- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Classification of joints
- Joints of skull
- Joints of spine
- Joints of lower limb
- Joints of pelvis
- Hip joint
- Knee joint
- Tibiofibular joints
- Joints of foot
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
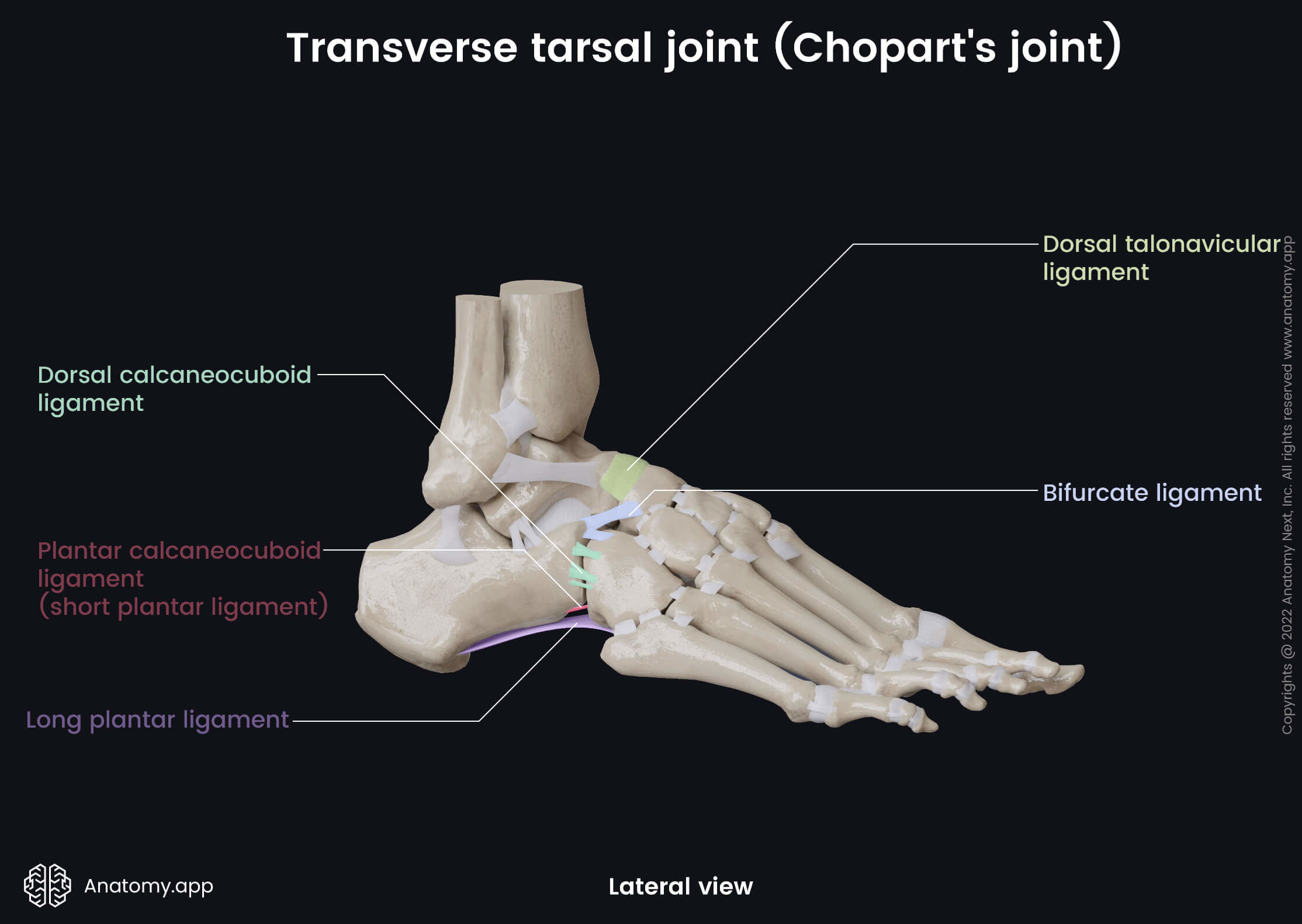
Transverse tarsal joint (Chopart's joint)
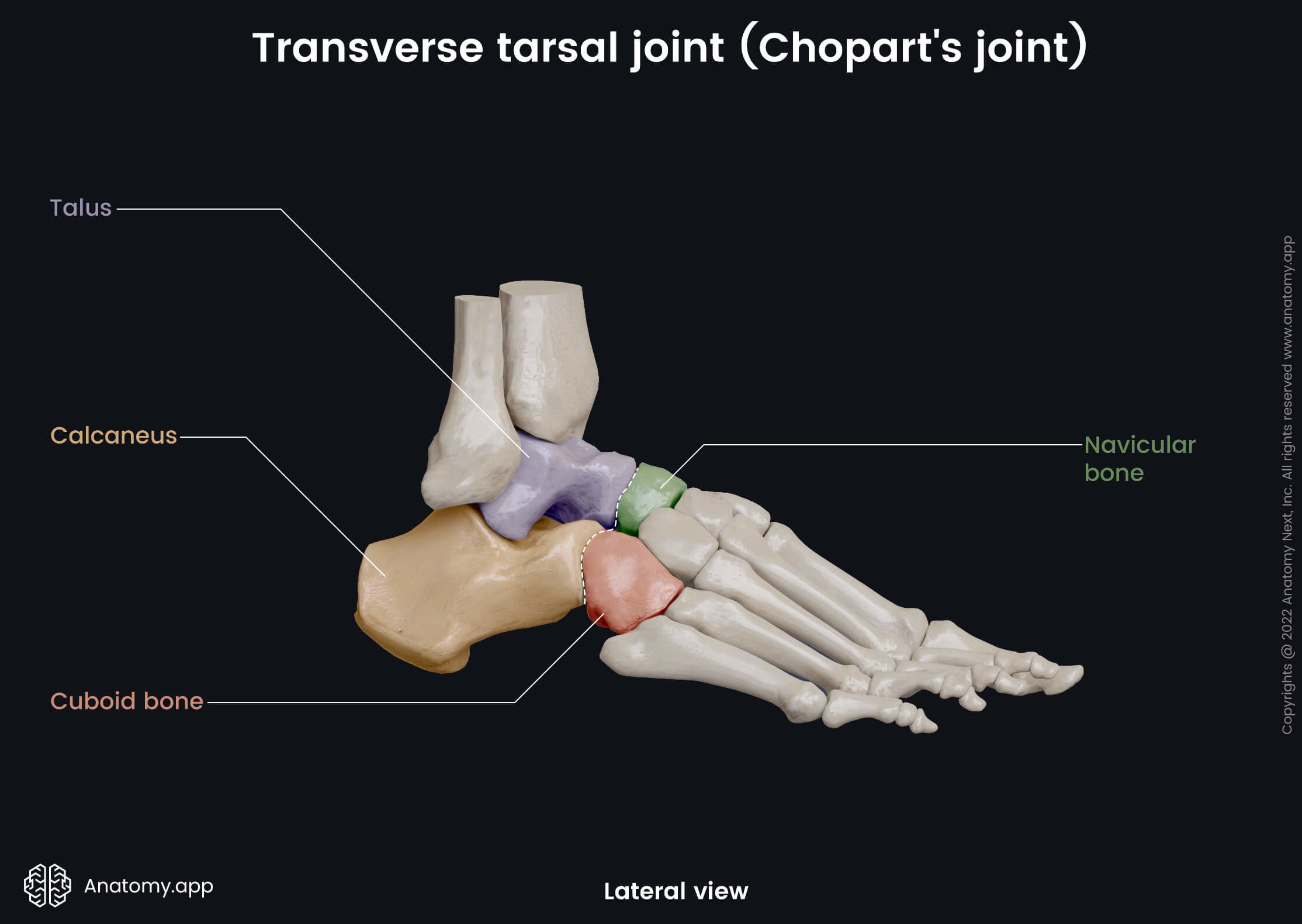
The transverse tarsal joint (Latin: articulatio tarsi transversa) is a compound intertarsal synovial joint located between the tarsal bones of the foot. It is also known as the Chopart's joint or articulation and the midtarsal joint. This articulation is formed by two smaller joints - the talonavicular and calcaneocuboid joints. Both joints are classified as saddle type multiaxial articulations.
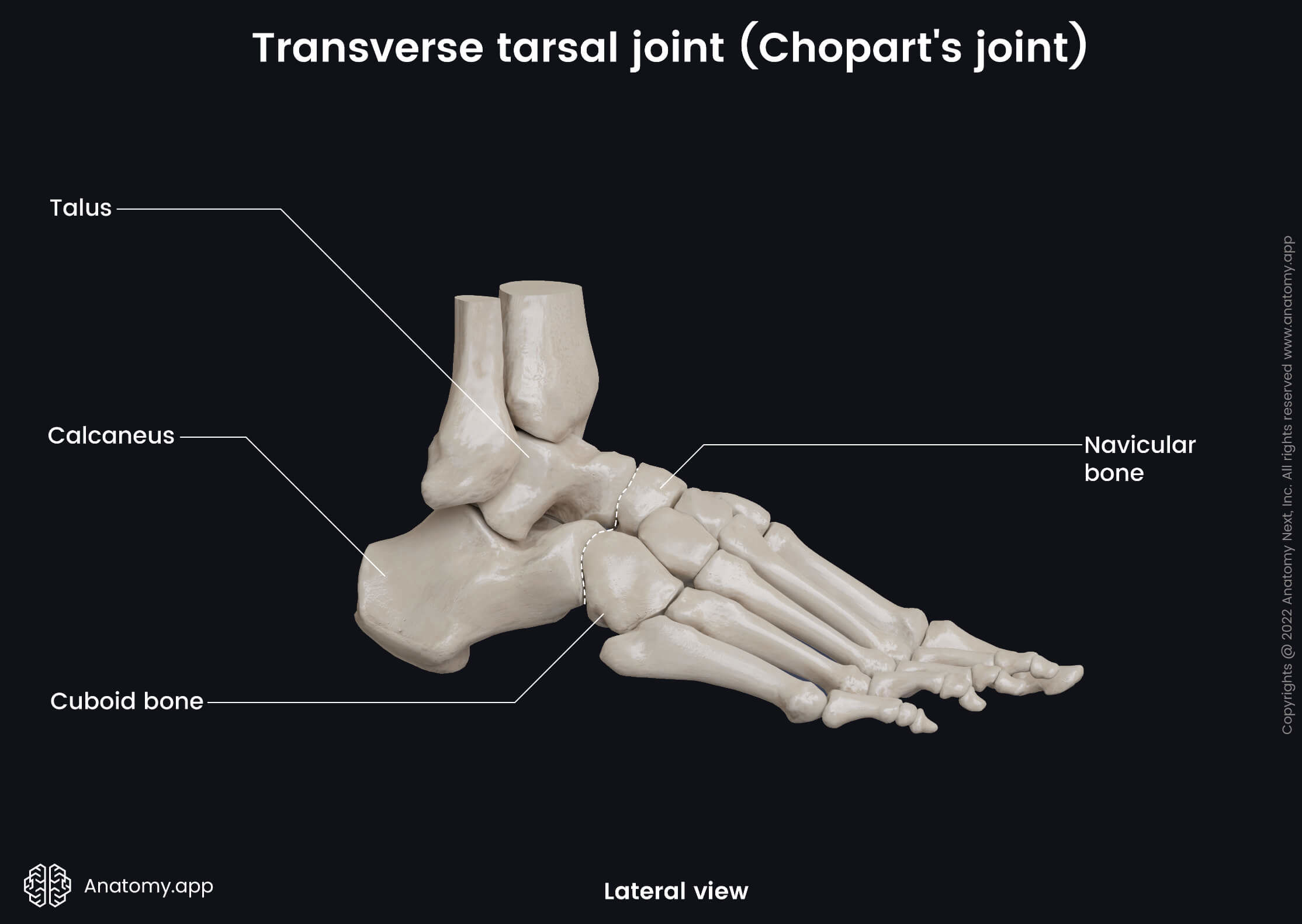
The talonavicular joint is formed between the talus and the navicular bone, while the calcaneocuboid joint is located between the calcaneus and the cuboid bone. The transverse tarsal joint is also known as the surgical joint named after the French surgeon Francois Chopart. He was the first surgeon who described one of the sites where foot amputation can be done.
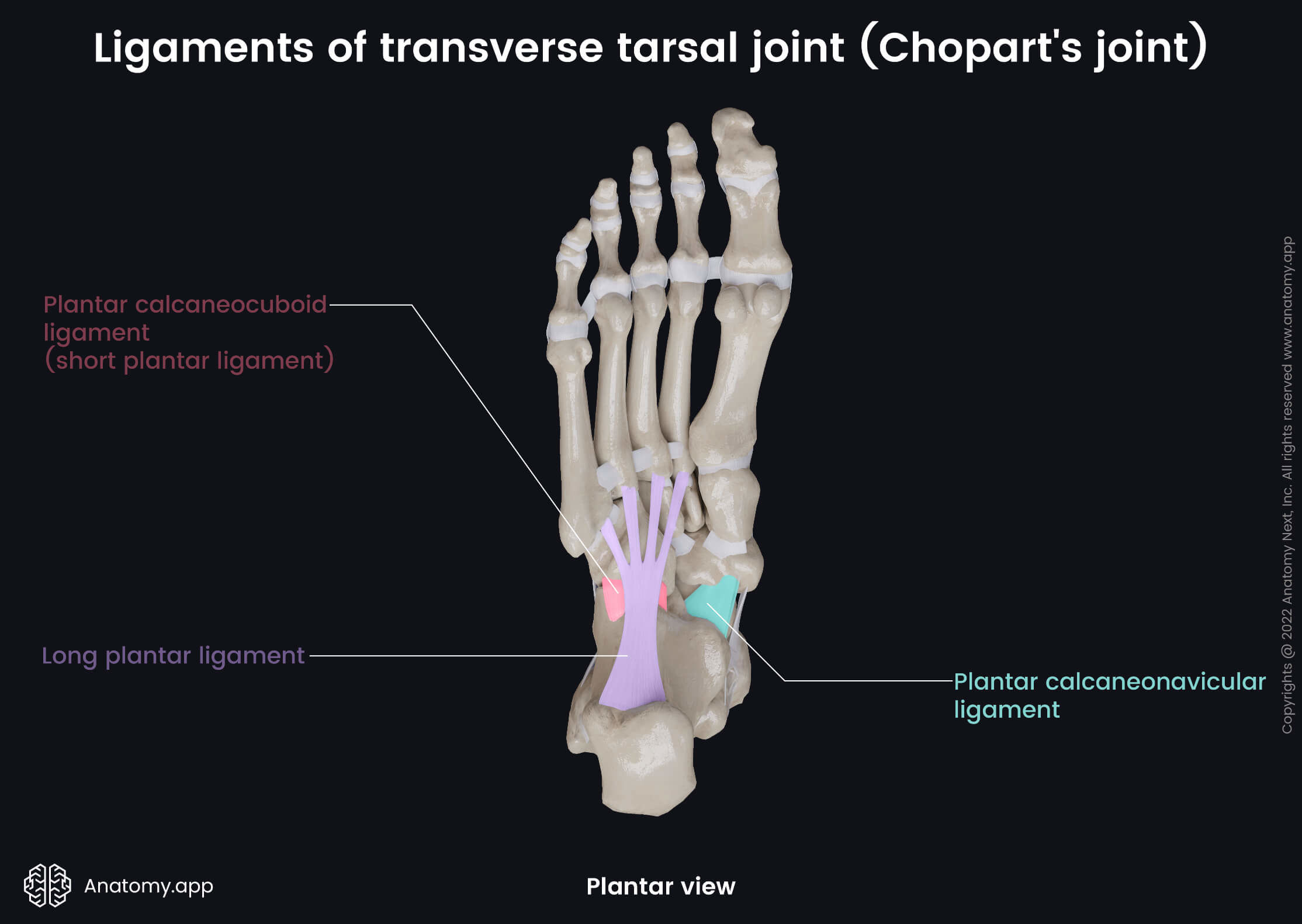
Ligaments of transverse tarsal joint
The Chopart's joint is strengthened by the following ligaments:
- Bifurcate ligament
- Plantar calcaneonavicular ligament
- Dorsal talonavicular ligament
- Plantar calcaneocuboid ligament (short plantar ligament)
- Dorsal calcaneocuboid ligament
- Long plantar ligament