- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Aorta
- Blood vessels of head and neck
- Arteries of head and neck
- Veins of head and neck
- Blood vessels of upper limb
- Blood vessels of thorax
- Blood vessels of abdomen
- Blood vessels of pelvis and lower limb
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
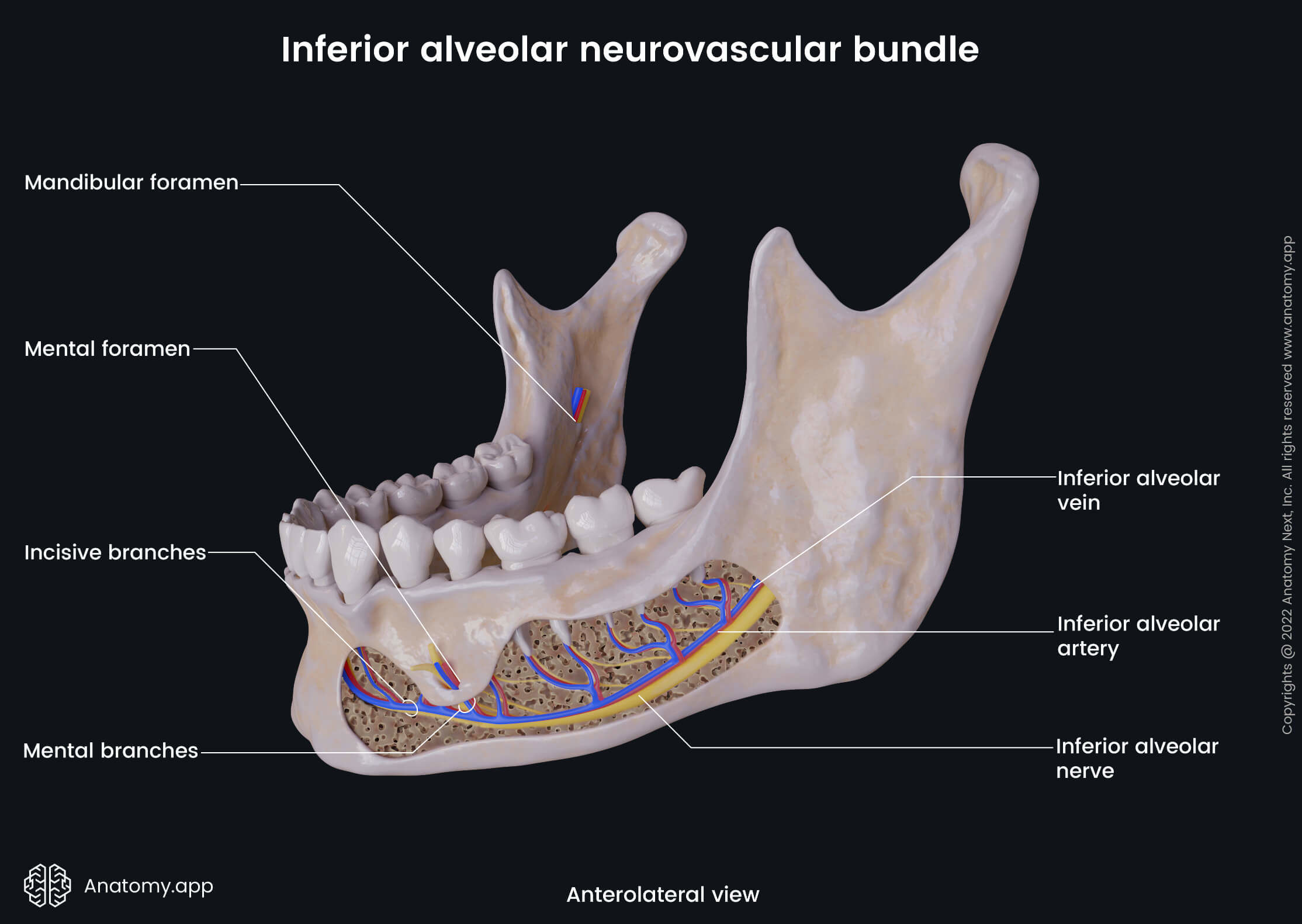
Inferior alveolar artery
The inferior alveolar artery (also known as inferior dental artery, Latin: arteria alveolaris inferior) is a branch of the maxillary artery that supplies the mylohyoid muscle, mandible, tooth sockets, lower teeth, skin, and muscles in the chin region.
The inferior alveolar artery descends in the infratemporal fossa. Before it passes through the mandibular foramen into the mandibular canal, the artery gives off a mylohyoid branch. This branch runs in the mylohyoid groove on the inner surface of the ramus of the mandible. It then distributes in the mylohyoid muscle and anastomoses with the submental artery.
Afterwards, the inferior alveolar artery runs along the mandibular canal within the mandible. On its way, it supplies the mandible, tooth sockets and teeth, and divides into the incisive and mental branches near the first premolar tooth.
The incisive branch of the inferior alveolar artery continues forward below the incisors to the midline, where it forms anastomoses with the corresponding vessel of the opposite side. The mental artery emerges onto the face via the mental foramen and supplies the chin. It also forms anastomoses with the submental and inferior labial arteries.