- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
-
Head muscles
- Extraocular muscles
-
Facial muscles
- Occipitofrontalis
- Corrugator supercilii
- Depressor supercilii
- Orbicularis oculi
- Malaris
- Buccinator
- Orbicularis oris
- Mentalis
- Depressor anguli oris
- Depressor labii inferioris
- Levator anguli oris
- Levator labii superioris
- Risorius
- Zygomaticus major
- Zygomaticus minor
- Levator labii superioris alaeque nasi
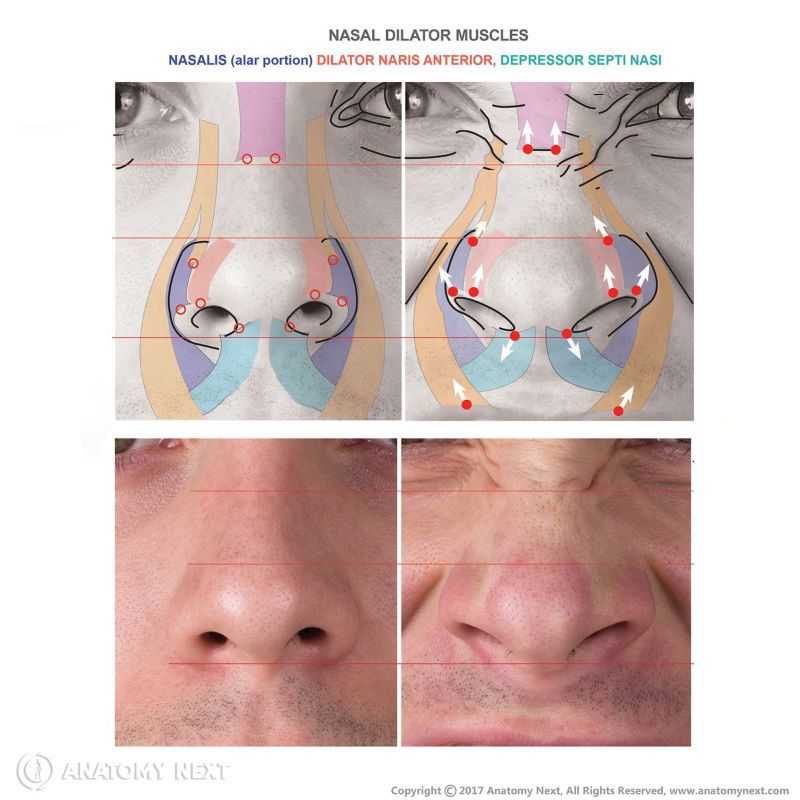
- Nasalis
- Procerus
- Depressor septi nasi
- Compressor narium minor
- Dilator naris anterior
- Muscles of mastication
- Neck muscles
- Muscles of upper limb
- Thoracic muscles
- Muscles of back
- Muscles of lower limb
-
Head muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
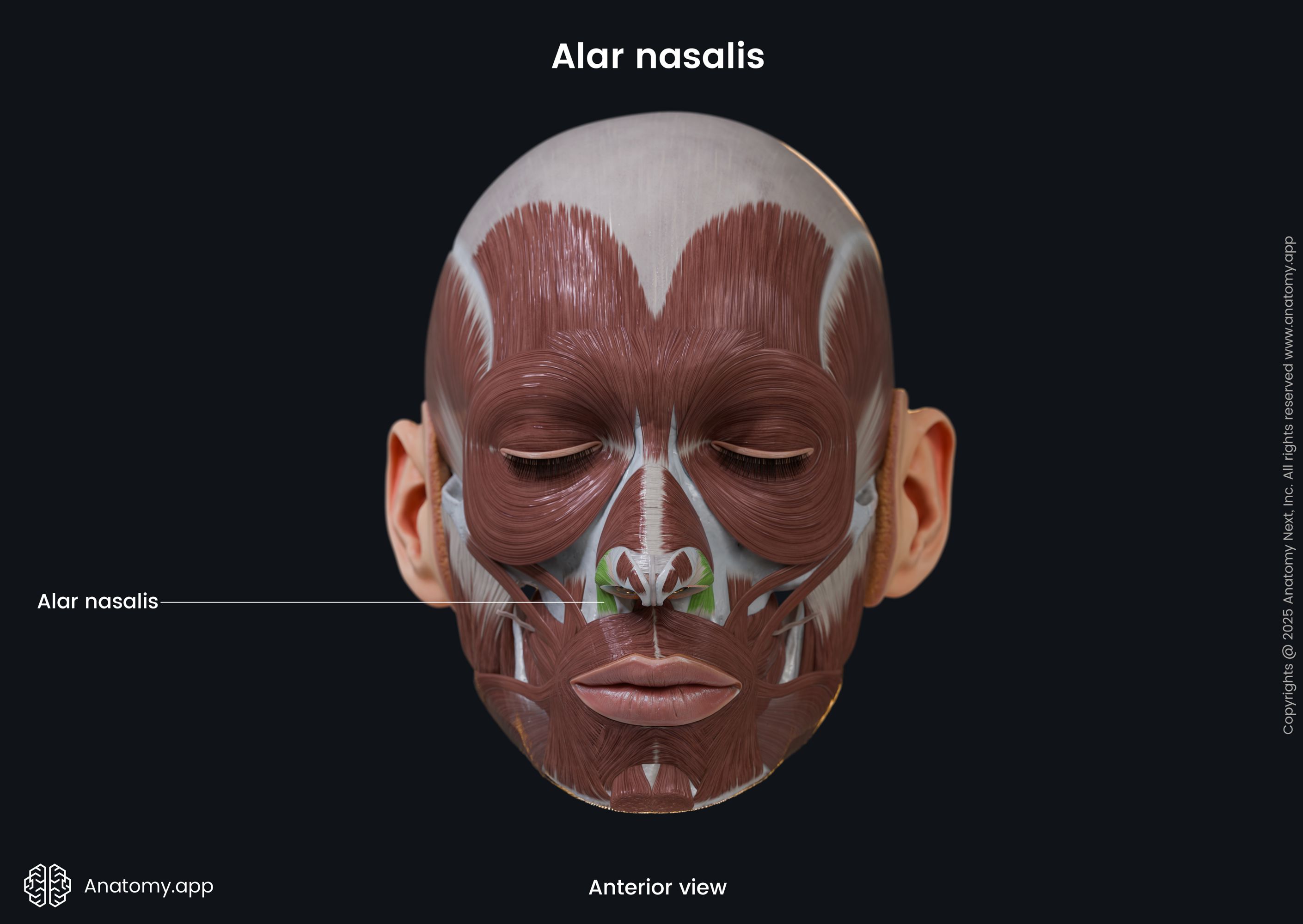
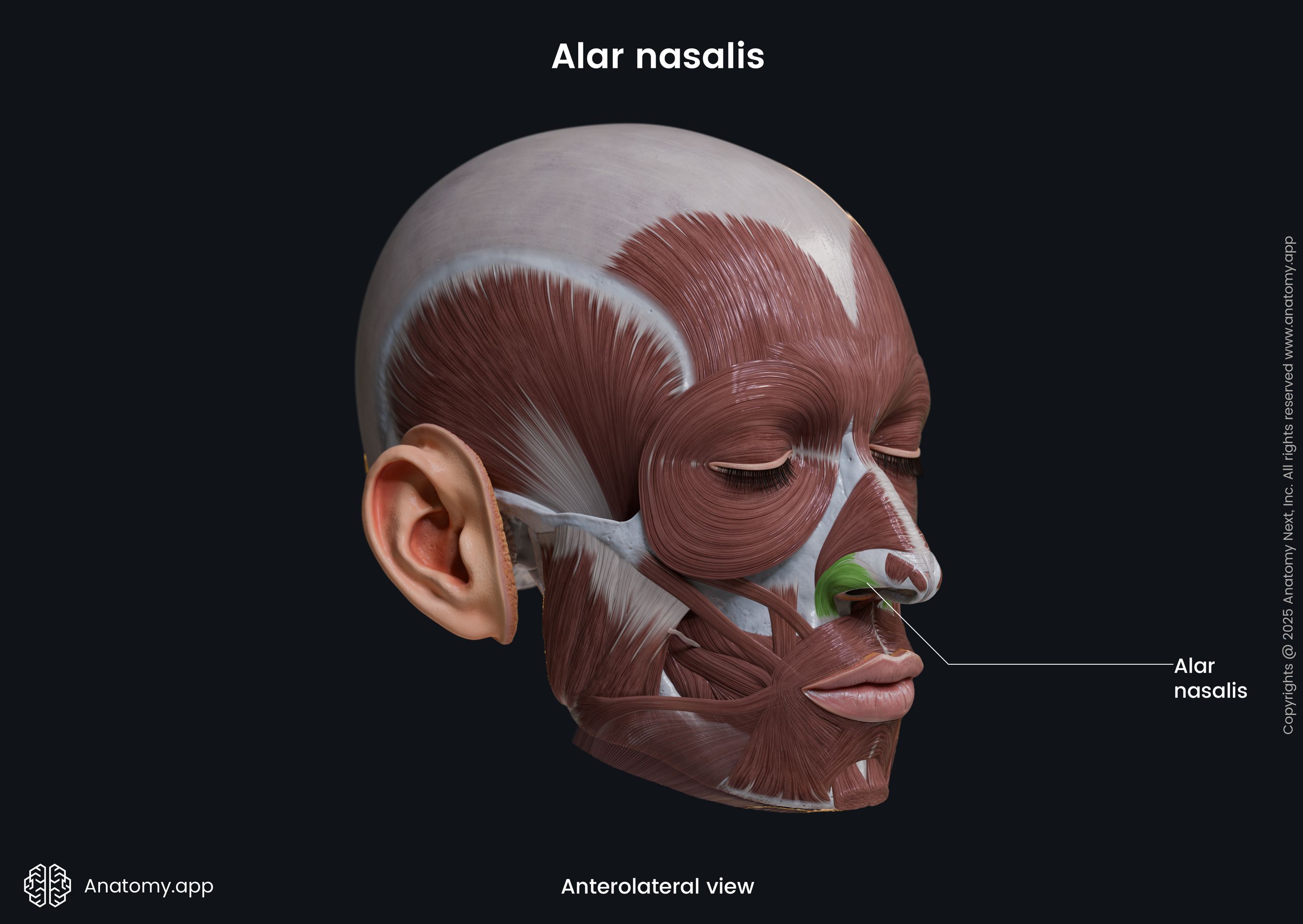
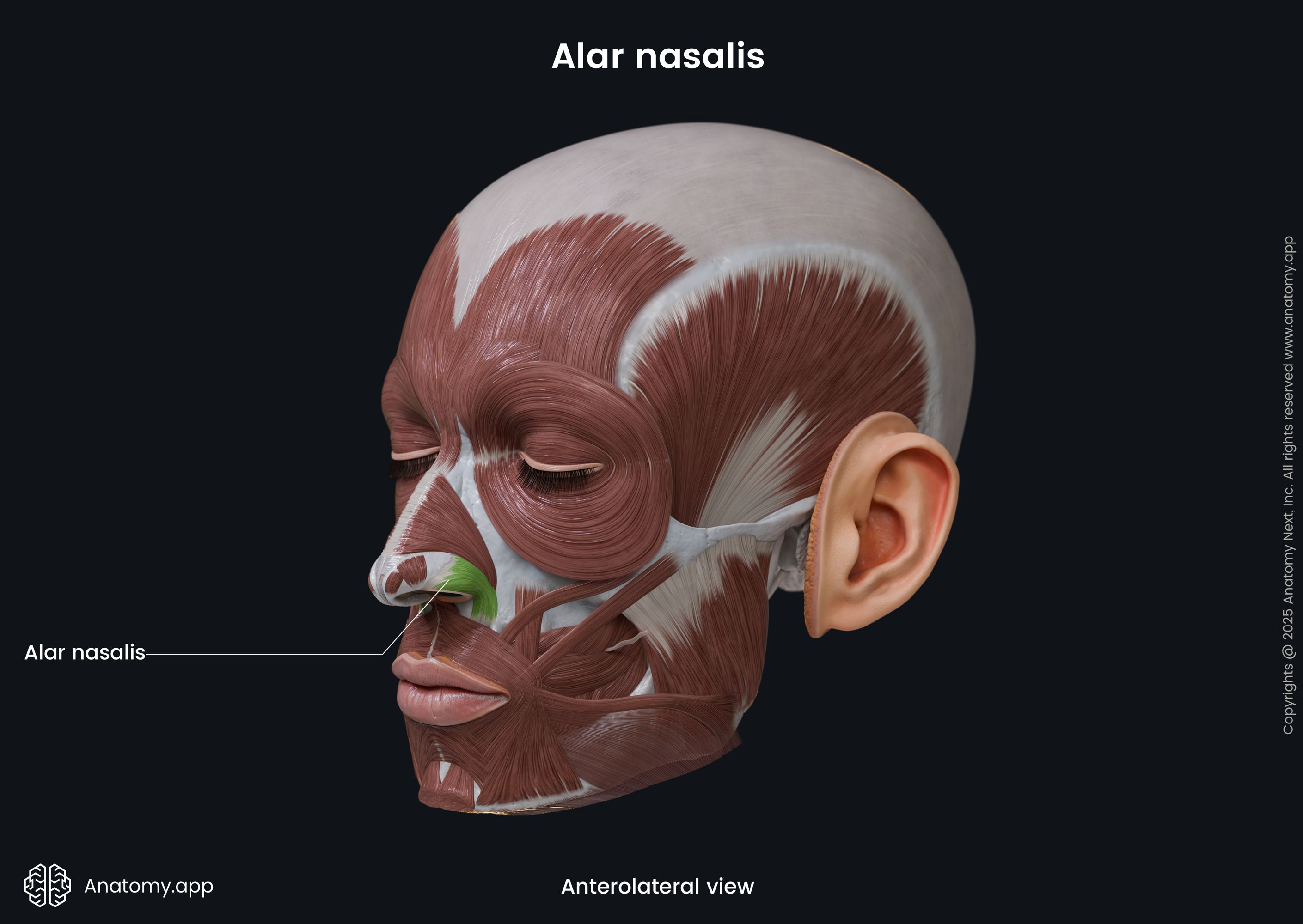
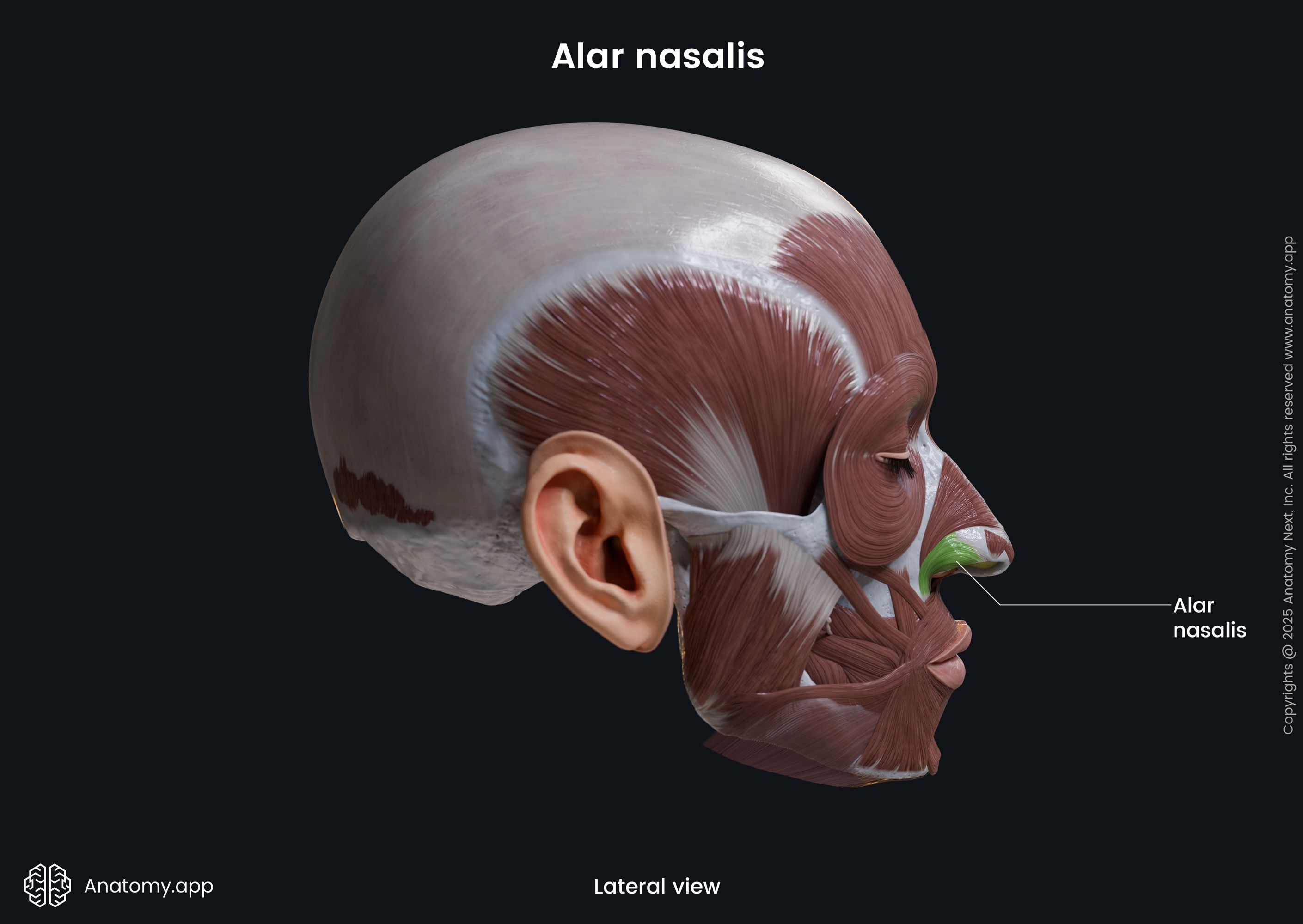
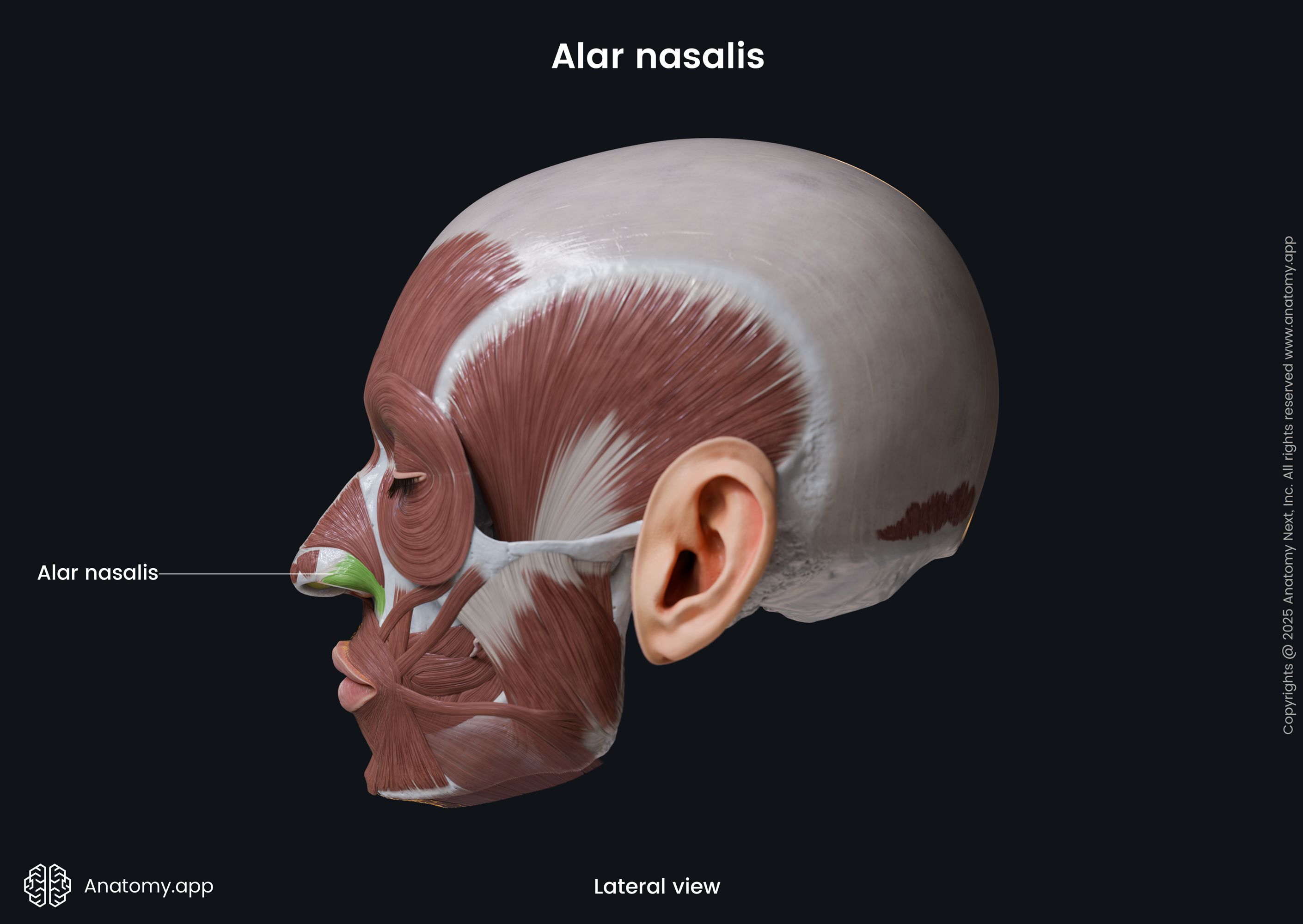
Alar nasalis
The alar part of the nasalis (Latin: pars alaris musculi nasalis), also known as the alar nasalis or dilator naris posterior, is one of the nasalis muscle parts. It is classified as the nasal facial muscle. The alar nasalis is located in the wing of the nose, and it forms the nostril. This muscle dilates the nostril.
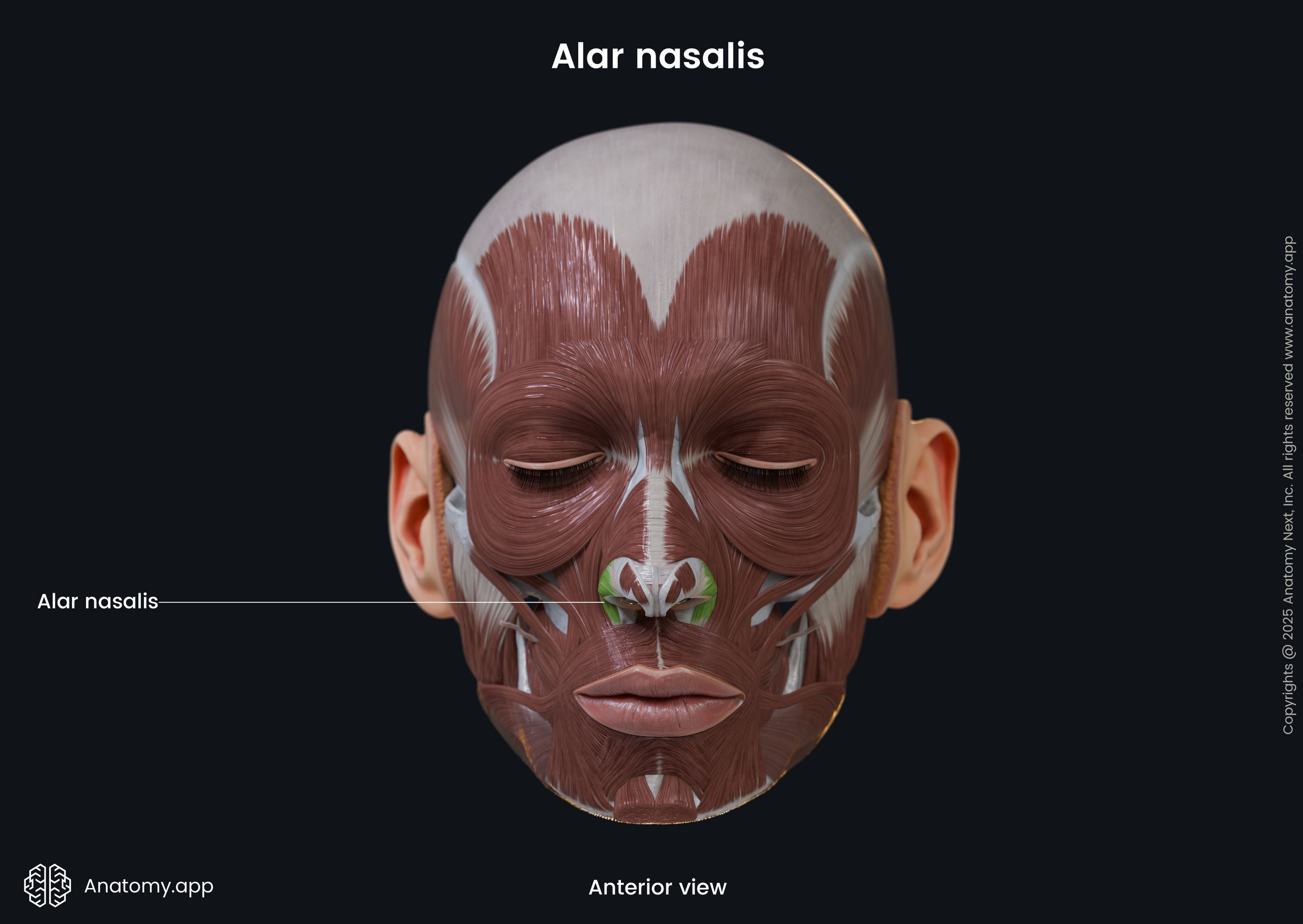
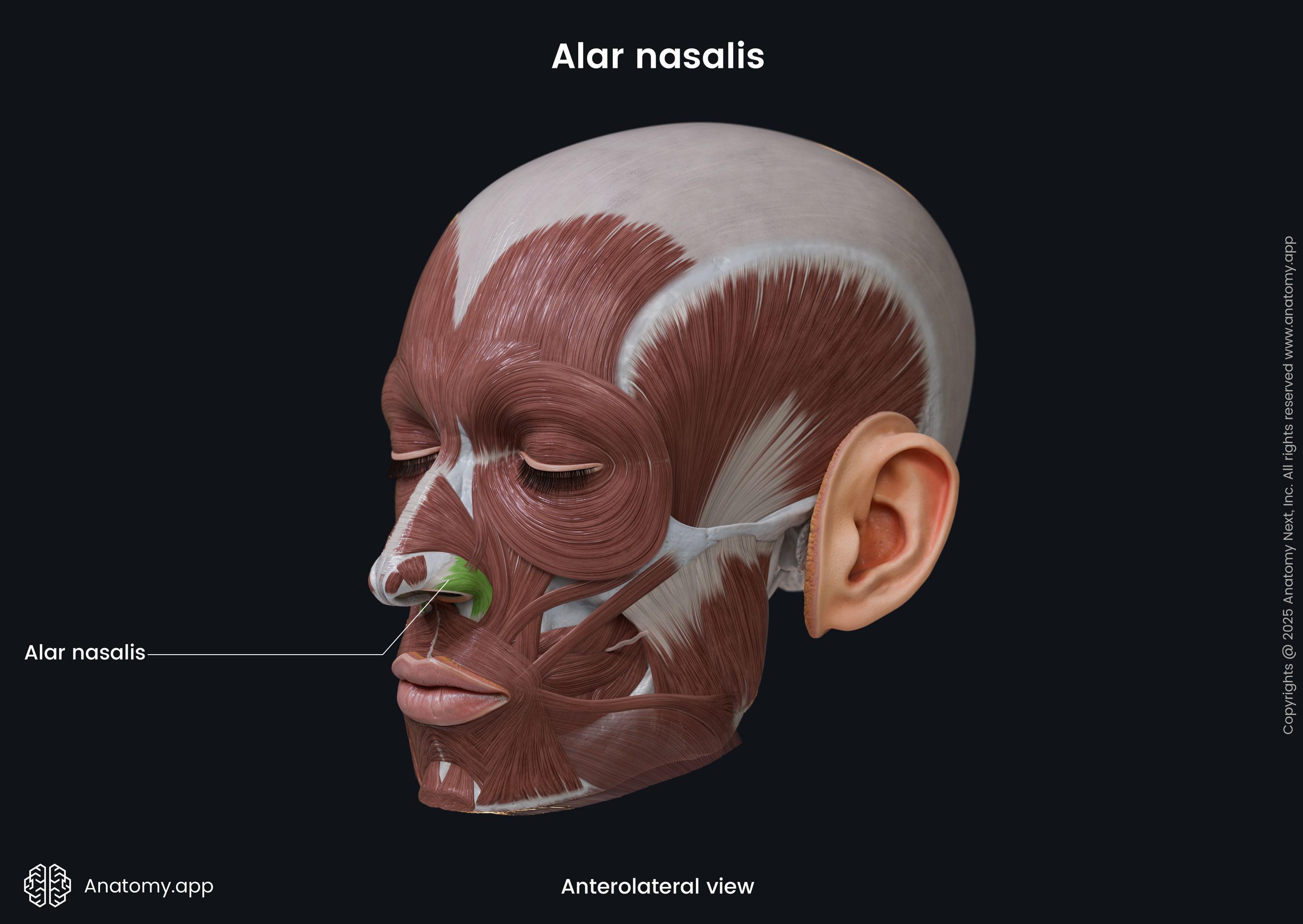
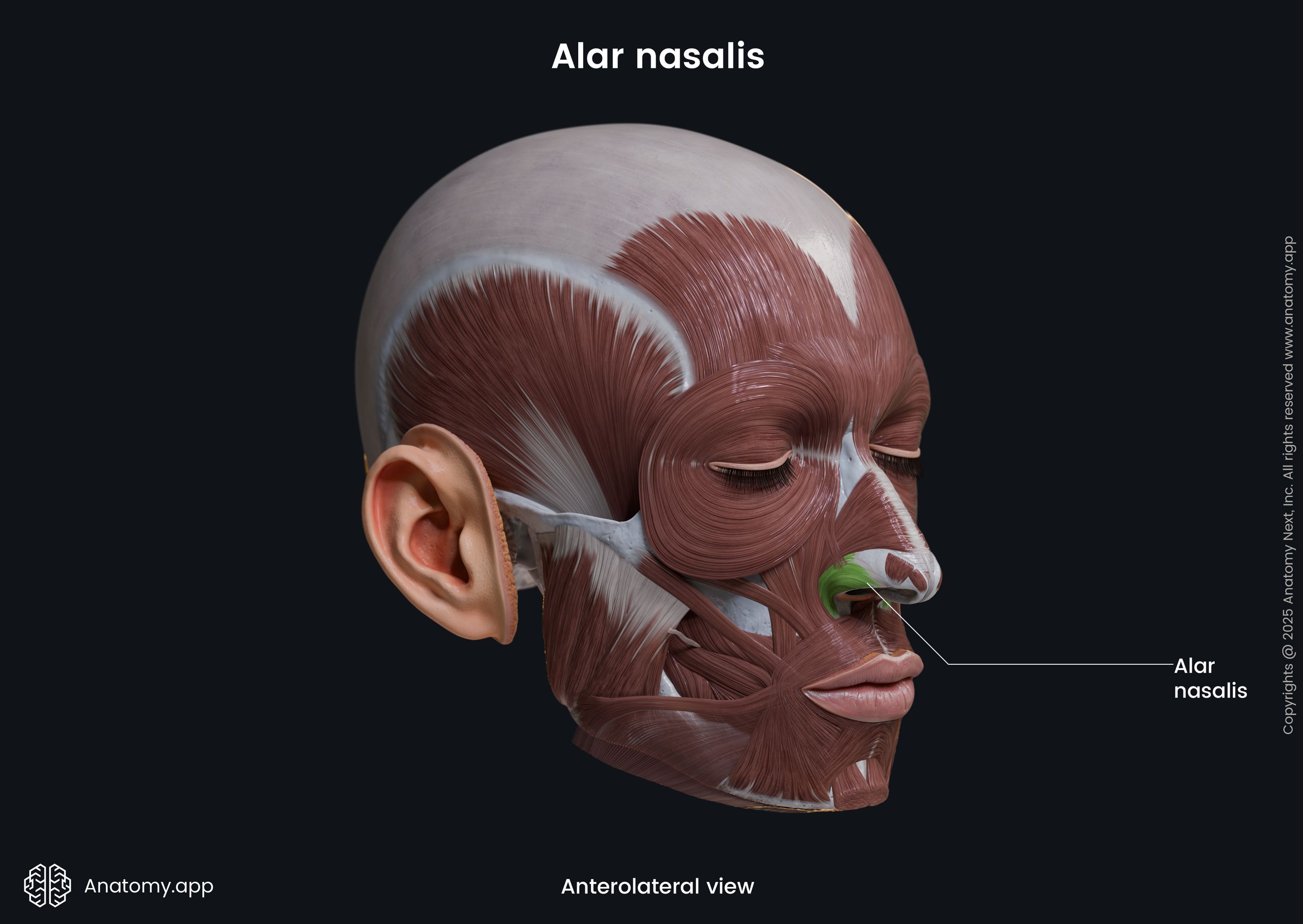
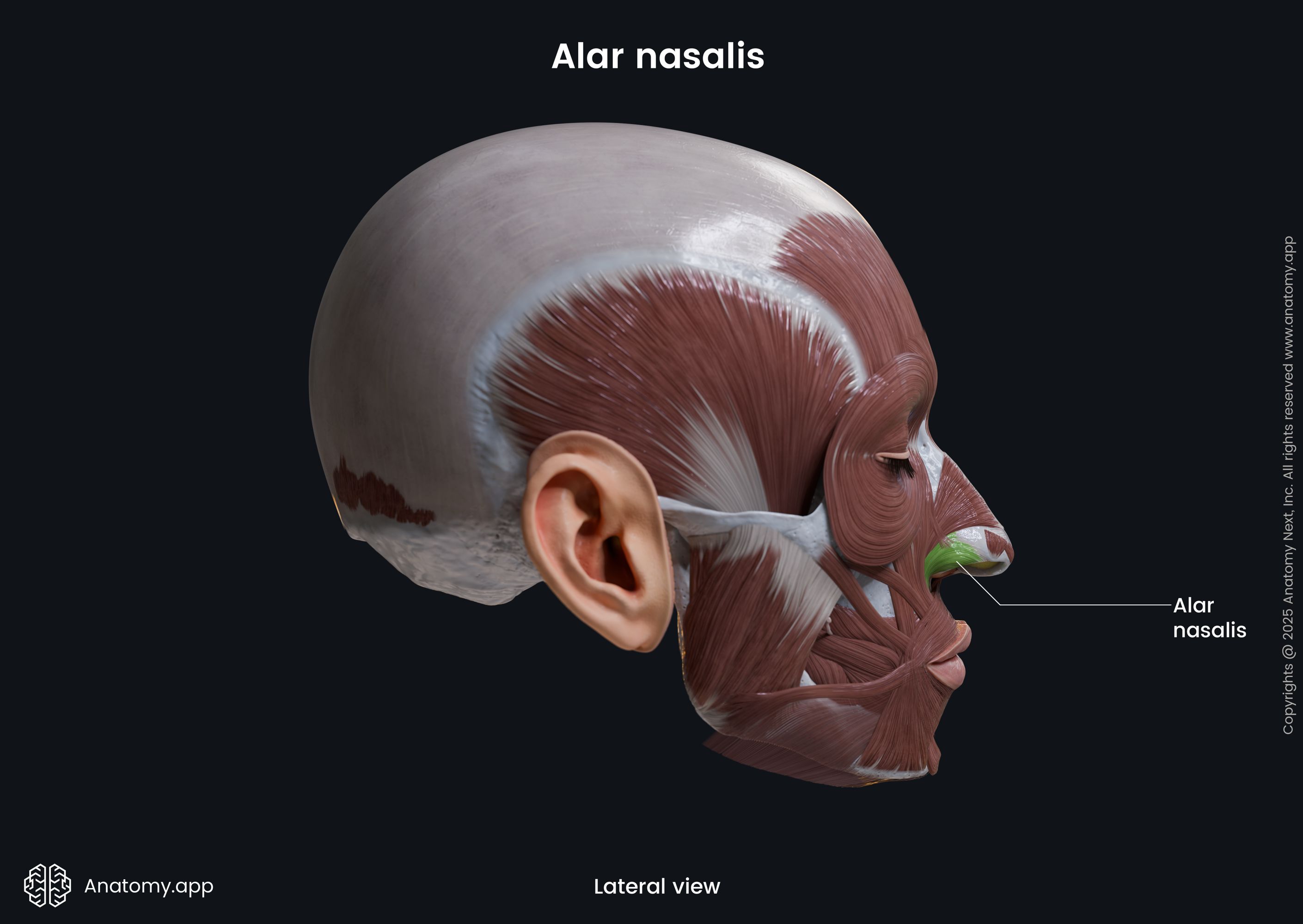
| Alar nasalis | |
| Origin | Frontal process of maxilla |
| Insertion | Skin along ala of nose |
| Action | Lengthens nose, dilates nostril |
| Innervation | Buccal branch of facial nerve (CN VII) |
| Blood supply | Superior labial, lateral nasal and septal branches of facial artery, infraorbital artery of maxillary artery |
Origin
The alar part of the nasalis muscle originates from the frontal process of the maxilla above the region of the maxillary lateral incisor tooth.
Insertion
The alar nasalis inserts into the skin along the wing of the nose.
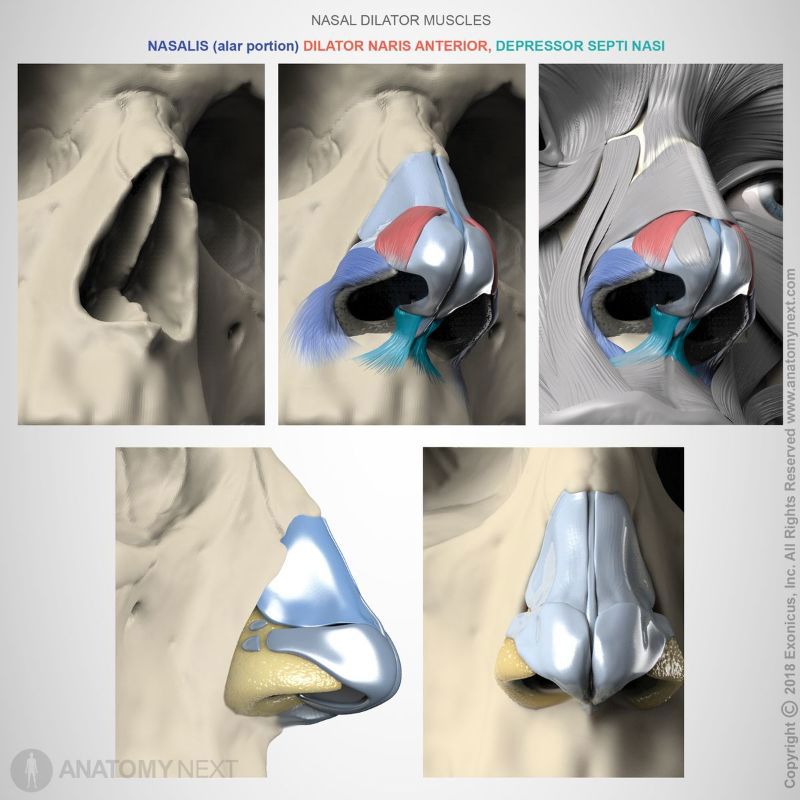
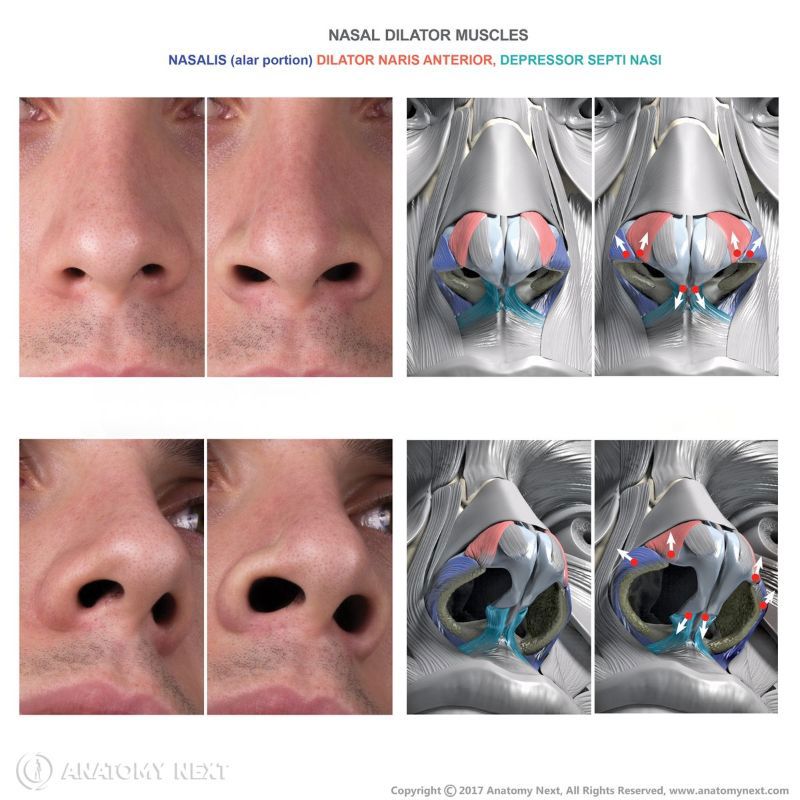
Action
The alar nasalis muscle lengthens the nose and dilates the nostril.
Innervation
The innervation of the alar nasalis muscle is provided by the buccal branch of the facial nerve (CN VII).
Blood supply
The alar nasalis receives arterial blood supply from the superior labial, lateral nasal and septal branches of the facial artery and the infraorbital branch of the maxillary artery.