- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
Bones of foot
The bones of foot (Latin: ossa pedis) participate in the formation of the terminal part of the lower limb. The foot bears weight and allows locomotion. It is a strong and biomechanically complex structure composed not only of bones but also of joints, muscles, tendons, soft tissue and ligaments.
The human foot typically has five toes. The skeleton of each foot is usually formed by 26 bones providing structural support. Sometimes the foot contains some accessory bones near the metatarsophalangeal joints called the sesamoid bones that vary in number in each individual.
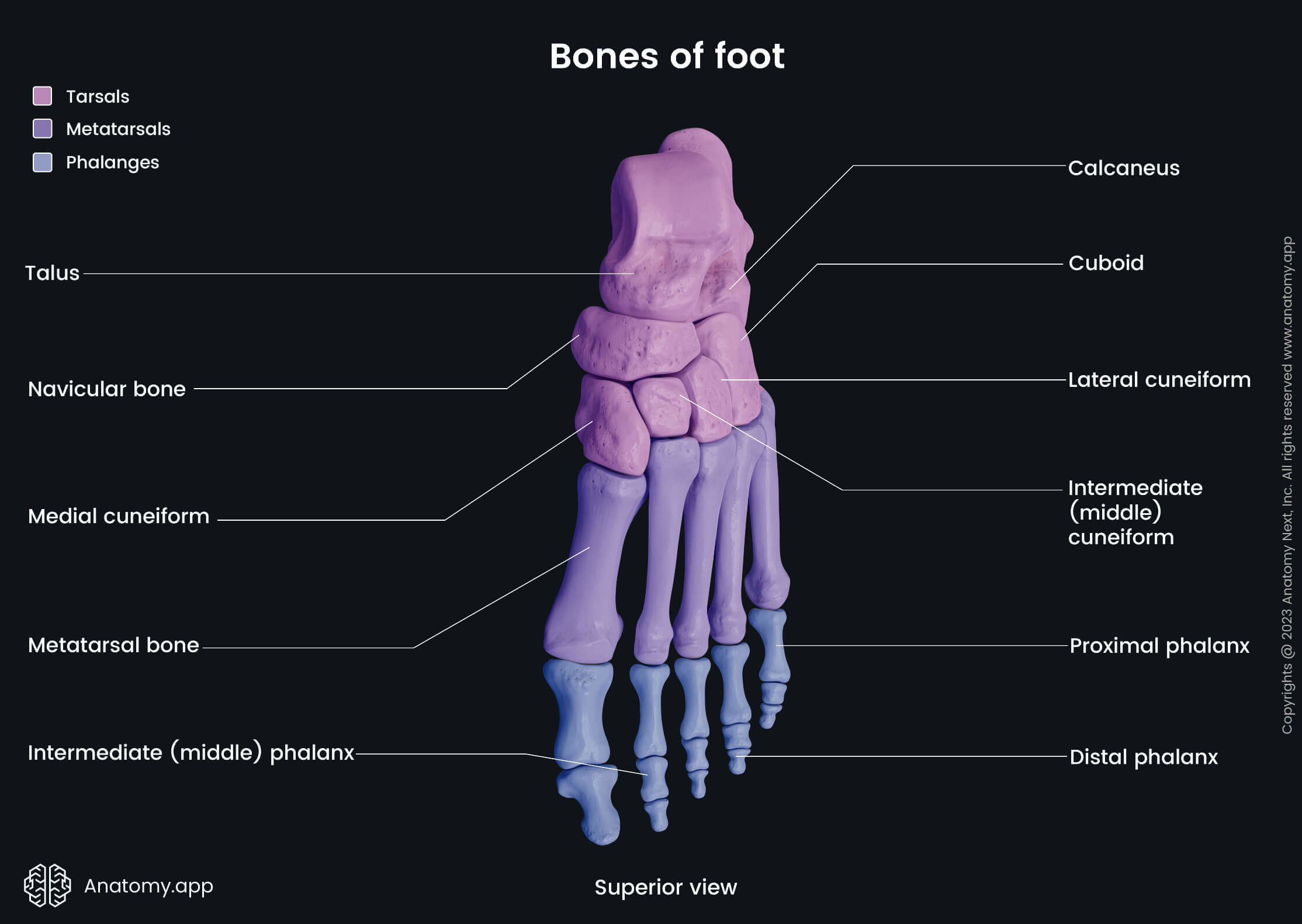
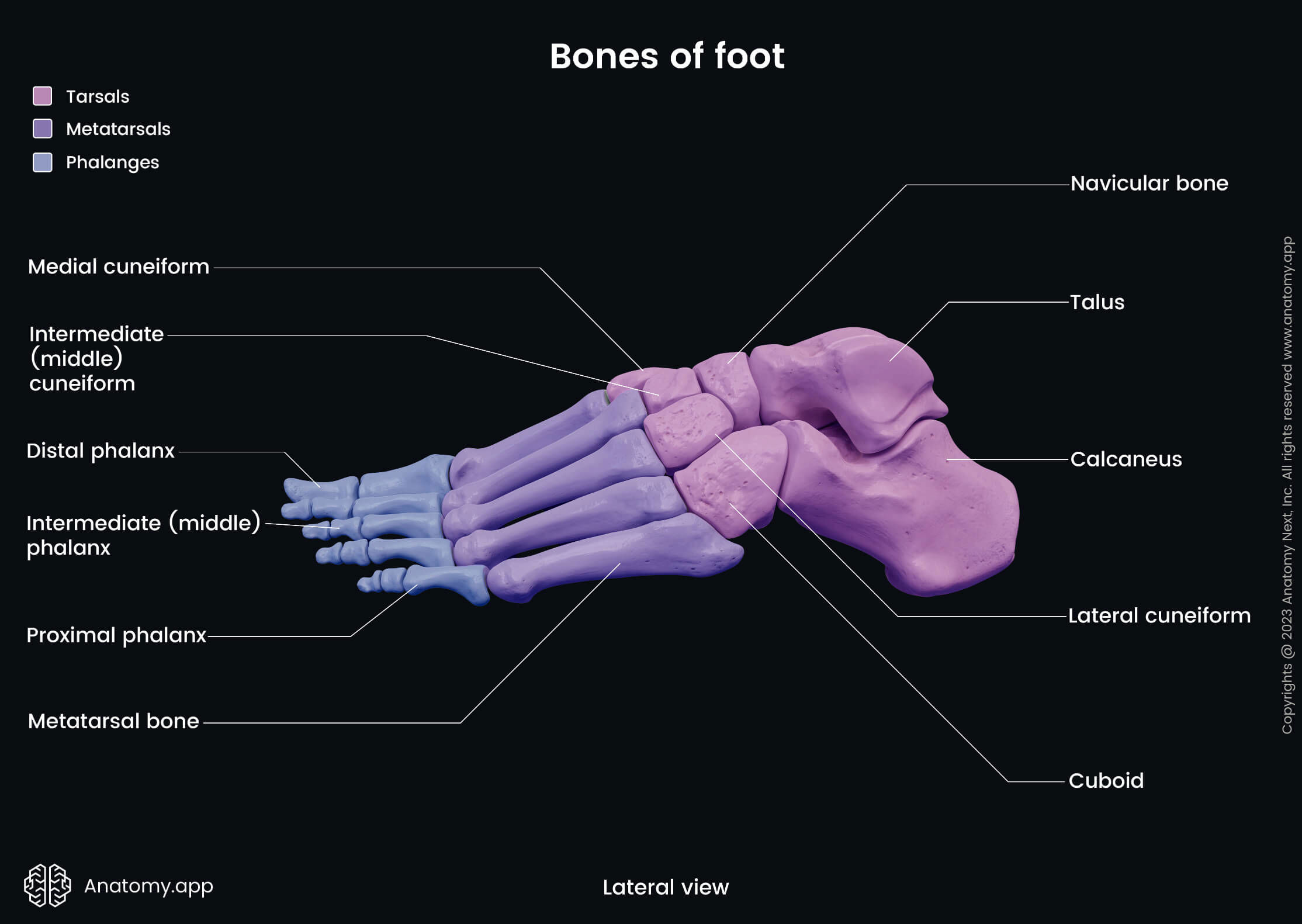
The bones of the foot can be subdivided into three groups:
- Tarsal bones (7) - located most proximally;
- Metatarsal bones (5) - form the middle part;
- Phalanges (14) - situated most distally.
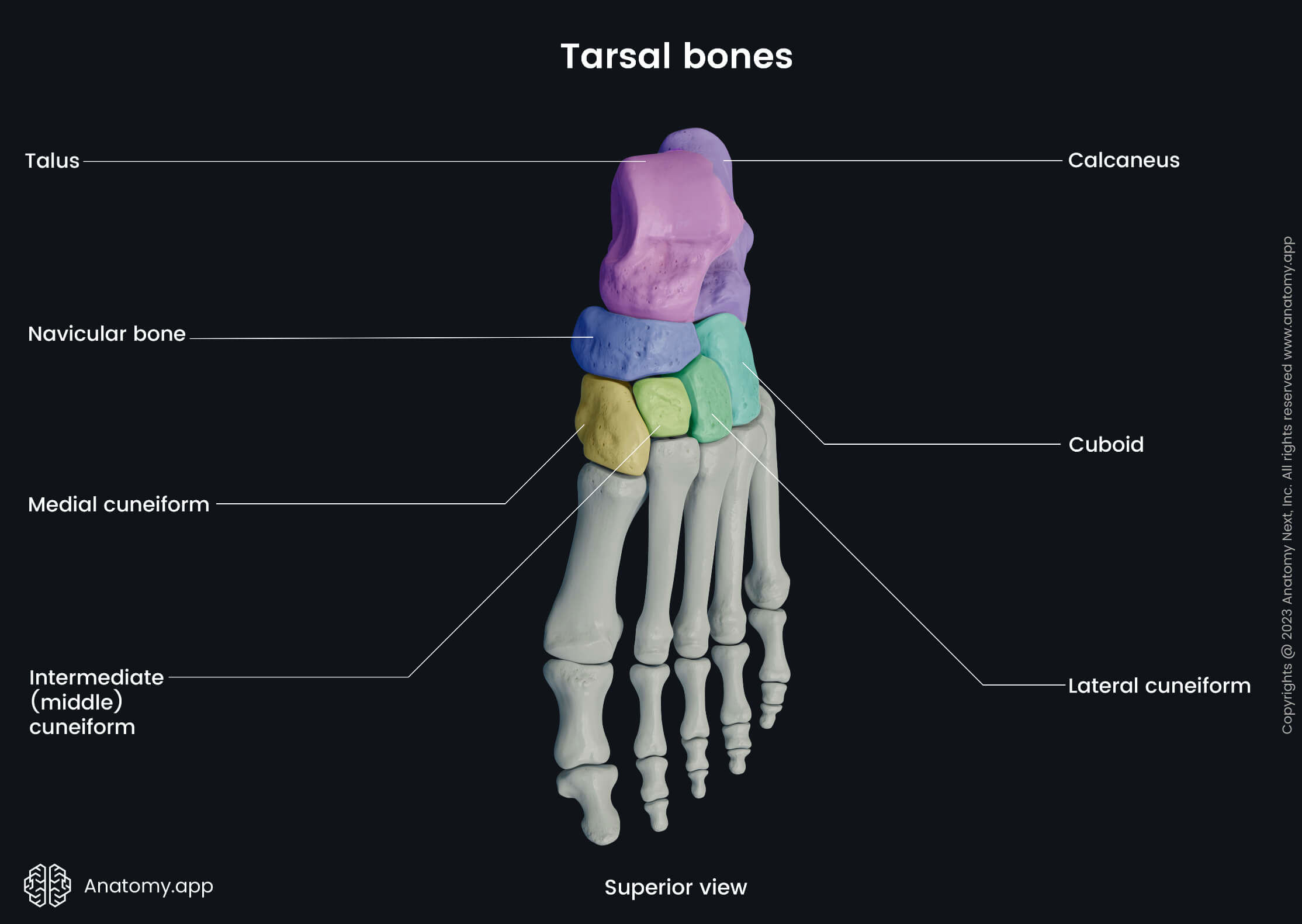
Tarsal bones
The tarsal bones are seven short bones located between the bones of the leg (tibia and fibula) and the metatarsal bones of the foot. Each of the tarsal bones has its unique shape, and they form many joints of the foot by articulating with each other, metatarsal bones and both bones of the leg.
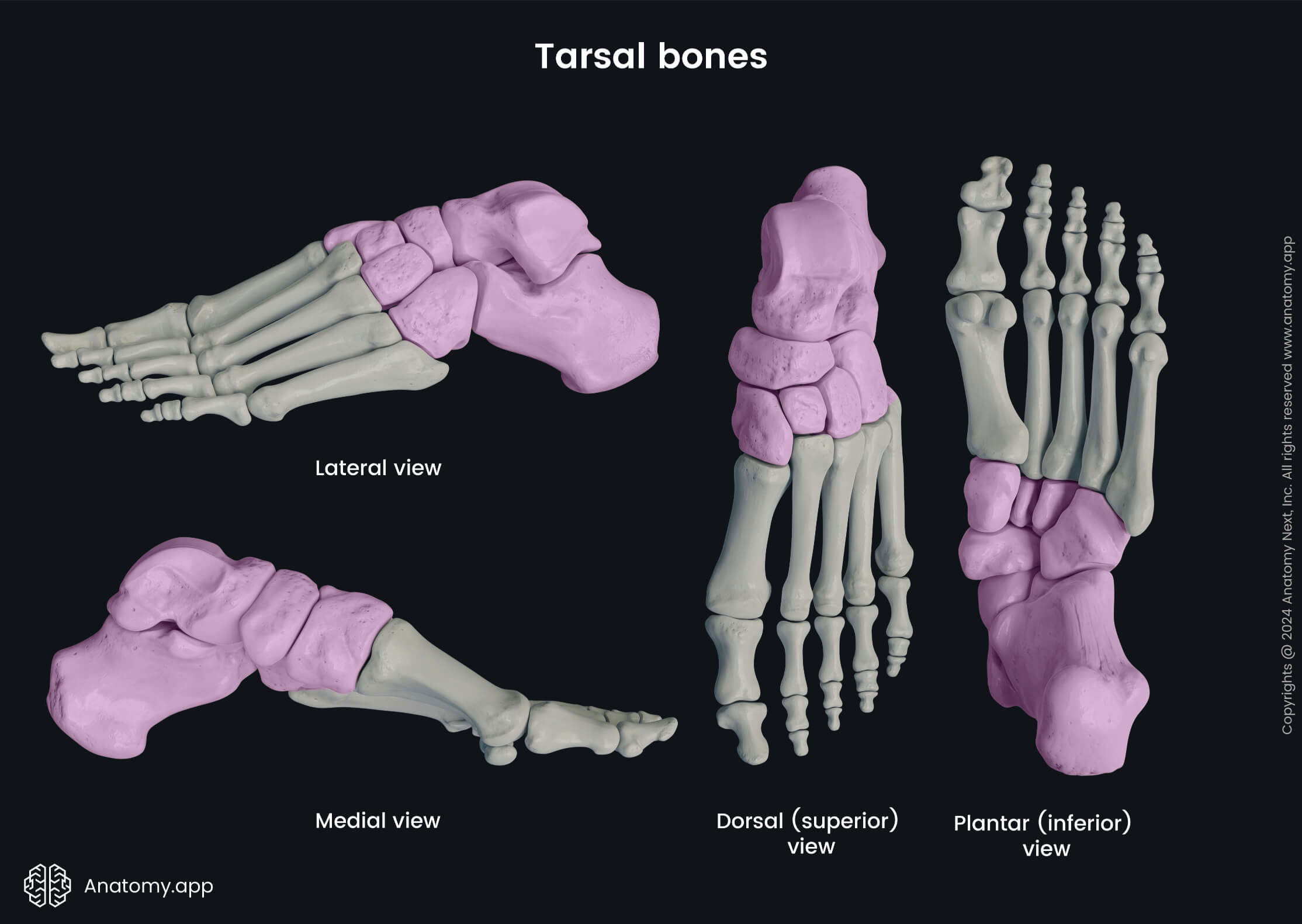
The tarsal bones of the foot include the following:
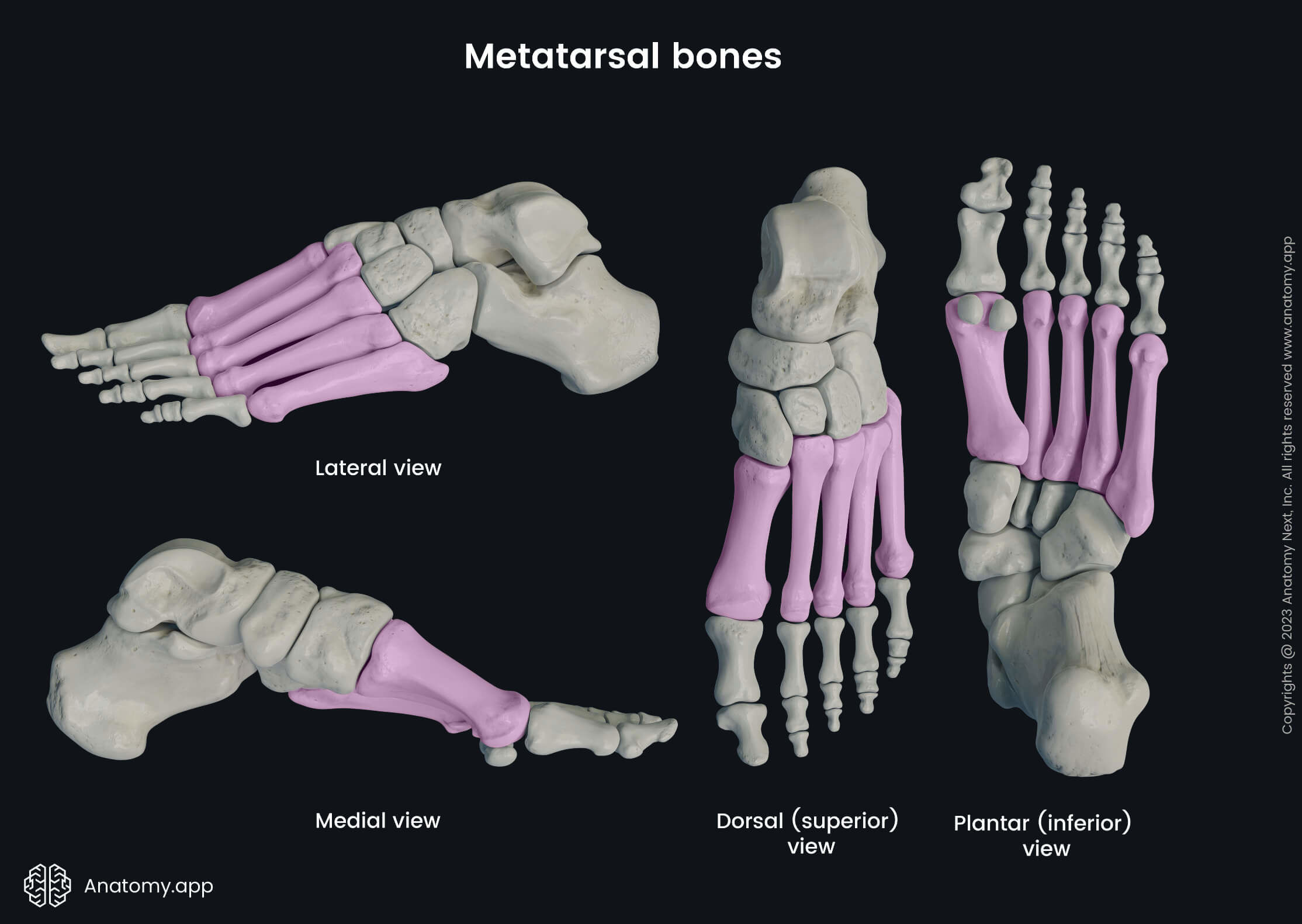
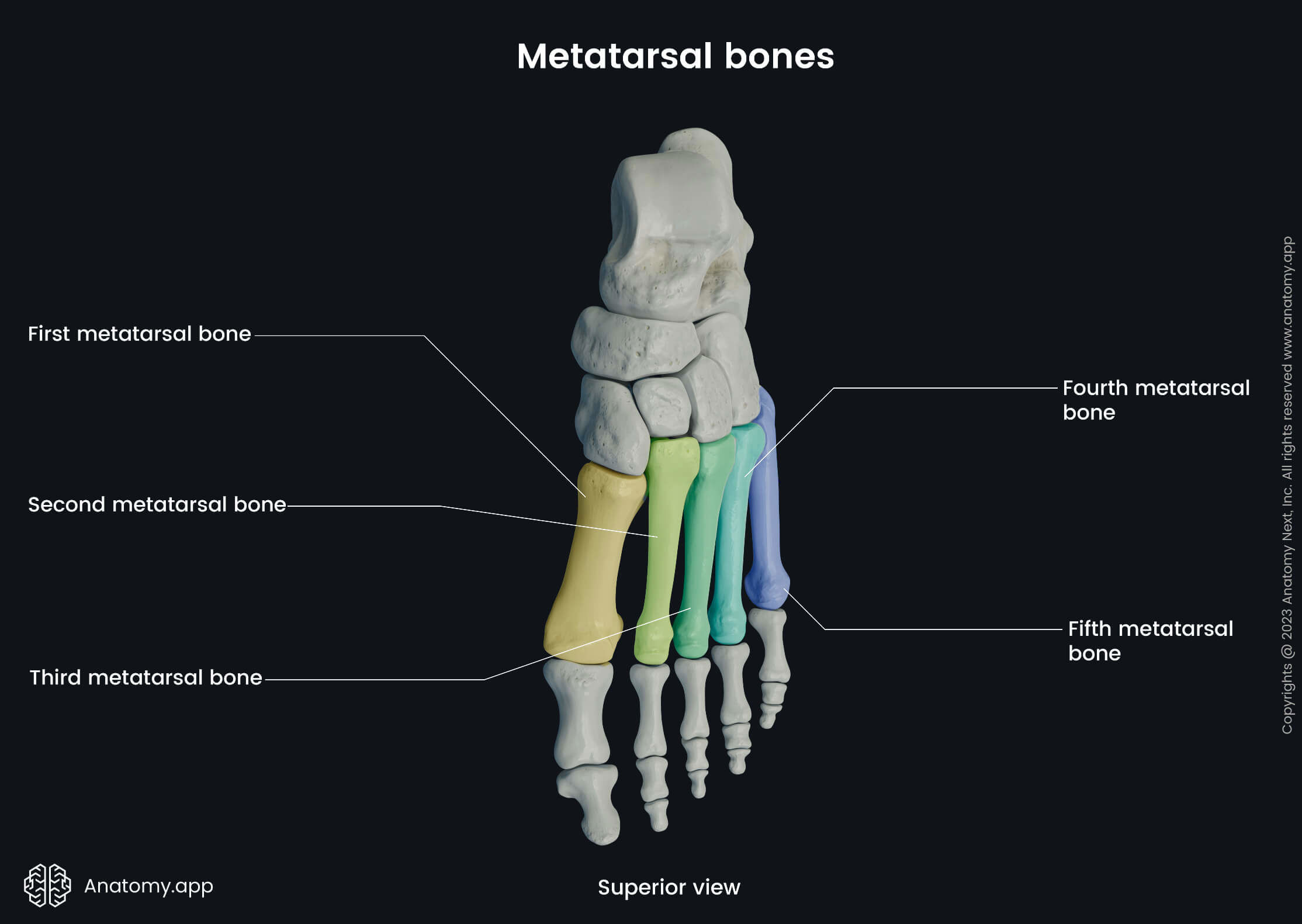
Metatarsal bones
The metatarsal bones are five long bones forming the middle part of the foot. These bones are located between the tarsal bones and the phalanges. Between two metatarsal bones is present a space called the interosseous metatarsal space.
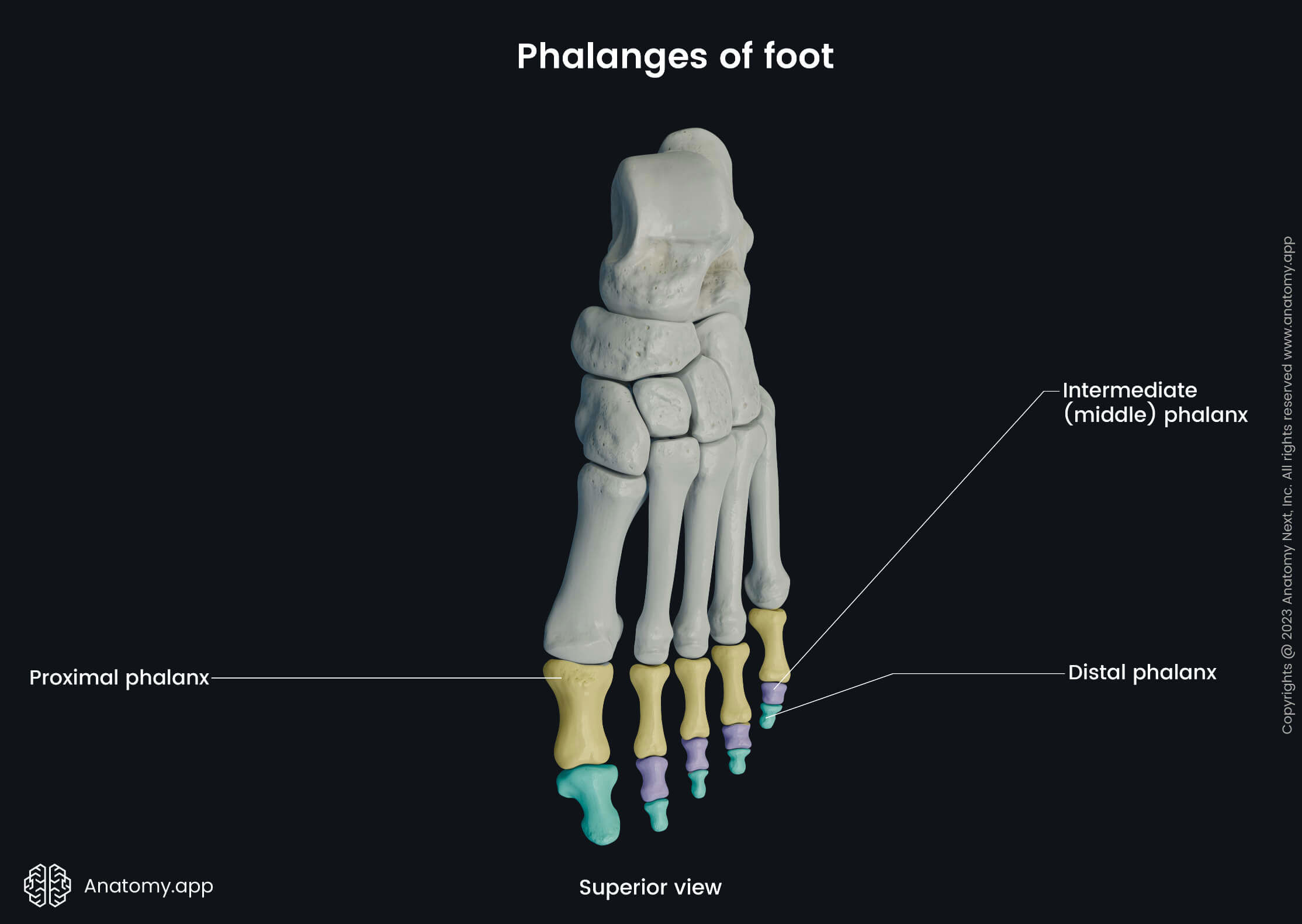
Phalanges
The phalanges are fourteen long bones found within the toes of the foot. They are the most distal bones of the lower extremity.
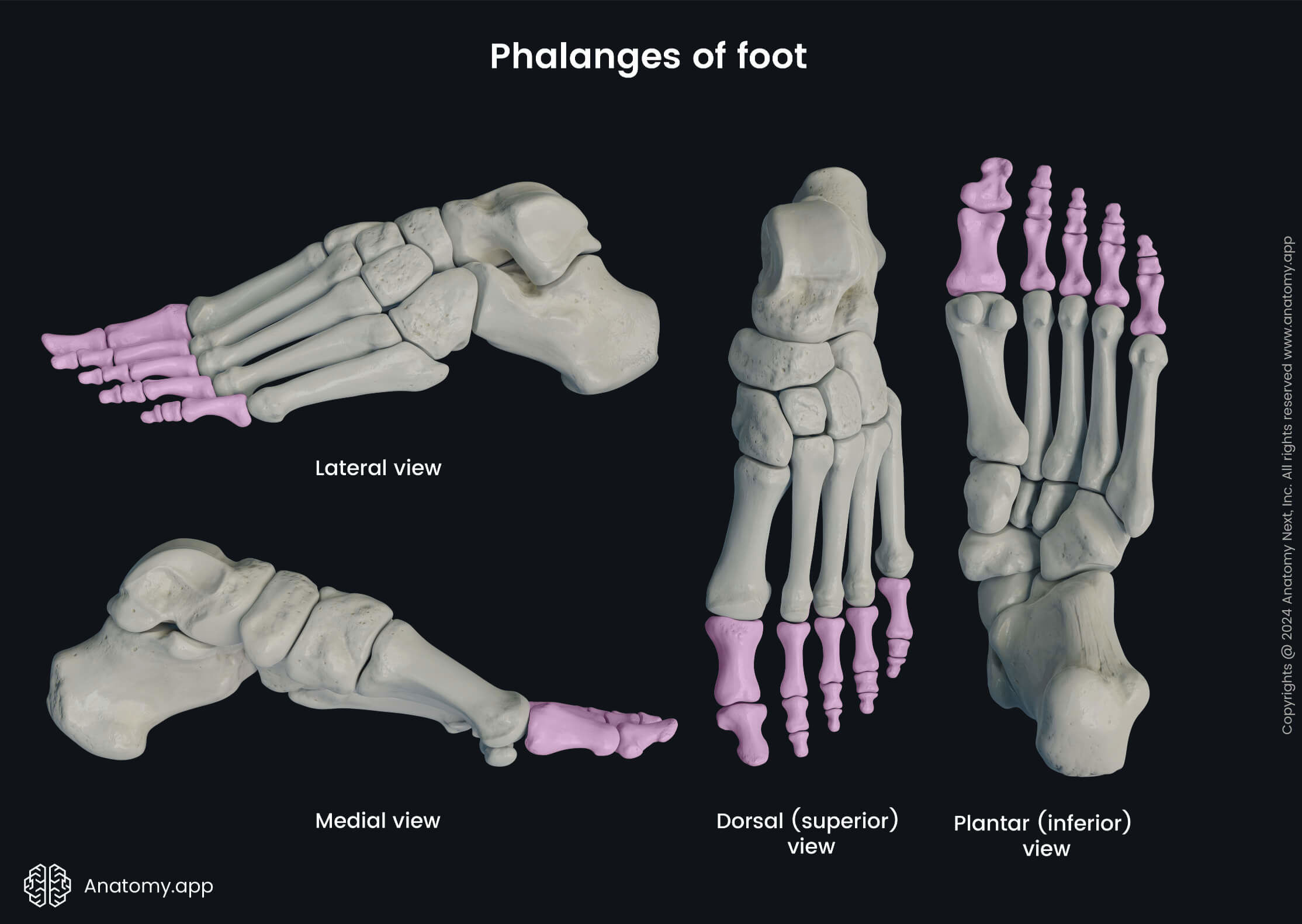
Almost all toes contain three phalanges - proximal, middle (intermediate) and distal. But the big toe, similar to the thumb of the hand, is composed of two phalanges - proximal and distal.