- Anatomical terminology
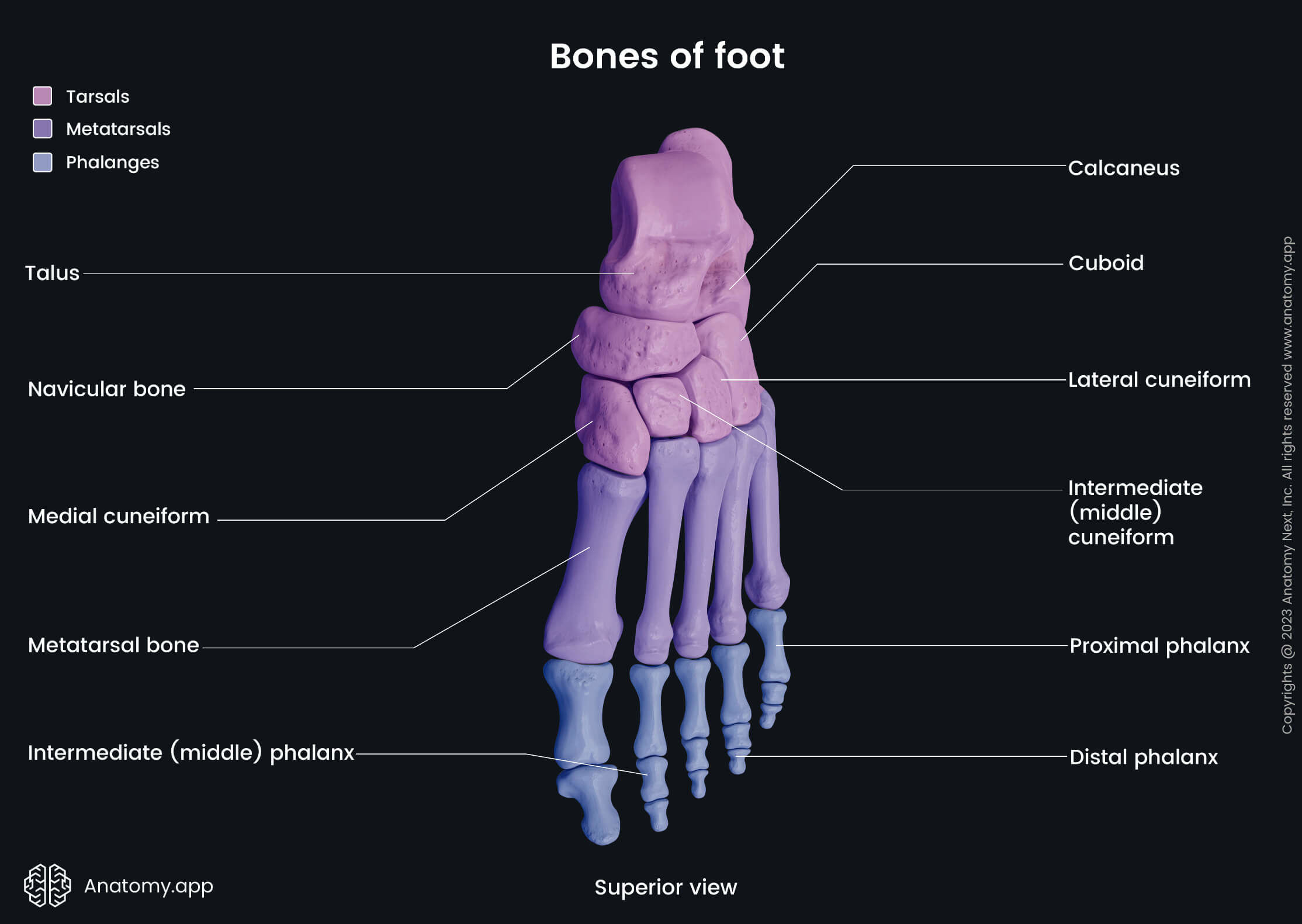
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
Phalanges of foot
The phalanges (Latin: phalanges) are small bones of fingers found in hands and feet.
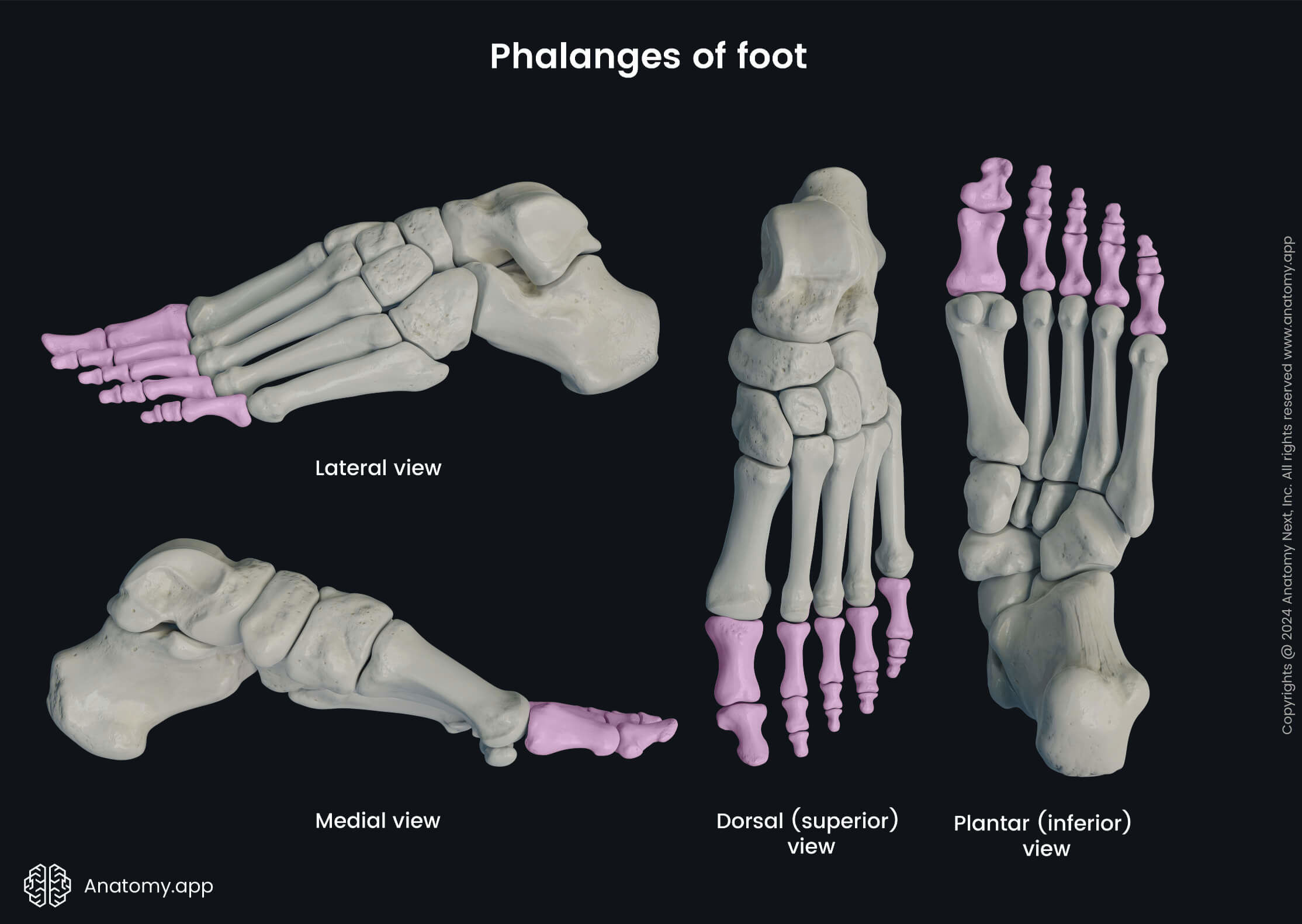
Each foot is composed of 14 phalanges. The big toes have two phalanges named the proximal and distal, while the rest of the toes have three - proximal, middle, and distal phalanges.
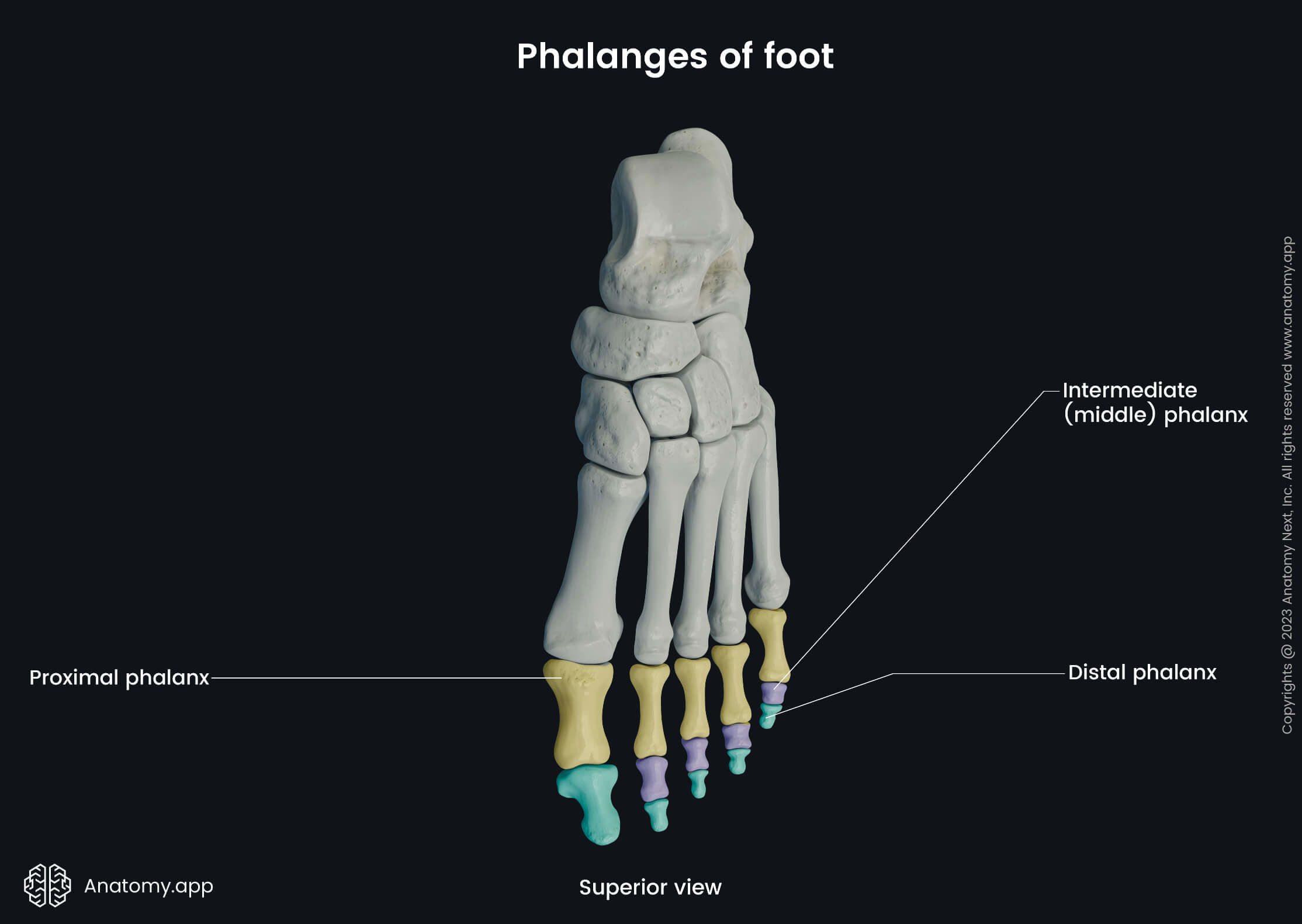
All phalanges within each toe articulate with one another, forming the interphalangeal joints. The proximal phalanges also articulate with the metatarsal bones of the foot to form the metatarsophalangeal joints. Each phalanx consists of three parts:
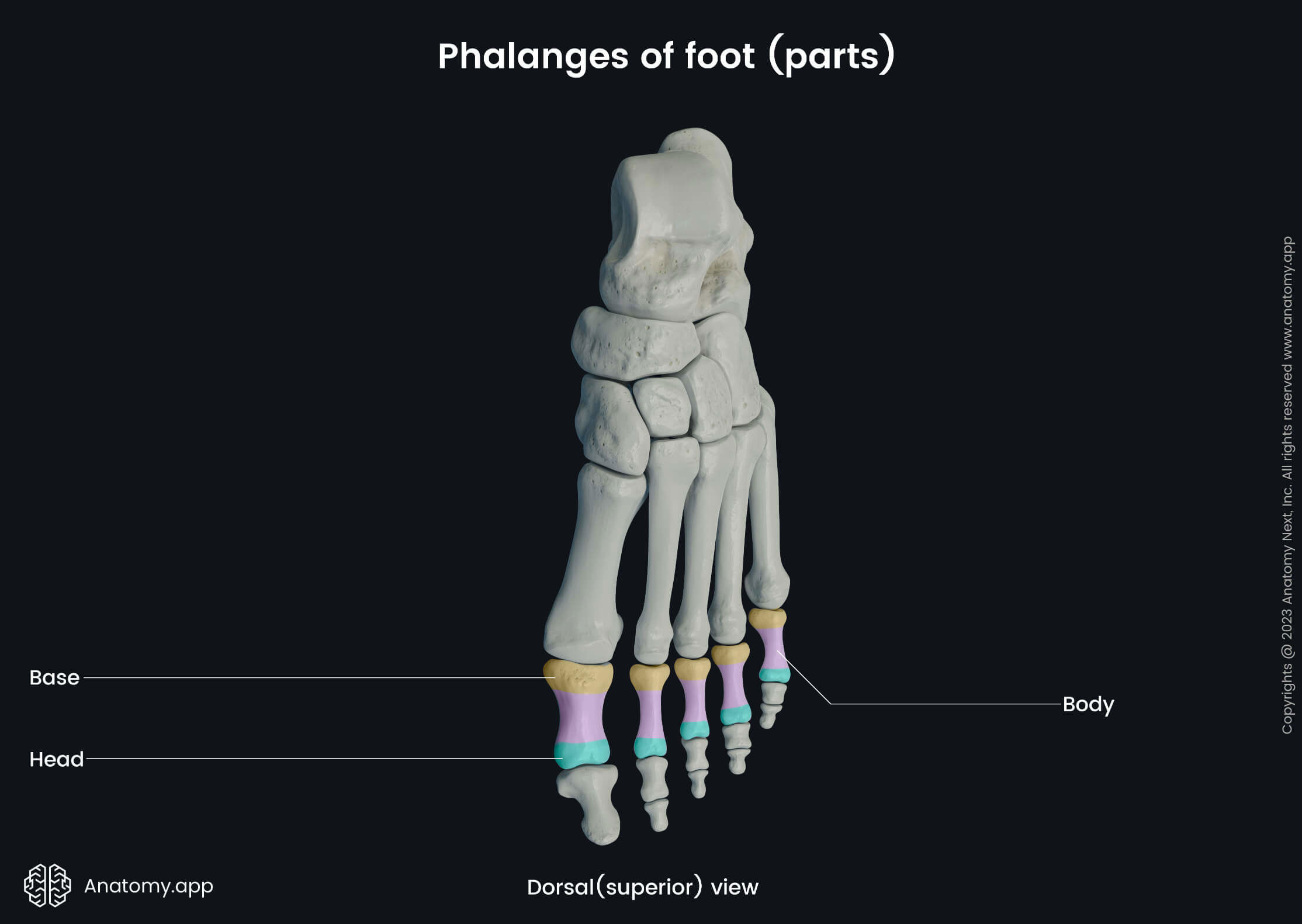
The base or proximal extremity is expanded proximal part. The base of each proximal phalanx presents oval and concave articular surfaces. In contrast, the bases of the middle and distal phalanges have double concave articular surfaces separated by a median ridge.
The body or shaft is a distal continuation of the base. The body of each phalanx presents two surfaces - plantar and dorsal, and it is more concave on the plantar and convex on the dorsal surface. The sides of the body have rough areas for attachment of flexor tendons.
The heads or distal extremities are expanded and rounded distal endings. The heads of phalanges are smaller than the bases. Each head contains articular surface, except for the distal phalanges, as their heads are flattened and contain distal tuberosities.
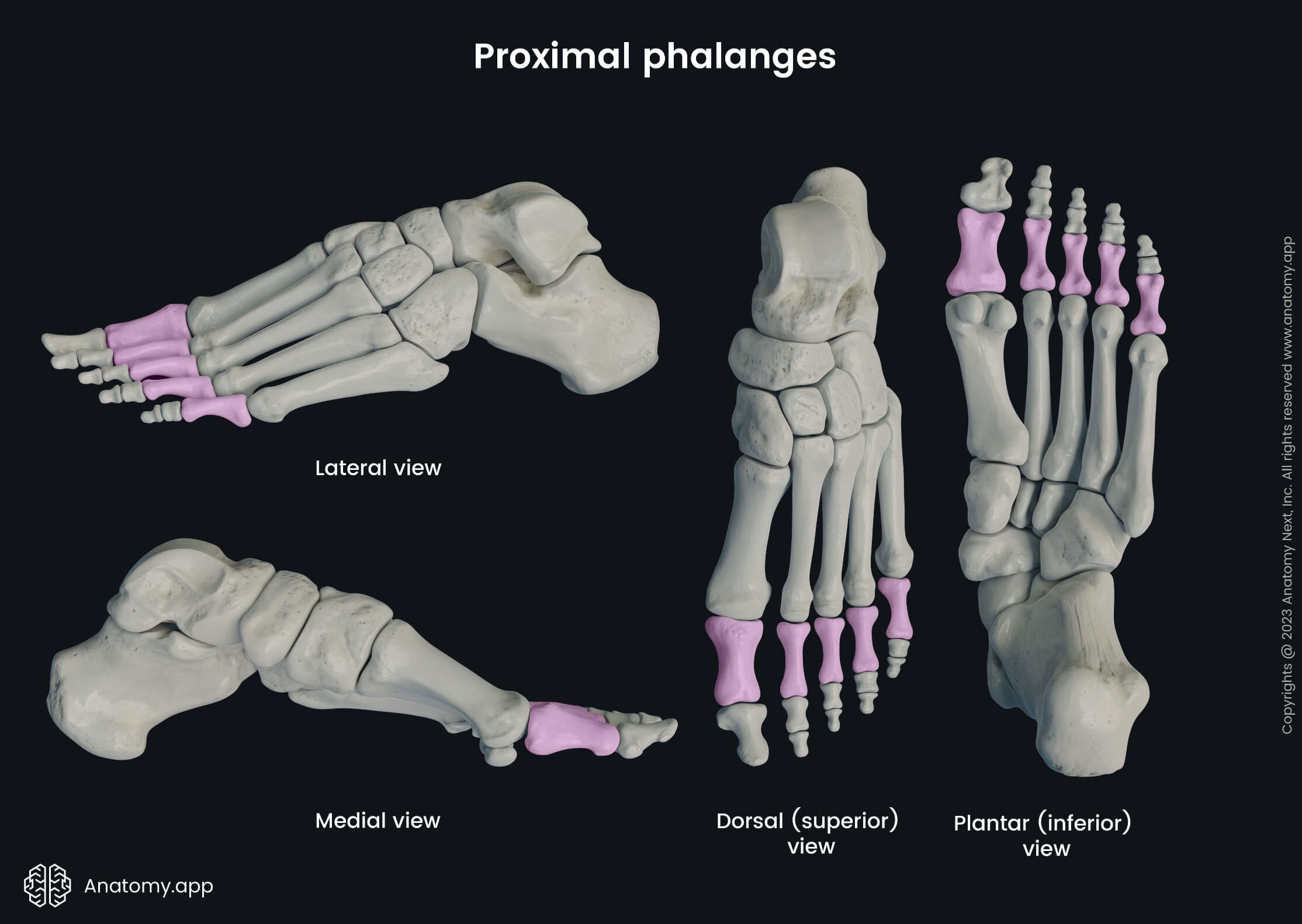
Proximal phalanges
The proximal phalanges (Latin: phalanges proximales) are the most proximal bones of the fingers of the hand and foot. Each foot is composed of five proximal phalanges corresponding to five toes. The proximal phalanges are the largest of all three phalanges.
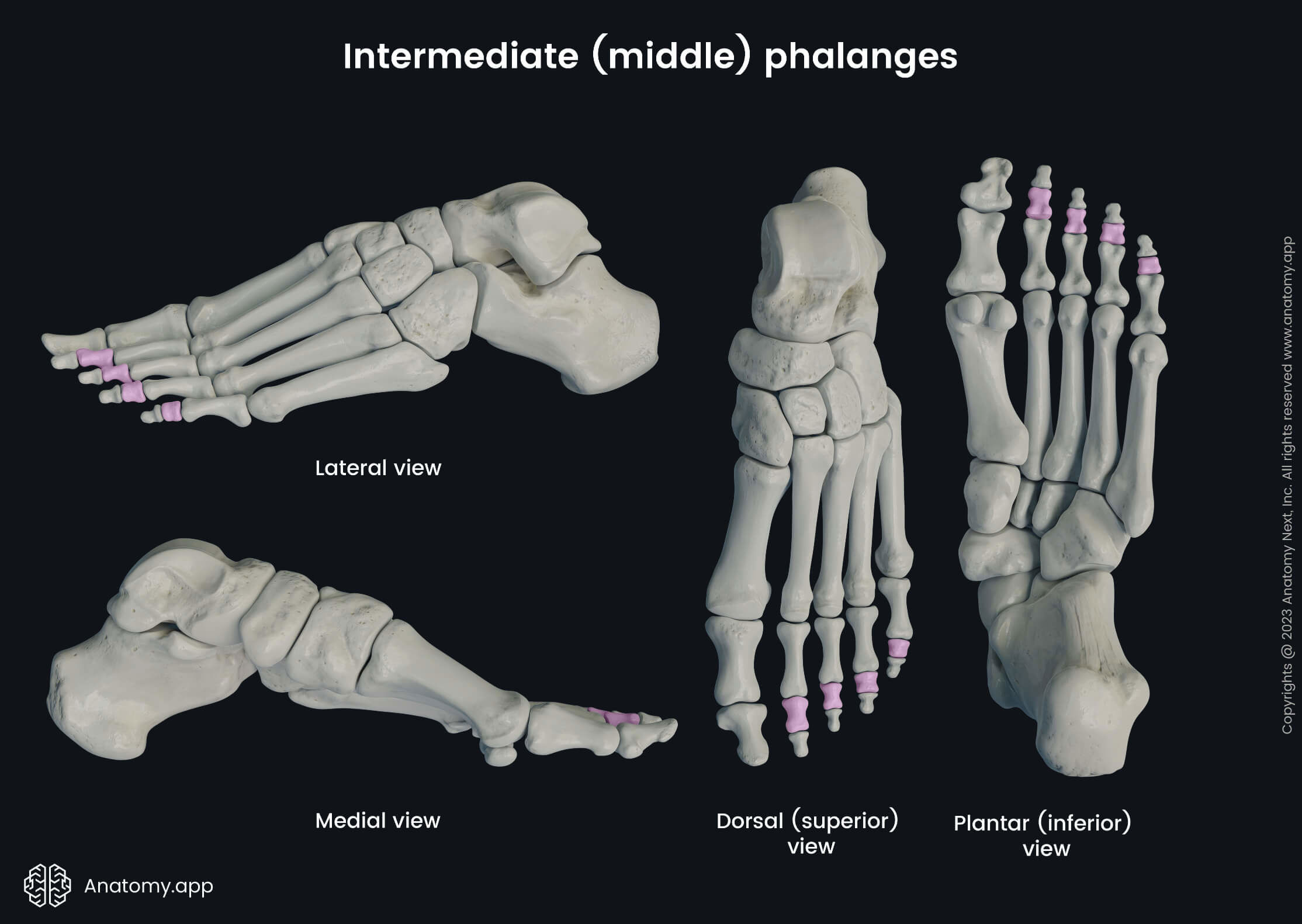
Middle phalanges
The middle phalanges (Latin: phalanges mediae), also known as intermediate phalanges, lie between the proximal and distal phalanges. In total, each foot contains four middle phalanges as the big toe lacks it. The middle phalanges are intermediate not only according to their location but also their size compared to the distal and proximal phalanges.
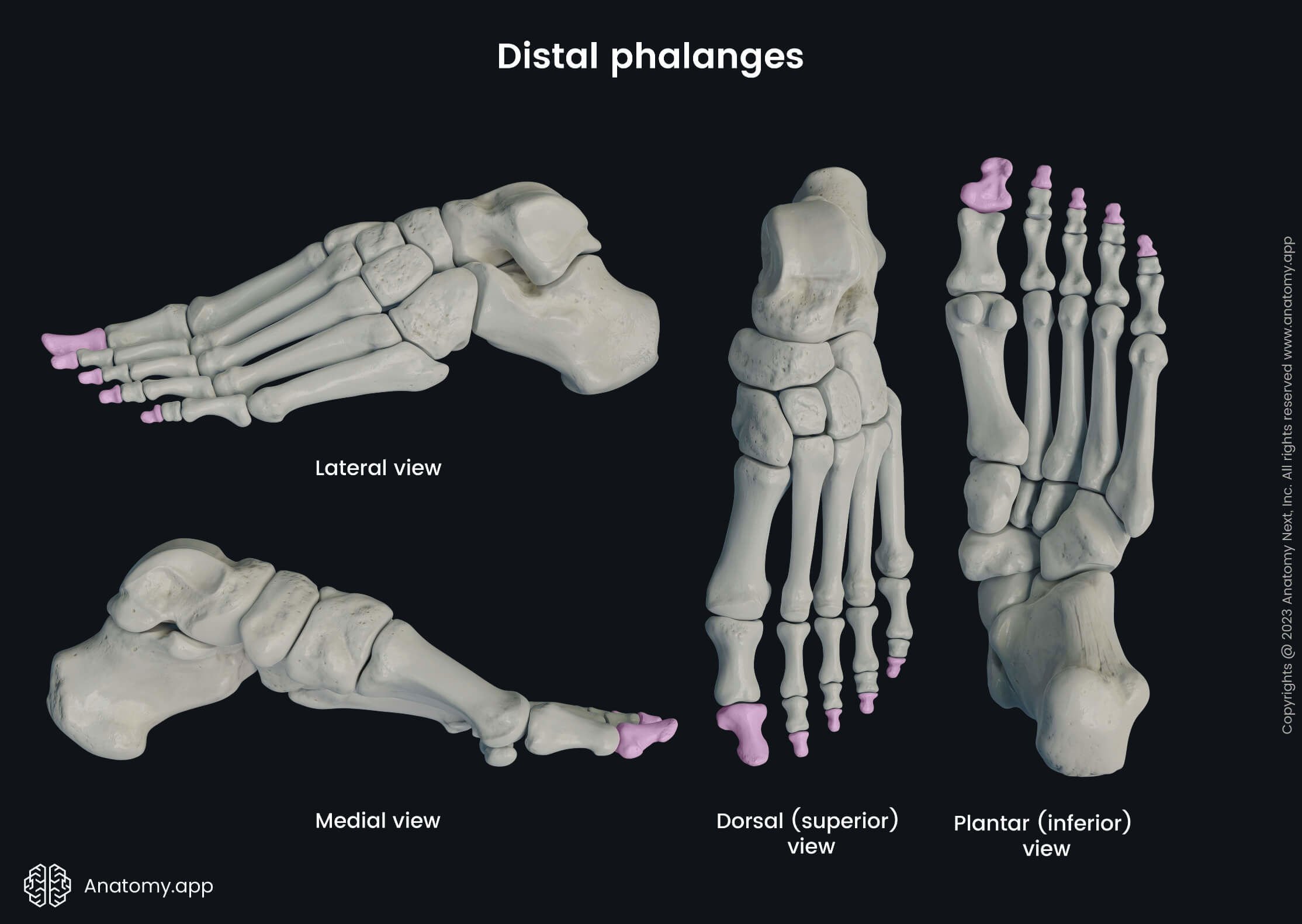
Distal phalanges
The distal phalanges (Latin: phalanges distales) are the last bones found in the tips of the toes. Each foot contains five distal phalanges that are tapered distally. The heads of the distal phalanges are flattened, and they present rough and elevated areas known as the tuberosities of the distal phalanges.