- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
-
Head muscles
- Extraocular muscles
-
Facial muscles
- Occipitofrontalis
- Corrugator supercilii
- Depressor supercilii
- Orbicularis oculi
- Malaris
- Buccinator
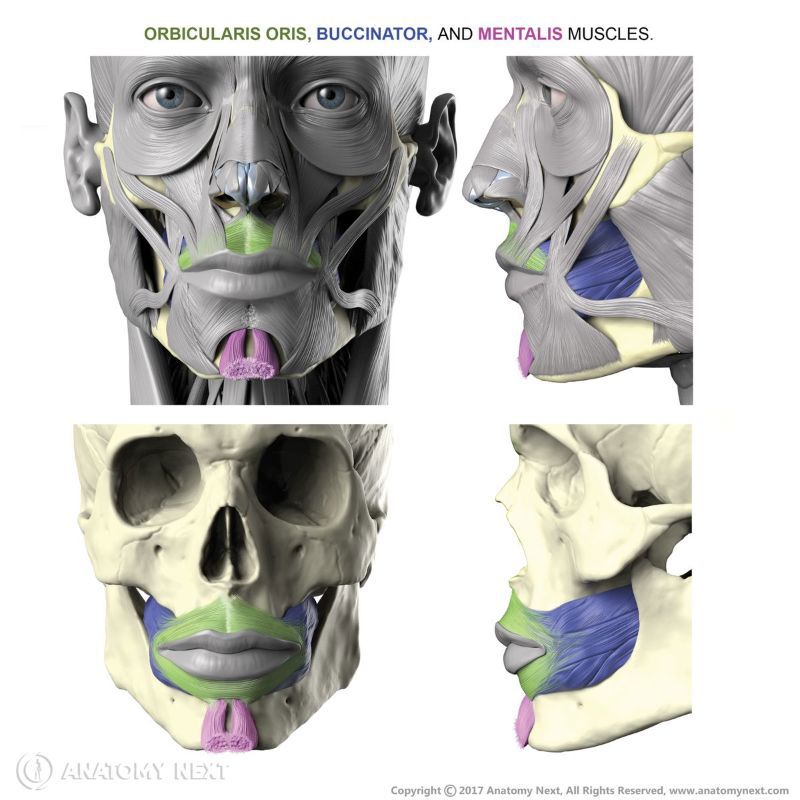
- Orbicularis oris
- Mentalis
- Depressor anguli oris
- Depressor labii inferioris
- Levator anguli oris
- Levator labii superioris
- Risorius
- Zygomaticus major
- Zygomaticus minor
- Levator labii superioris alaeque nasi
- Nasalis
- Procerus
- Depressor septi nasi
- Compressor narium minor
- Dilator naris anterior
- Muscles of mastication
- Neck muscles
- Muscles of upper limb
- Thoracic muscles
- Muscles of back
- Muscles of lower limb
-
Head muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
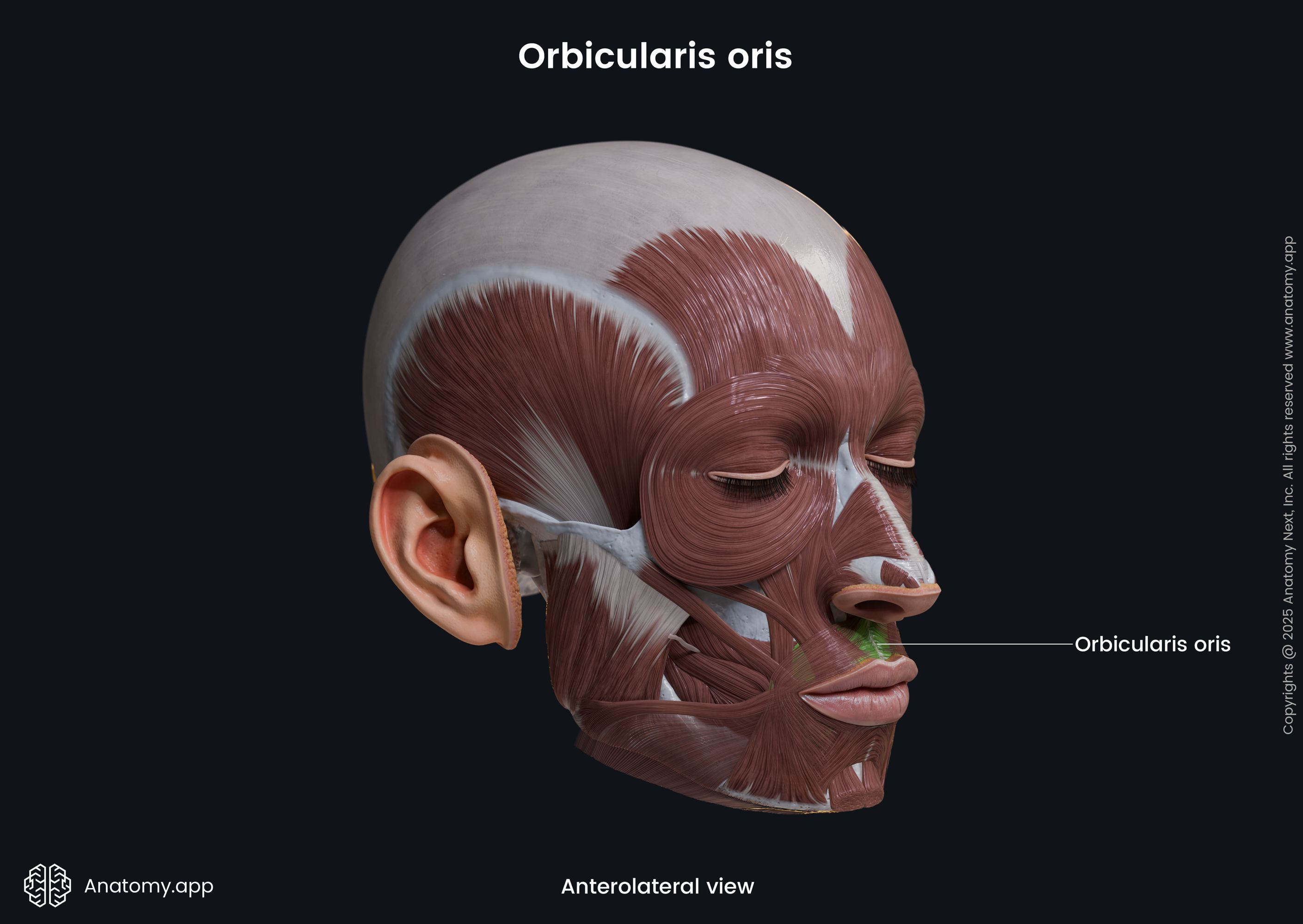
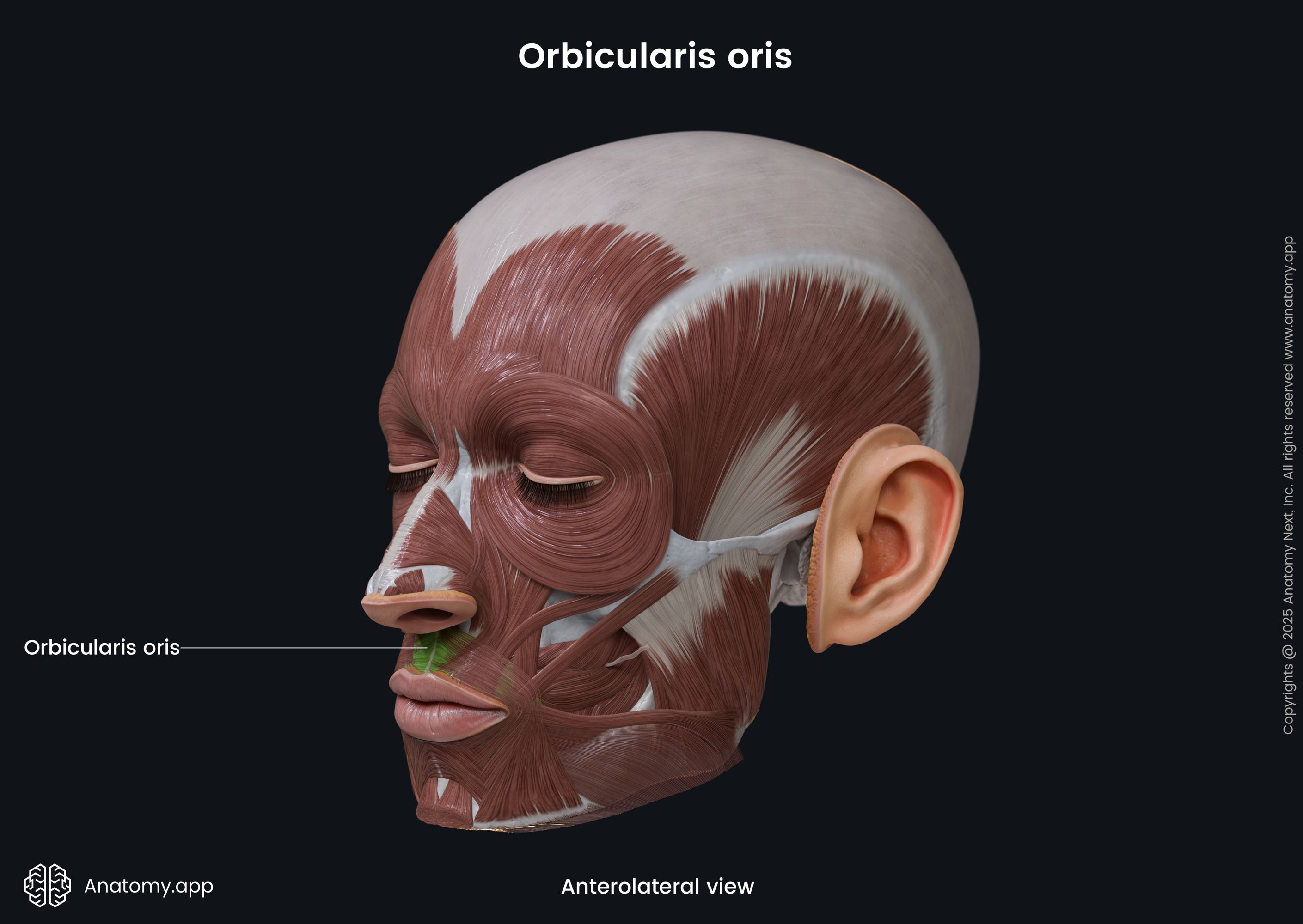
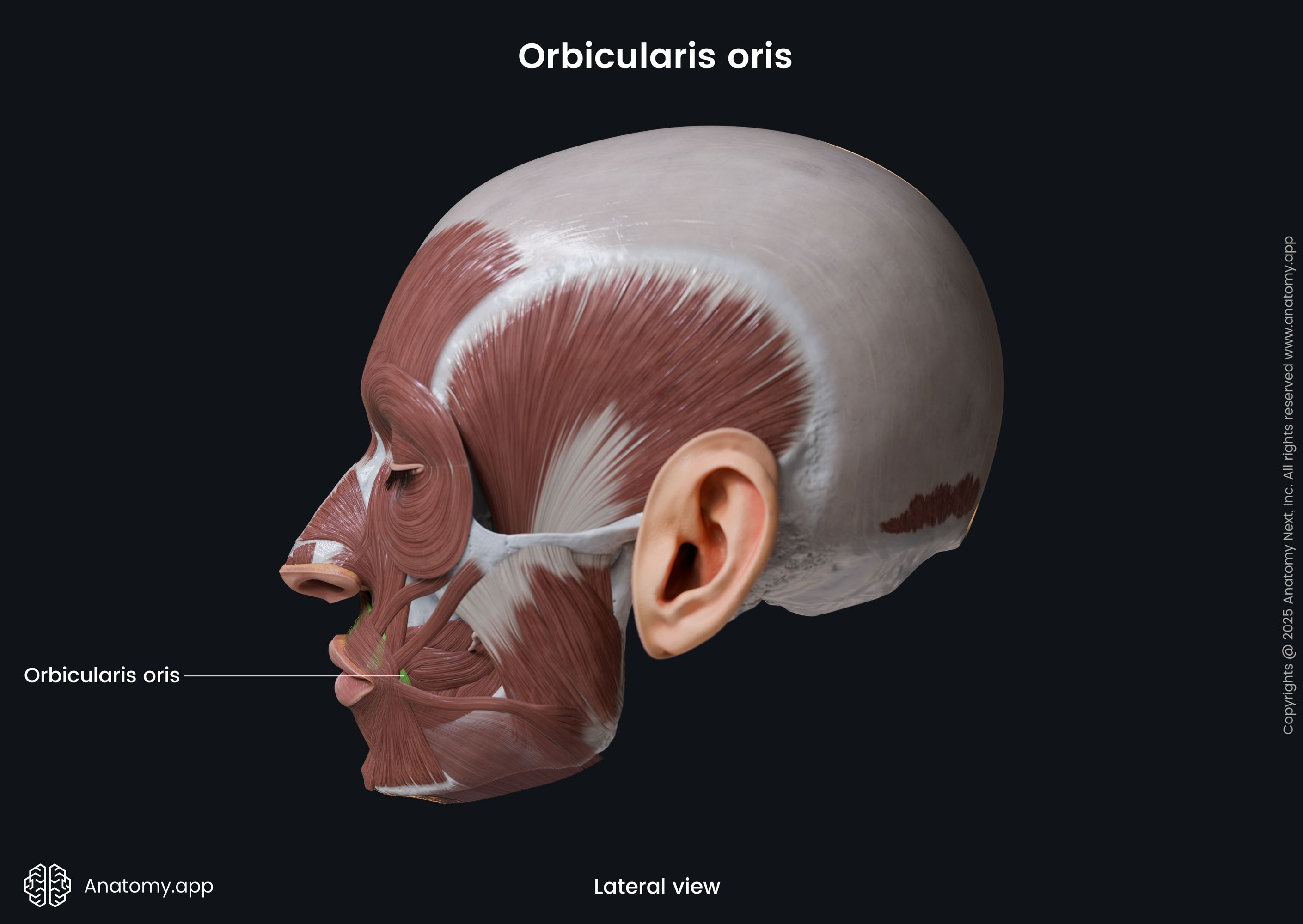
Orbicularis oris
The orbicularis oris (Latin: musculus orbicularis oris) is a circular-shaped facial muscle that is located around the mouth. It is classified as the buccolabial facial muscle. The orbicularis oris is composed of two main parts, named the marginal (smaller) and peripheral parts (larger) parts.
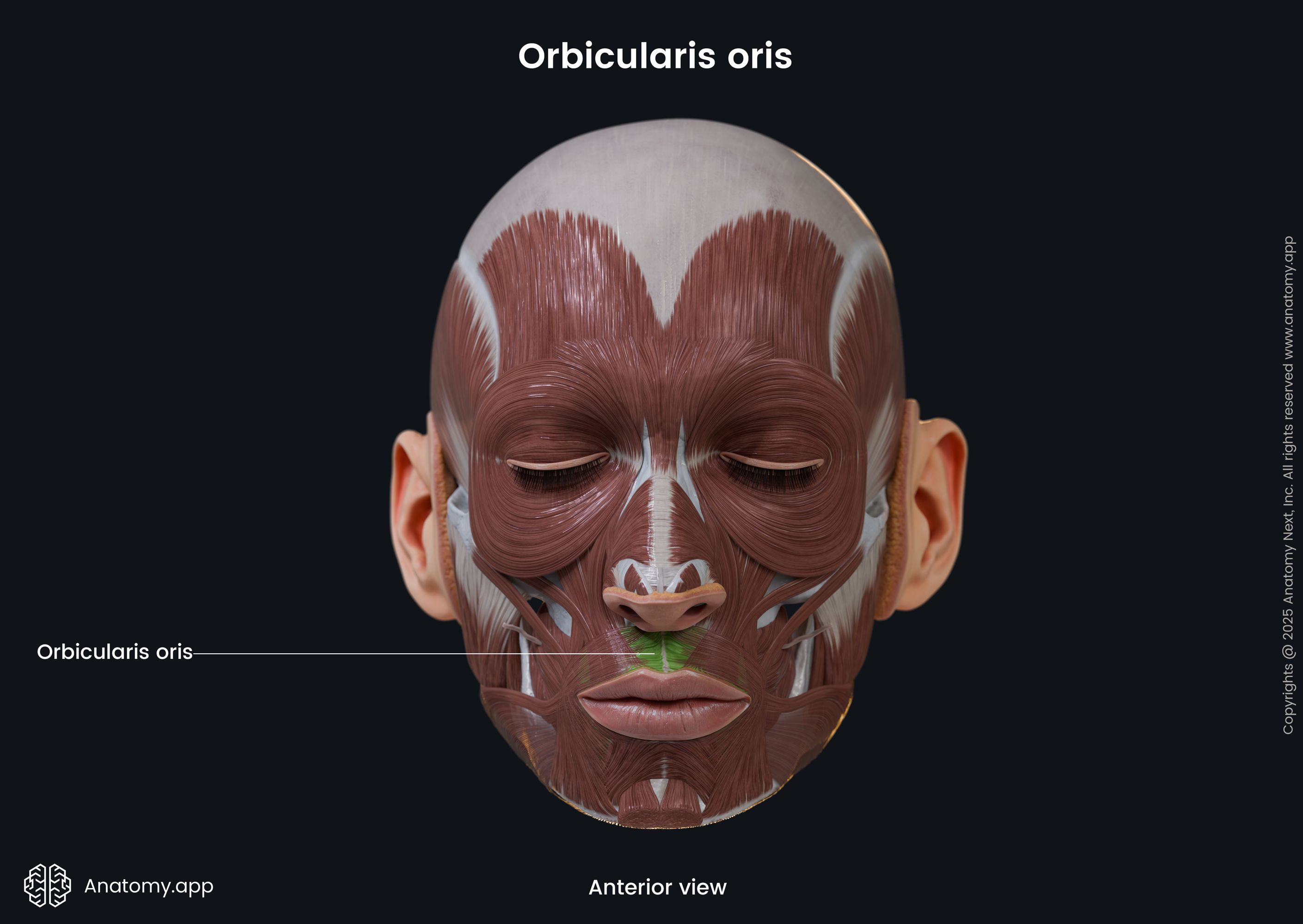
The marginal is the inner, while the peripheral is the outer part of the muscle. Superior and inferior aspects of both parts stretch between the right and left modiolus. The modiolus is a fibromuscular structure at each angle of the mouth. It is a connection site where several buccolabial facial muscles meet and blend with each other.
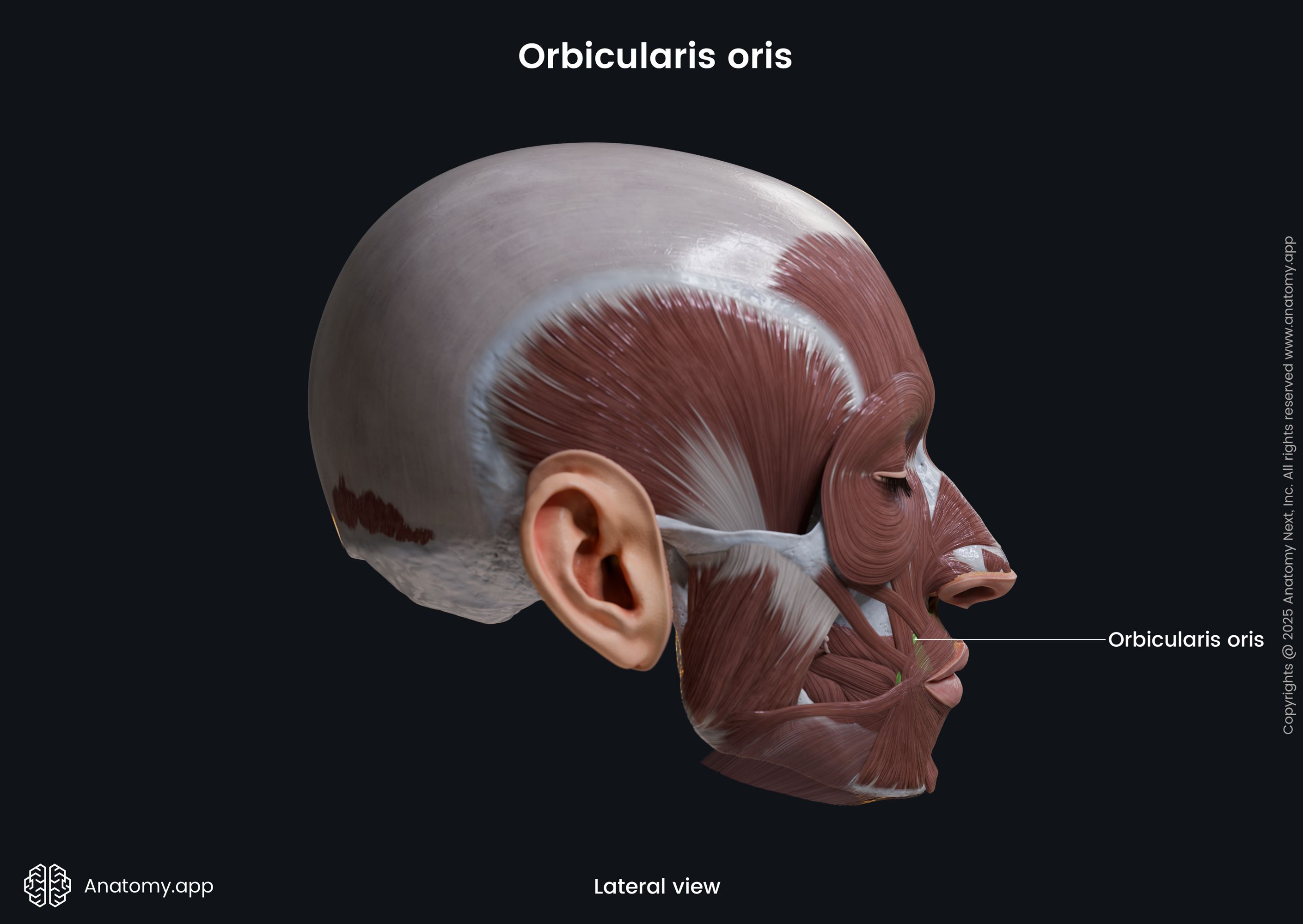
| Orbicularis oris | |
| Origin | Modiolus, skin and muscles of mouth |
| Insertion | Skin and mucous membrane of lips |
| Action | Closes mouth, pushes lips forward |
| Innervation | Buccal branch of facial nerve (CN VII) |
| Blood supply | Superior and inferior labial arteries of facial artery, mental and infraorbital arteries of maxillary artery, transverse facial artery of superficial temporal artery |
Origin
The fibers of the marginal and peripheral parts of the orbicularis oris muscle originate from the modiolus, skin of the mouth and other muscles of facial expression.
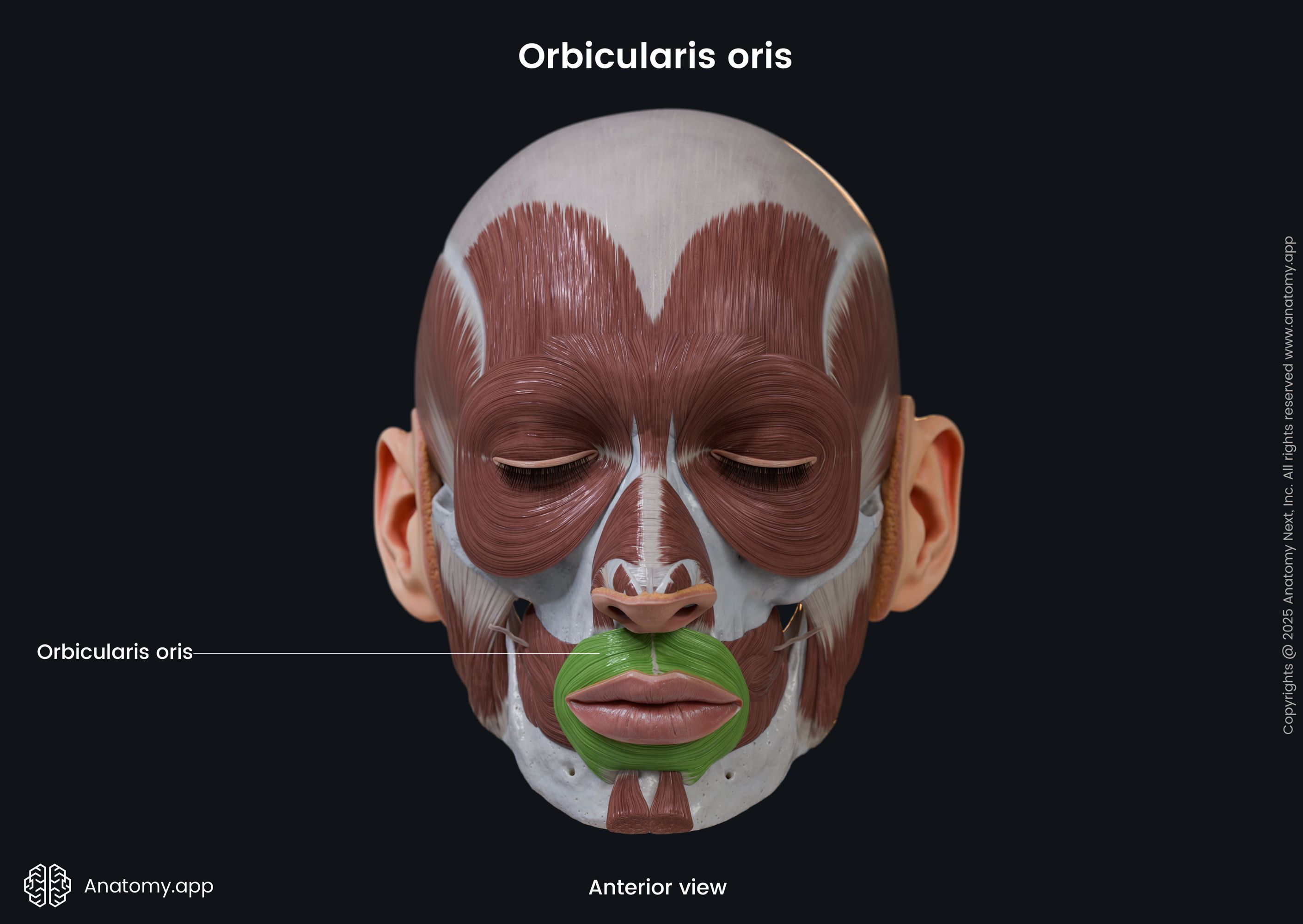
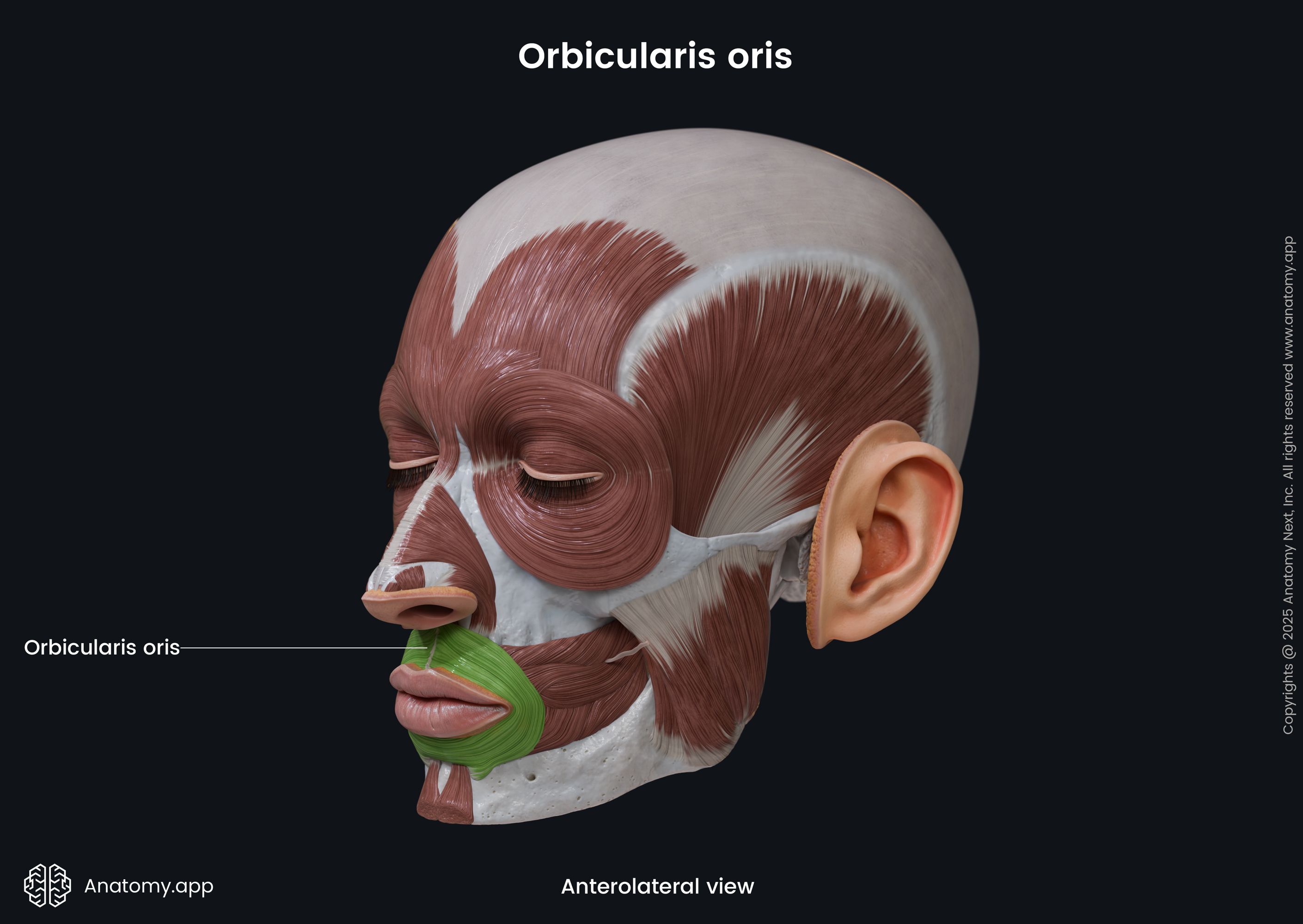
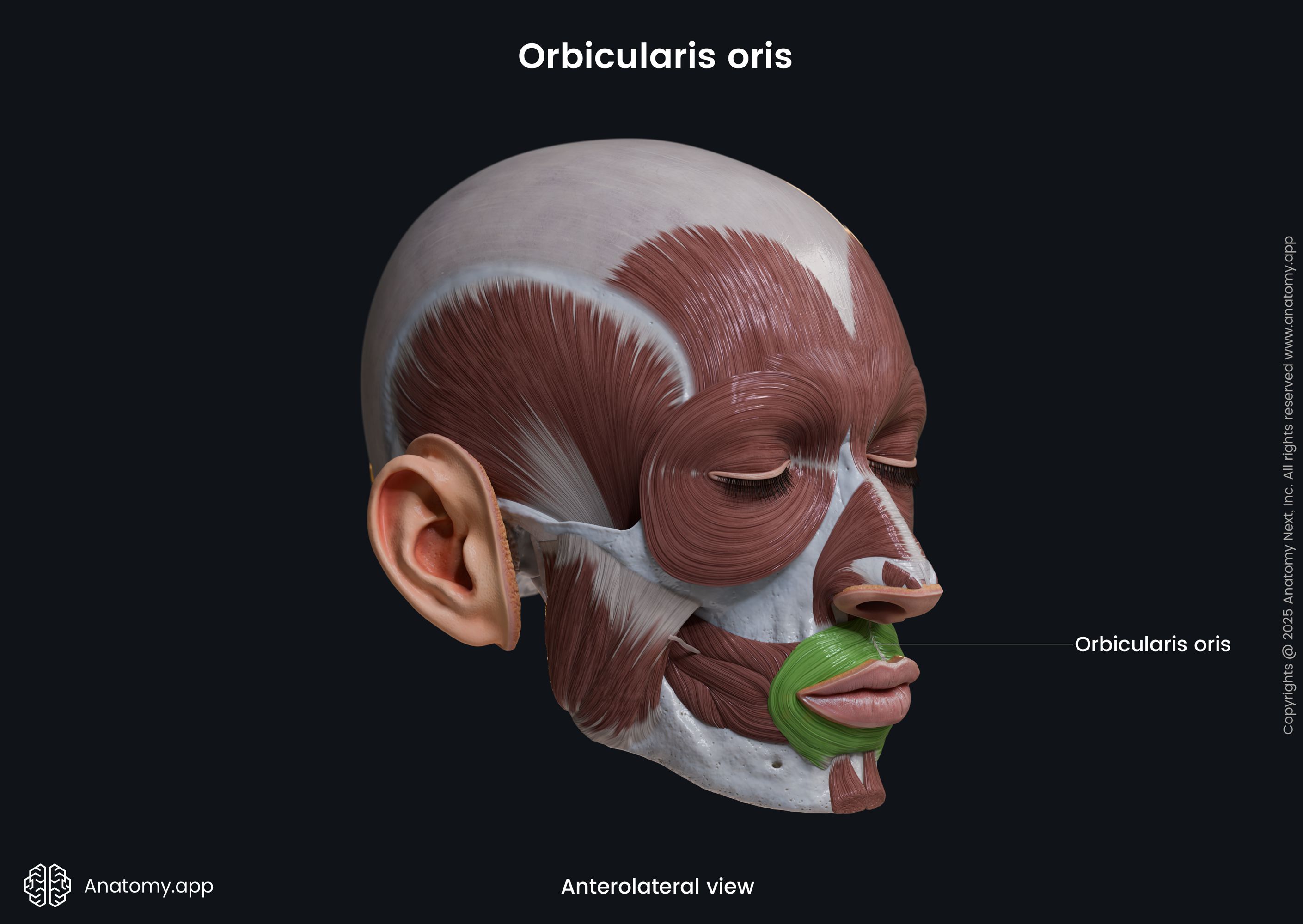
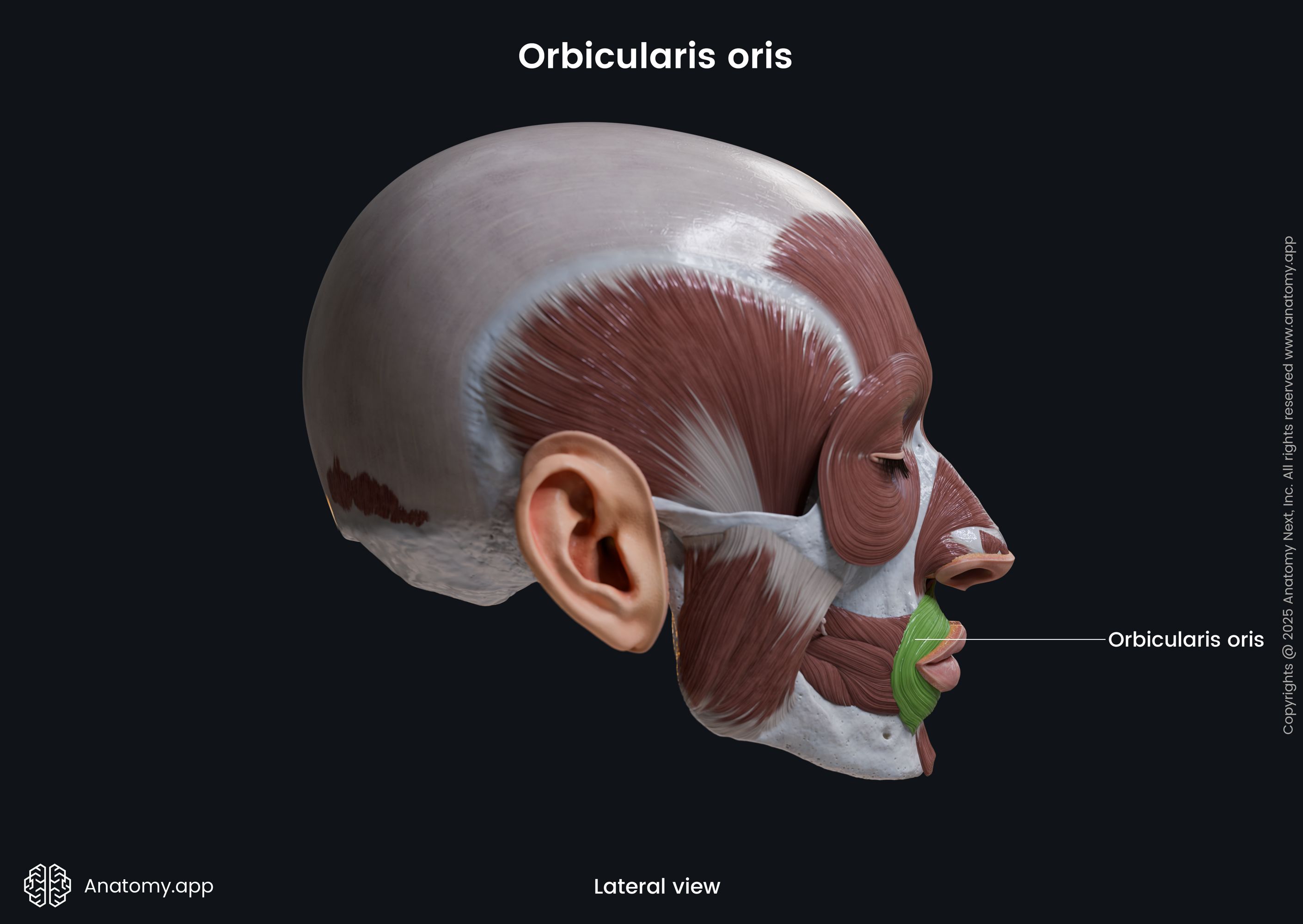
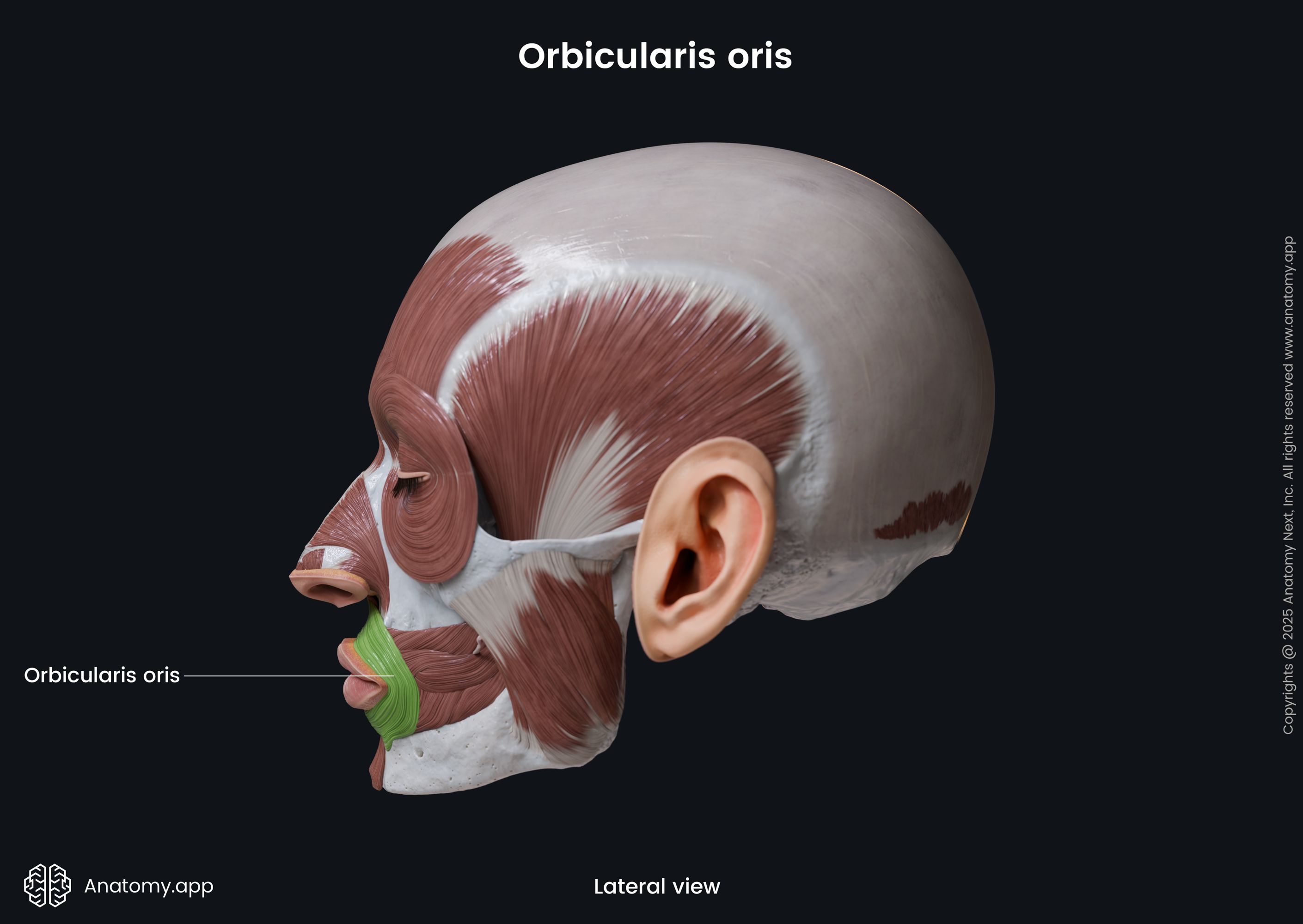
Insertion
Both parts of the muscle insert in the skin and mucous membrane of the lips.
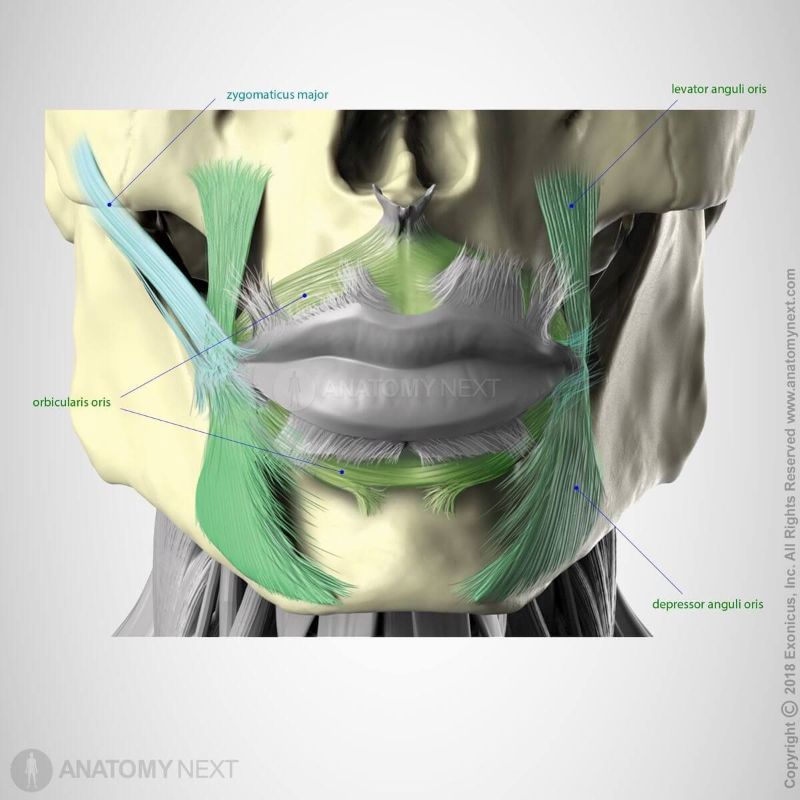
Action
The orbicularis oris muscle closes the mouth and pushes the lips forward (protrudes the lips).
Innervation
Both parts of the orbicularis oris are innervated by the buccal branch of the facial nerve (CN VII).
Blood supply
The orbicularis oris is supplied with the arterial blood mainly by the superior and inferior labial branches of the facial artery, mental and infraorbital branches of the maxillary artery and transverse facial branch of the superficial temporal artery.