- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Aorta
- Blood vessels of head and neck
- Arteries of head and neck
- Veins of head and neck
- Blood vessels of upper limb
- Blood vessels of thorax
- Blood vessels of abdomen
- Blood vessels of pelvis and lower limb
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
Superficial temporal artery
The superficial temporal artery (Latin: arteria temporalis superficialis) is one of the terminal branches of the external carotid artery. It provides arterial blood supply to the upper and lateral parts of the scalp.
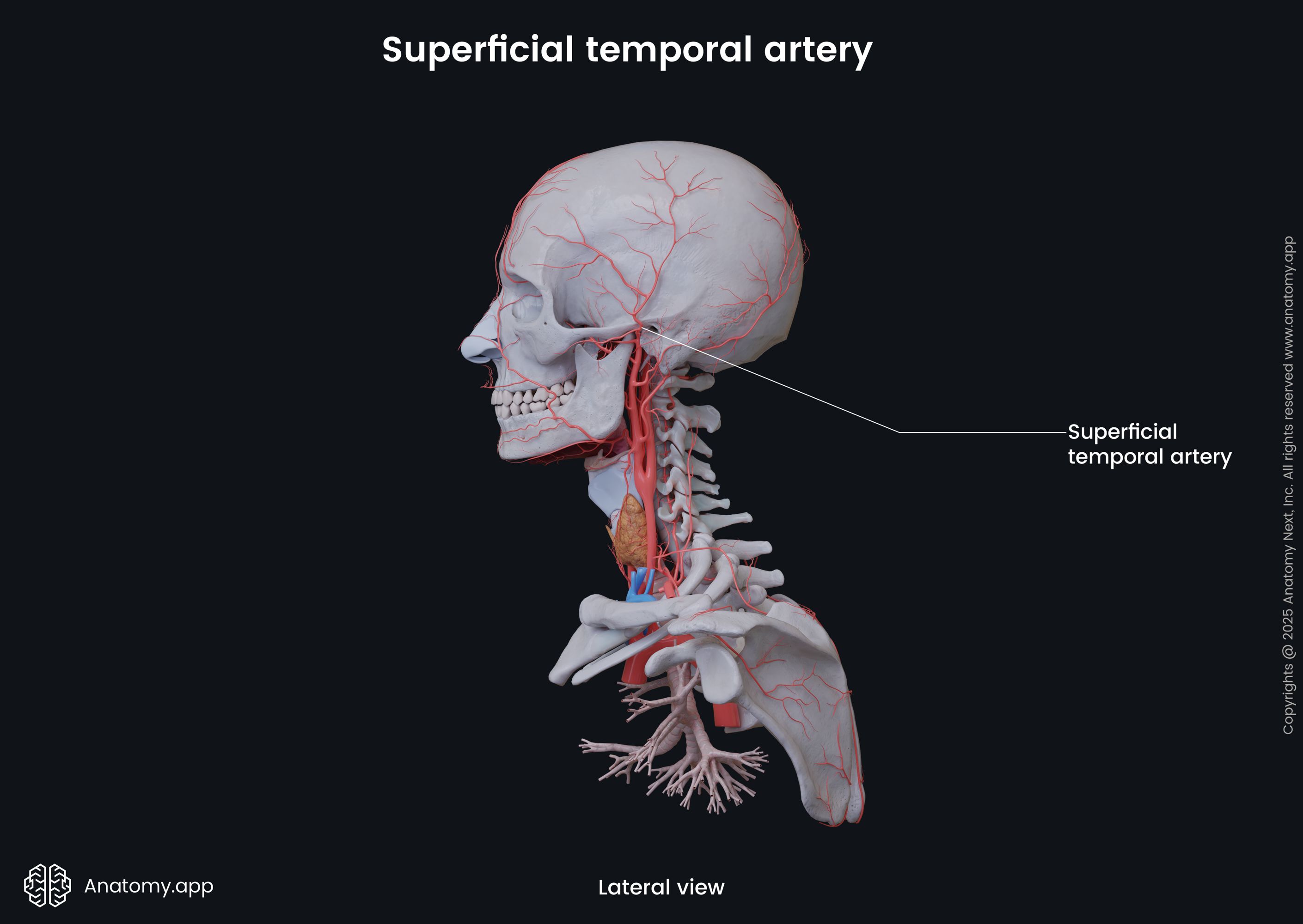
Course of superficial temporal artery
The superficial temporal artery separates from the external carotid artery behind the neck of the mandible. It passes upward near the auricle, and over the posterior root of the zygomatic process of the temporal bone. At this point, the pulse of the superficial temporal artery is palpable.
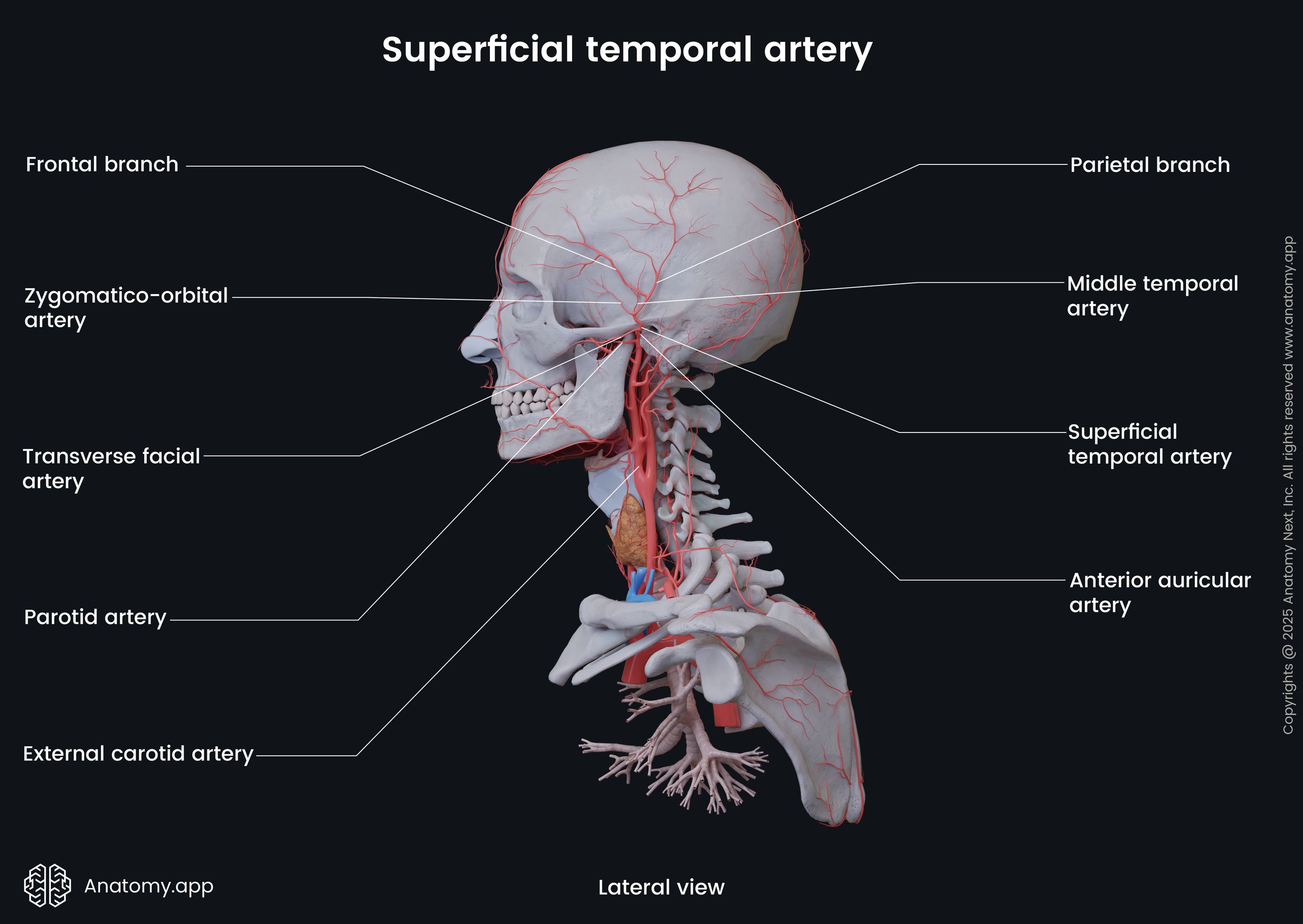
Branches of superficial temporal artery
Above the zygomatic process, the superficial temporal artery divides into two branches, the frontal and parietal branches. The frontal branch supplies the forehead area and anastomoses with the ophthalmic artery. The parietal branch of the superficial temporal artery supplies the temporal and parietal regions of the scalp. It also may form anastomoses with the posterior auricular artery and the occipital artery.
The superficial temporal artery also gives off the following side branches:
- Transverse facial artery - mainly supplies parotid gland, parotid duct, and masseter muscle;
- Anterior auricular branches - supply the anterior aspect of the auricle, lobule and external auditory meatus (partly);
- Middle temporal artery - mainly supplies the orbicularis oculi muscle, and also anastomoses with the lacrimal and palpebral branches of the ophthalmic artery.
Common pathology
The superficial temporal artery is frequently involved in a pathology called the giant-cell arteritis (or temporal arteritis). It is a form of systemic inflammatory vasculitis. The temporal arteritis damages blood vessels resulting in subsequent distal ischemia. Clinical symptoms include headache, visual disturbances, neck pain, and scalp tenderness.