- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
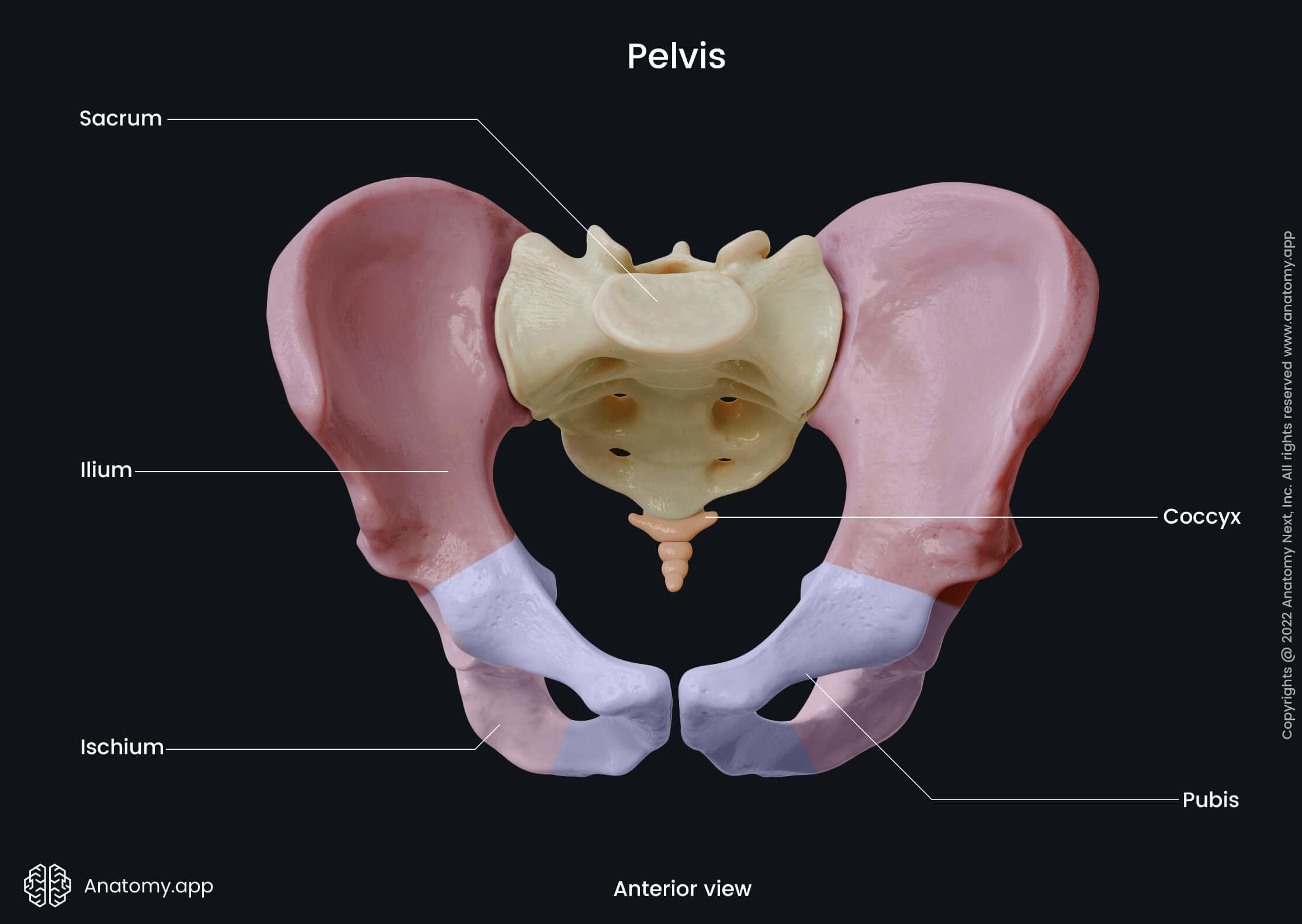
Pubic bone
The pubic bone (Latin: os pubis), also known as the pubis, is a paired bone that forms the anterior part of the hip bone. It also participates in the formation of the anterior and inferior boundary of the obturator foramen. The left and right pubic bones join at the pubic symphysis.
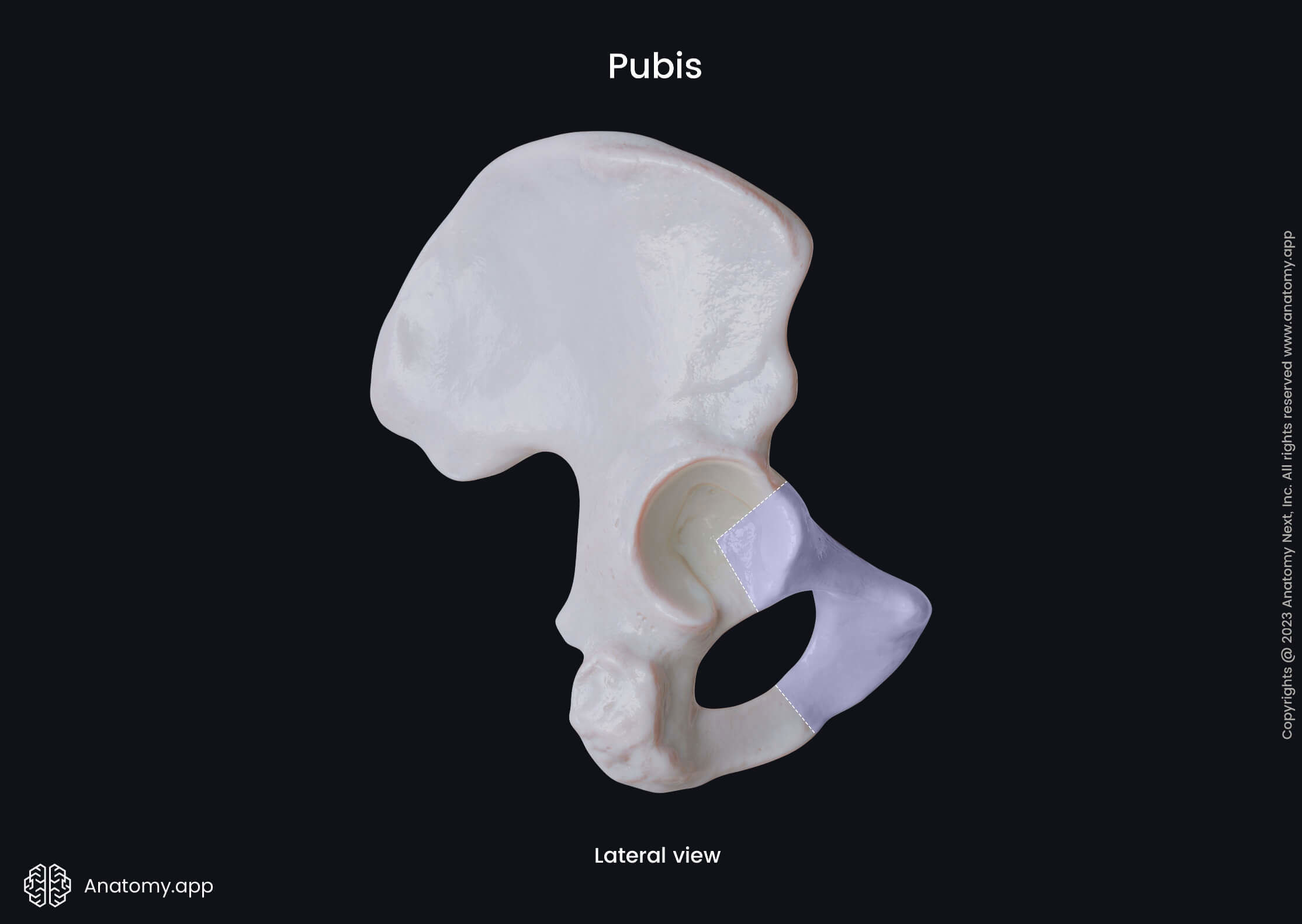
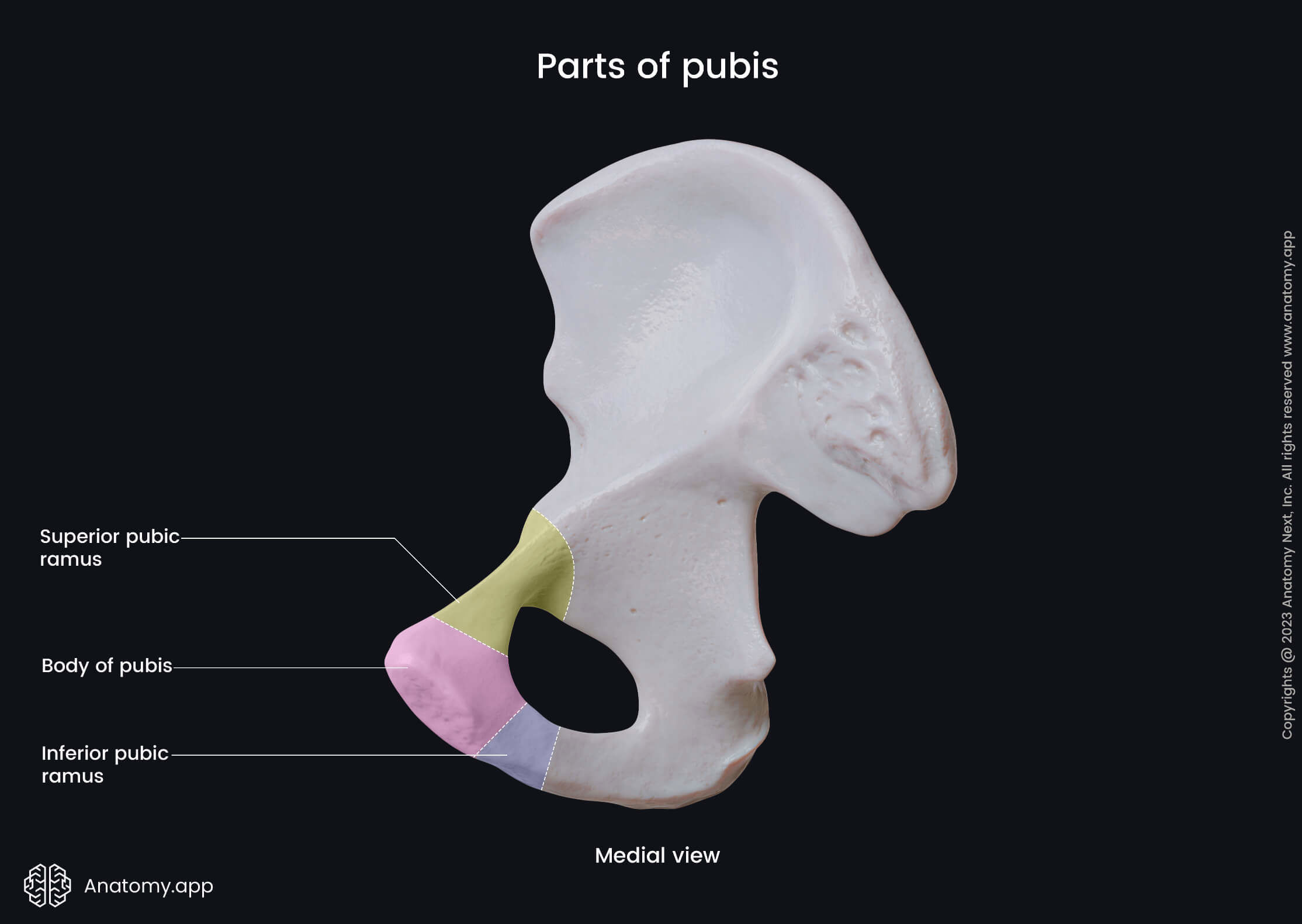
The pubic bone is the smallest hip bone, and it is continuous with the ischium posteriorly and ilium superiorly. Each pubic bone has three parts - inferior and superior rami and the body. Each body is located in the middle of both rami.
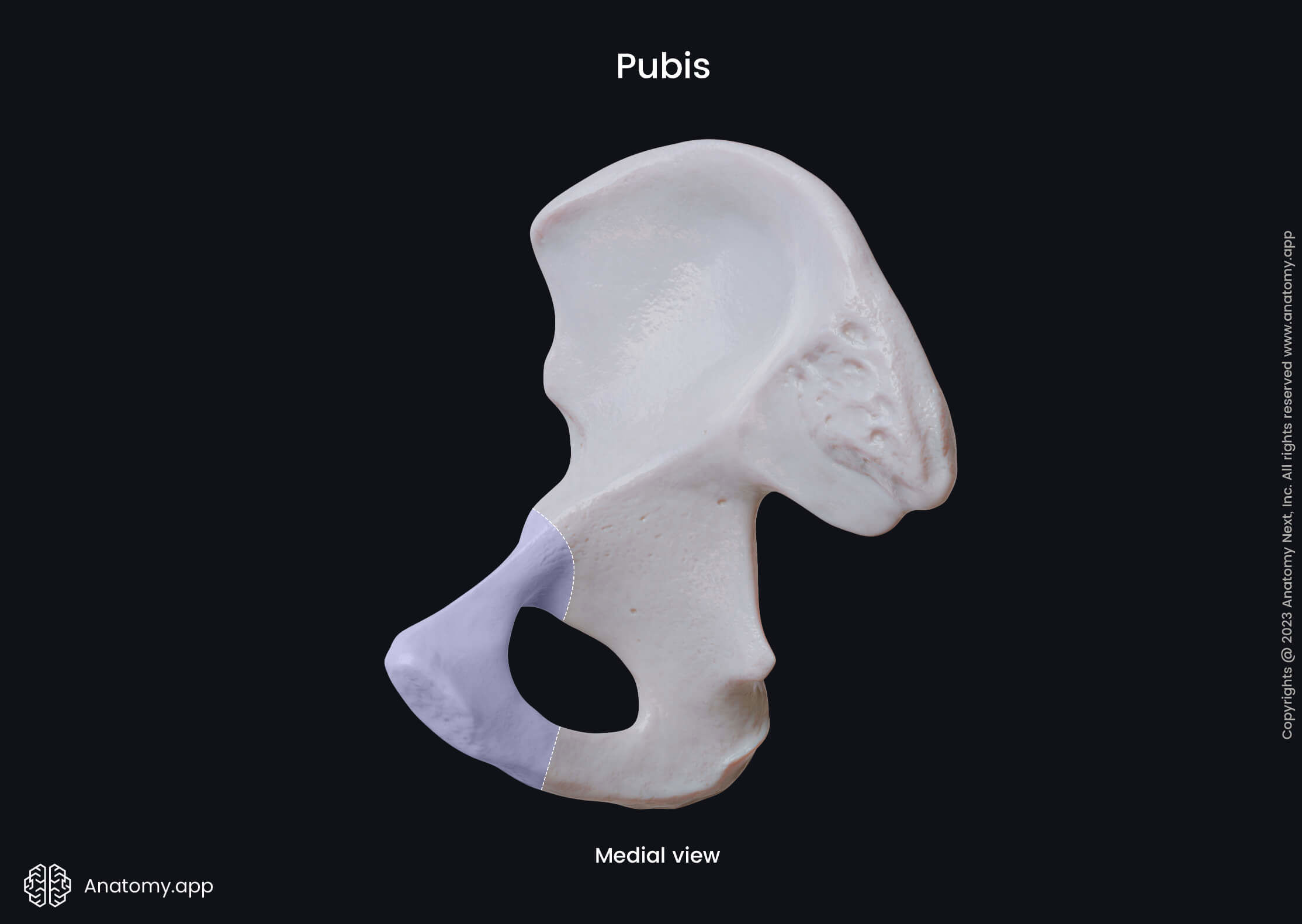
Body of pubis
The body of pubis is the smallest part of the pubic bone. It contains three surfaces - anterior or external, posterior or internal and medial. The medial surface is also known as the symphysial surface, and it is the site where bodies of both pubic bones fuse.
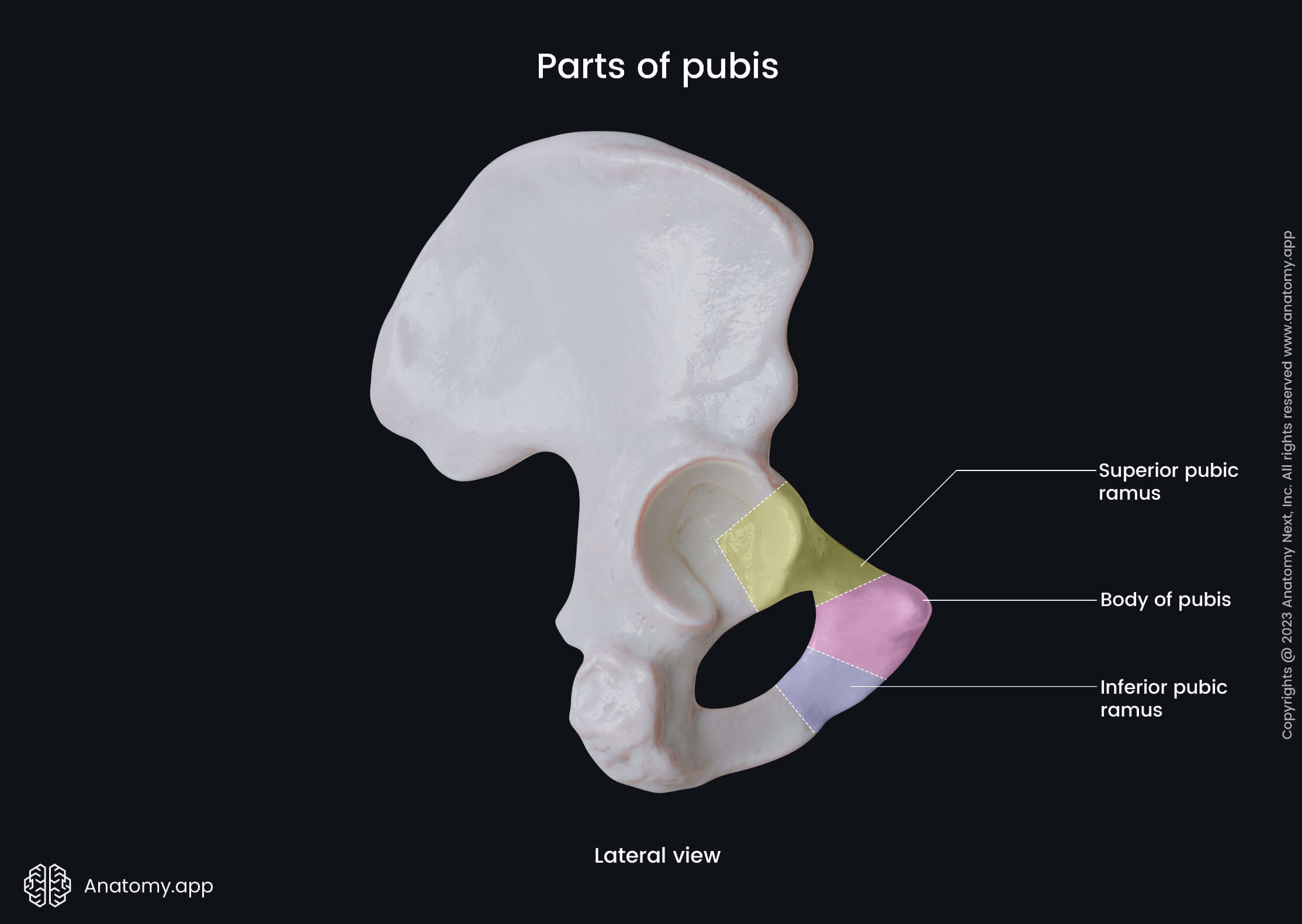
Inferior ramus of pubis
The inferior ramus of the pubic bone extends posteroinferiorly from the body part, and it merges with the ramus of the ischium. The inferior ramus has two surfaces - anterolateral and posteromedial - and two borders named the medial and anterior borders.
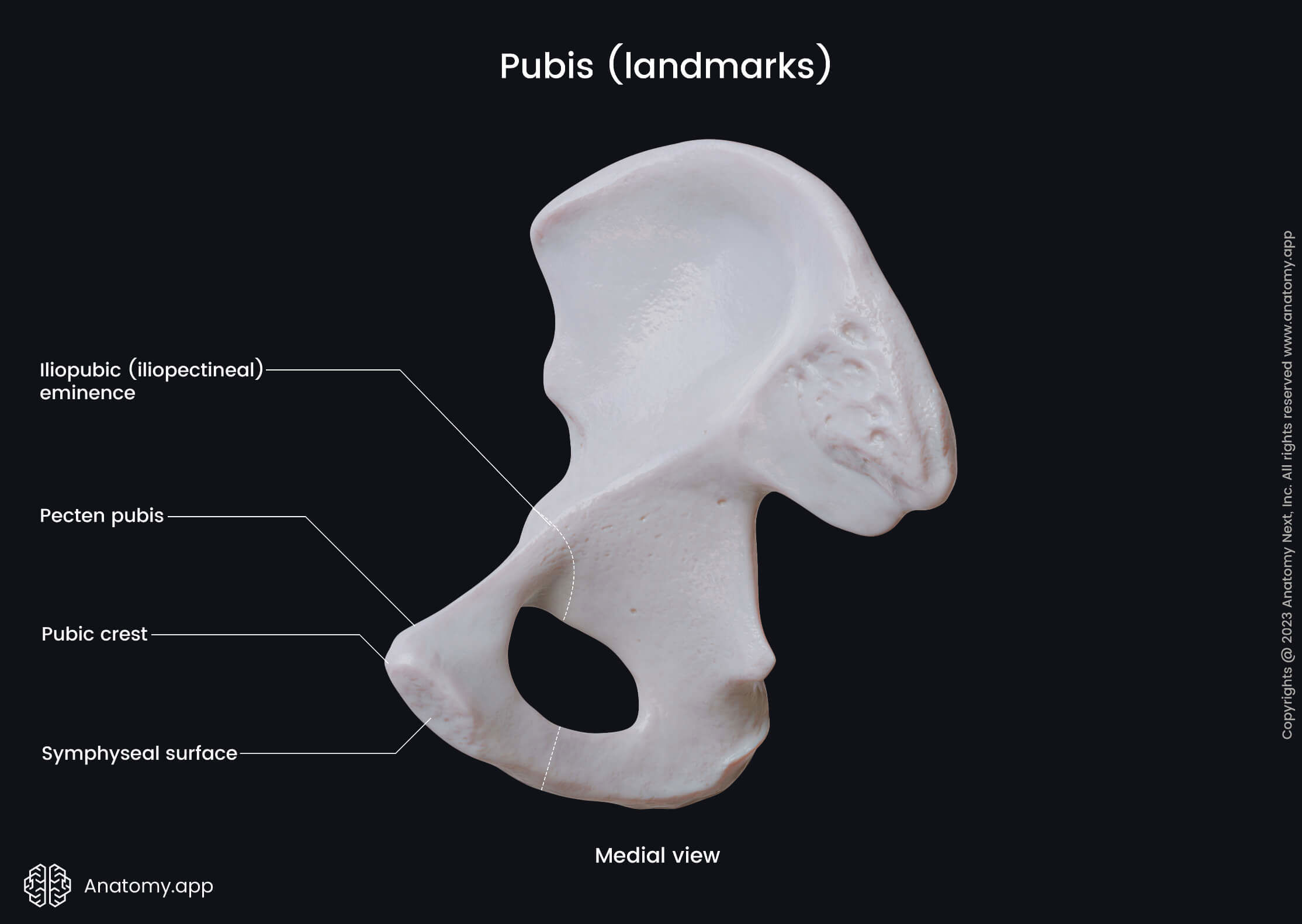
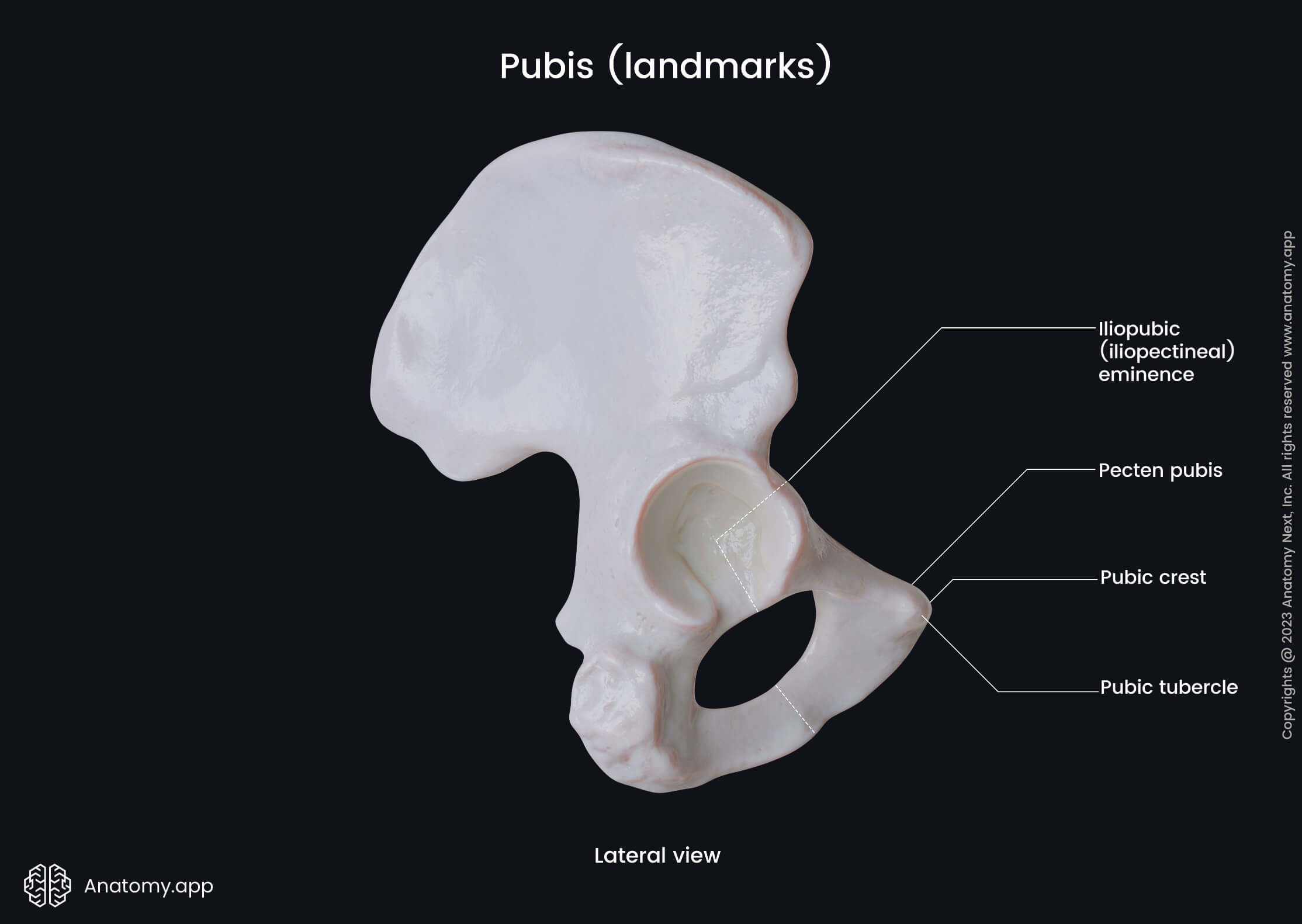
Superior ramus of pubis
The superior ramus of the pubis extends superiorly and backward from the body part. The superior ramus of the pubic bone features several landmarks, and they include the following:
The pubic tubercle is a bony prominence located on the upper aspect of the superior ramus. It serves as an attachment site for the inguinal ligament.
The pecten pubis or the pectineal line is a sharp bony ridge. It reaches the pubic tubercle as the continuation of the arcuate line and serves as the origin site for the pectineus muscle.
The obturator groove is a deep sulcus located on the inner surface of the superior ramus above the acetabulum. The obturator vessels and nerves pass through the groove.