- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Aorta
- Blood vessels of head and neck
- Arteries of head and neck
- Veins of head and neck
- Blood vessels of upper limb
- Blood vessels of thorax
- Blood vessels of abdomen
- Blood vessels of pelvis and lower limb
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
Ascending pharyngeal artery
The ascending pharyngeal artery (Latin: arteria pharyngea ascendens) is a small branch of the external carotid artery. The artery with its branches provides arterial blood supply to the pharynx, auditory tube, and the tympanic cavity.
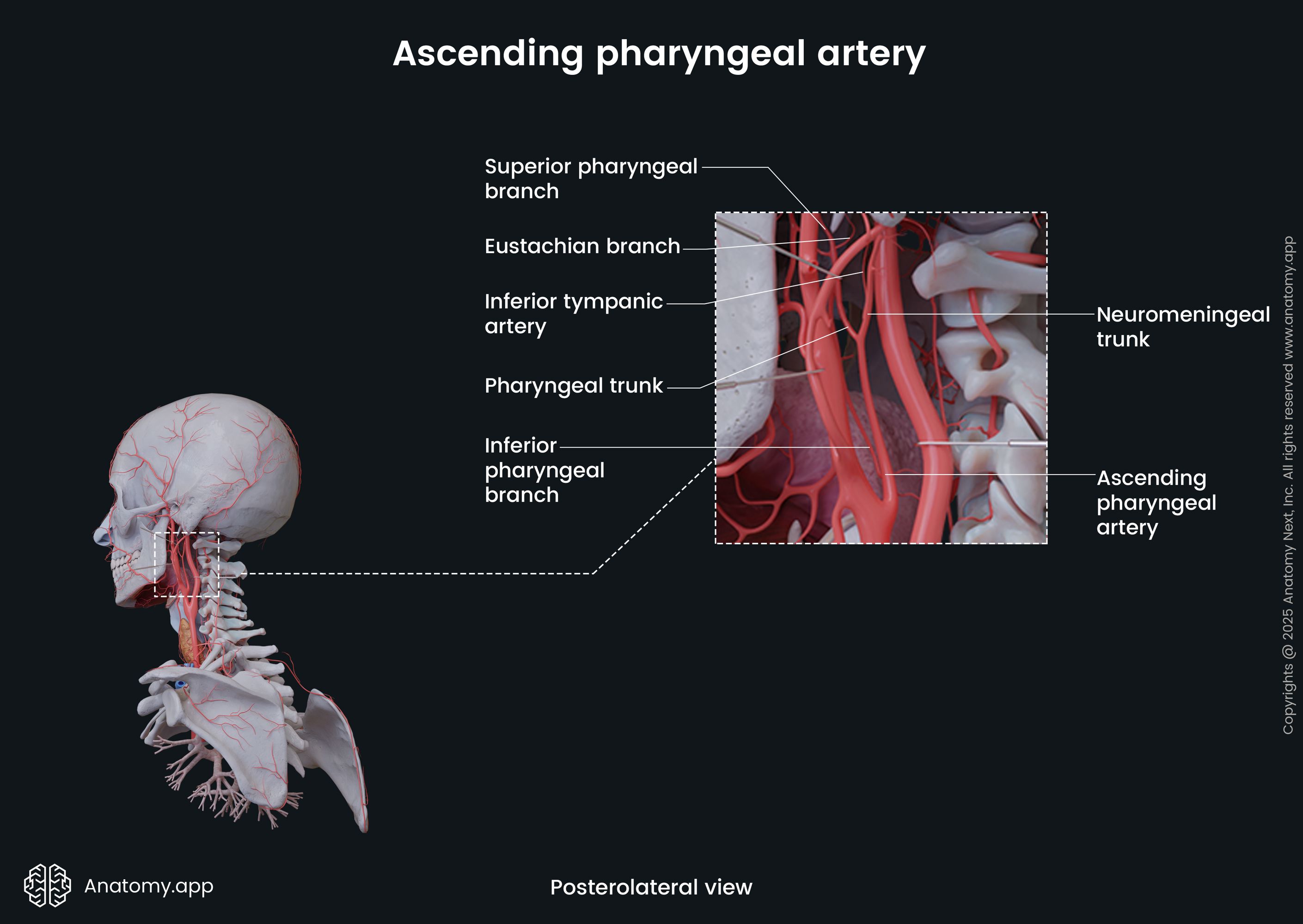
The ascending pharyngeal artery arises near the origin of the external carotid artery. It travels vertically upwards along the lateral side of the pharynx and reaches the base of the skull. Further, the ascending pharyngeal artery continues as the meningeal artery, which is its terminal branch.
On its course, the ascending pharyngeal artery gives rise the following side branches: pharyngeal branches and inferior tympanic artery. The pharyngeal branches supply muscles and mucosa of the pharynx, as well as the pharyngotympanic (auditory) tube. The inferior tympanic artery enters the tympanic cavity through the tympanic canaliculus and supplies the medial wall of the cavity.