- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Classification of joints
- Joints of skull
- Joints of spine
- Joints of lower limb
- Joints of pelvis
- Hip joint
- Knee joint
- Tibiofibular joints
- Joints of foot
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
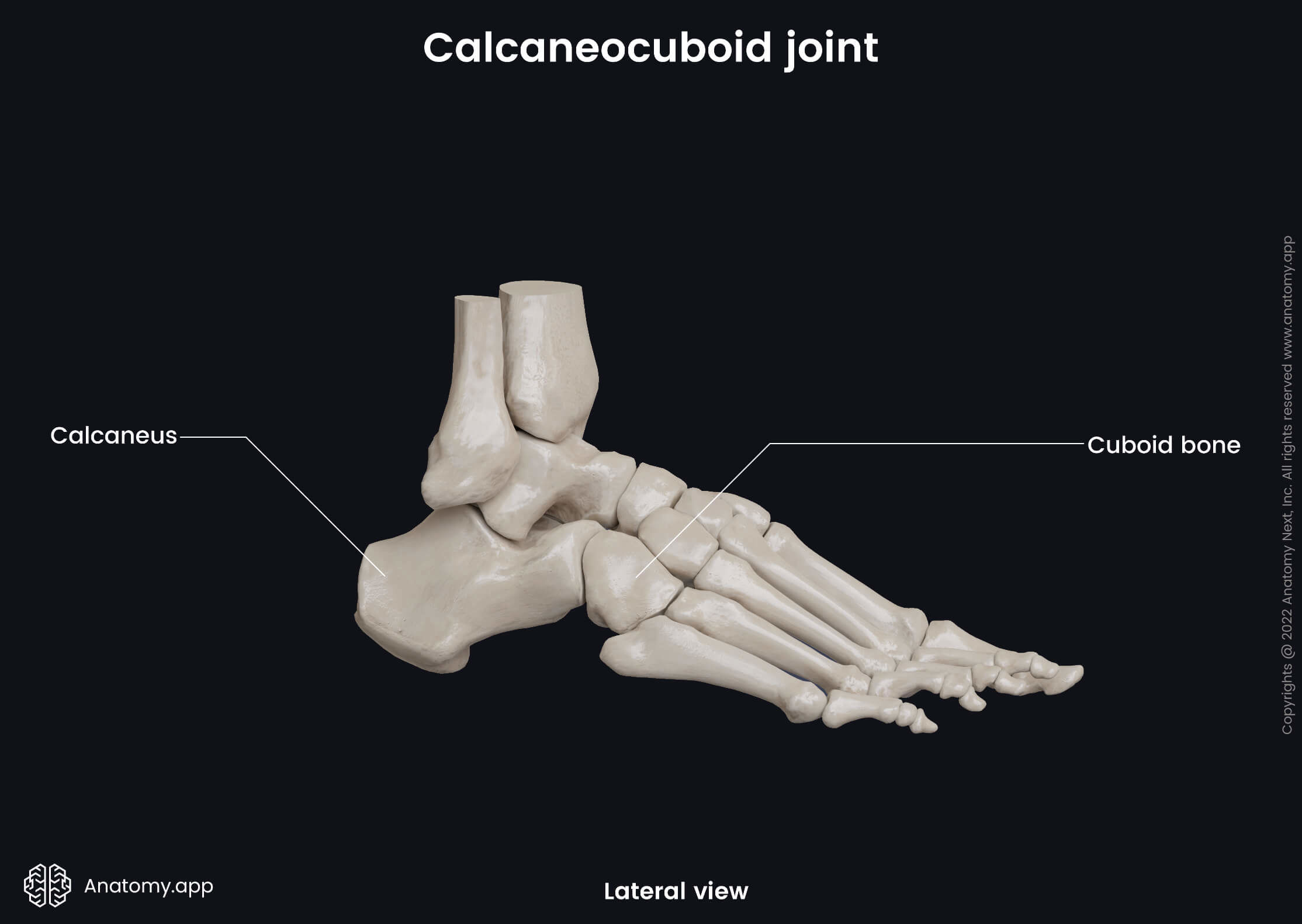
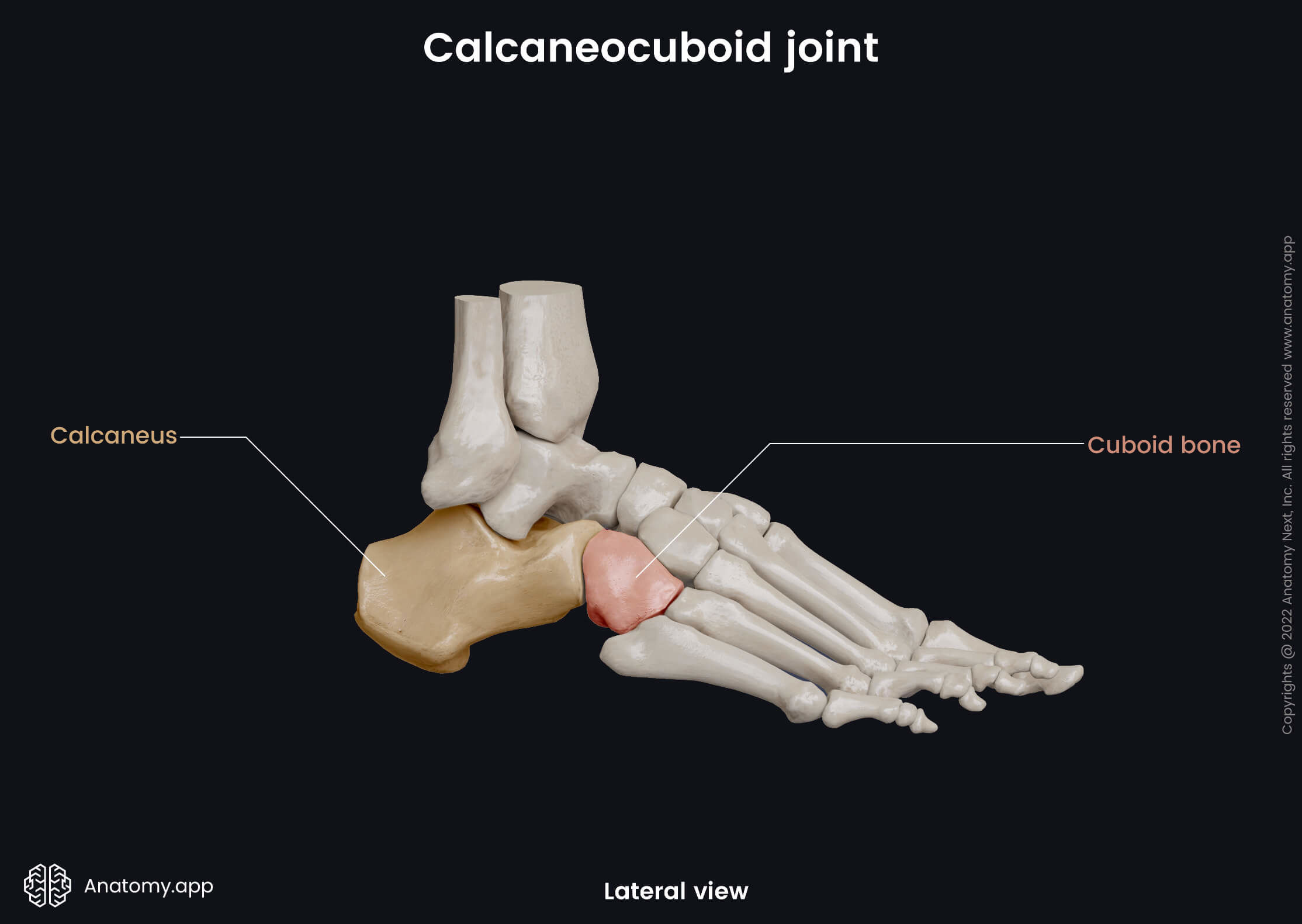
Calcaneocuboid joint
The calcaneocuboid joint (Latin: articulatio calcaneocuboidea) is a synovial saddle type articulation between the tarsal bones of the foot. This joint is located between the calcaneus and cuboid bone.
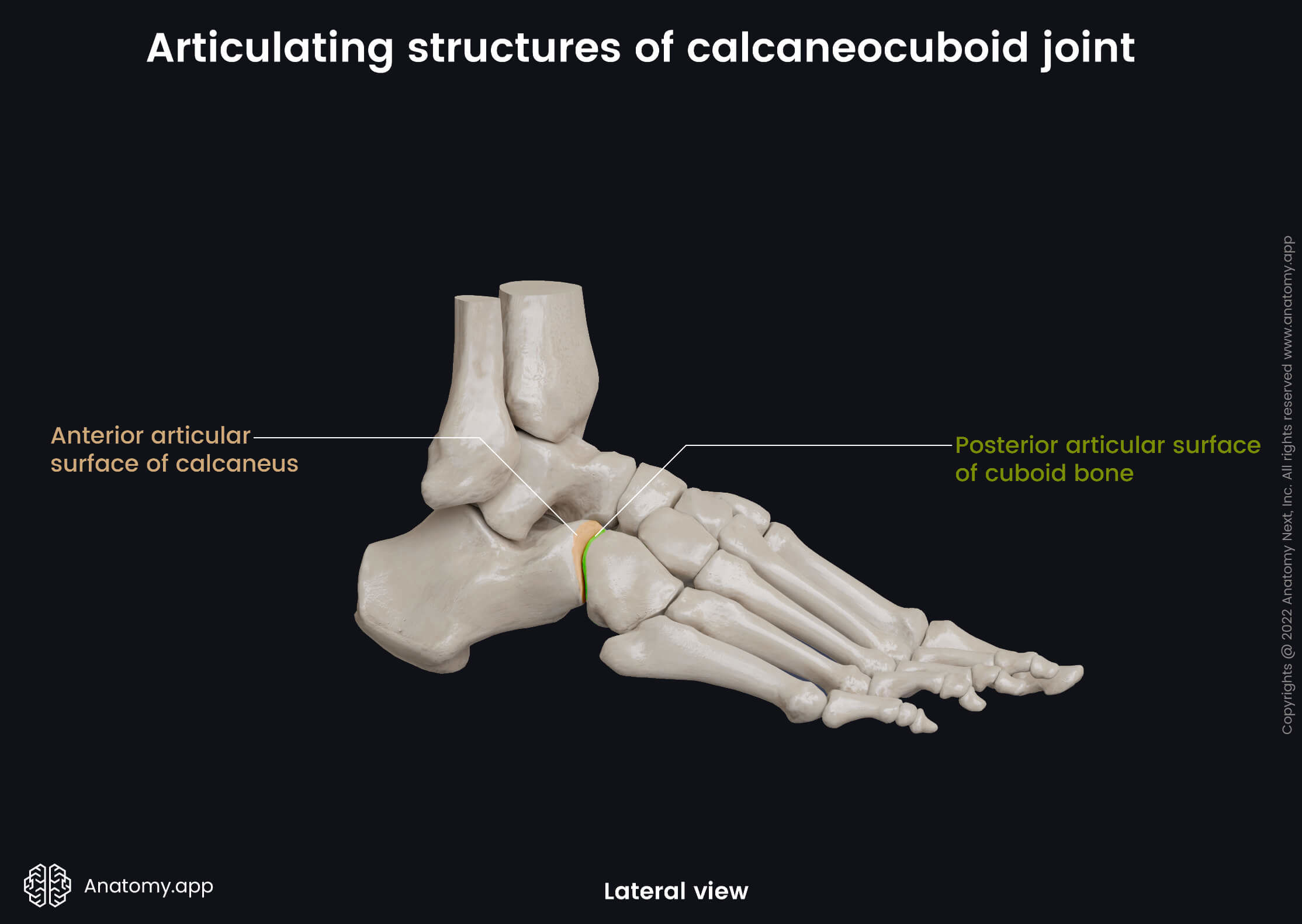
Articulating structures of calcaneocuboid joint
The articular surfaces of the calcaneocuboid joint include the following:
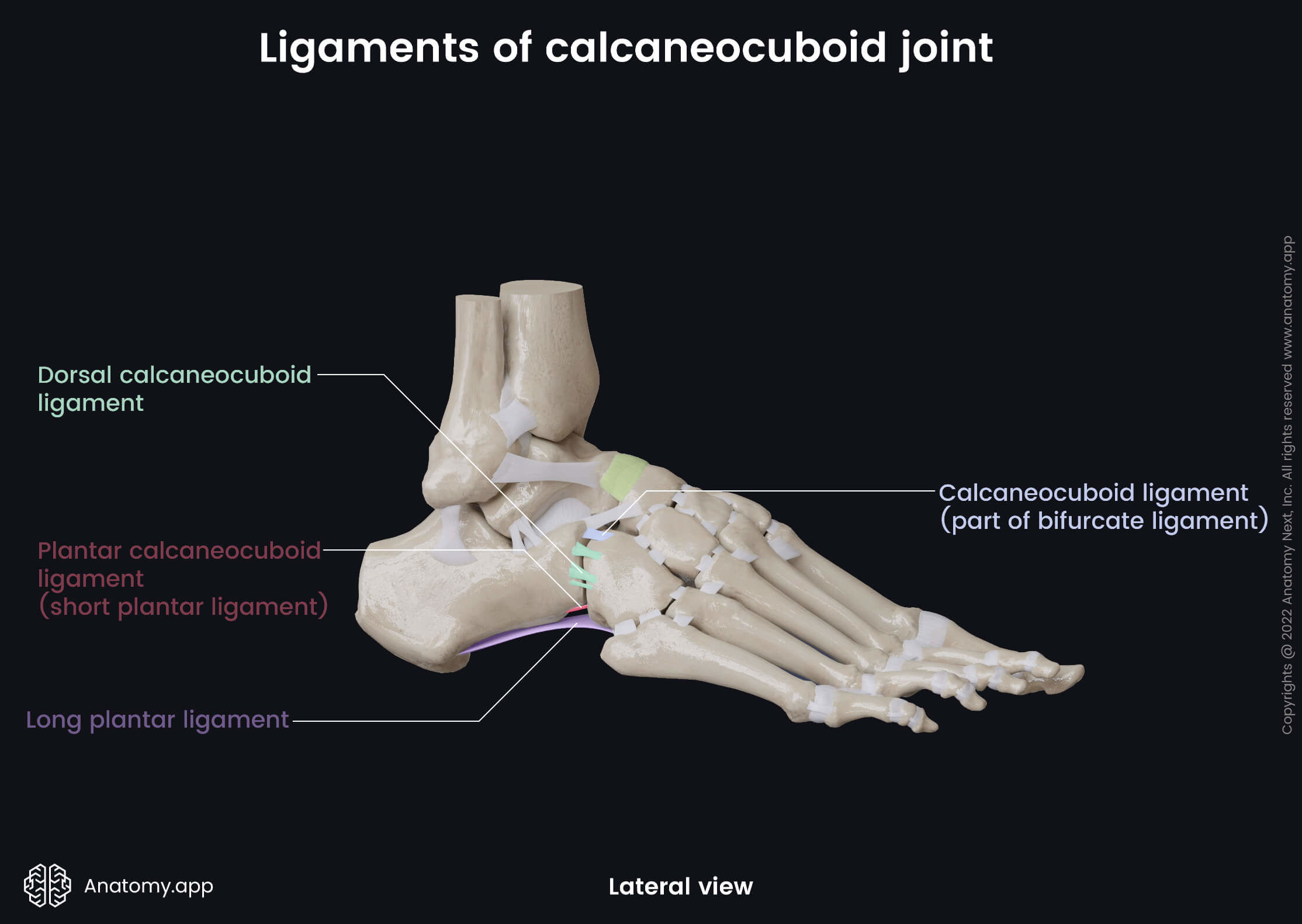
Joint capsule and ligaments
The calcaneocuboid joint is embraced by a fibrous joint capsule that posteriorly is thickened as the dorsal calcaneocuboid ligament. This joint is strengthened by three following ligaments:
- Calcaneocuboid part of the bifurcate ligament - bifurcate ligament is a strong Y-shaped band that is attached to the calcaneus and distally divides into calcaneocuboid and calcaneonavicular parts; the calcaneocuboid part attaches to the cuboid bone;
- Dorsal calcaneocuboid ligament - attaches to the calcaneus; located lateral to the bifurcate ligament, and extends to the dorsolateral side of the cuboid bone;
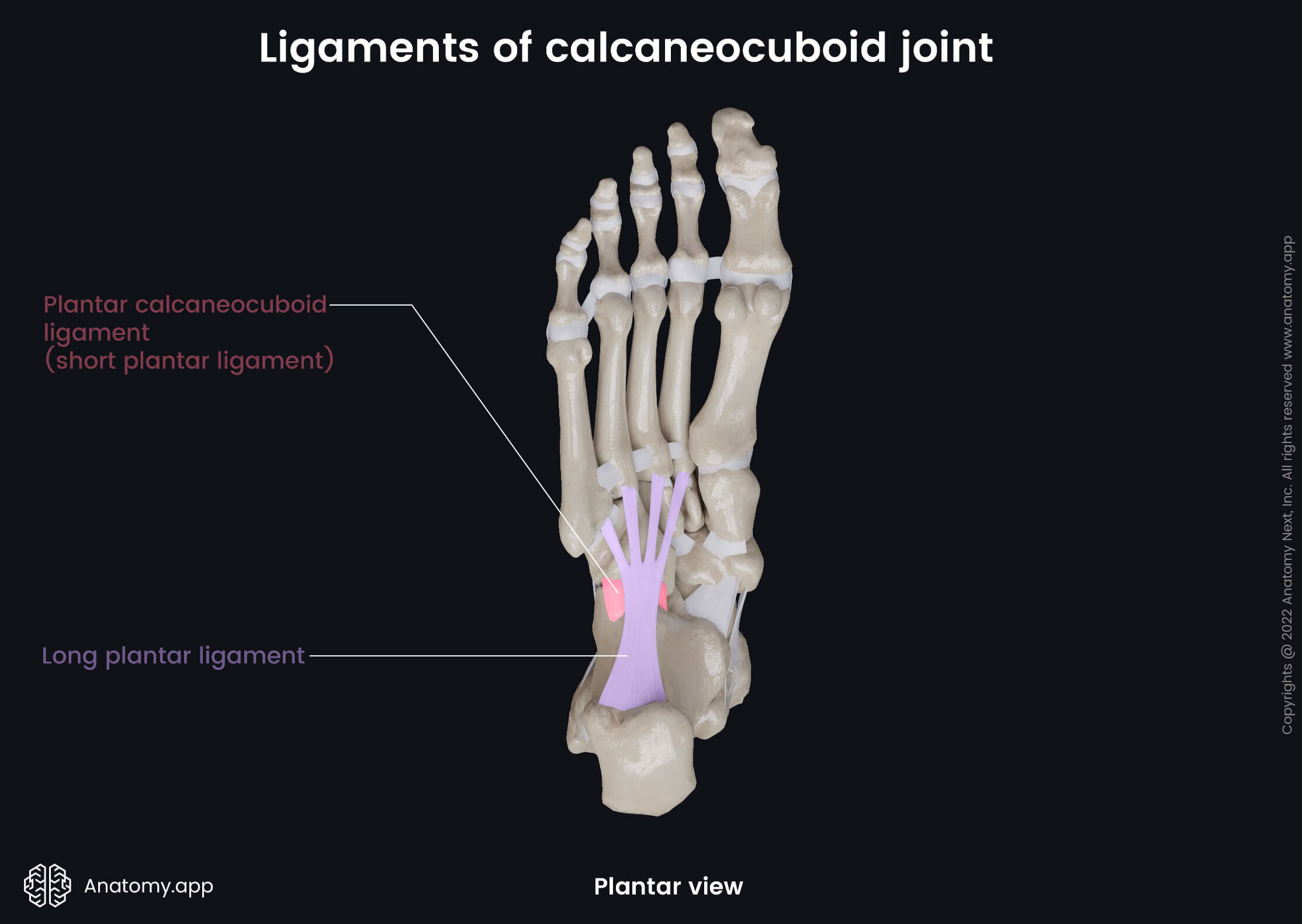
- Long plantar ligament - the longest ligament of the foot; it is attached to the calcaneus and extends to the plantar surface of the second to fifth metatarsal bones;
- Plantar calcaneocuboid ligament (short plantar ligament) - a short, wide band that extends from the anterior calcaneal tubercle to the plantar surface of the cuboid bone.
Movements of calcaneocuboid joint
The calcaneocuboid joint allows only limited and small amplitude movements. They include the gliding and rotational motions between the calcaneus and cuboid bone.