- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Skeleton of trunk
- Skull
- Skeleton of upper limb
- Skeleton of lower limb
- Joints
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
Patella
The patella (Latin: patella) is also known as the kneecap, and it is a flat movable bone covering the anterior aspect of the knee joint. It is embedded in the quadriceps femoris muscle tendon, and it is the largest sesamoid bone in the human body.
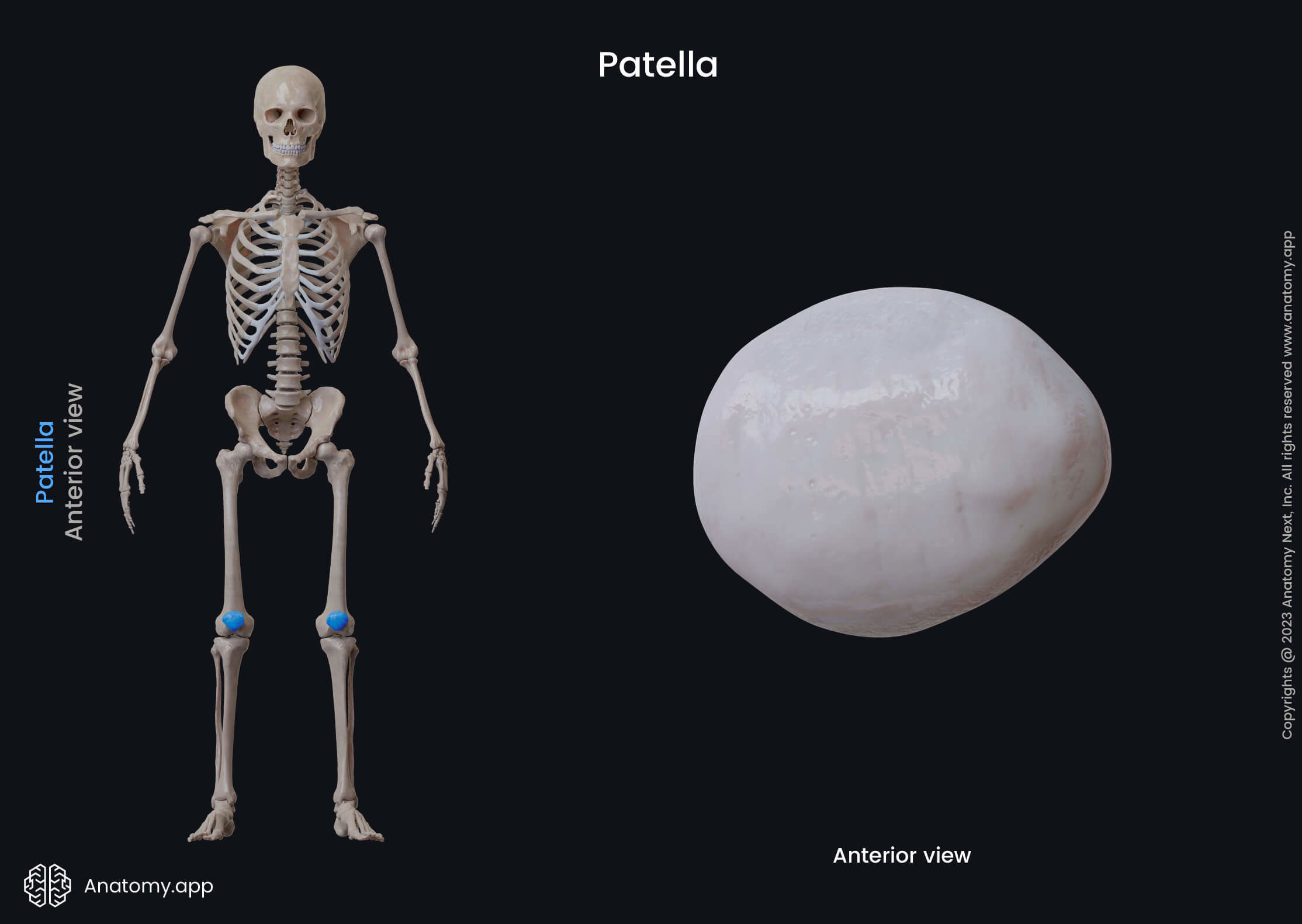
The patella is roughly triangular-shaped with three main parts:
Base of patella
The base of the patella is the broad, superior border of the bone. The tendon of the quadriceps femoris muscle attaches to the base of the patella. The vastus intermedius of the muscle is attached to the base, while the vastus lateralis and vastus medialis attach to the outer and medial borders of the bone.
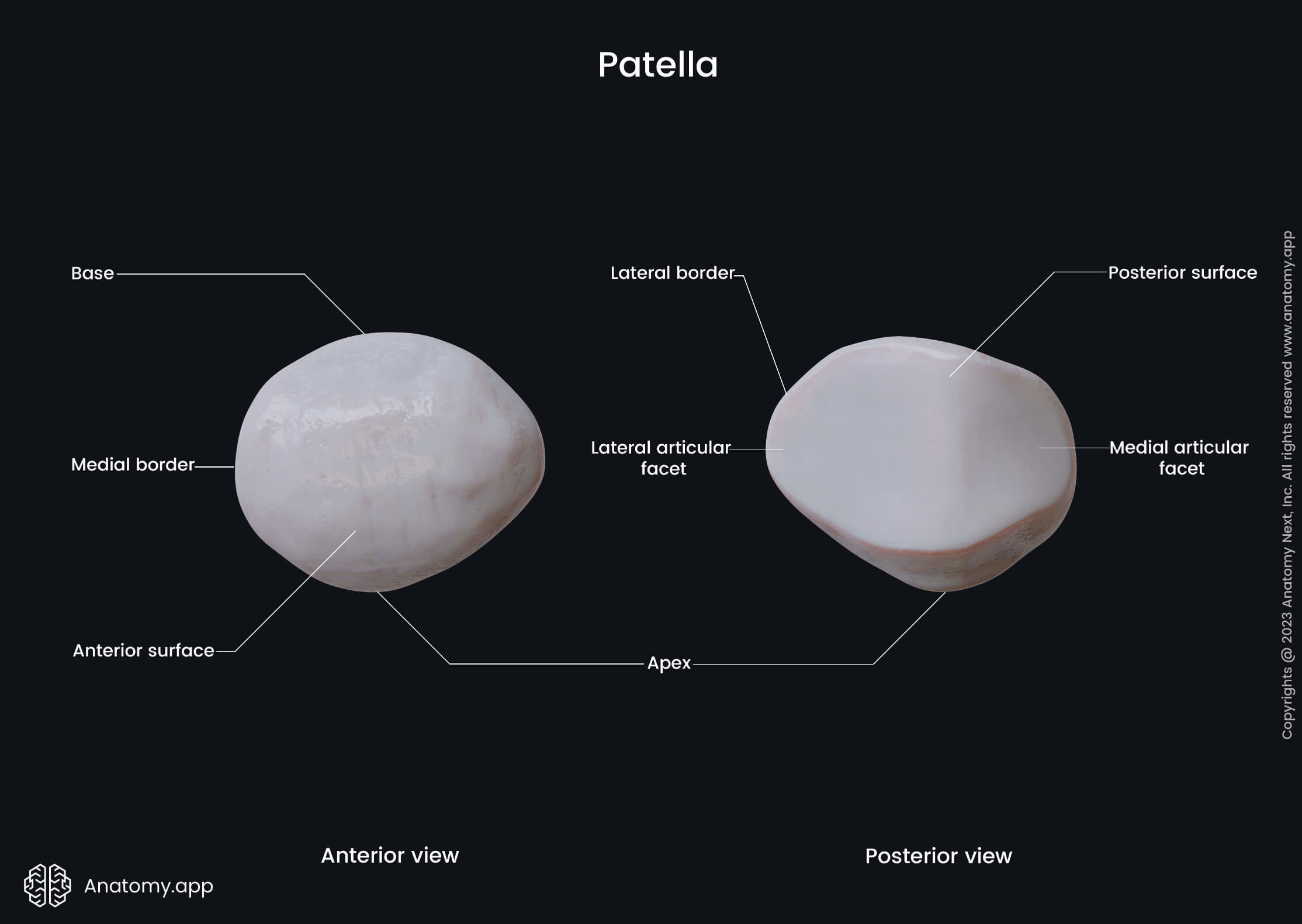

Apex of patella
The apex of the patella is the pointed and most inferior portion of the bone. It gives attachment to the patellar ligament.
Articular surface
The articular surface is the cartilage-covered posterior upper part of the patella. It faces the femur and articulates with its patellar surface. The articular cartilage that covers the patella is among the thickest cartilages in the human body.