- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Classification of joints
- Joints of skull
- Joints of spine
- Joints of lower limb
- Joints of pelvis
- Hip joint
- Knee joint
- Tibiofibular joints
- Joints of foot
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
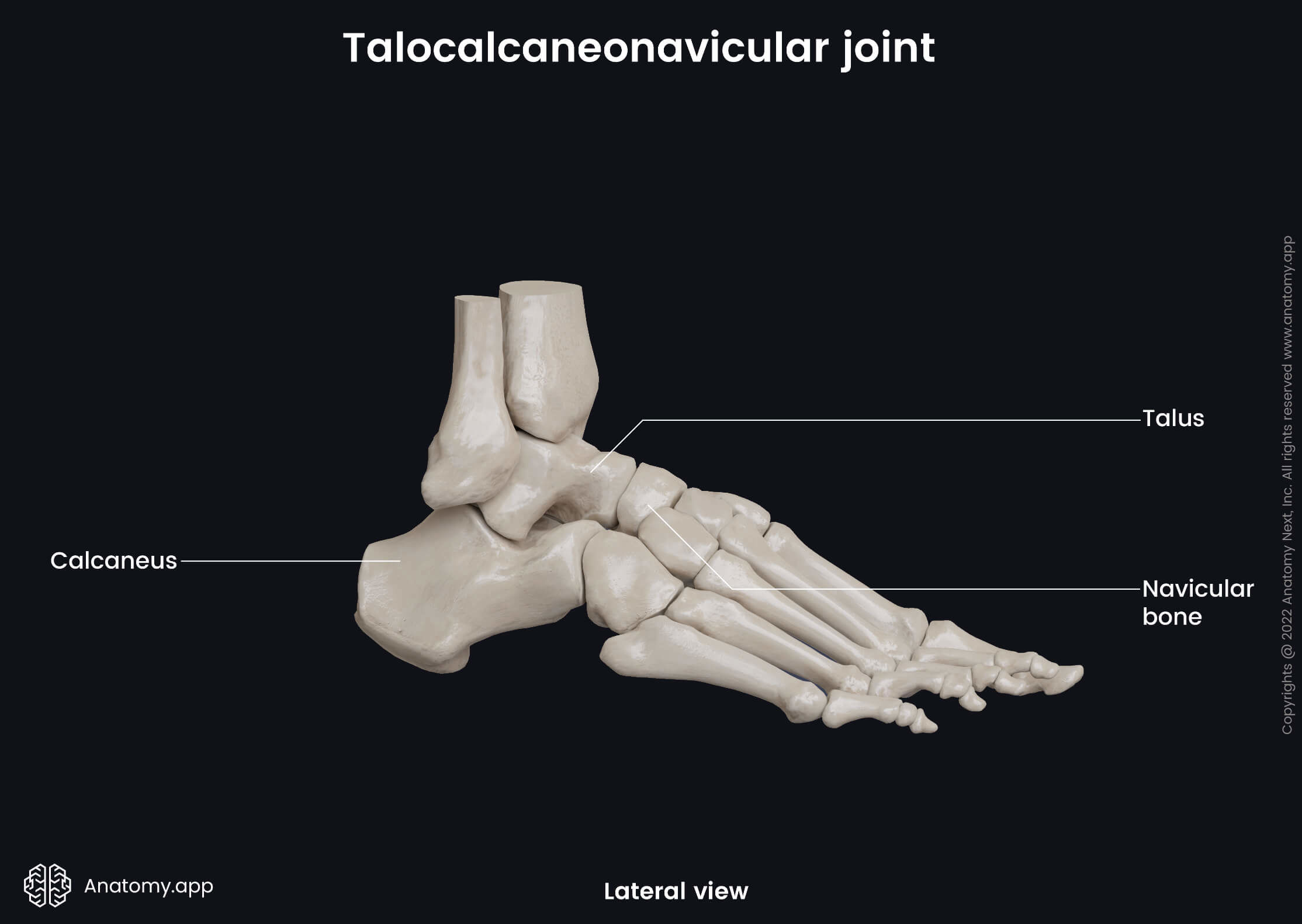
Talocalcaneonavicular joint
The talocalcaneonavicular joint (Latin: articulatio talocalcaneonavicularis) is a synovial joint located in the foot. It is formed between the tarsal bones of the foot - talus, navicular bone and calcaneus. This joint is classified as the intertarsal ball and socket type articulation.
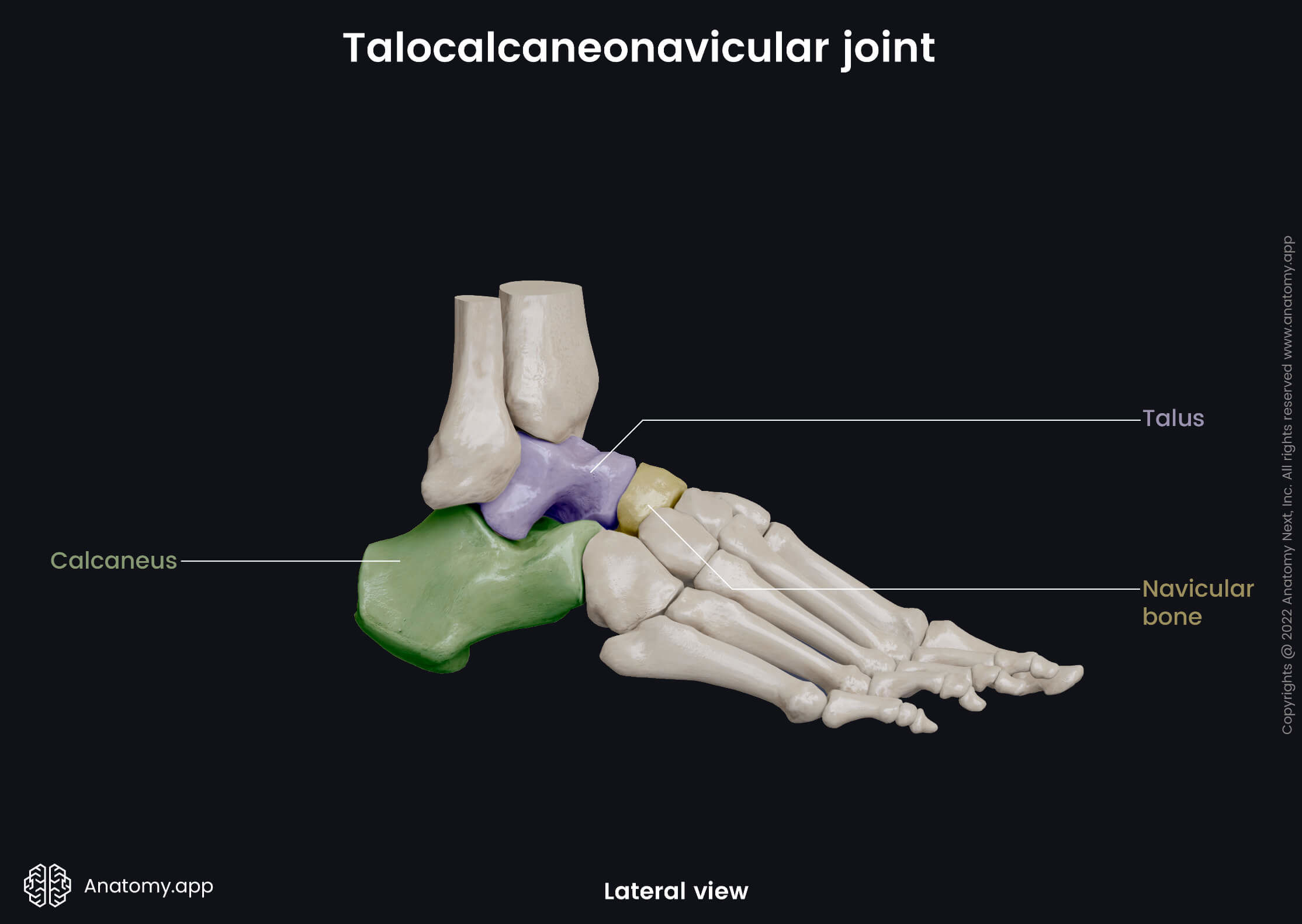
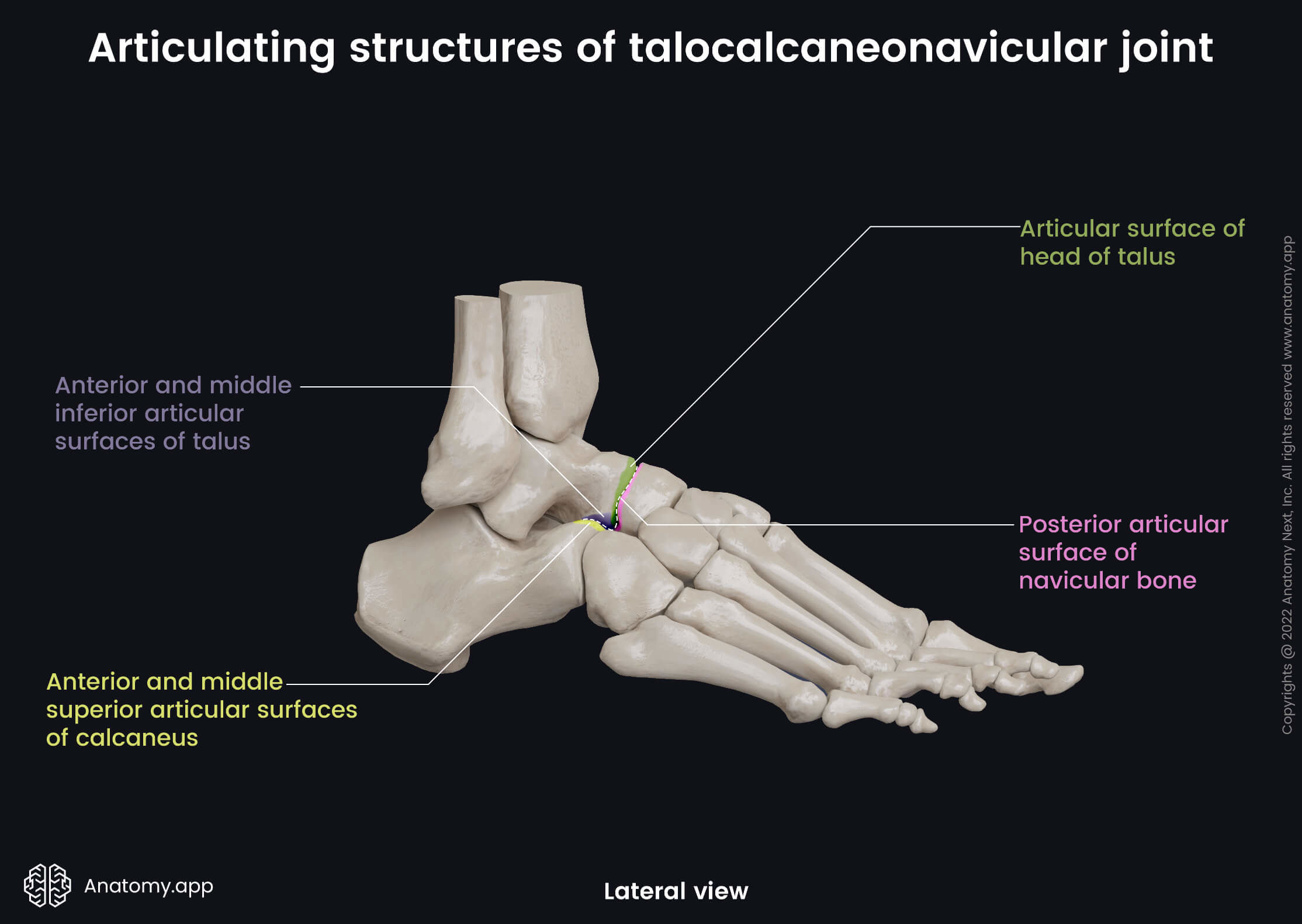
Articulating structures of talocalcaneonavicular joint
The structures that articulate in the talocalcaneonavicular joint include the following:
- Anterior and middle inferior articular surfaces of the talus
- Anterior and middle superior articular surfaces of the calcaneus
- Articular surface of the head of the talus
- Posterior articular surface of the navicular bone
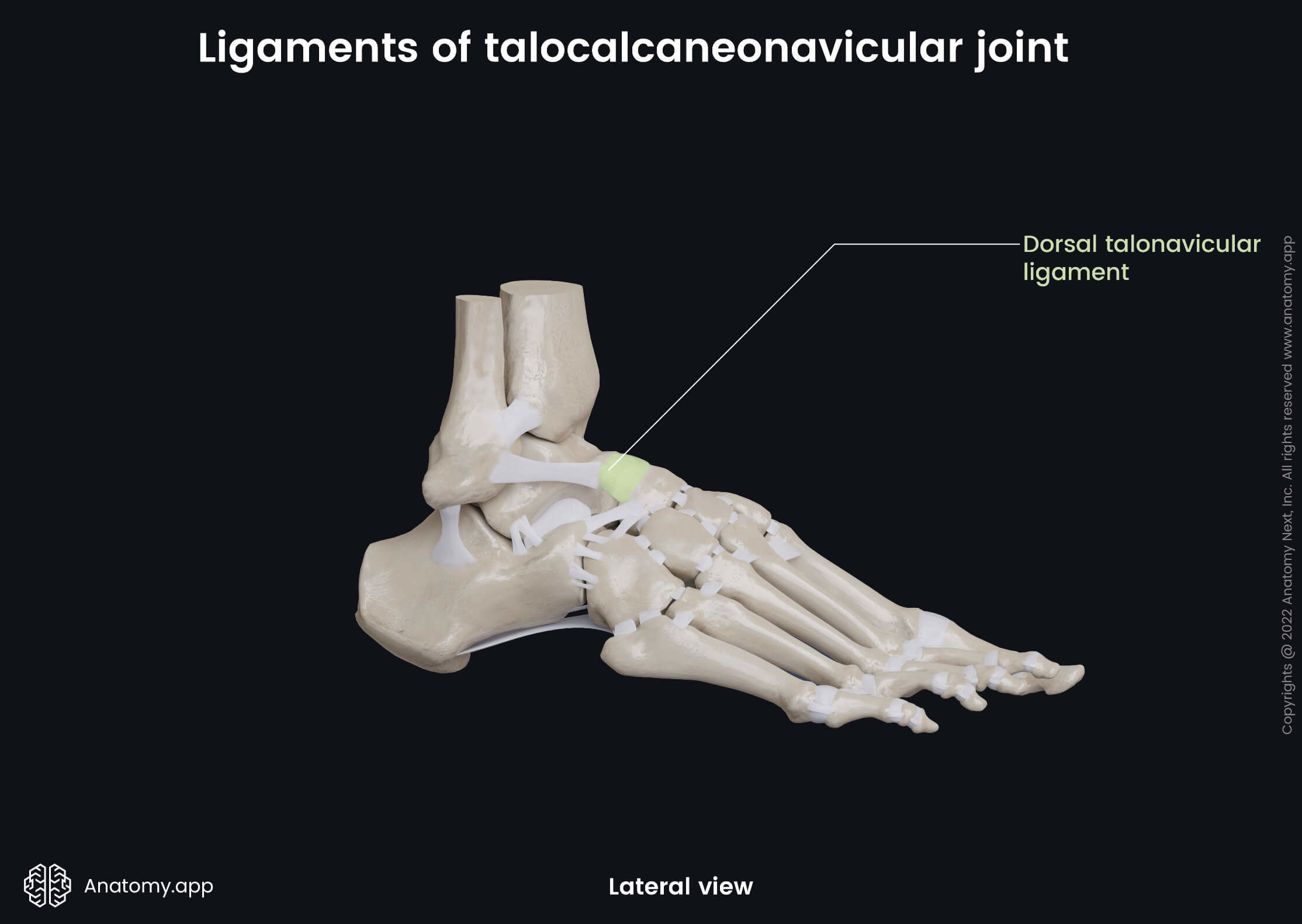
Joint capsule and ligaments
The bones of the talocalcaneonavicular joint are surrounded by a fibrous joint capsule that is attached to the sides of the articular surfaces. And this joint is reinforced by the following ligaments:
- Dorsal talonavicular ligament - stretches between the dorsal surfaces of the neck of the talus and navicular bone;
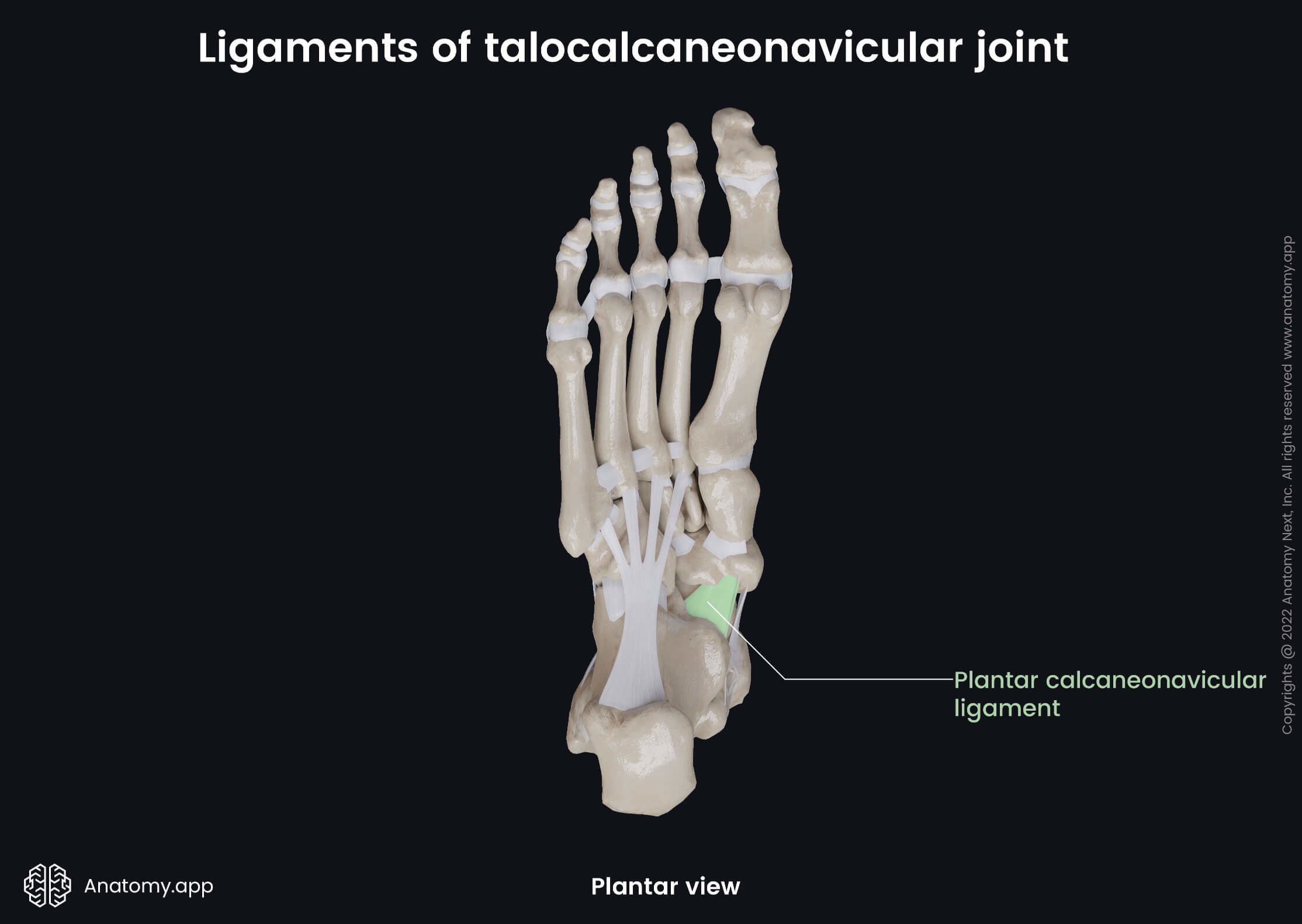
- Plantar calcaneonavicular ligament - extends between the anterior margin of the sustentaculum tali (of the calcaneus) and the plantar surface of the navicular bone;
- Interosseous talocalcaneal ligament - located in the tarsal sinus; stretches from the talus to the calcaneus.
Movements of talocalcaneonavicular joint
The movements of this joint happen simultaneously with the motions provided by the subtalar joint. This articulation permits the following movements:
- Supination and adduction of the foot
- Pronation and abduction of the foot