- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Aorta
- Blood vessels of head and neck
- Arteries of head and neck
- Veins of head and neck
- Blood vessels of upper limb
- Blood vessels of thorax
- Blood vessels of abdomen
- Blood vessels of pelvis and lower limb
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
Lingual artery
The lingual artery (Latin: arteria lingualis) is a branch of the external carotid artery. The branches of the lingual artery provide blood supply to the tongue, sublingual gland, gingiva and mucosa lining the floor of the mouth.
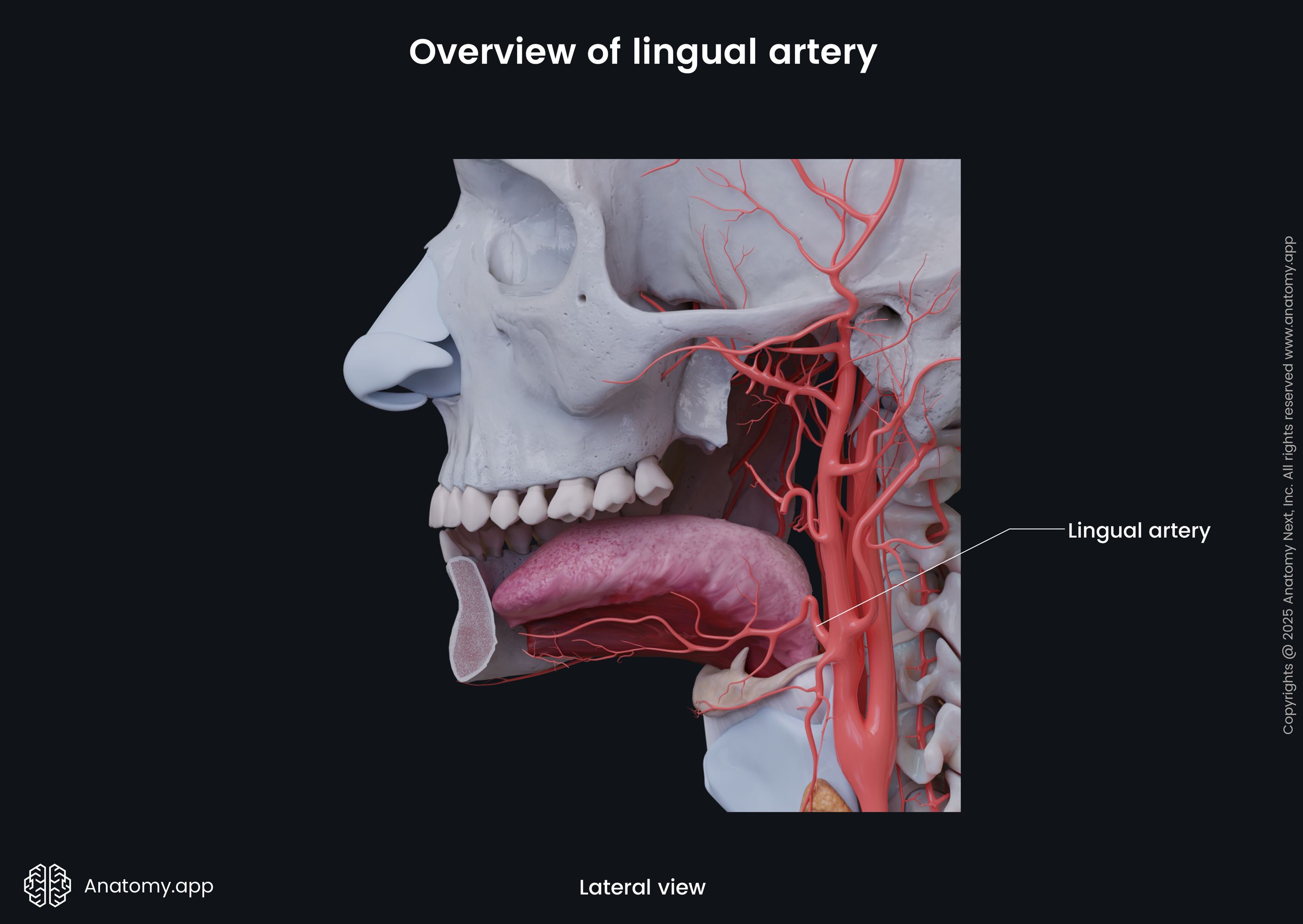
The lingual artery arises medially from the external carotid at the level of the greater horn of the hyoid bone. It loops antero-inferiorly and passes, at first, to the posterior border of the hyoglossus, then forwards deep to it.
Further, the lingual artery runs upward and forward on the inferior surface of the tongue and continues as the terminal branch till its tip. The terminal branch of the lingual artery is called the deep lingual artery.
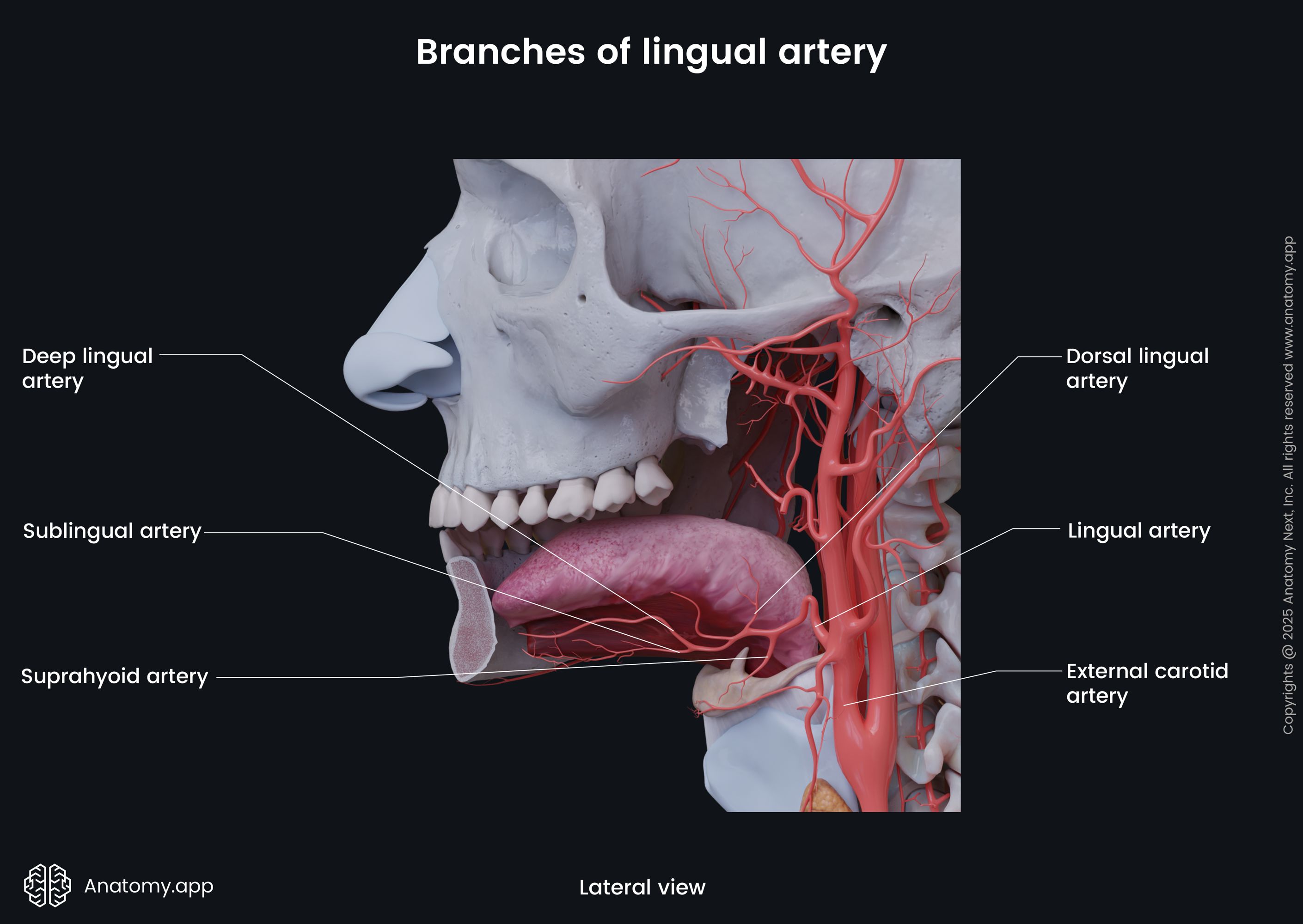
On its course, the lingual artery also gives off side branches, including the dorsal lingual branches and the sublingual artery. The dorsal lingual branches supply the dorsum of the tongue till the epiglottis. The sublingual artery supplies the sublingual gland.