- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Skeleton of trunk
- Skull
- Skeleton of upper limb
- Skeleton of lower limb
- Joints
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
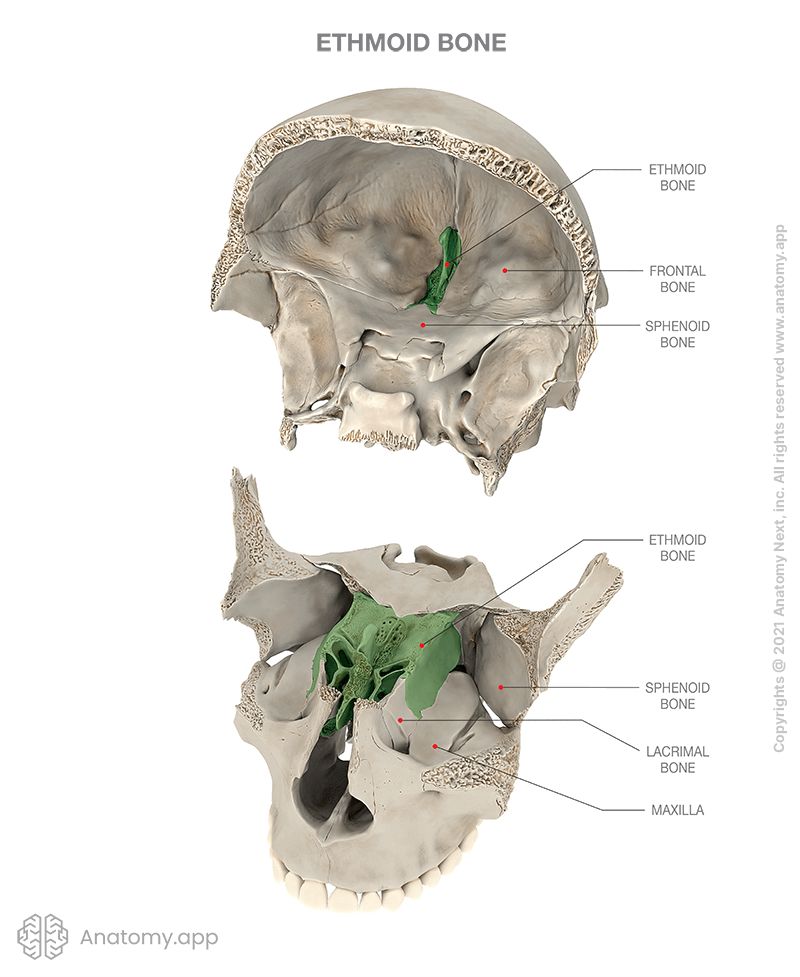
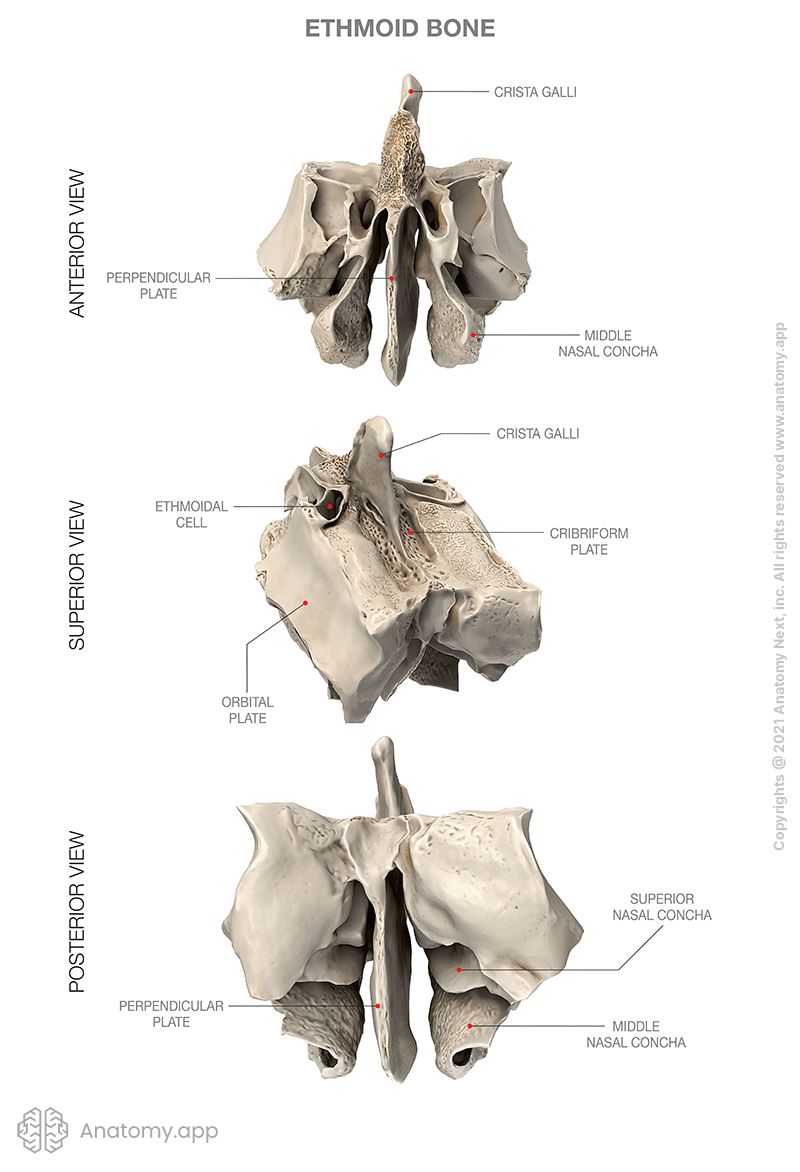
Ethmoid bone
The ethmoid bone (also ethmoidal bone, ethmoid, Latin: os ethmoidale) is an unpaired bone of the skull that contributes to the medial wall of the orbit and parts of the nasal cavity. The ethmoid bone includes the cribriform plate with openings that transmit the olfactory nerves (CN I). This bone also houses paranasal sinuses called the ethmoidal air cells.
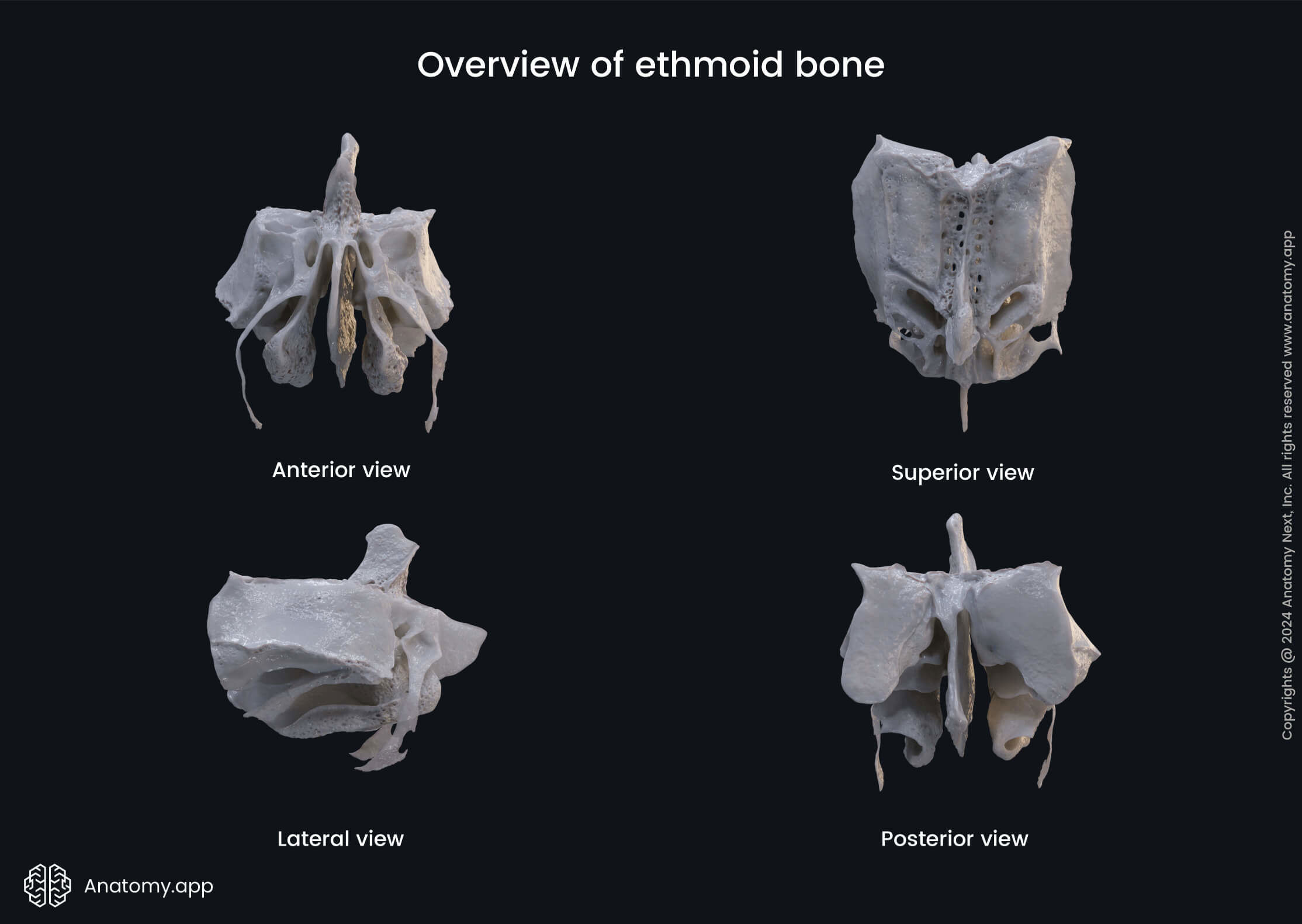
Parts of ethmoid bone
The ethmoid bone has four parts:
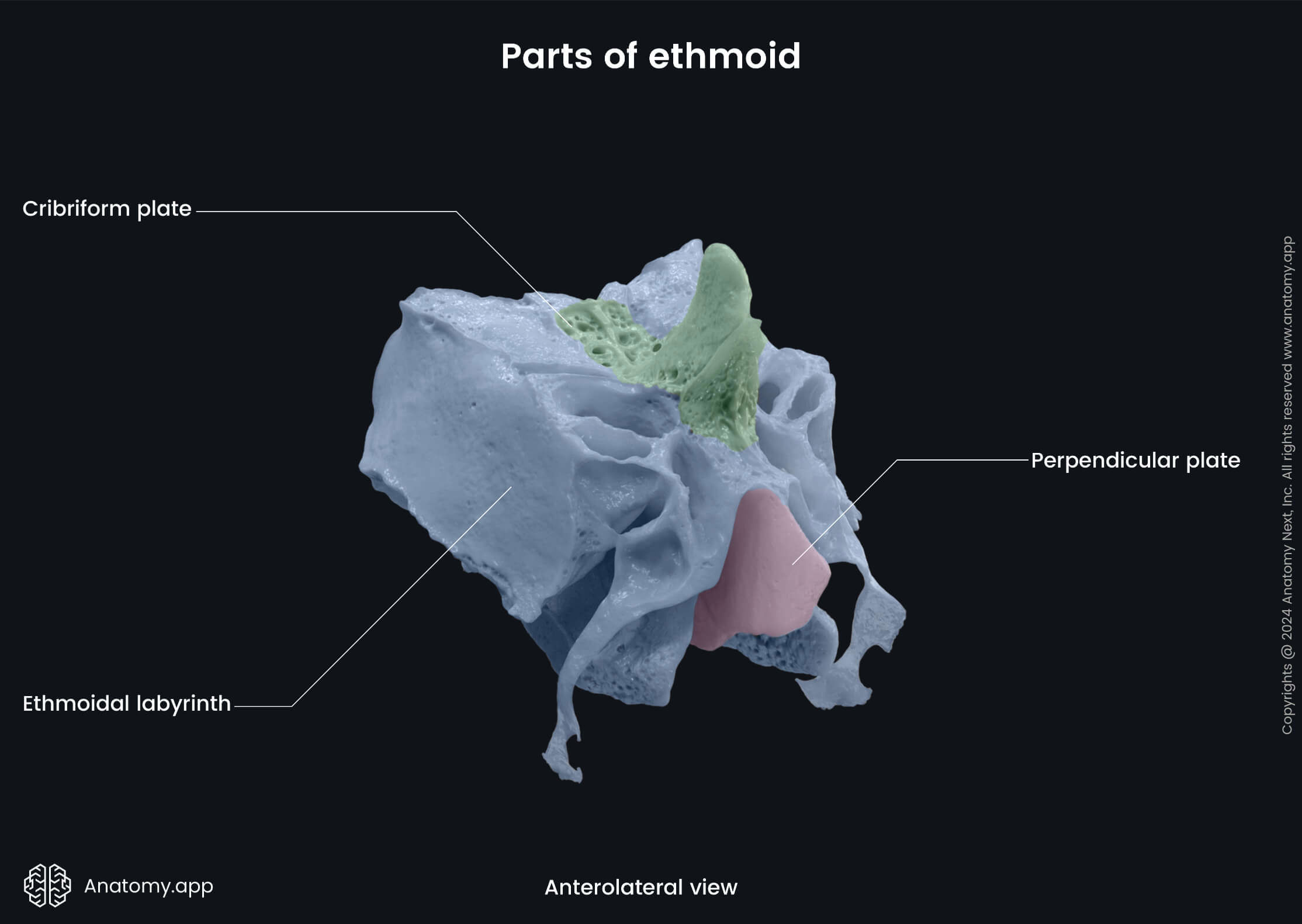
Cribriform plate of ethmoid
The cribriform plate is a part of the ethmoid bone situated in the horizontal plane. It covers the ethmoidal notch of the frontal bone. The cribriform plate forms the roof of the nasal cavity and part of the anterior cranial fossa of the internal cranial base.
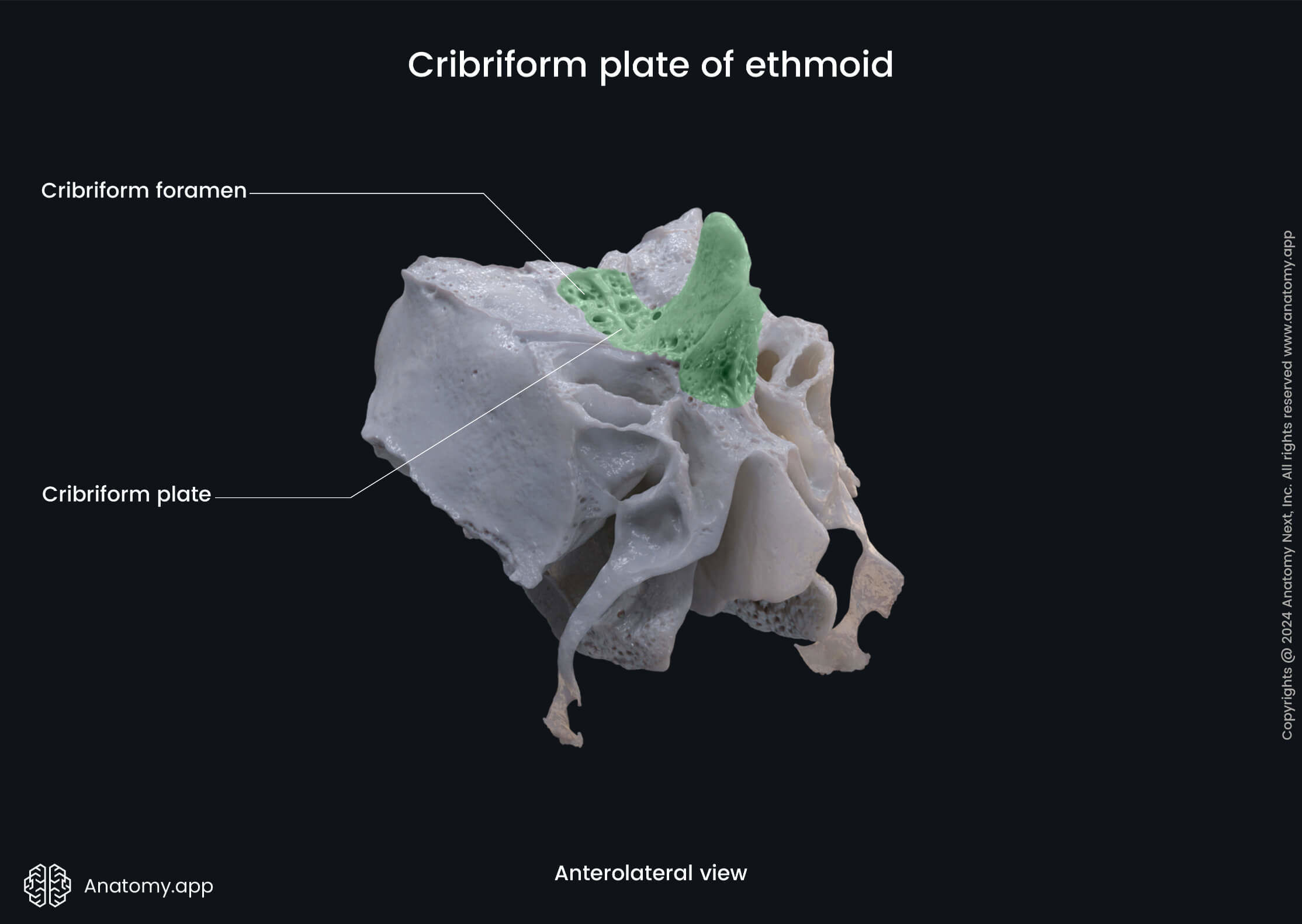
The cribriform plate of the ethmoid features small openings - cribriform foramina. These openings transmit the fibers of the olfactory nerves (CN I) from the olfactory epithelium (nasal cavity) to the brain (cranial cavity).
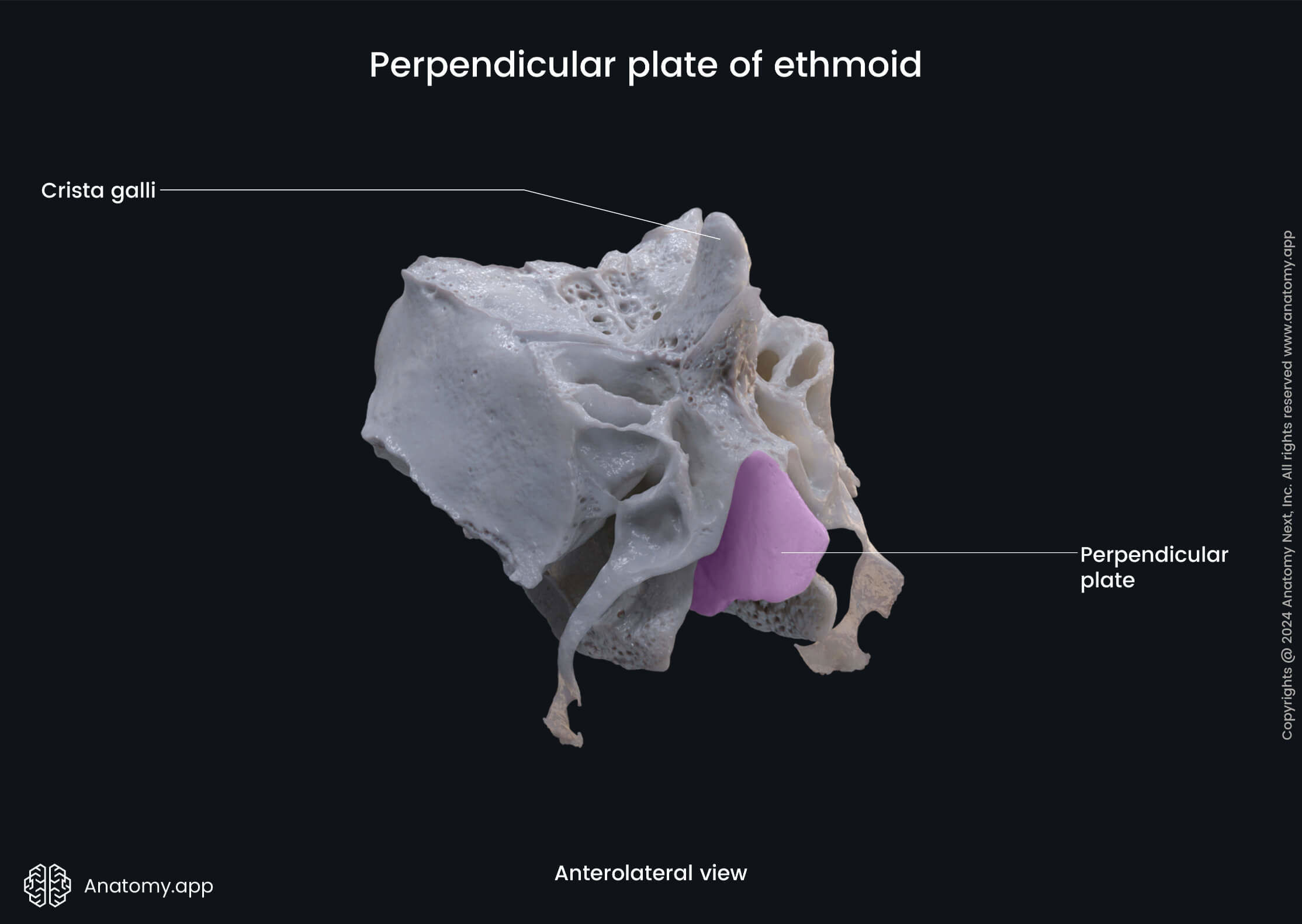
Perpendicular plate of ethmoid
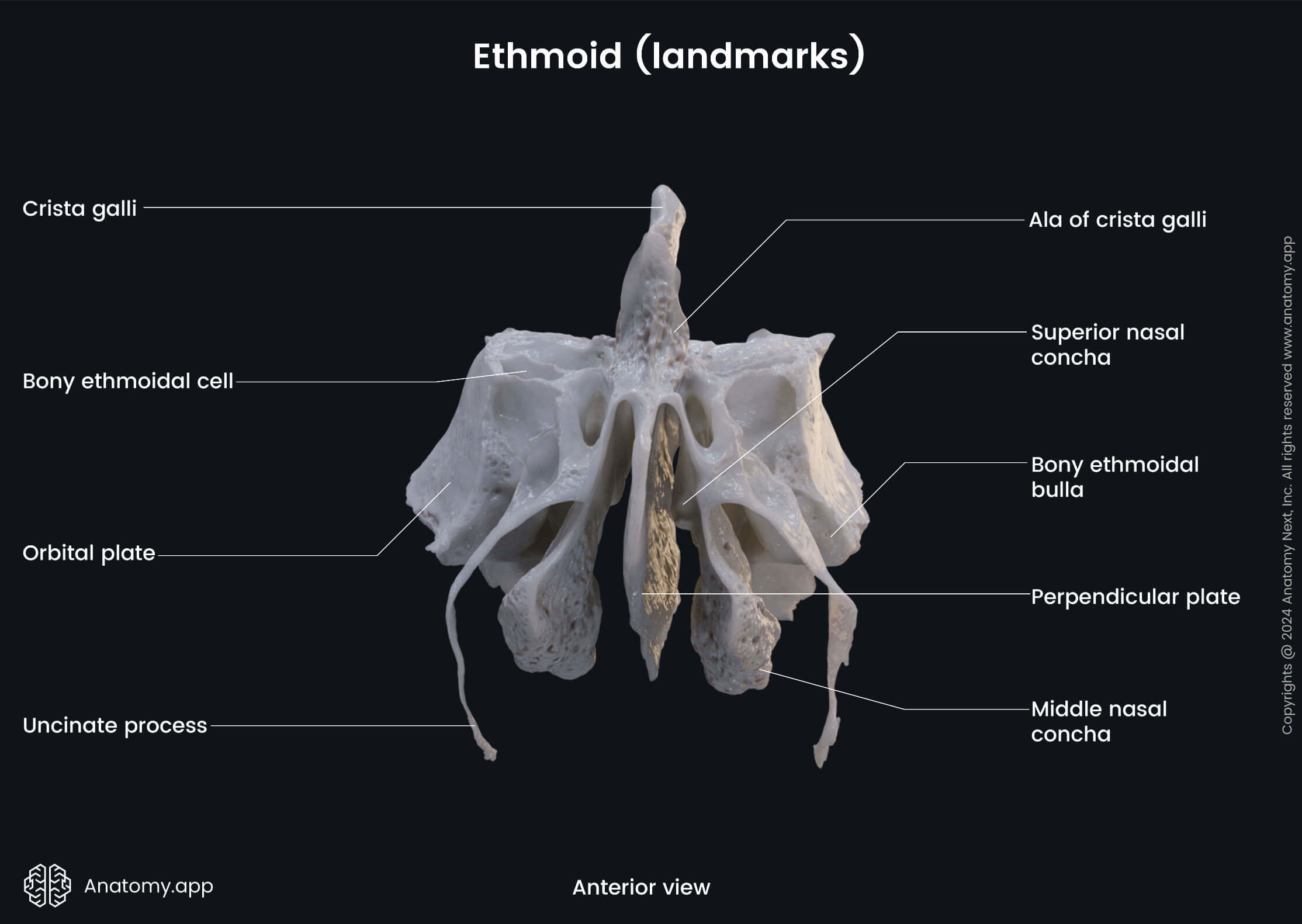
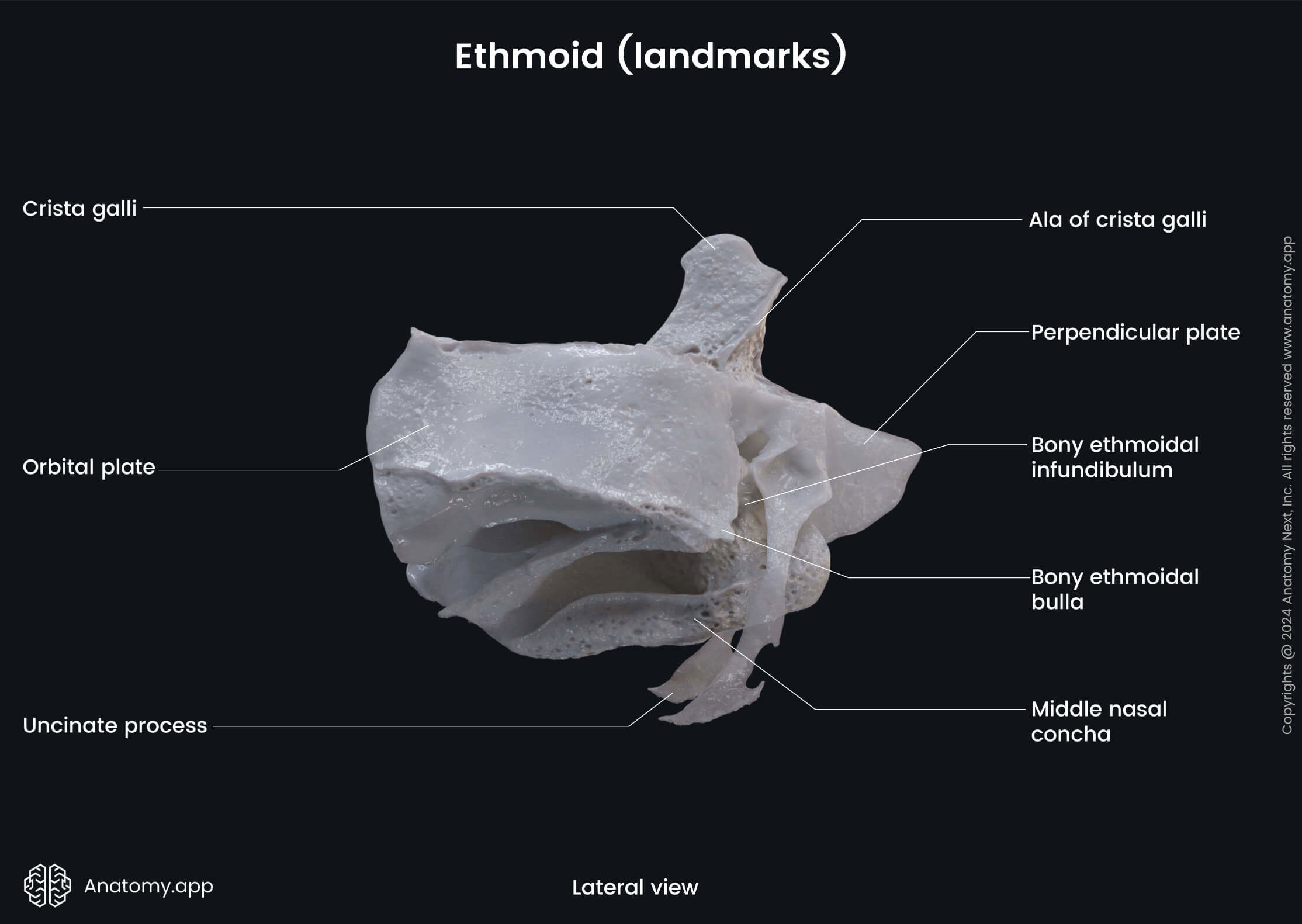
The perpendicular plate is a part of the ethmoid bone situated in the sagittal plane below the cribriform plate. The lower part of the perpendicular plate forms the posterior nasal septum. Its upper part rises above the cribriform plate as the crista galli.
Ethmoidal labyrinth
The ethmoidal labyrinth is a paired structure of the ethmoid bone situated in the sagittal plane below the lateral margin of the cribriform plate. The ethmoidal labyrinth separates the orbit from the nasal cavity.
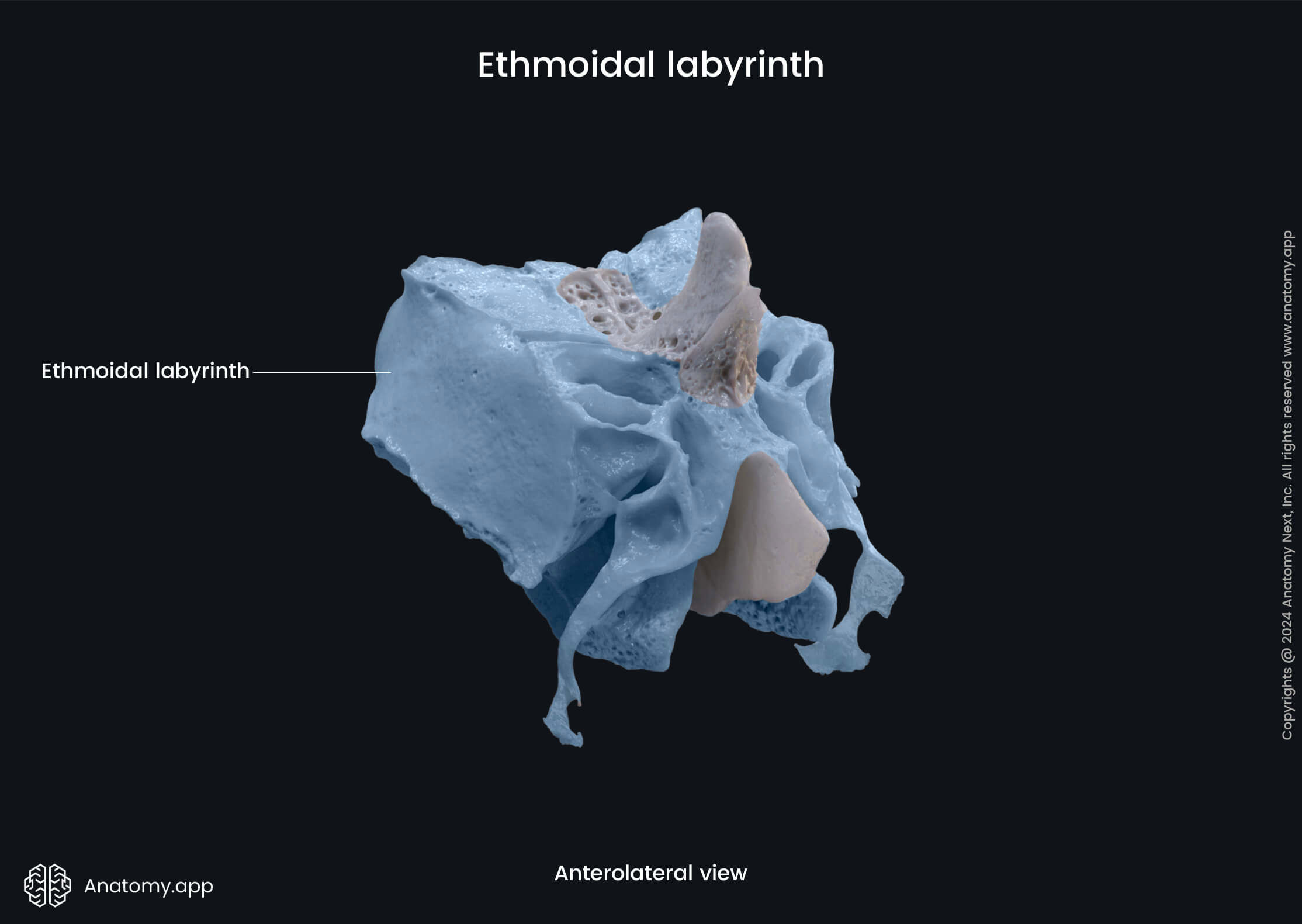
This part of the ethmoid features several important structures:
- Ethmoidal air cells (anterior, middle, posterior)
- Orbital plate
- Superior nasal concha
- Middle nasal concha
The ethmoidal air cells are paranasal sinuses - air-filled spaces - found in each ethmoidal labyrinth of the ethmoid bone. On each side there can be distinguished anterior, middle, and posterior ethmoidal air cells.
The orbital plate of the ethmoidal labyrinth is a thin bony plate covering the ethmoidal cells from the orbital side. It forms the lateral surface of the labyrinth and participates in forming the medial wall of the orbit.
Nasal conchae (singular: concha) are curved bony plates that form passages of the nasal cavity (nasal meatuses). In total, there are three nasal conchae found on each lateral wall of the nasal cavity:
- Superior nasal concha
- Middle nasal concha
- Inferior nasal concha
The paired superior nasal conchae and middle nasal conchae are parts of the ethmoid bone. They cover the ethmoidal air cells from the side of the nasal cavity and form the medial surface of the labyrinth. The inferior nasal conchae are separate bones of the skull.