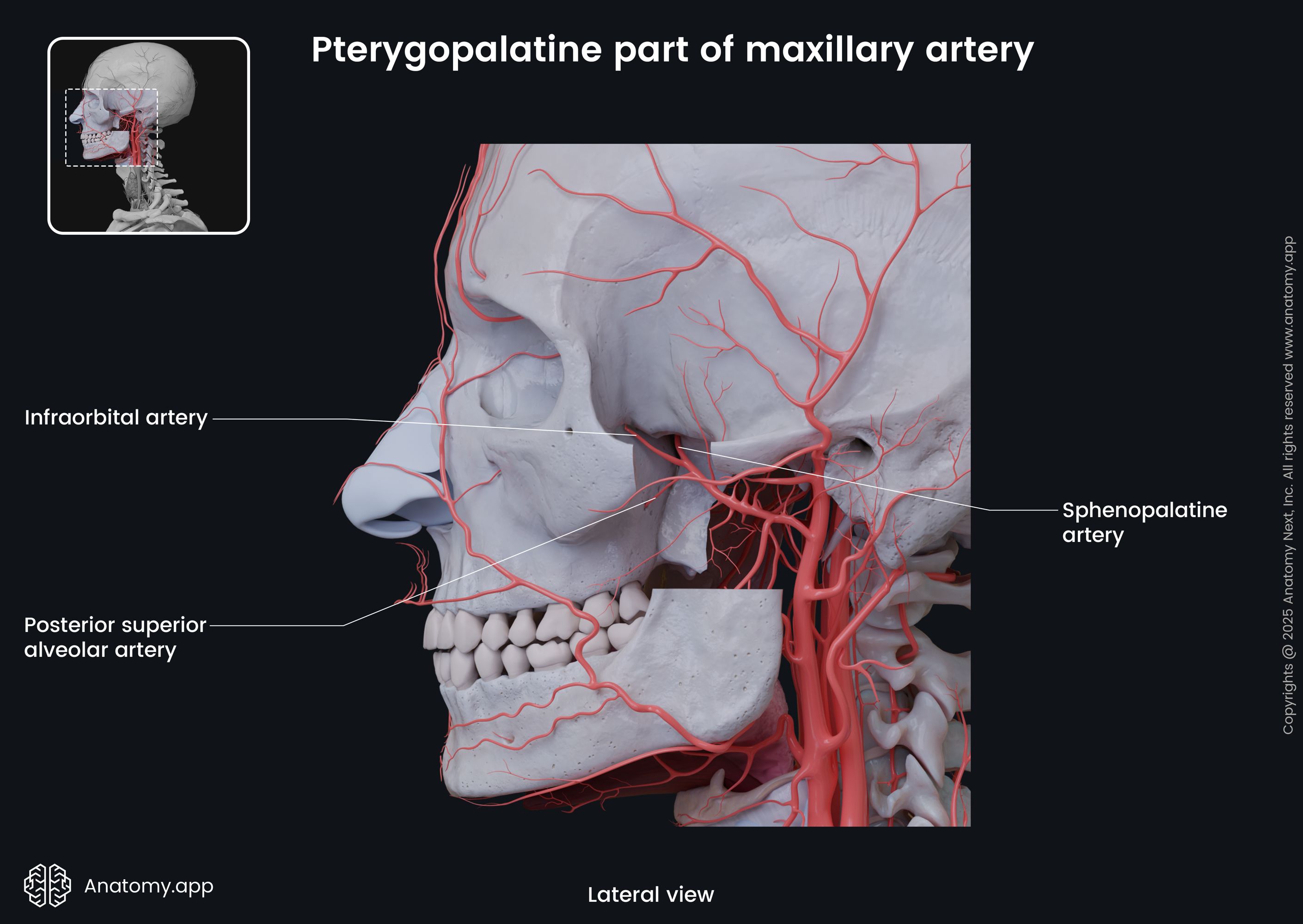
The pterygopalatine part of the maxillary artery provides four branches that accompany similarly named branches of the maxillary nerve. These branches include:
- Posterior superior alveolar artery
- Infraorbital artery
- Descending palatine artery
- Sphenopalatine artery