- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Skeleton of trunk
- Skull
- Skeleton of upper limb
- Skeleton of lower limb
- Joints
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
Nasal bone
The nasal bone (Latin: os nasale) is a paired bone forming the anterior wall of the nasal cavity and is largely responsible for the shape of the nose.
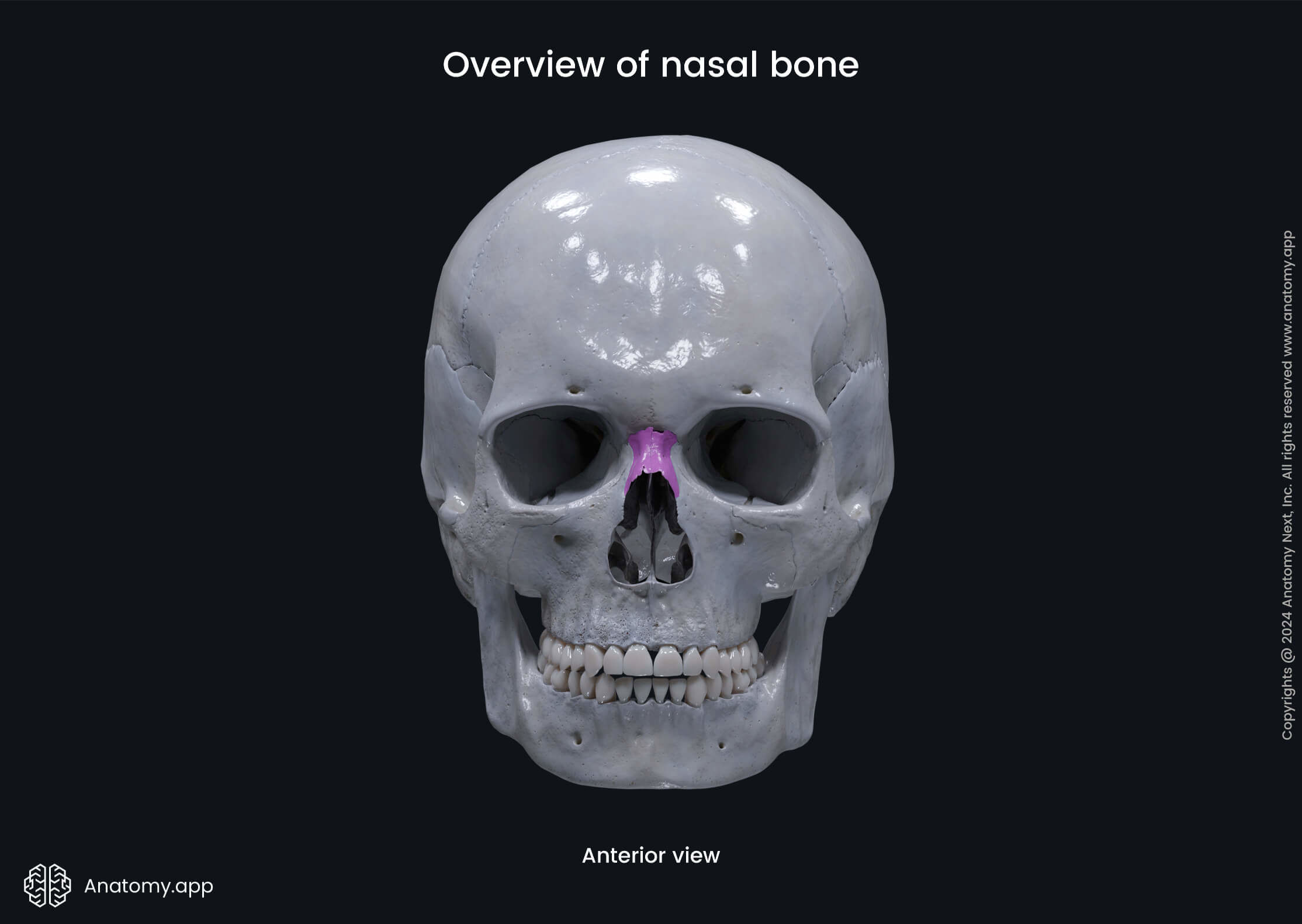
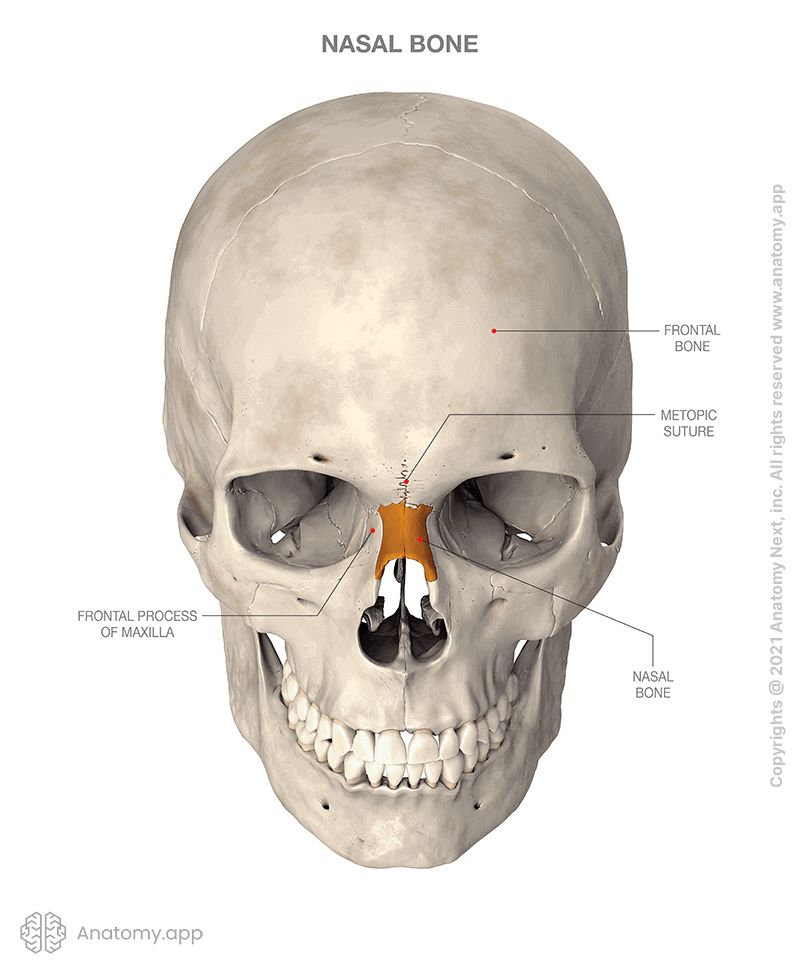
The nasal bone articulates with four bones. Two of them are bones of the neurocranium - the frontal bone and ethmoid bone, and two are bones of the viscerocranium - the opposite nasal bone and the maxilla.
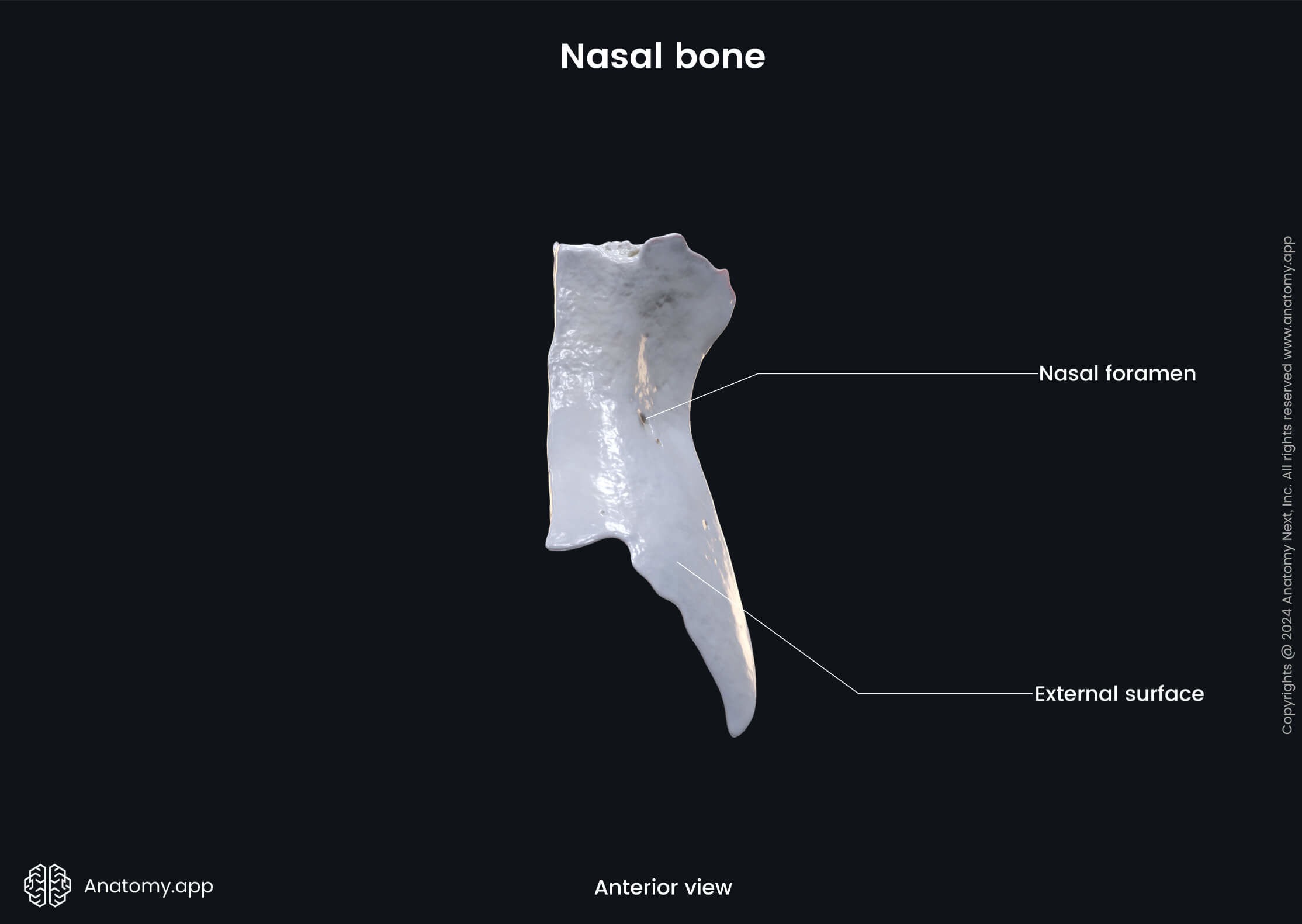
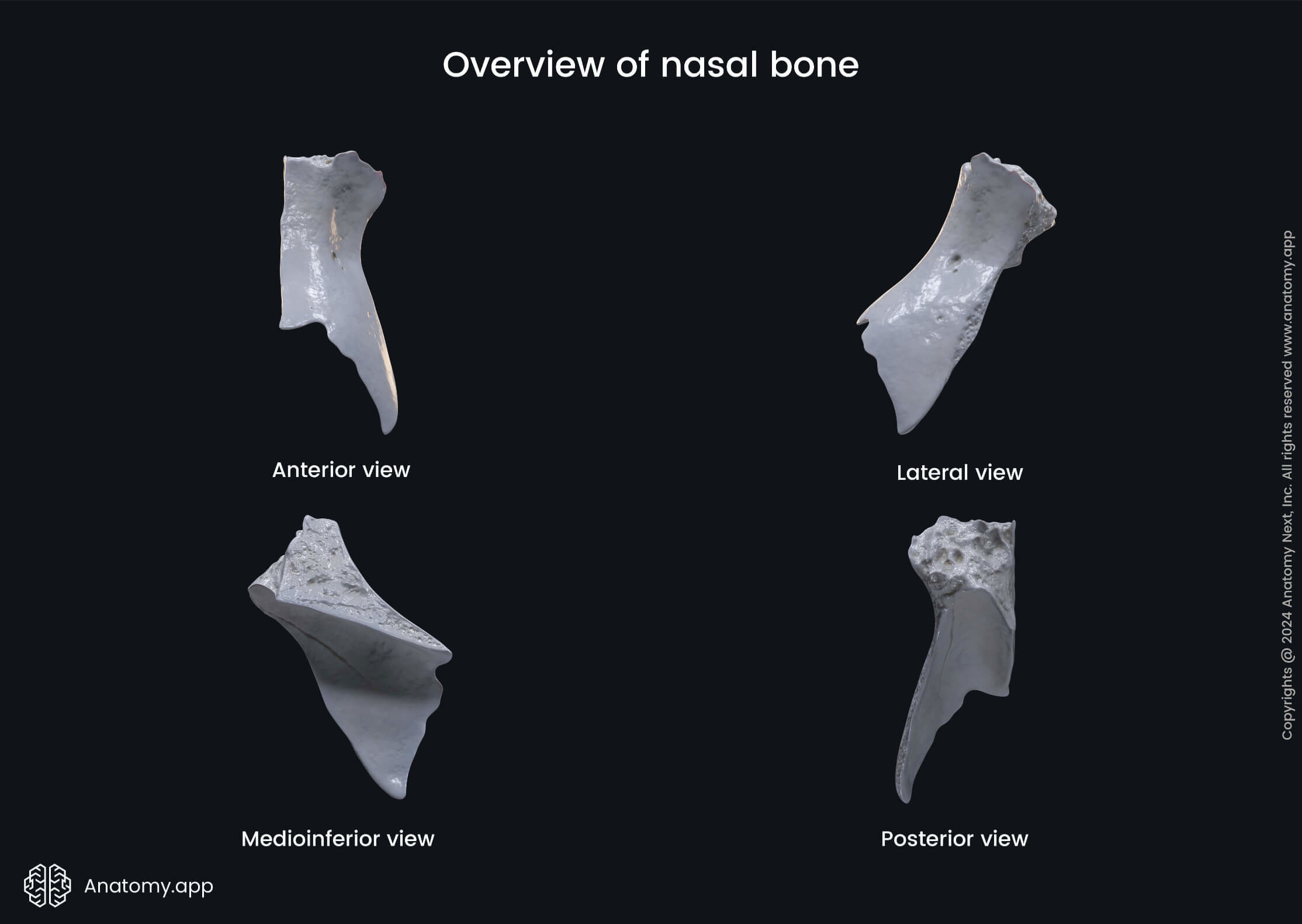
The nasal bones are variable in size and form in different individuals. Each nasal bone has two surfaces (outer and inner) and four borders (superior, inferior, medial, lateral).
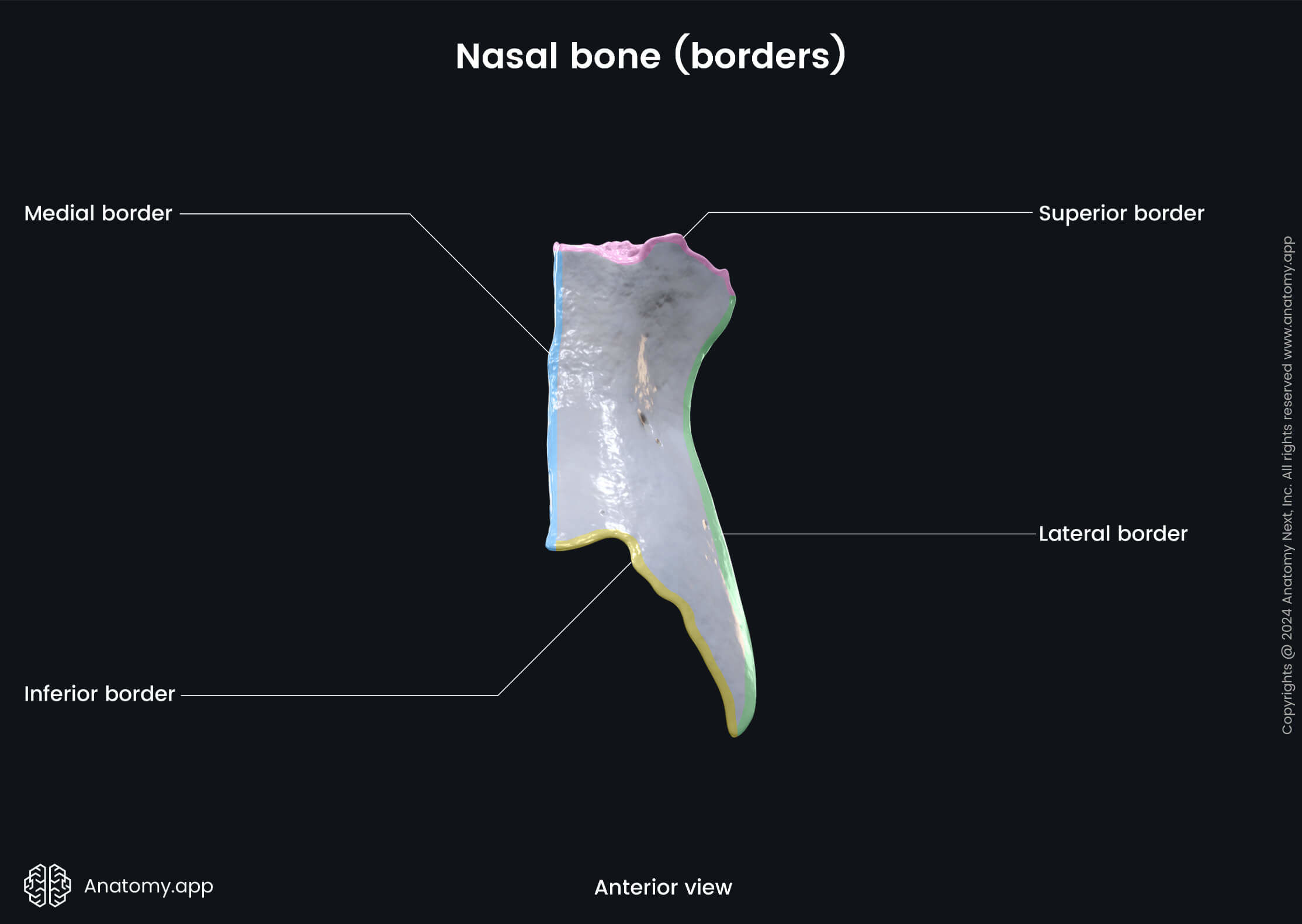
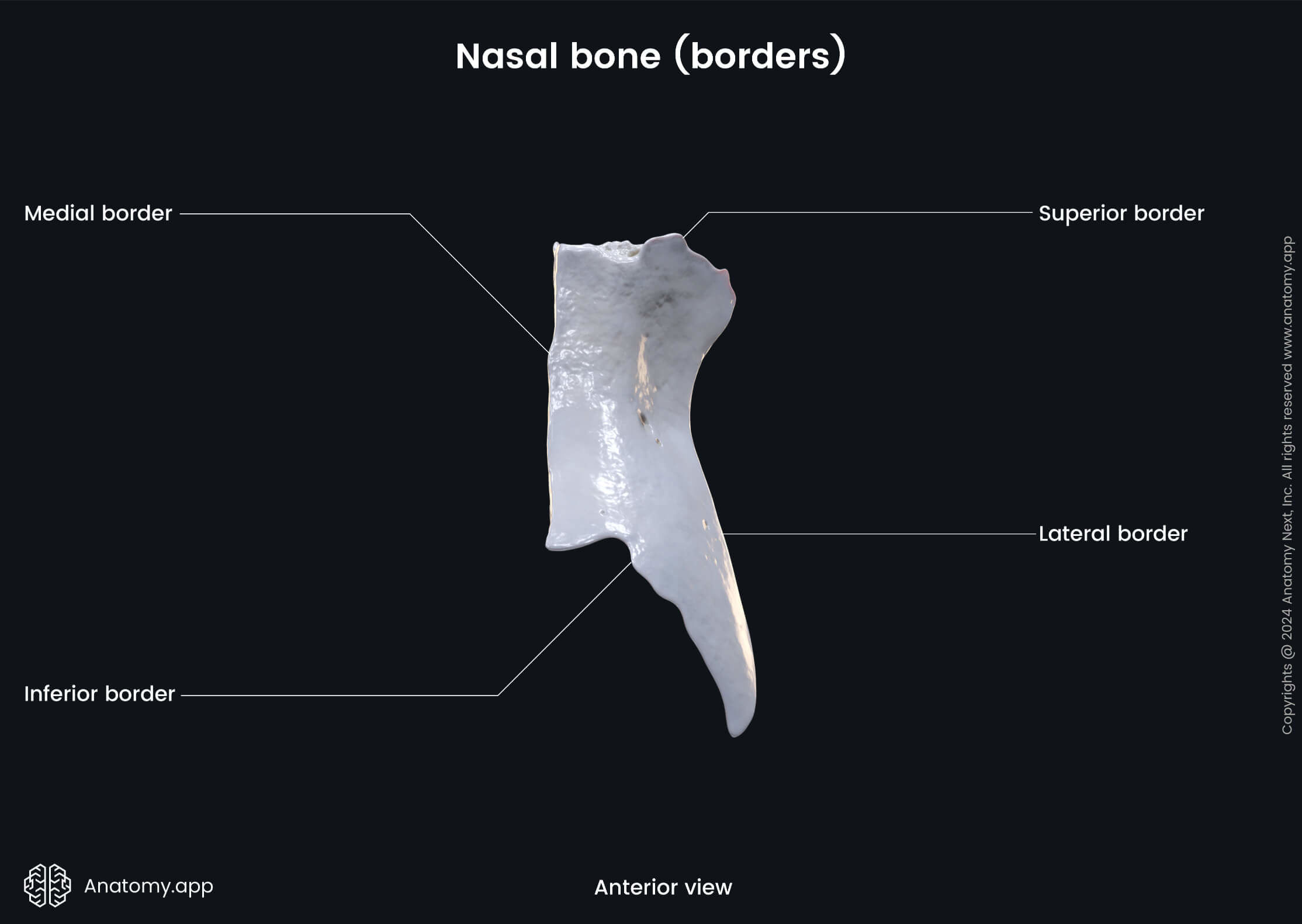
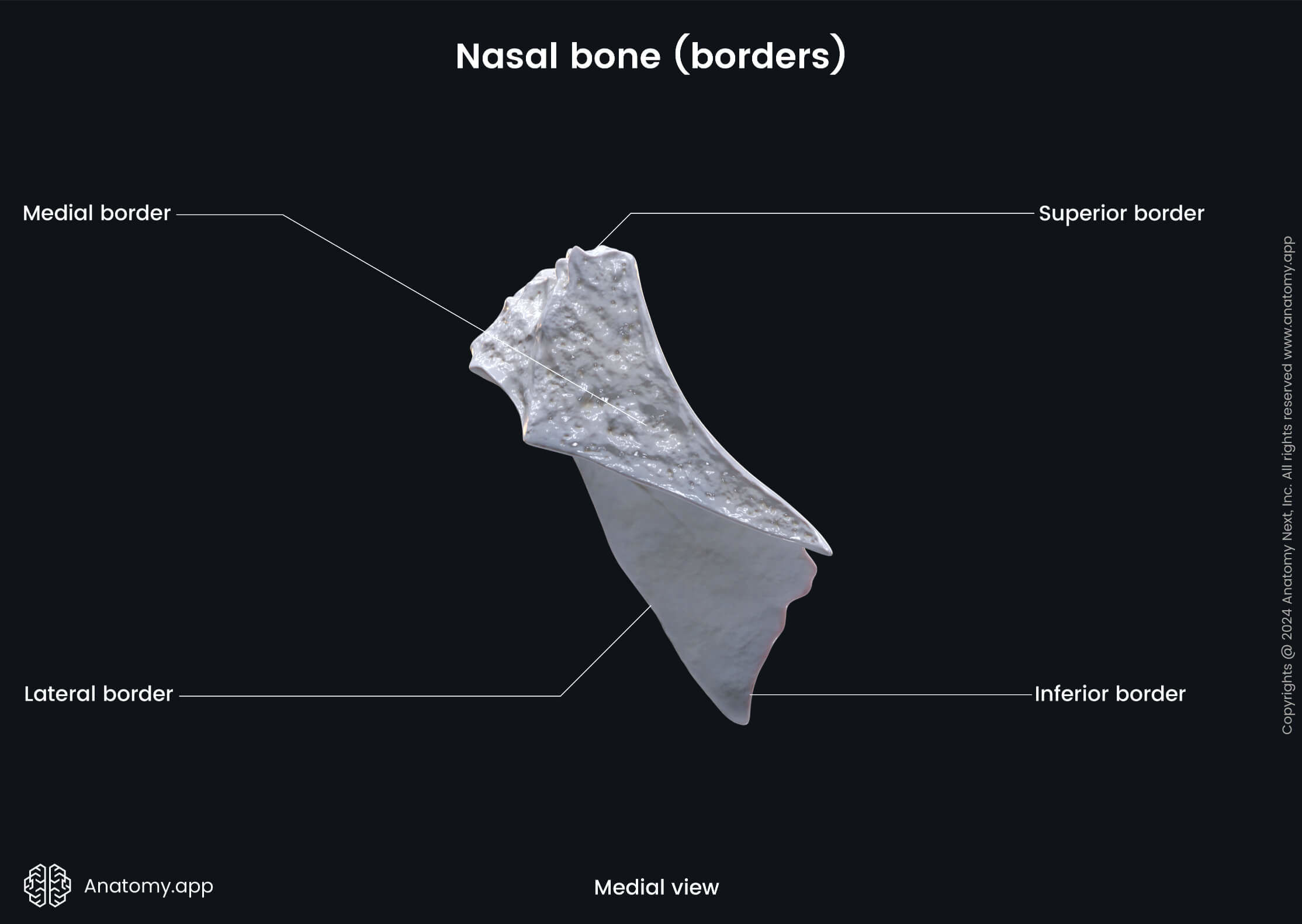
Surfaces and landmarks
The outer surface of the nasal bone is convex from side to side, and covered by two facial muscles - the procerus and nasalis.
The inner surface of this bone is concave from side to side. It features a groove that serves as the passage for a branch of the nasociliary nerve, which itself is a branch of the first division of the opthalmic nerve (CN V1).