- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
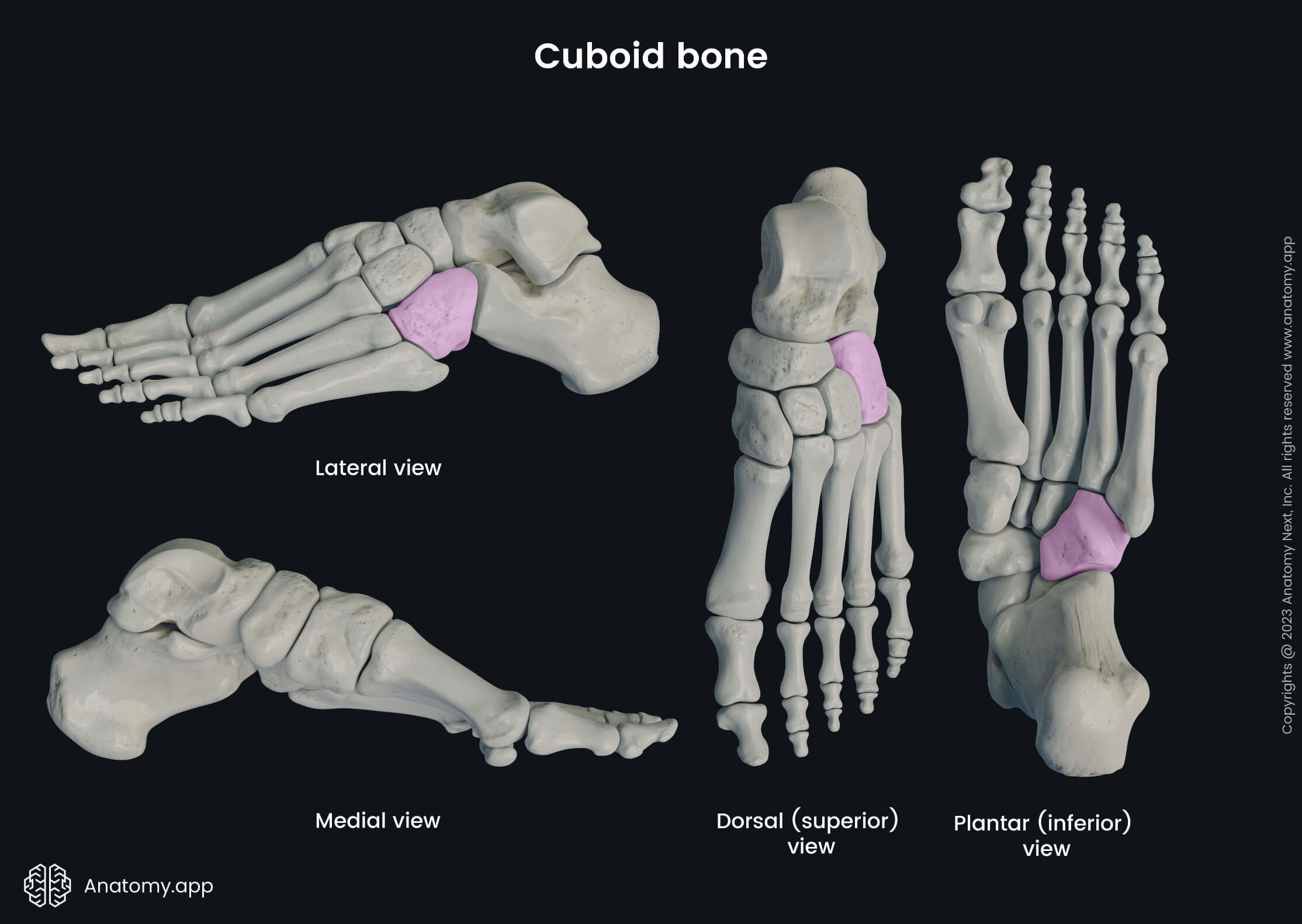
Cuboid bone
The cuboid bone (Latin: os cuboideum) is one of the tarsal bones of the foot, and it is the most laterally located tarsal bone lying anterior to the calcaneus. It articulates with several bones - calcaneus, lateral cuneiform bone, and fourth and fifth metatarsal bones.
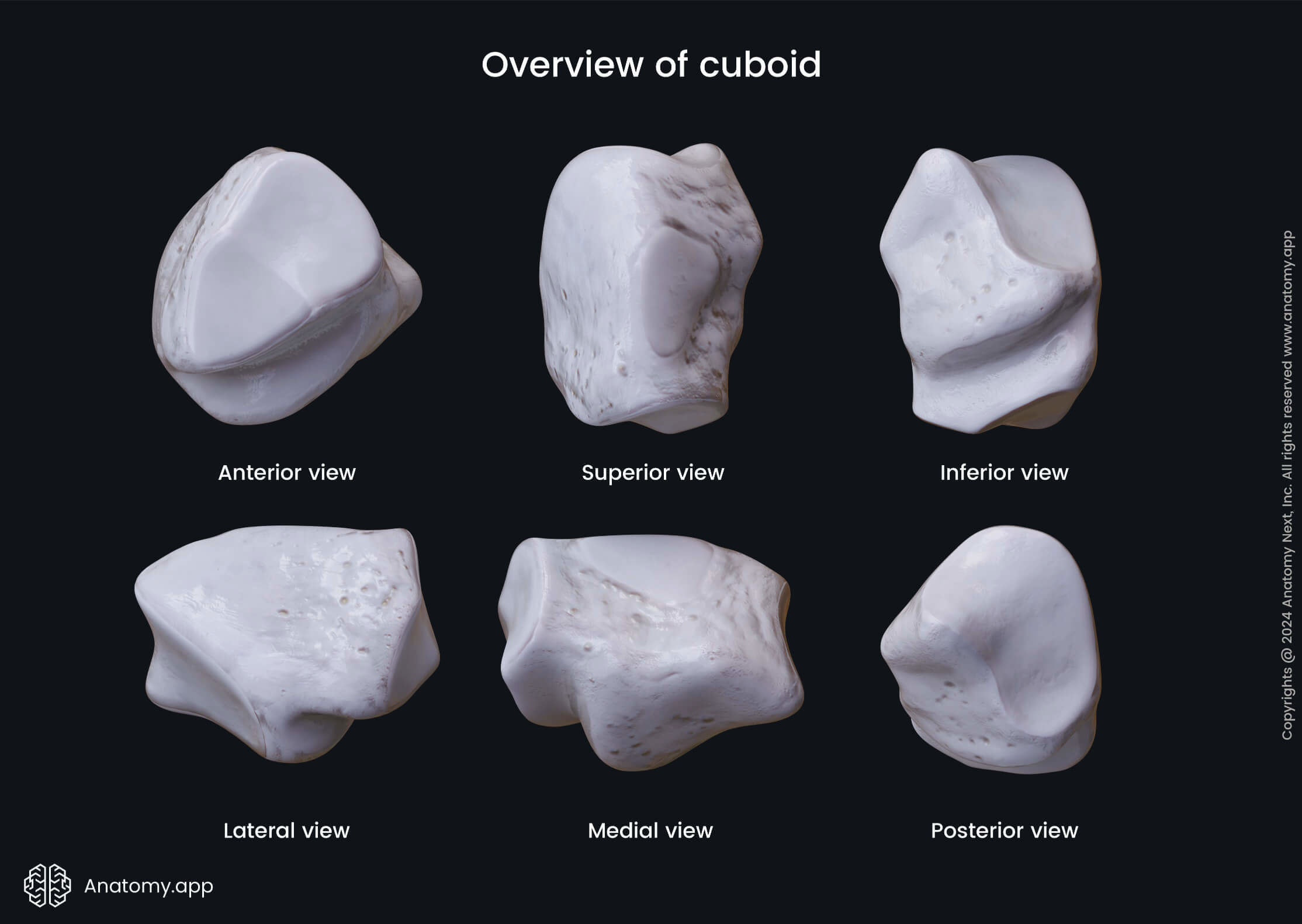
The cuboid is a cube-shaped bone, therefore it has six surfaces. The dorsal surface serves as an attachment site for ligaments, but the plantar surface contains a deep groove called the peroneal sulcus that lodges the tendon of the peroneus longus muscle. The lateral surface contains a deep notch formed by the initial part of the peroneal sulcus.
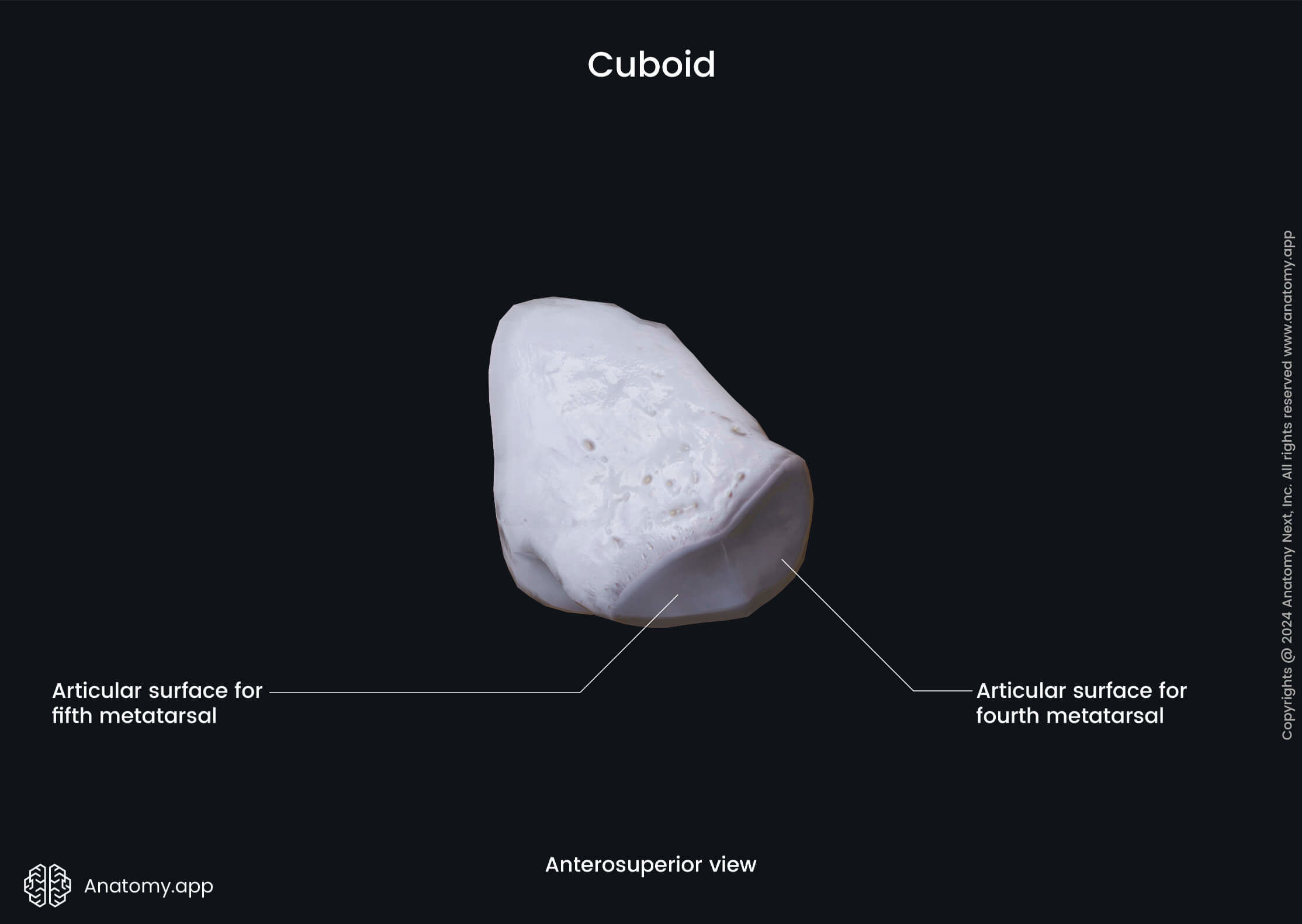
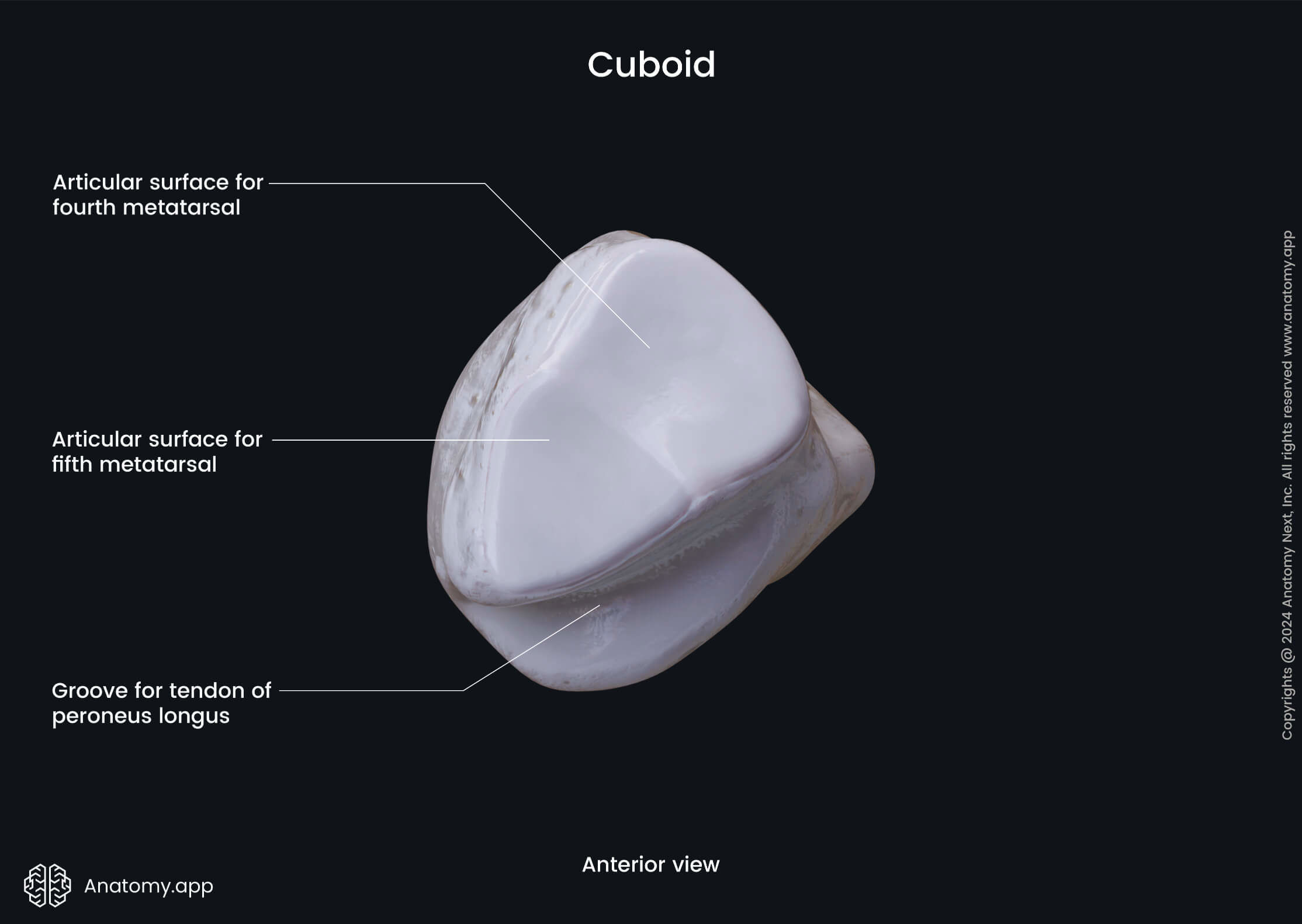


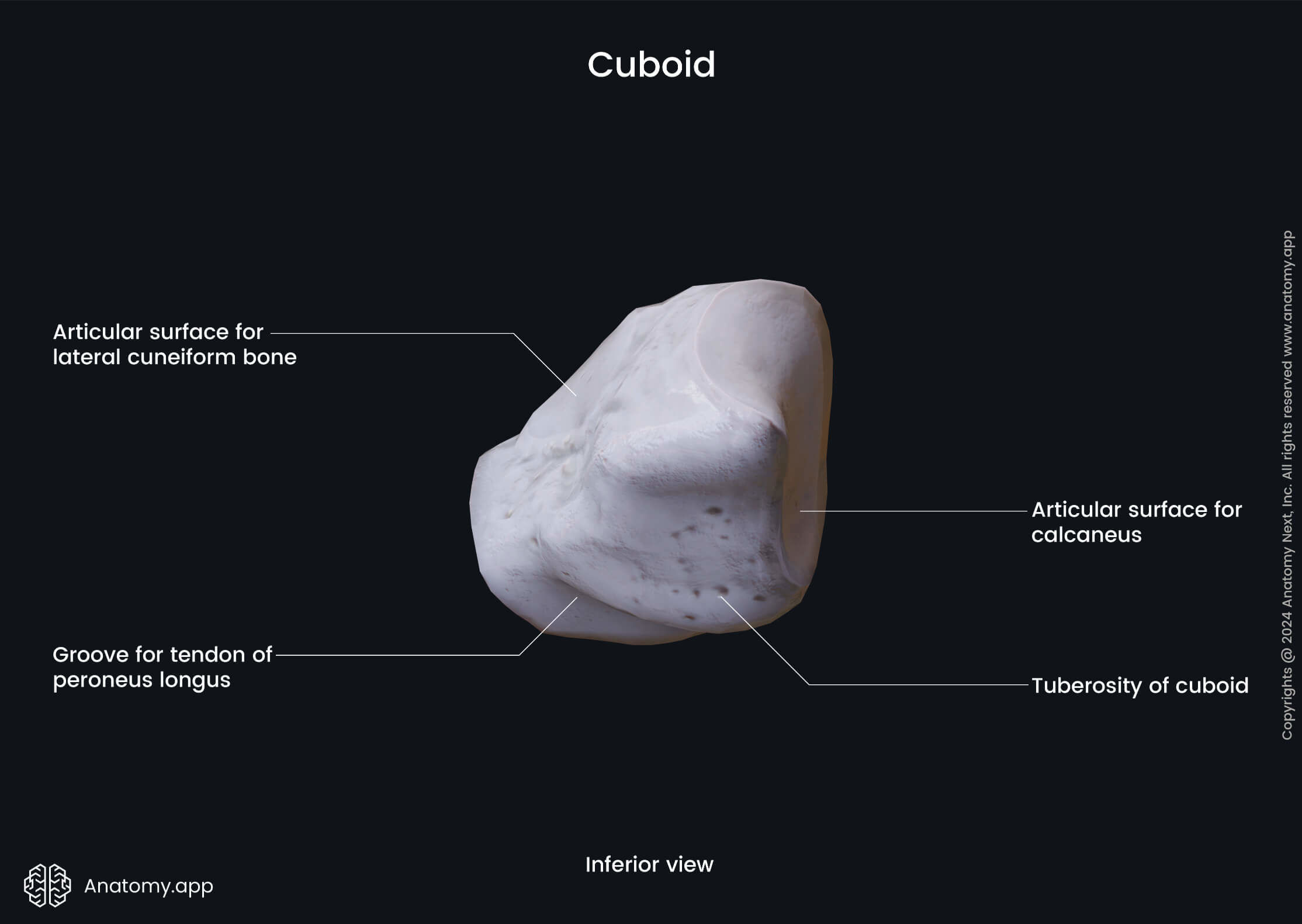
Three surfaces articulate with the adjacent bones and are the articular surfaces. The posterior surface articulates with the calcaneus but the anterior surface articulates with the fourth and fifth metatarsal bones. And, finally, the medial surface of the cuboid bone articulates with the lateral cuneiform bone.