- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Aorta
- Blood vessels of head and neck
- Arteries of head and neck
- Veins of head and neck
- Blood vessels of upper limb
- Blood vessels of thorax
- Blood vessels of abdomen
- Blood vessels of pelvis and lower limb
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
Brachiocephalic trunk
The brachiocephalic trunk (Latin: truncus brachiocephalicus), also called the brachiocephalic artery or innominate artery, is the first and largest branch of the aortic arch. It is short in length and only 1.6 - 2 inches (4 - 5 centimeters) long. The brachiocephalic trunk is located within the superior mediastinum, right behind the manubrium of the sternum. It supplies arterial blood to the right side of the head, neck and upper limb.
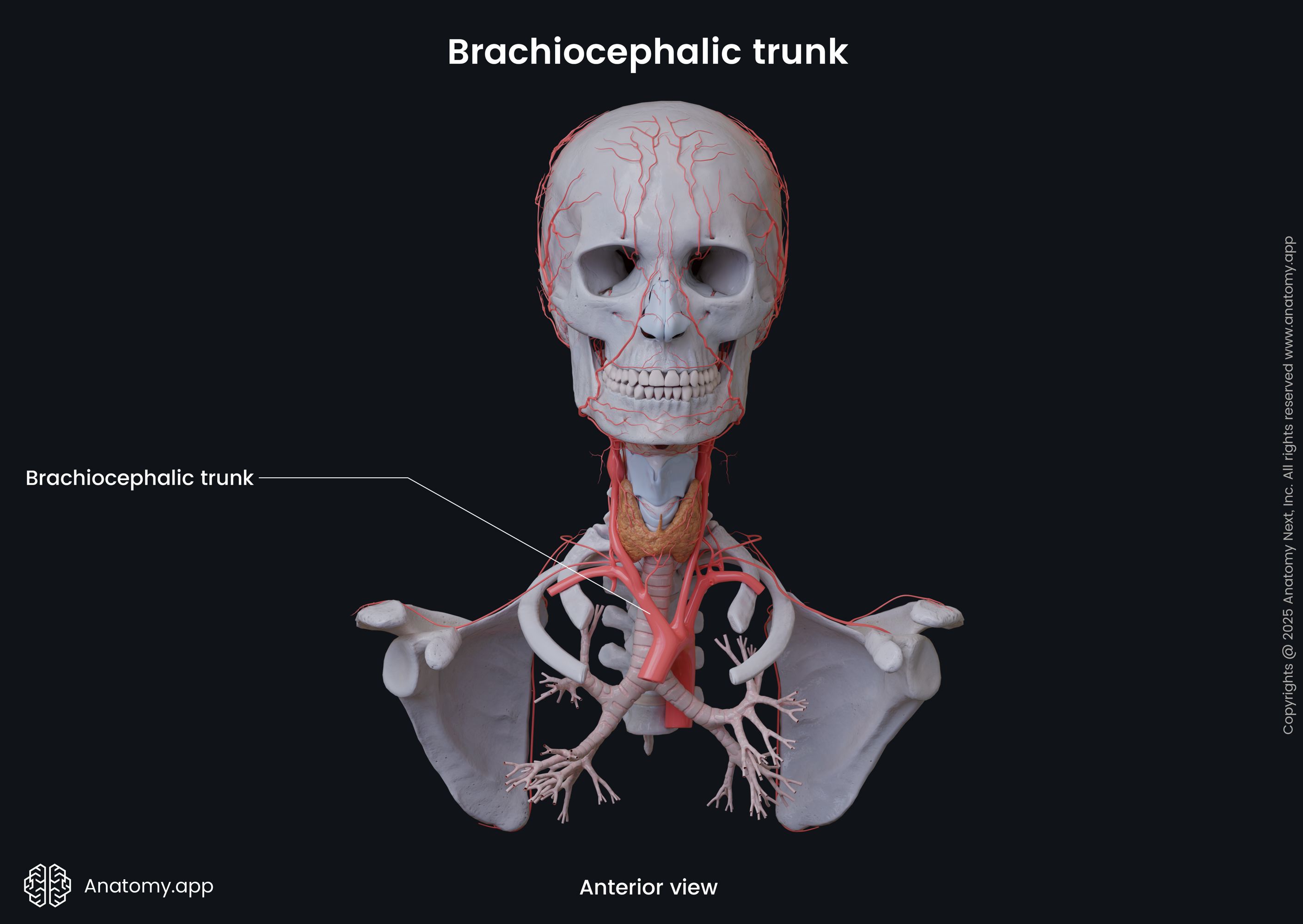
Brachiocephalic trunk course
The brachiocephalic trunk originates from the aortic arch and extends superiorly and posteriorly to the right side. It marks the junction site between the ascending aorta and aortic arch. At first, the brachiocephalic trunk is situated anterior to the trachea. But as it extends further, it reaches the right side of the trachea. The brachiocephalic trunk usually crosses the trachea from left to right at the level of the ninth tracheal ring. However, it has many variations, and it can cross the trachea at any level from the sixth to the thirteenth tracheal ring.
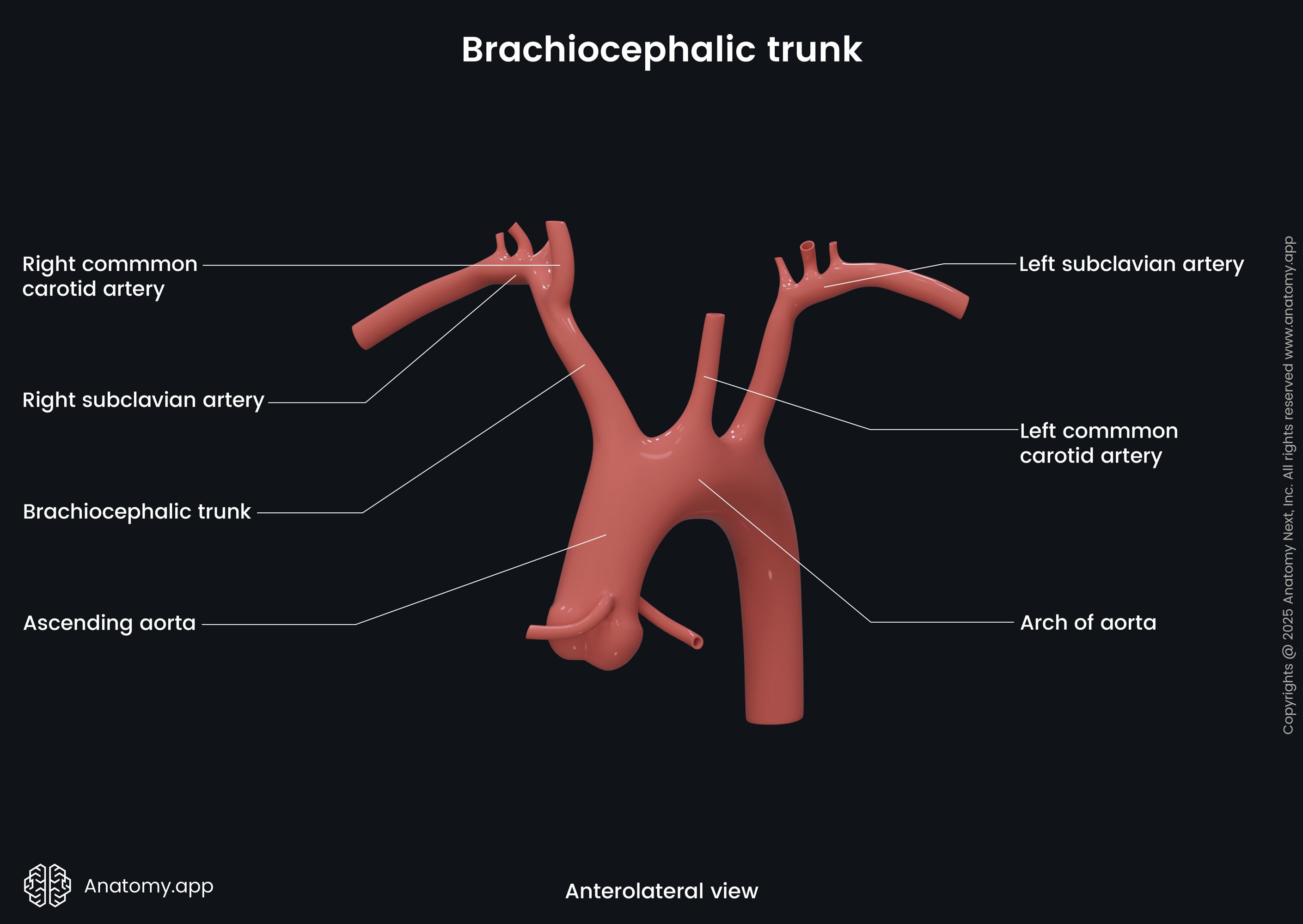
The brachiocephalic trunk terminates at the superior margin of the right sternoclavicular joint, where it divides into two branches - the right common carotid artery and the right subclavian artery. The right common carotid artery bifurcates into the internal and external carotid arteries that supply blood to the right side of the neck and head, including the right side of the brain. The right subclavian artery supplies the right upper extremity, and it also provides arterial blood supply to the head via the right vertebral artery.
Brachiocephalic trunk branches
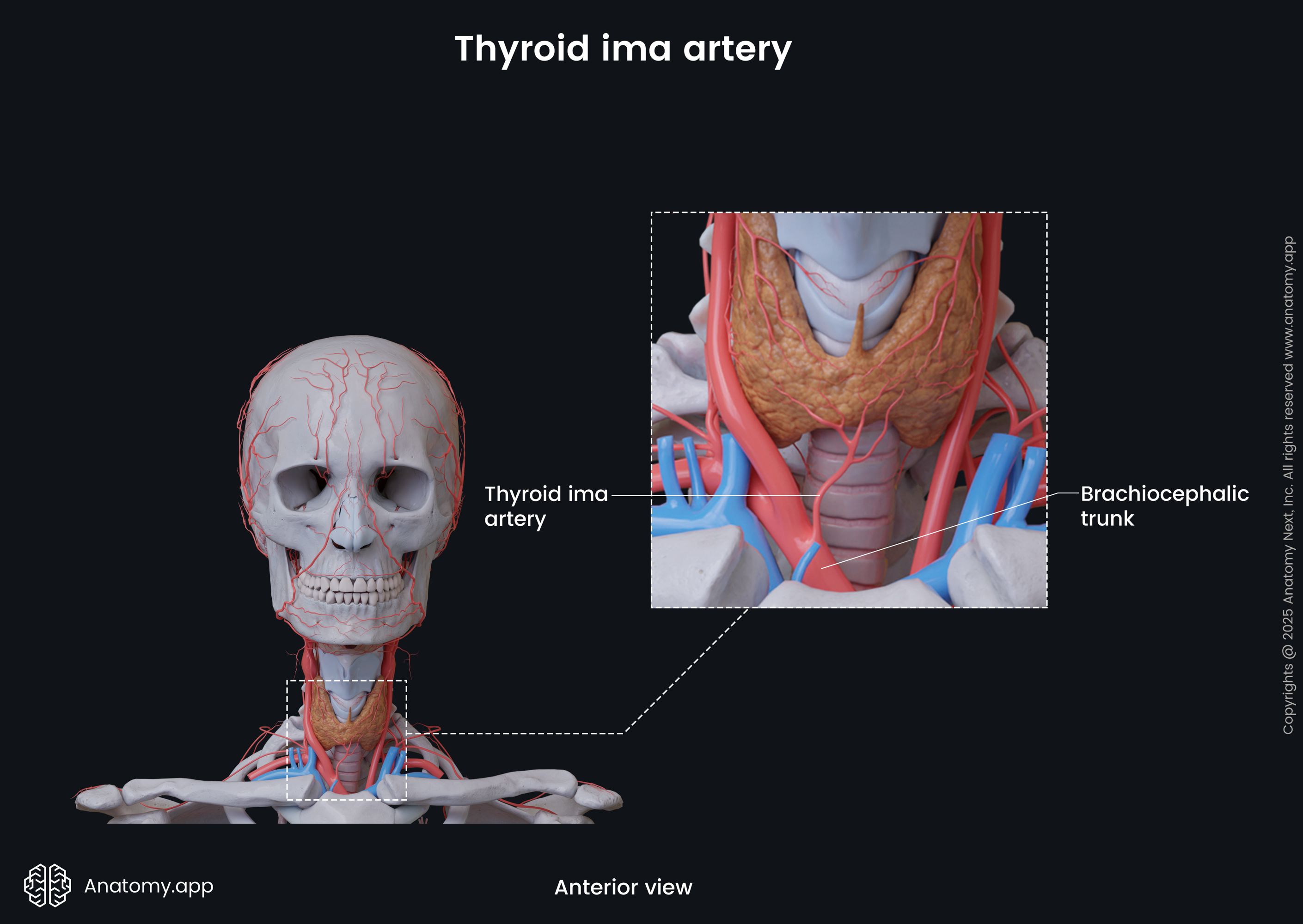
As mentioned previously, the brachiocephalic trunk terminates by dividing into two branches - the right common carotid artery and the right subclavian artery. It does not have any pre-terminal branches. However, sometimes it can give off such arteries as the thymic or bronchial arteries, as well as the thyroid ima artery.
The thyroid ima artery is a small variant artery that is not present in all individuals. Its origin site is quite variable. However, the brachiocephalic artery is its most common origin site. Overall, the thyroid ima artery arises either from the aortic arch, brachiocephalic trunk, right subclavian artery or right common carotid artery. It supplies the isthmus and inferior aspects of the thyroid gland.
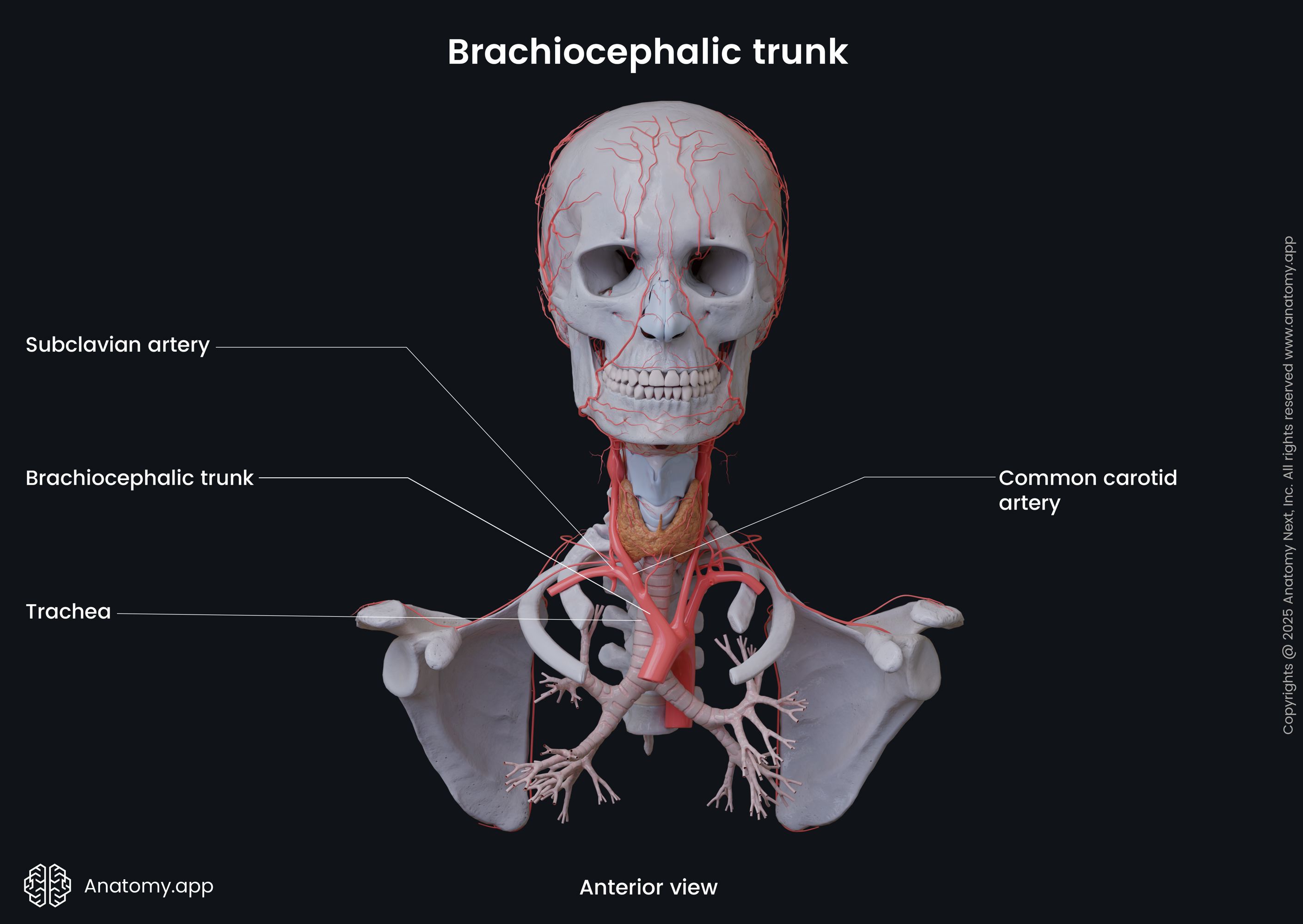
The right subclavian artery exits the superior thoracic aperture of the rib cage and enters the root of the neck. After it has emerged, it is located posterior to the insertion site of the anterior scalene muscle and the sternal end of the clavicle. Then it travels across the superior surface of the first rib and passes below the clavicle. Here, the right subclavian artery is a part of the neurovascular bundle that consists of the subclavian artery, subclavian vein and brachial plexus. The right subclavian artery continues as the right axillary artery at the external border of the first rib.

The right common carotid artery extends upward on the right side of the neck as a part of the neurovascular bundle located within the carotid sheath. The neurovascular structures within the sheath include the common carotid artery, internal jugular vein and vagus nerve (CN X). At the level of the upper border of the thyroid cartilage (junction between C3 - C4 vertebrae), the common carotid artery bifurcates into its terminal branches - internal and external carotid arteries. The right internal carotid artery supplies arterial blood to the right side of the brain. The right external carotid artery provides arterial blood supply to the right side of the head and neck.
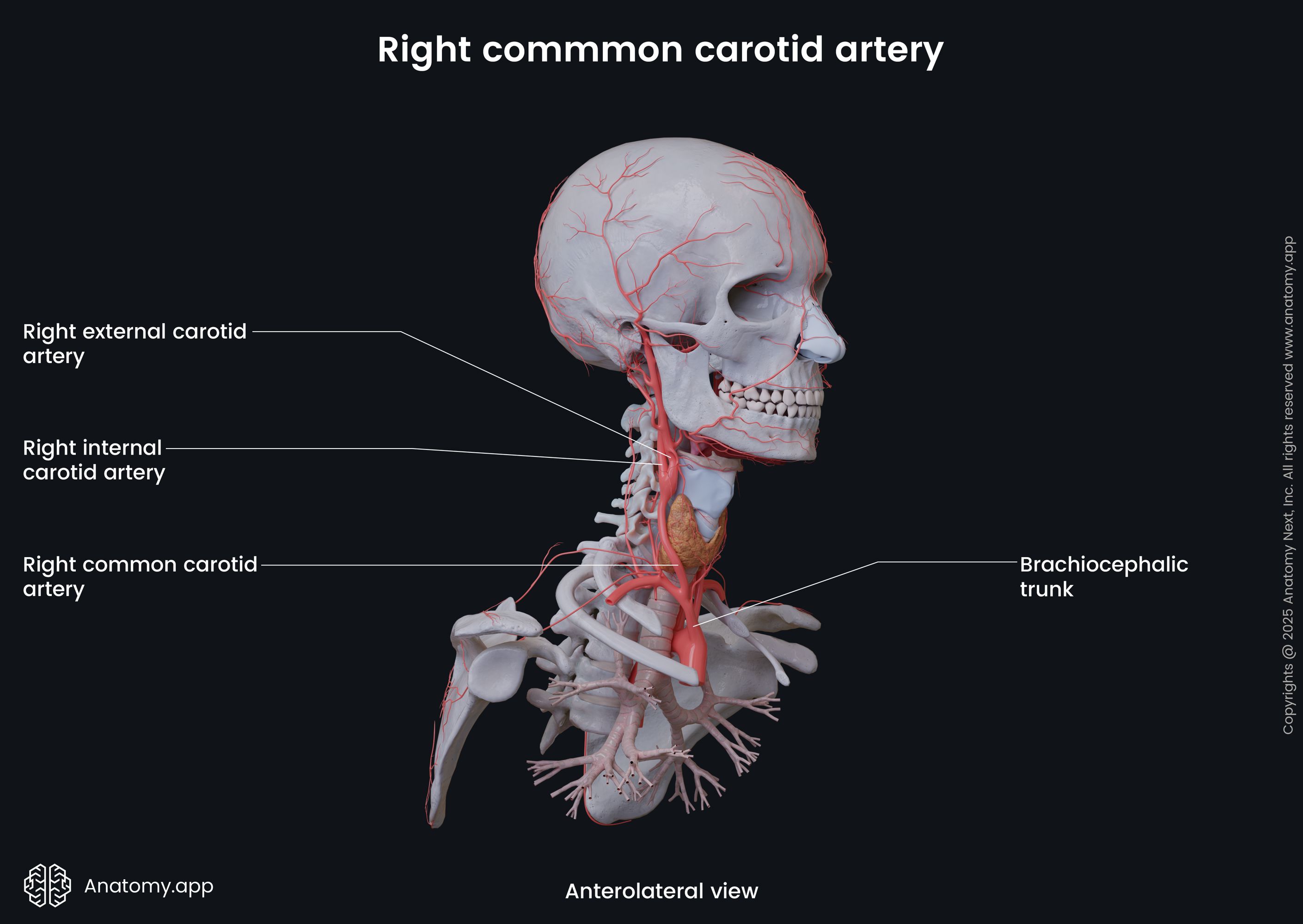
Brachiocephalic trunk relations
Anteriorly, the brachiocephalic trunk relates to the remnants of the thymus, right inferior thyroid veins, left brachiocephalic vein and right cardiac branches of the vagus nerve (CN X). Also, the sternohyoid and sternothyroid muscles are in front of the brachiocephalic trunk. Posteriorly, the brachiocephalic trunk borders with the lower portion of the trachea and the mediastinal part of the right parietal pleura.
On its right side lies the brachiocephalic vein and the upper portion of the superior vena cava. On the left side of the brachiocephalic trunk are the remnants of the thymus, inferior thyroid veins, left common carotid artery and trachea.
The brachiocephalic trunk lies close to the vagus nerve (CN X) and its branch - the right recurrent laryngeal nerve. The vagus nerve passes anterior to the bifurcation of the brachiocephalic trunk. In contrast, the right recurrent laryngeal nerve runs posterior to the bifurcation.
References:
- Dugas, B.A., Samra, N.S. (2021). Anatomy, Thorax, Brachocephalic (Right Innominate) Arteries. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island (FL): Aug 11, 2021.
- Gray, H., & Carter, H. (2021). Gray’s Anatomy (Leatherbound Classics) (Leatherbound Classic Collection) by F.R.S. Henry Gray (2011) Leather Bound (2010th Edition). Barnes & Noble.
- Rahimi, O., Geiger, Z. (2021). Anatomy, Thorax, Subclavian Arteries. StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island (FL): Jul 26, 2021.