- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Skeleton of trunk
- Skull
- Skeleton of upper limb
- Skeleton of lower limb
- Joints
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
Tibia
The tibia (Latin: tibia), also known as the shinbone, is the largest and strongest of two lower leg bones. It lies on the medial side of the leg, located parallel to the other bone of the leg named the fibula. Both bones extend between the knee and the ankle joints.
The tibia participates in forming four joints - the knee, ankle, superior tibiofibular and inferior tibiofibular joints. It is a long bone, and as with every long bone, the tibia also has three parts - a diaphysis or shaft and two ends or epiphyses (proximal and distal).
Proximal end of tibia
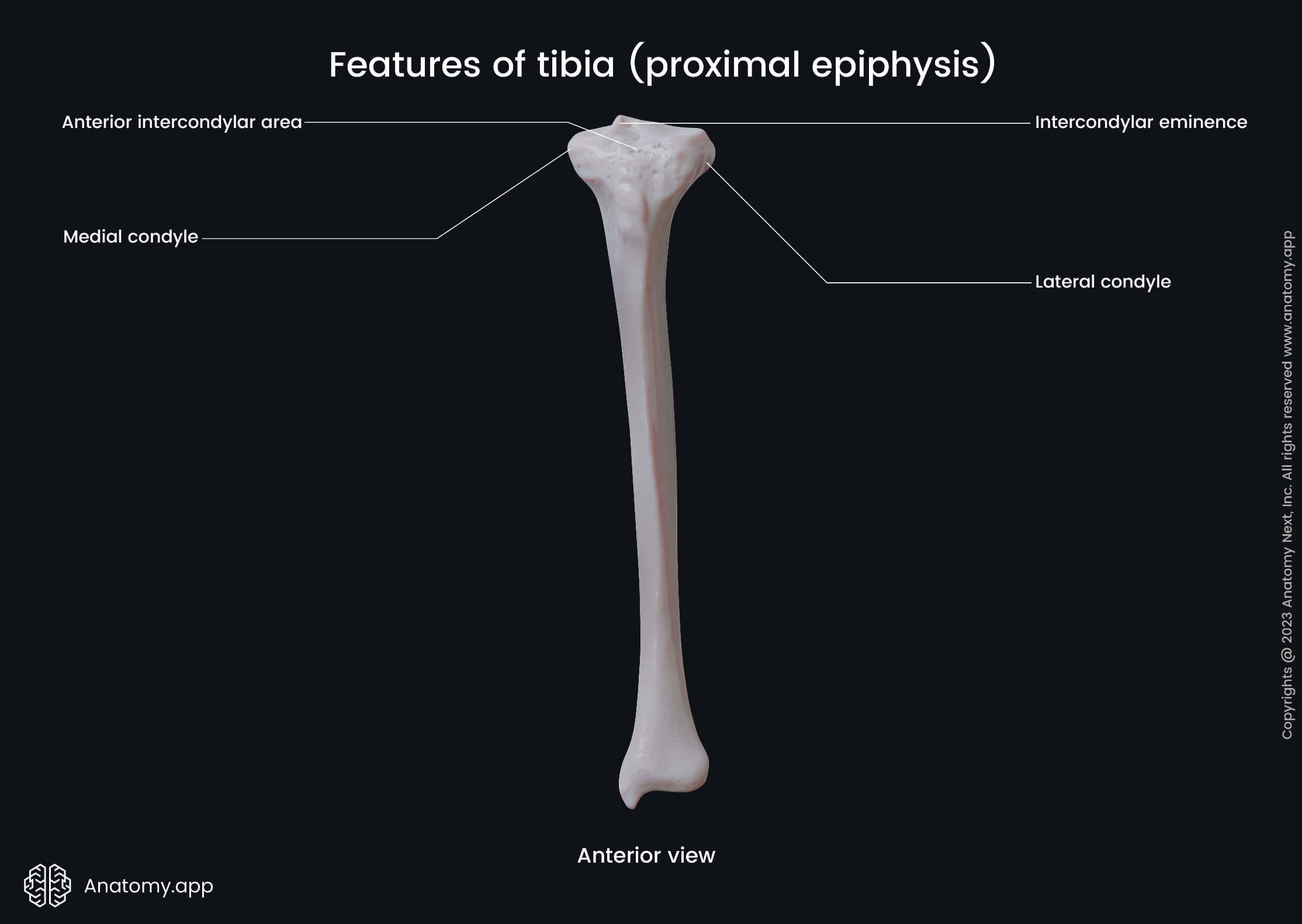
The proximal end or epiphysis is the upper end of the tibia that is located closer to the body. It features the following landmarks:
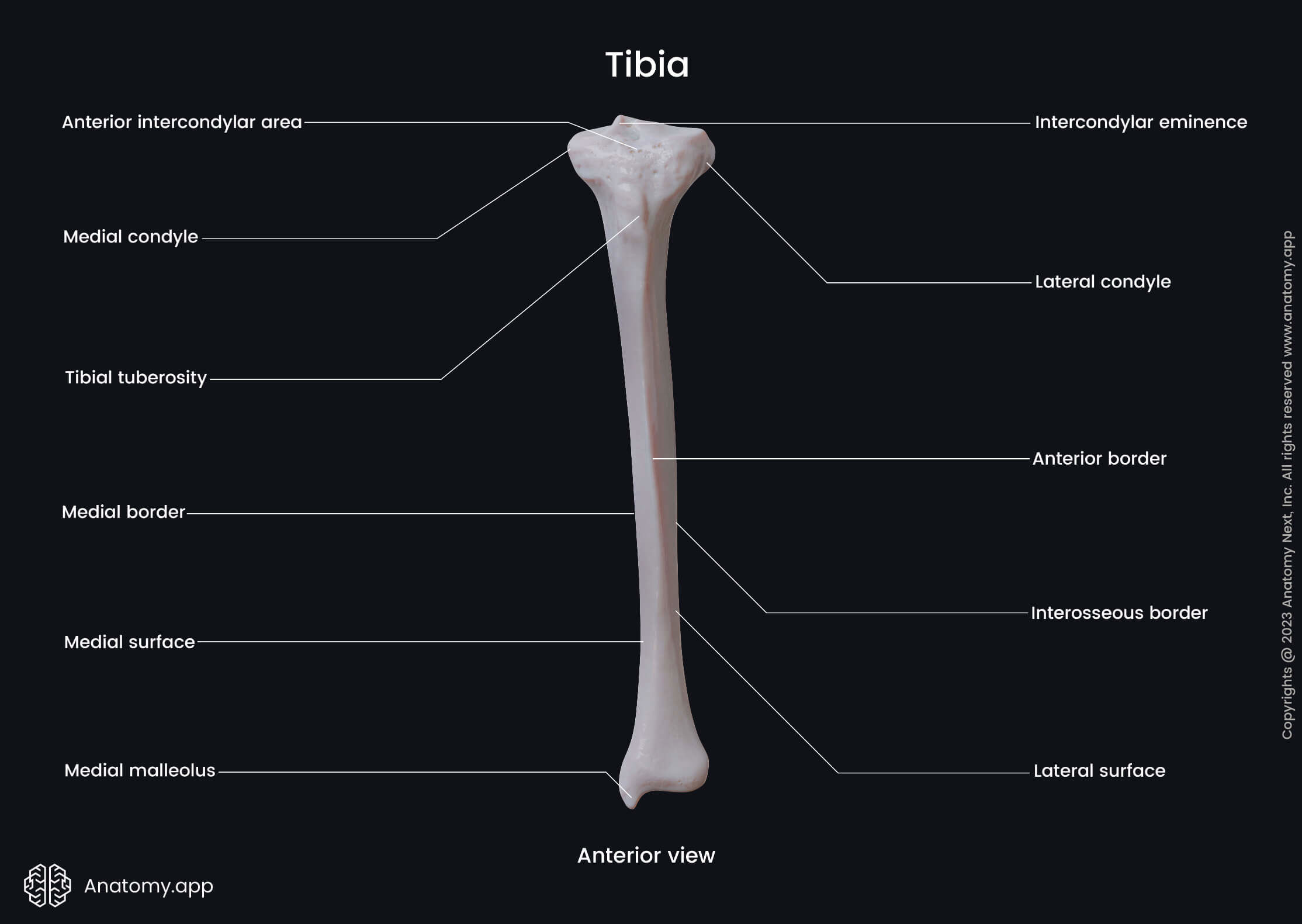
- Medial condyle
- Lateral condyle
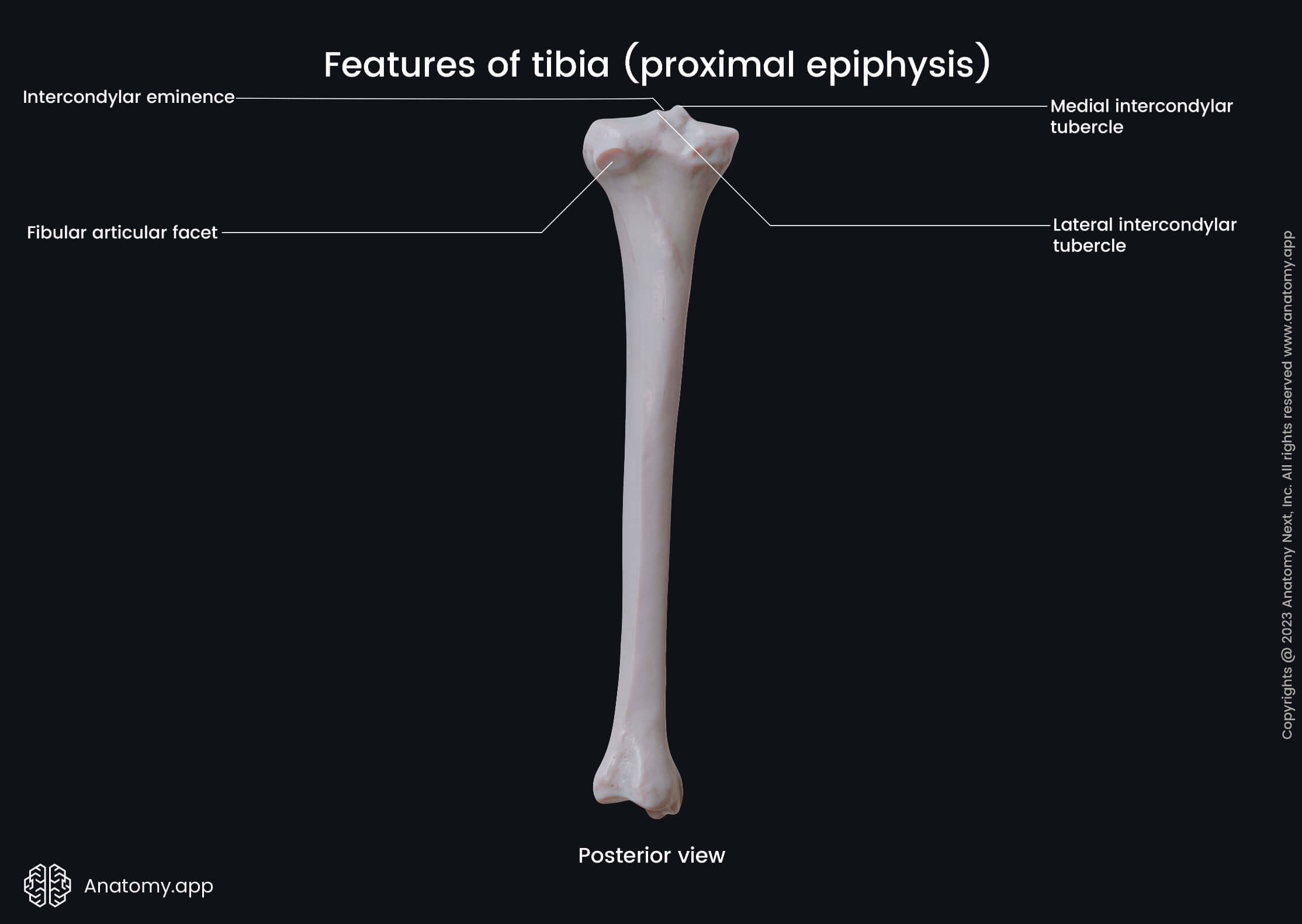
- Intercondylar area
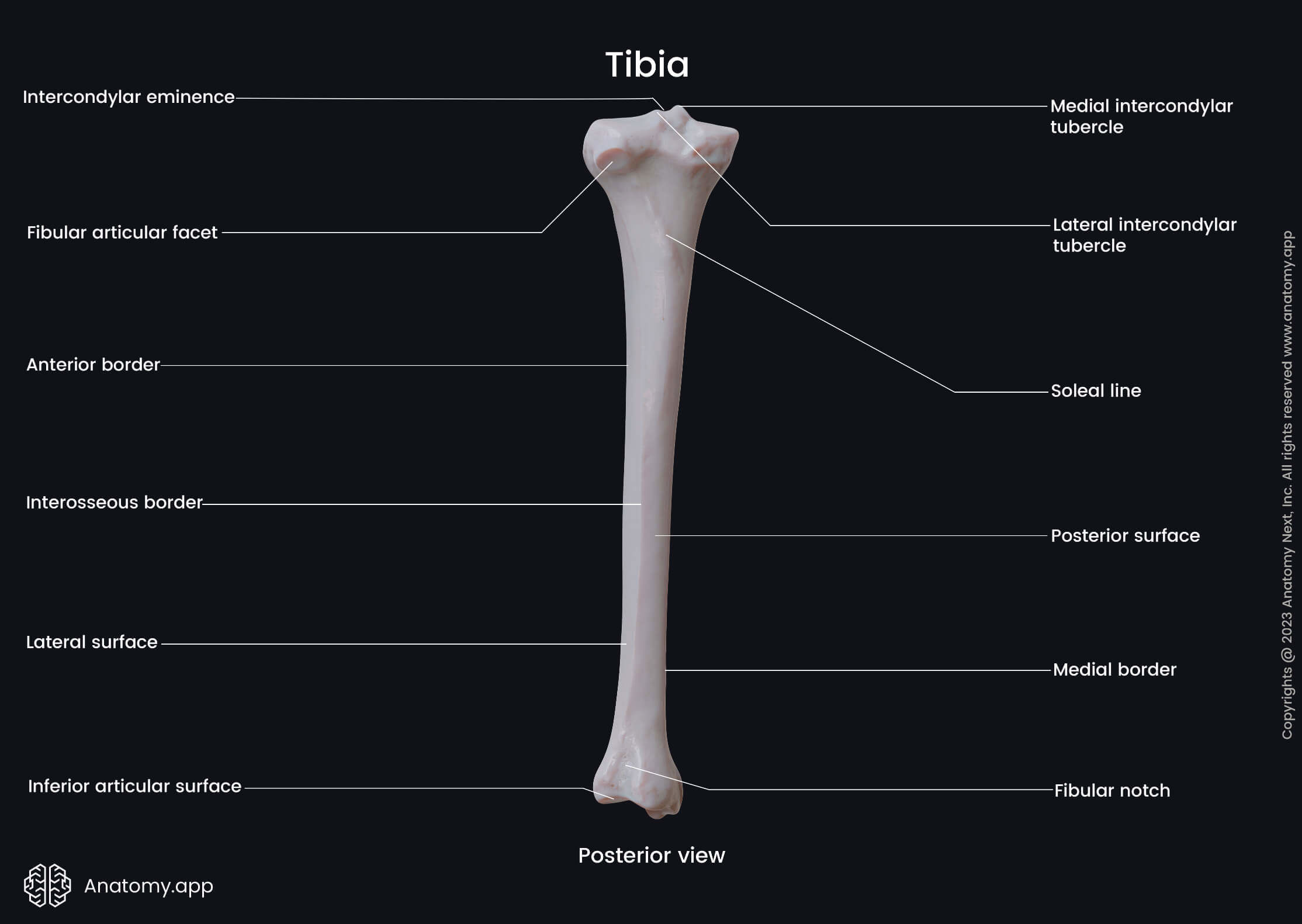
- Intercondylar eminence
- Anterior intercondylar area
- Posterior intercondylar area
- Superior articular surface
- Fibular articular surface
The medial condyle of the tibia is a medial expansion at the proximal end. In contrast, the lateral condyle is a lateral expansion at the proximal end of the bone.
Both condyles are separated by the intercondylar area, subdivided into two smaller areas - the anterior and posterior intercondylar areas. Between both is the intercondylar eminence.
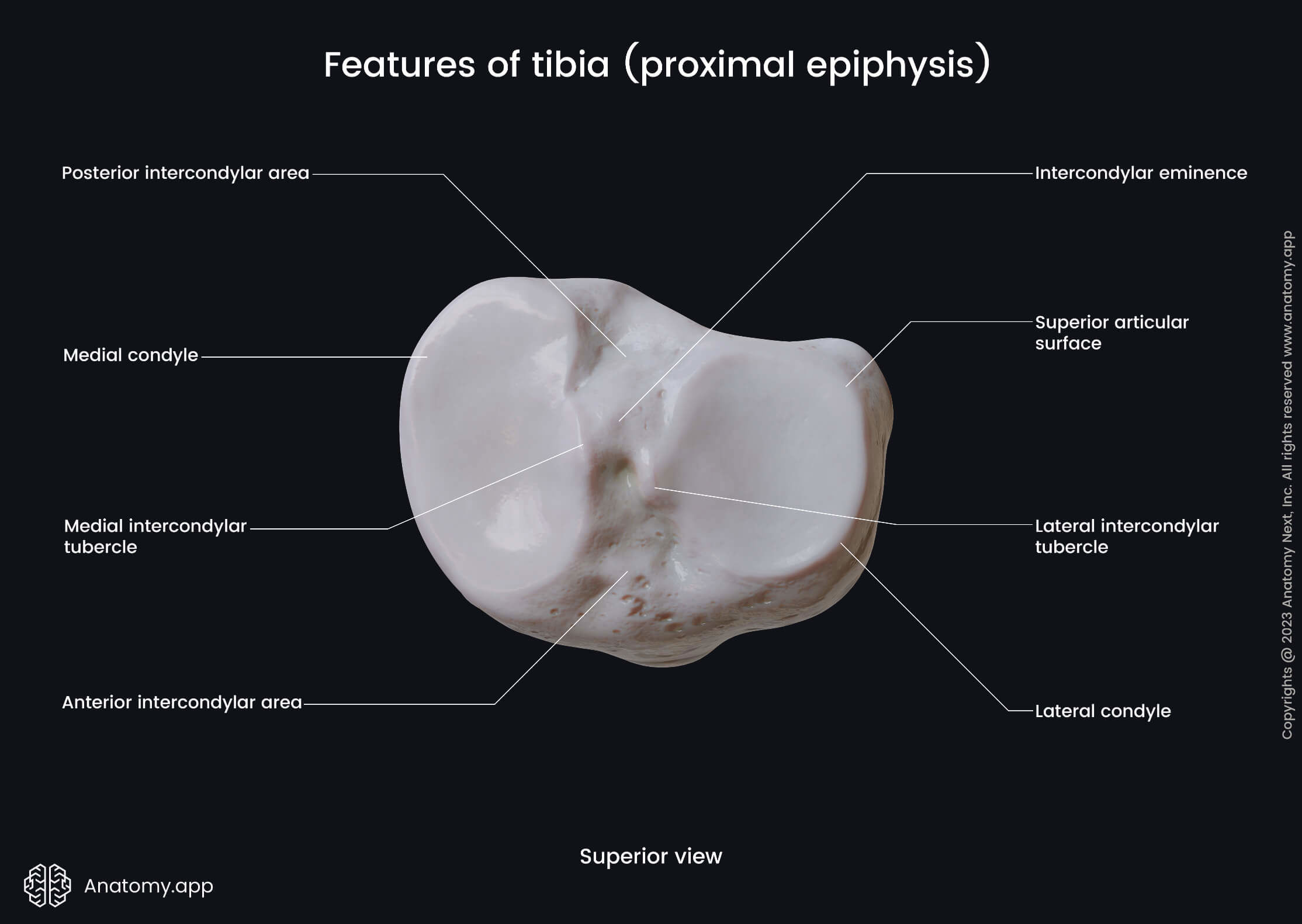
The intercondylar eminence is a bony elevation between both superior articular surfaces of the tibia. It serves as an attachment site for the cruciate ligaments and menisci.
The anterior intercondylar area is located anterior to the intercondylar eminence. This area also is positioned between both superior articular surfaces of the tibia.
The posterior intercondylar area is located posterior to the intercondylar eminence. Like the anterior intercondylar area, this area is also situated between both superior articular surfaces.
The proximal end contains three articular surfaces - two superior and one fibular articular surface. The first ones are located on the superior aspect, while the second is situated on the posterolateral aspect of the lateral condyle.
Both superior articular surfaces articulate with the femur at the knee joint. The fibular articular surface articulates with the head of the fibula, forming the proximal (superior) tibiofibular joint.
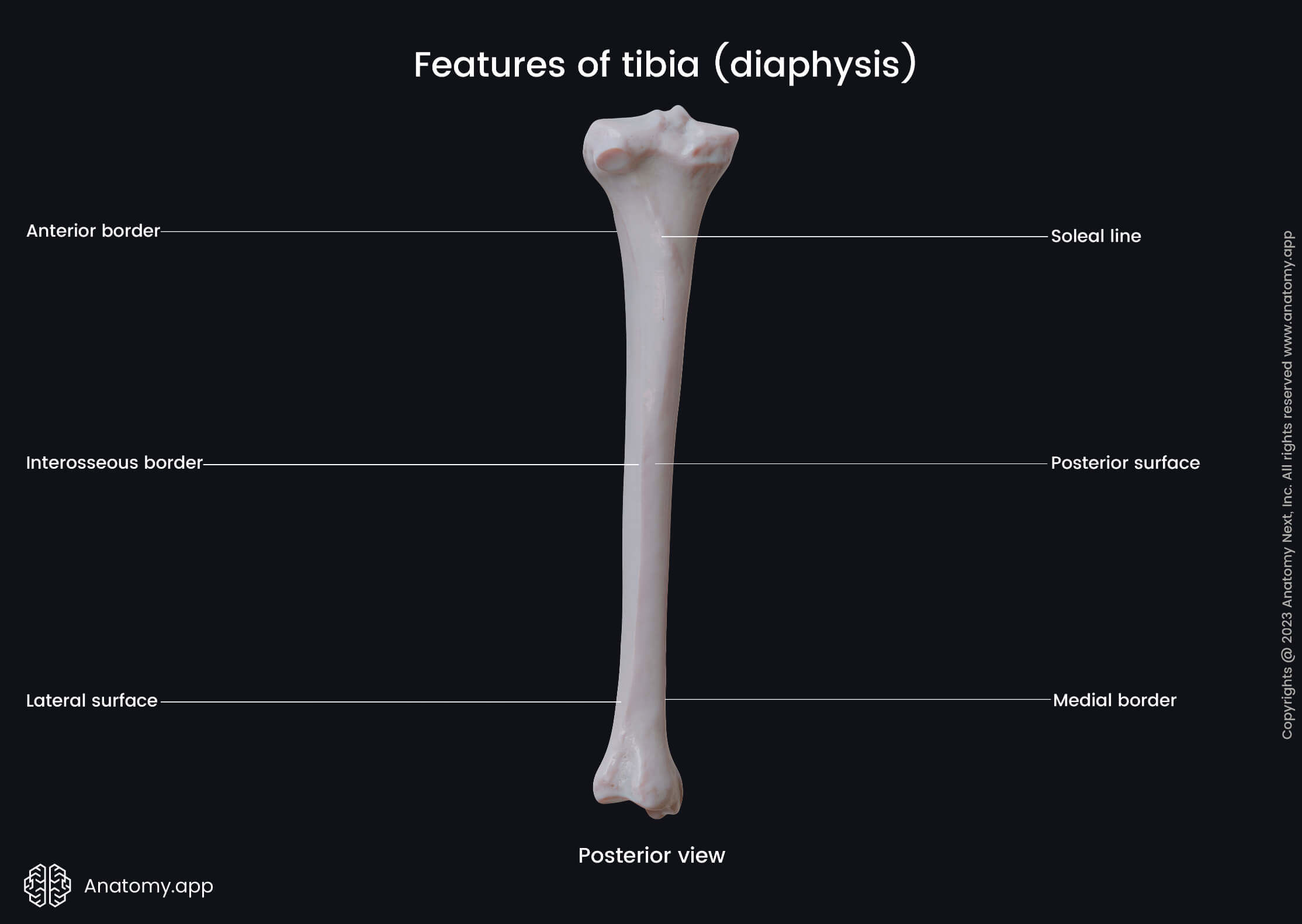
Shaft of tibia
The shaft or body of the tibia is the middle part of the bone located between both ends. It appears triangular in cross-section studies and has three margins:
The interosseous margin of the tibia faces the fibula. It serves as an attachment site for the interosseous membrane attached to the border along most of its length.
The tibial tuberosity is a roughened and elevated area on the upper aspect of the anterior margin. It serves as an attachment site for the patellar ligament.
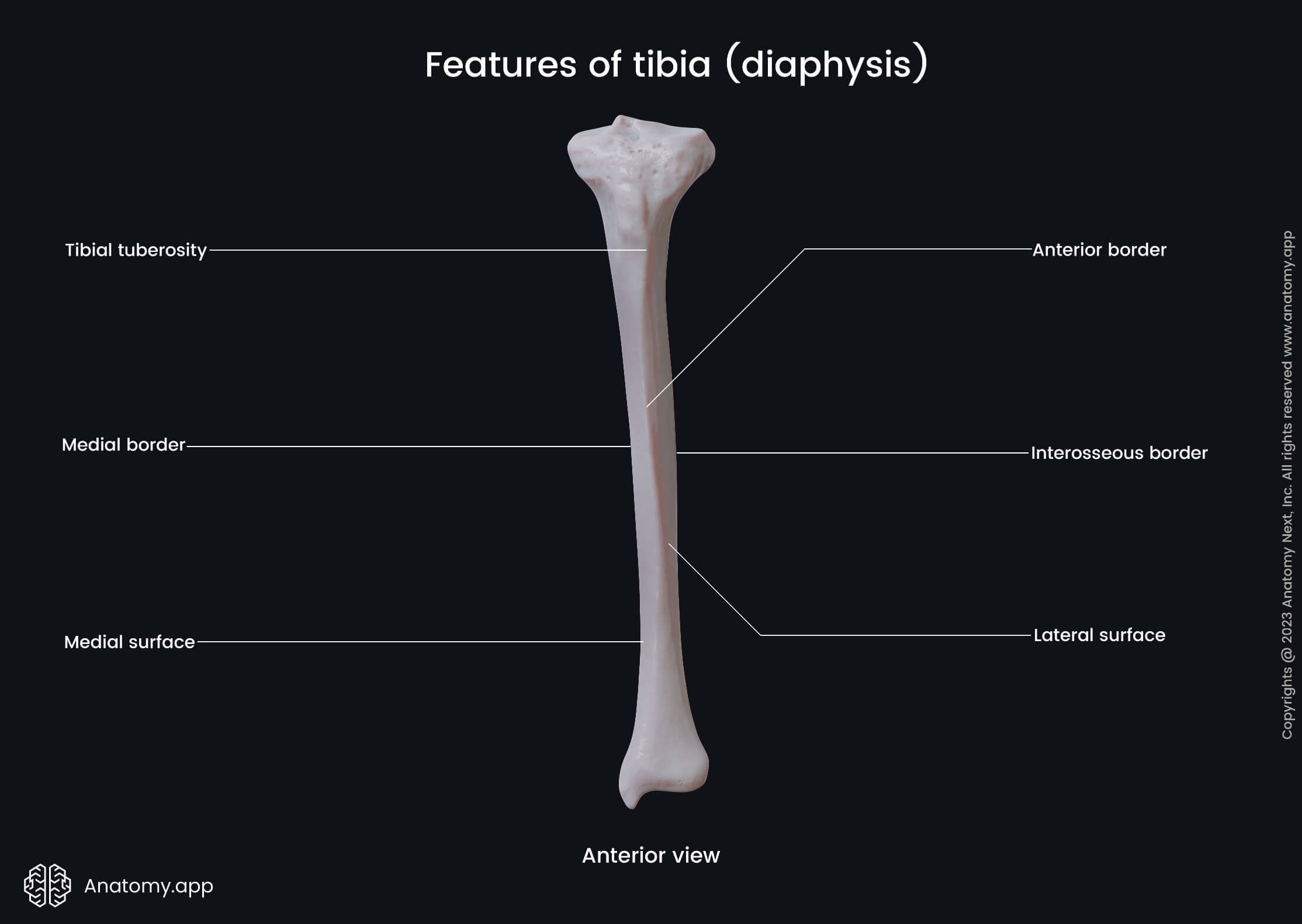
Besides three margins, the shaft of the tibia also presents three surfaces:
- Medial surface - directed anteromedially;
- Lateral surface - facing anterolaterally;
- Posterior surface - directed posteriorly.
The posterior surface presents soleal line - an oblique line on its upper aspect. It extends downward from the upper and lateral parts of the shaft to its medial side. This line serves as an attachment site for the soleus muscle.
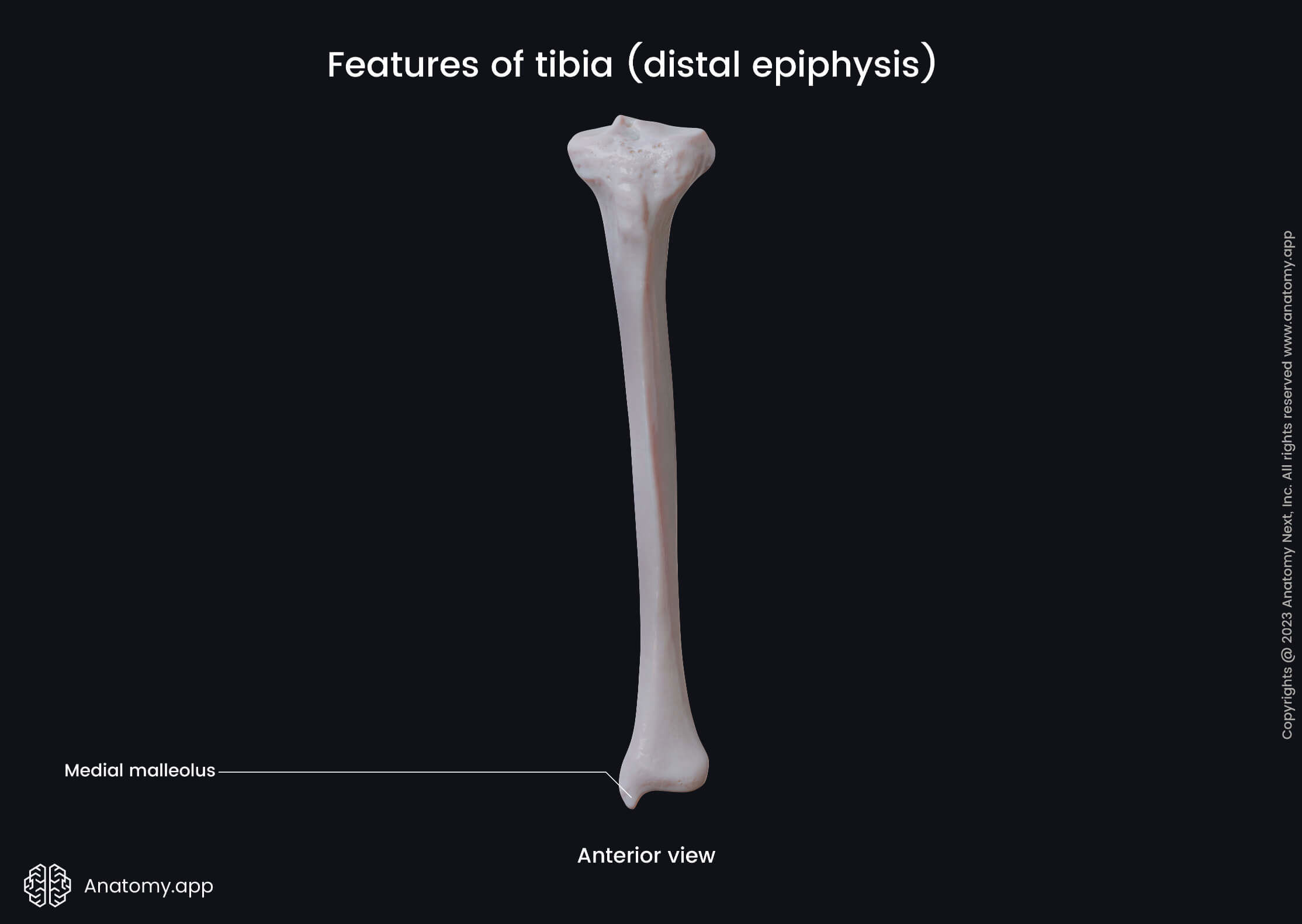
Distal end of tibia
The distal end or epiphysis is the lower end of the bone that forms articulations with the bones of the foot. It contains several landmarks, and they include the following:
The medial malleolus is a bony prominence on the tibial side of the ankle. The malleolar articular surface is an articular surface of the malleolus that articulates with the talus.
The malleolar groove is a small narrow groove located on the posterior aspect of the medial malleolus. It is an attachment site for the tendon of the tibialis posterior muscle.
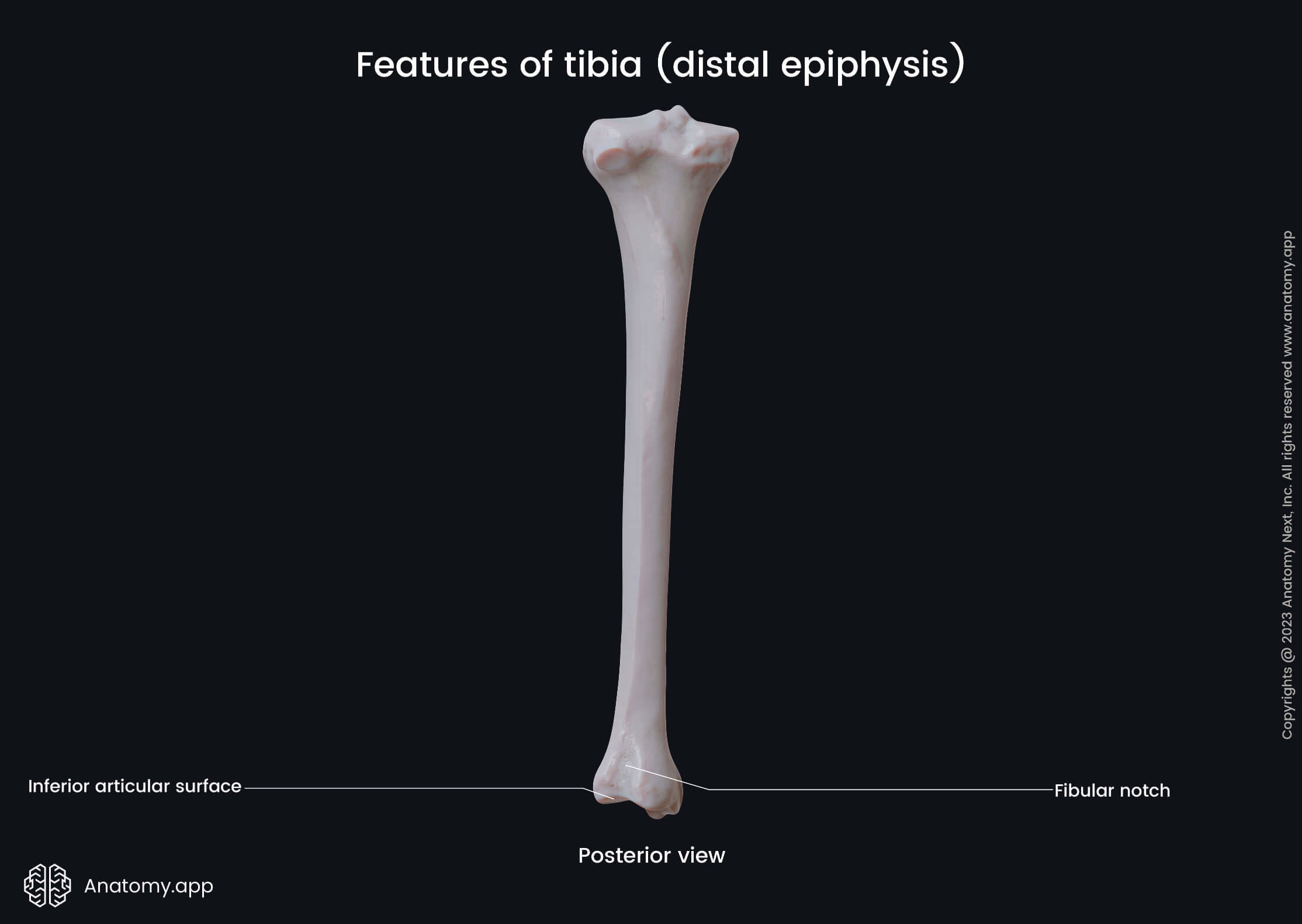
The fibular notch is a depression on the lateral aspect of the distal end. It articulates with the distal end of the fibula, and both bones form the distal (inferior) tibiofibular joint.
The inferior articular surface is the inferior surface of the tibia. This surface faces the talus and participates in the formation of the ankle joint.