- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Head muscles
-
Neck muscles
- Superficial neck muscles
- Scalene muscles
- Suprahyoid muscles
- Infrahyoid muscles
- Prevertebral muscles
- Suboccipital muscles
- Muscles of upper limb
- Thoracic muscles
- Muscles of back
- Muscles of lower limb
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
Mylohyoid
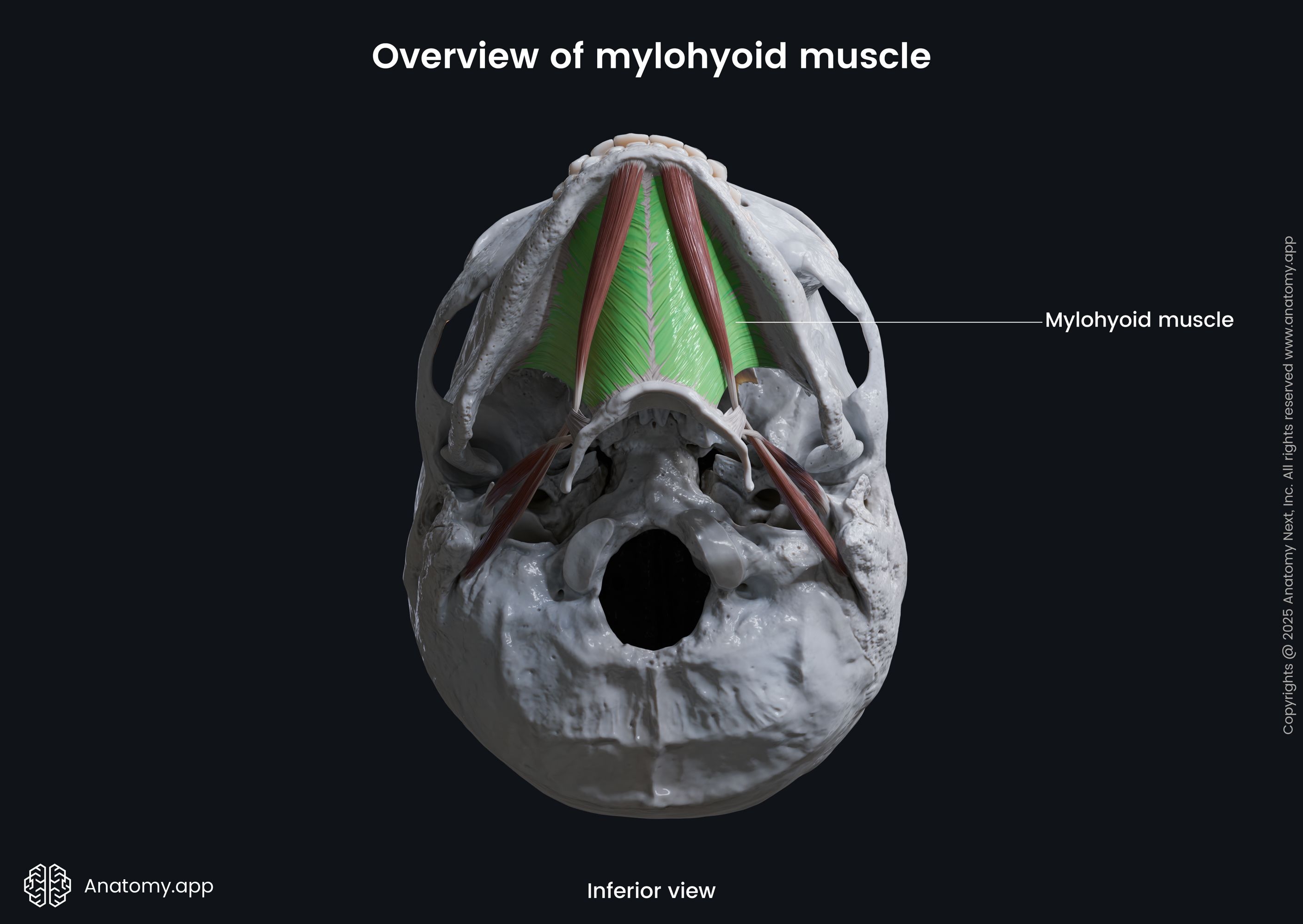
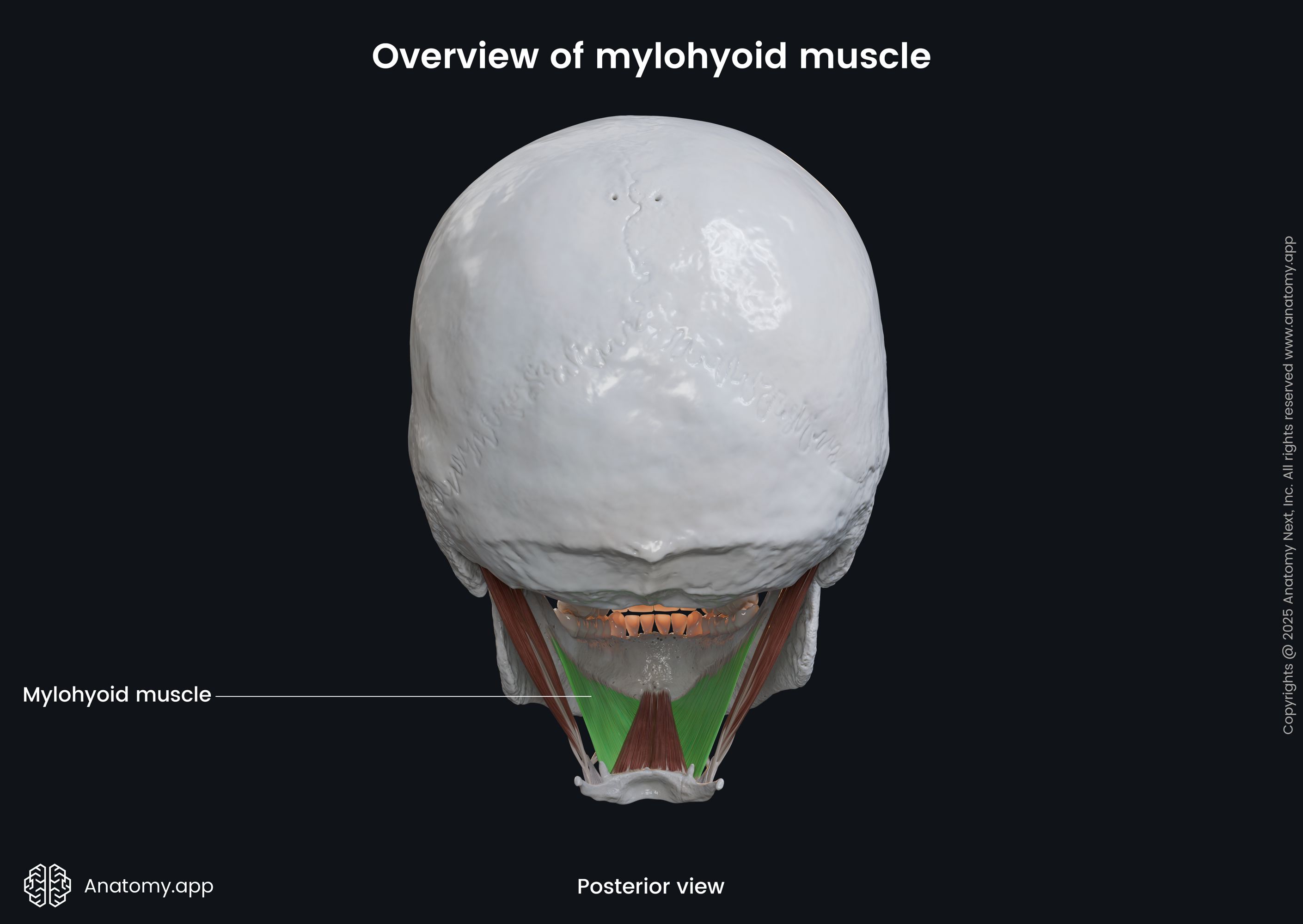
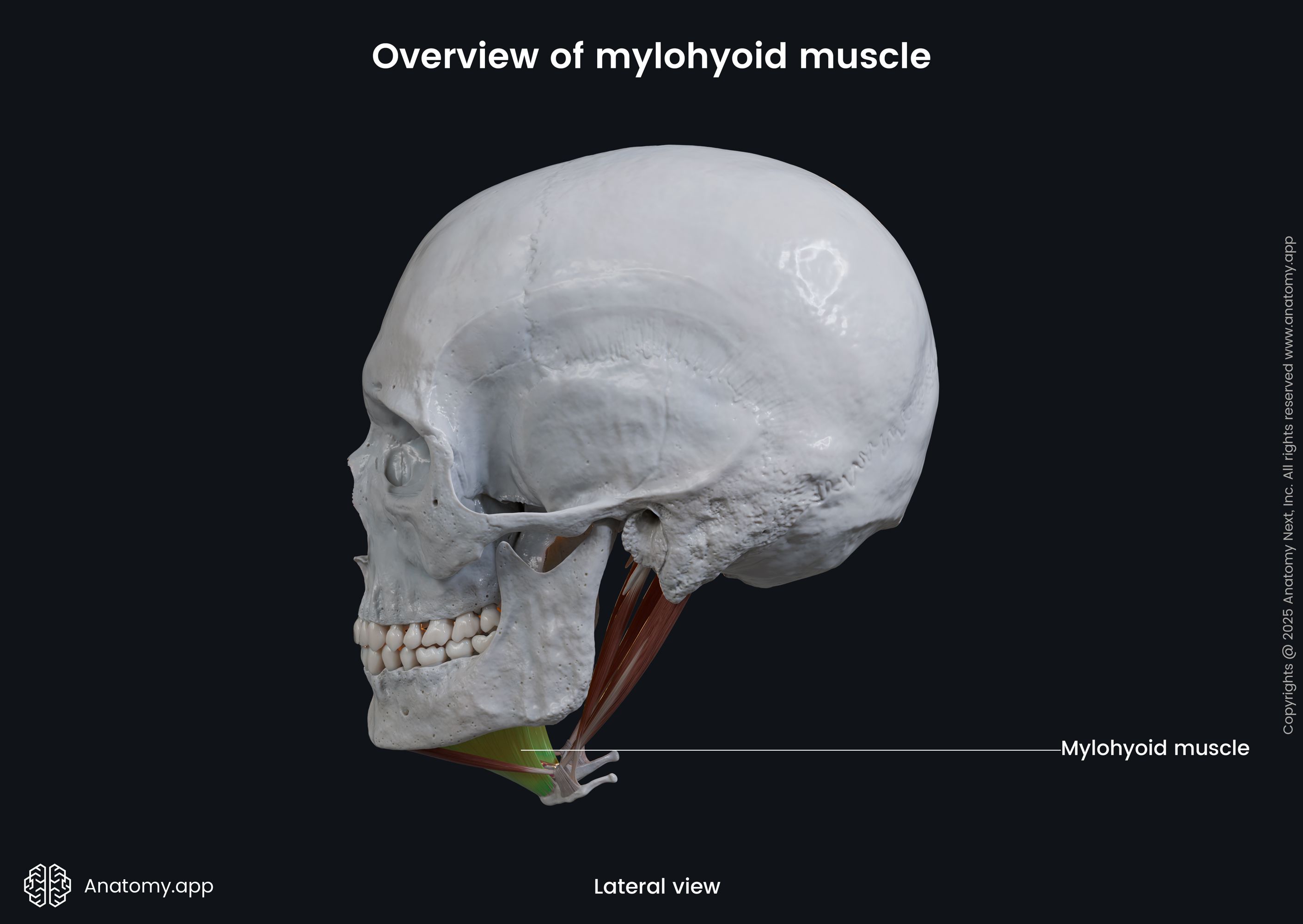
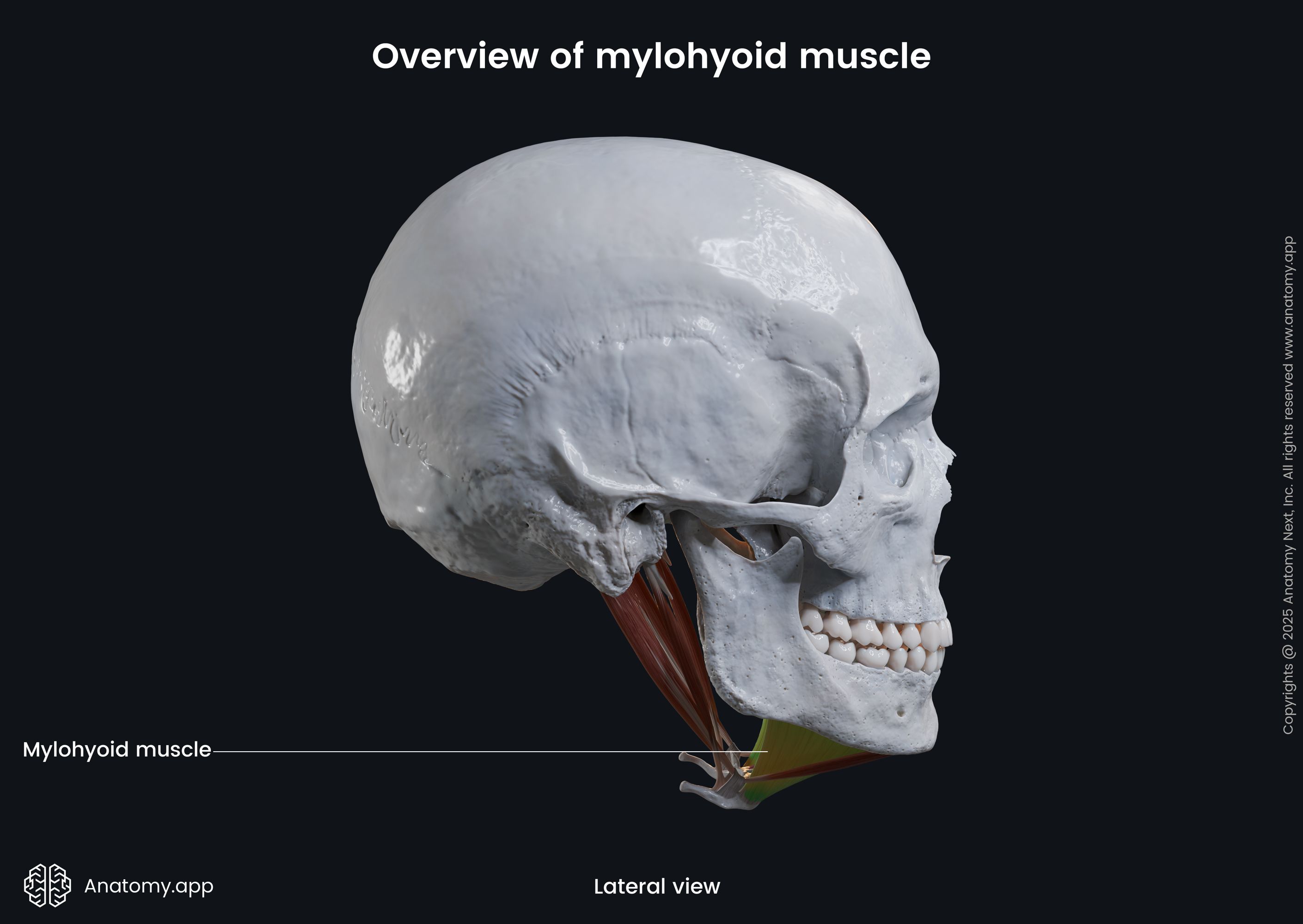
The mylohyoid (Latin: musculus mylohyoideus) is a paired neck muscle located above the hyoid bone. Therefore, the mylohyoid is classified as the suprahyoid muscle of the neck. This muscle is also included in the anterior neck muscles group. The mylohyoid extends from the mandible to the hyoid bone. Besides moving the hyoid bone, the mylohyoid, together with the geniohyoid muscle, forms the oral diaphragm (floor of the oral cavity).
| Mylohyoid | |
| Origin | Mylohyoid line of mandible |
| Insertion | Body of hyoid bone, mylohyoid raphe |
| Action | Elevates hyoid bone, elevates floor of oral cavity, depresses mandible |
| Innervation | Mylohyoid nerve |
| Blood supply | Mylohyoid, sublingual and submental arteries |
Origin
The mylohyoid muscle originates from the mylohyoid line located on the internal surface of the mandible.
Insertion
The mylohyoid inserts on the superior aspect of the body of the hyoid bone and in the midline fuses together with the opposite mylohyoid muscle. The fusion site of both mylohyoid muscles forms the mylohyoid raphe.
Action
Contractions of the mylohyoid muscle pull the hyoid bone forward and upward (elevate the hyoid bone). This muscle also depresses the lower jaw. As written above, both mylohyoid muscles participate in the formation of the oral diaphragm as they fuse in the midline. Therefore, the mylohyoid elevates the floor of the oral cavity. Besides all the mentioned functions, this muscle also aids in mastication and swallowing.
Innervation
The mylohyoid is innervated by the mylohyoid nerve (nerve to mylohyoid), a branch of the inferior alveolar nerve. The latter is a branch of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (CN V3).
Blood supply
The mylohyoid muscle receives arterial blood supply from three arteries - mylohyoid, sublingual and submental arteries. The first artery is a branch of the inferior alveolar artery, the sublingual artery is a branch of the lingual artery and the latter - a branch of the facial artery.