- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Head muscles
- Neck muscles
- Muscles of upper limb
- Thoracic muscles
- Muscles of back
- Muscles of lower limb
- Pelvic muscles
- Muscles of thigh
- Muscles of leg
- Anterior compartment
- Lateral compartment
- Posterior compartment
- Superficial layer
- Deep layer
- Muscles of foot
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
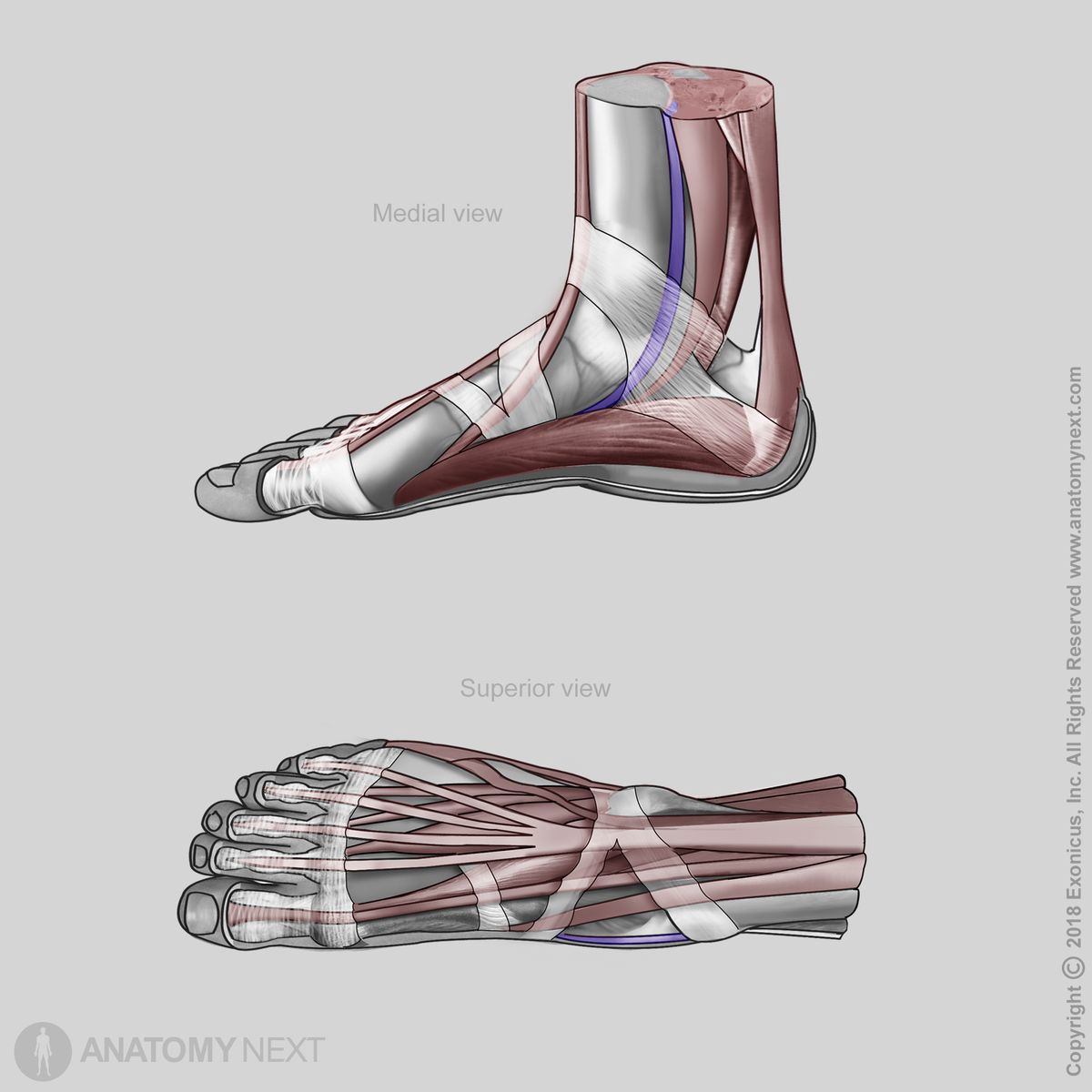
Tibialis posterior
The tibialis posterior (Latin: musculus tibialis posterior) is a long, relatively thin leg muscle. It is the deepest muscle of the posterior compartment of the leg. The tibialis posterior is situated most centrally of all leg muscles and is also the strongest among the posterior compartment muscles. The deep group of the posterior compartment of leg muscles also includes the popliteus, flexor digitorum longus and flexor hallucis longus muscles.
| Tibialis posterior | |
| Origin | Posterior surface of tibia, posterior surface of fibula, interosseous membrane of leg |
| Insertion | Tuberosity of navicular bone, cuboid bone, cuneiform bones, bases of metatarsal bones 2-4, sustentaculum tali of calcaneus |
| Action | Foot plantarflexion, foot inversion, supports medial longitudinal arch of foot |
| Innervation | Tibial nerve (L4 - L5) |
| Blood supply | Branches of posterior tibial artery, peroneal (fibular) artery |
Origin
The tibialis posterior muscle originates from the upper half of the posterior surfaces of the tibia and fibula. Also, it arises from the interosseous membrane of the leg.
Insertion
The tibialis posterior inserts on the tuberosity of the navicular bone, cuboid bone, all cuneiform bones, bases of the second to fourth metatarsal bones and sustentaculum tali of the calcaneus.
Action
The tibialis posterior muscle provides foot plantarflexion at the talocrural (ankle) joint and foot inversion at the subtalar and midtarsal joints. It also supports the medial longitudinal arch of the foot.
Innervation
The tibialis posterior is innervated by the tibial nerve (L4 - L5) - a branch of the sciatic nerve.
Blood supply
The tibialis posterior receives arterial blood supply from the branches of the posterior tibial artery, mainly from the peroneal (fibular) artery.