- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Aorta
- Blood vessels of head and neck
- Blood vessels of upper limb
- Blood vessels of thorax
- Systemic arteries of thorax
- Systemic veins of thorax
- Blood vessels of abdomen
- Blood vessels of pelvis and lower limb
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
Ascending aorta
The ascending aorta (or ascending part of aorta, Latin: aorta ascendens, pars ascendens aortae) is the first portion of the aorta, which is the largest artery in the human body and the main artery of the systemic circulation. The ascending aorta arises from the left ventricle of the heart within the middle mediastinum.
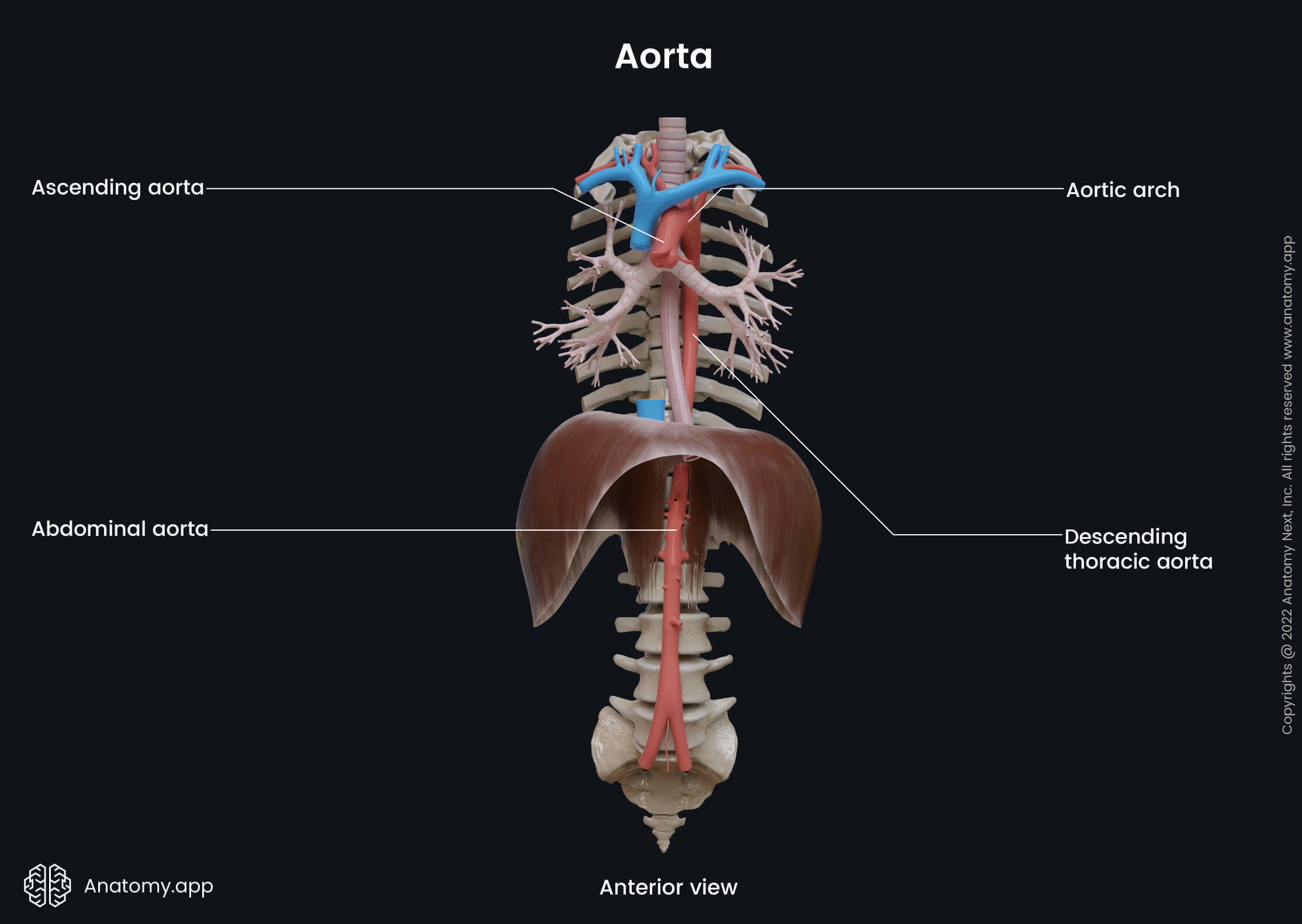
The ascending part of the aorta is located within the pericardial sac and is about 2 to 3 inches (5 to 8 cm) long. It passes through the mediastinum and continues as the aortic arch, after emerging from the pericardium. The ascending aorta is related to the following structures:
- Anteriorly - with the pericardium (covers the ascending aorta), thymus, and sternum;
- Posteriorly - with the left atrium of the heart, right pulmonary artery, and right main bronchus;
- On the right (and posteriorly) - with the superior vena cava and the right atrium;
- On the left - with the left atrium of the heart.
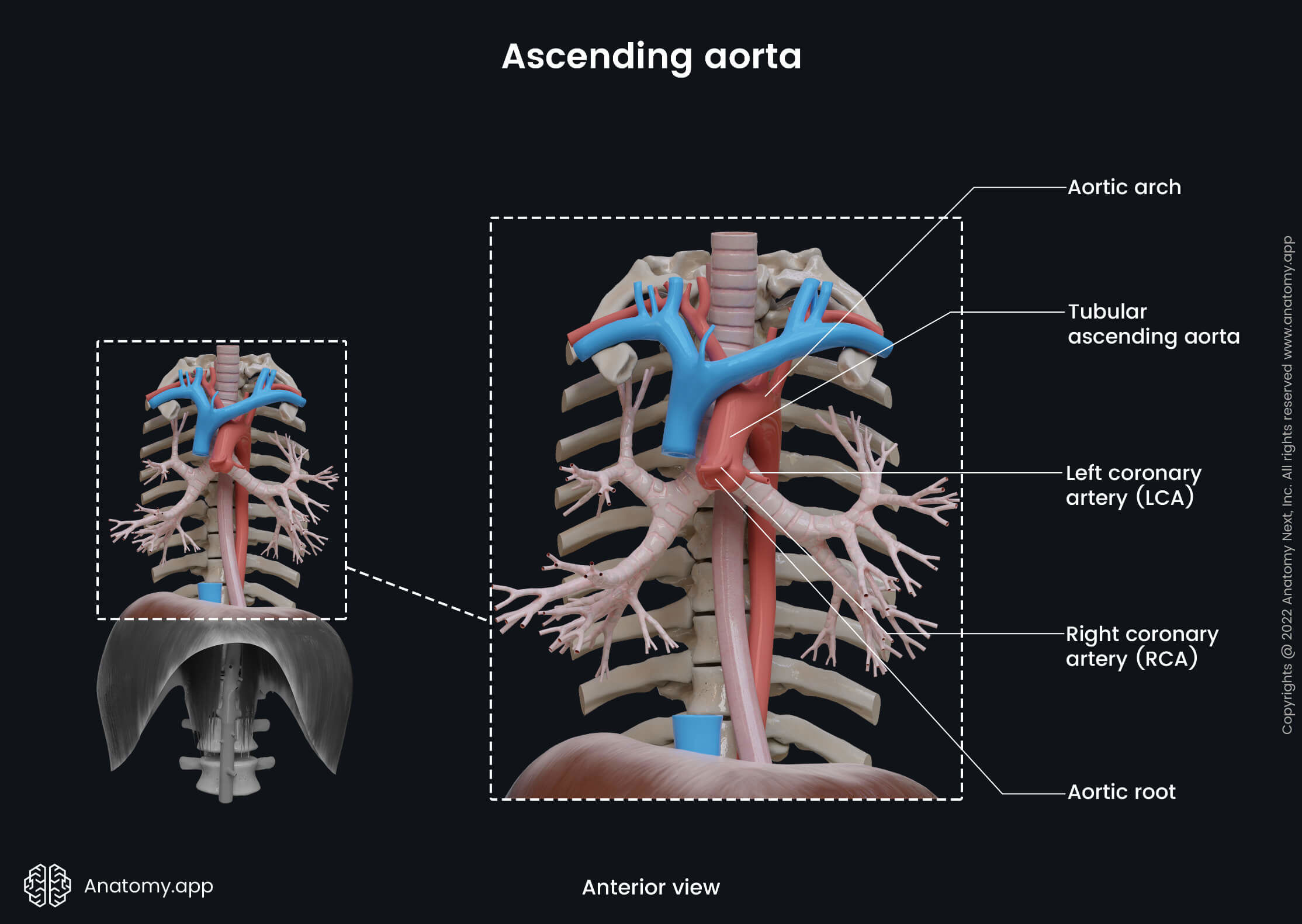
Two essential blood vessels arise from the ascending aorta - the right and left coronary arteries. Both coronary arteries originate immediately above the aortic valve on their respective sides. They supply the heart with oxygenated blood.