- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
Ansa cervicalis
The ansa cervicalis (Latin: ansa cervicalis), also known as the ansa hypoglossi, is a loop of nerves that arises from the cervical plexus. It contains motor fibers from the ventral rami of the first through third cervical spinal nerves (C1 - C3).
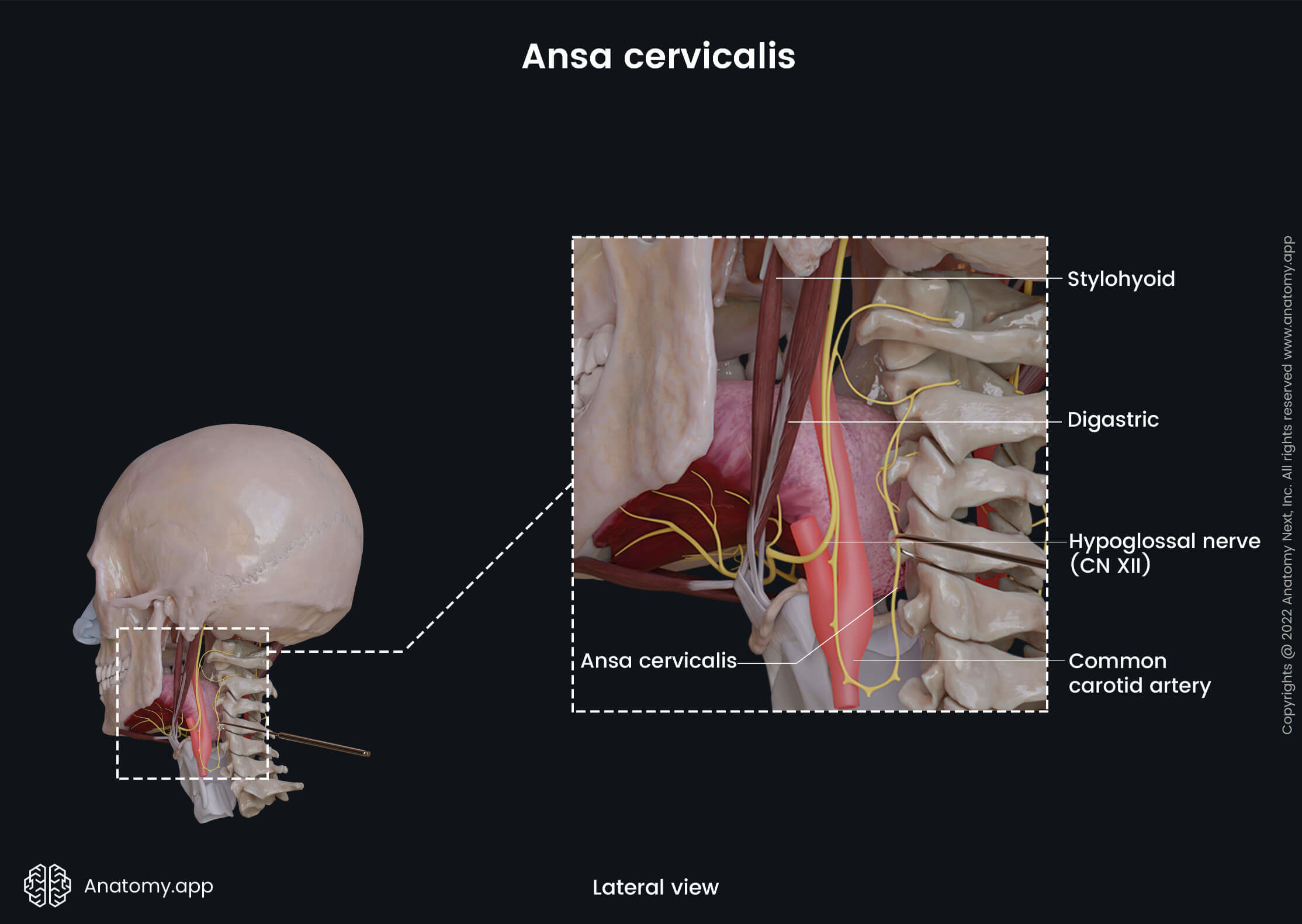
The ansa cervicalis is situated deep to the sternocleidomastoid and anterior to the carotid sheath within the carotid triangle. Overall, it gives four muscular branches that provide motor innervation to the infrahyoid muscles of the neck. The branches of the ansa cervicalis innervate almost all infrahyoid muscles, except the thyrohyoid that receives nerve supply from the first cervical spinal nerve (C1). The ansa cervicalis is formed by two roots - superior and inferior.
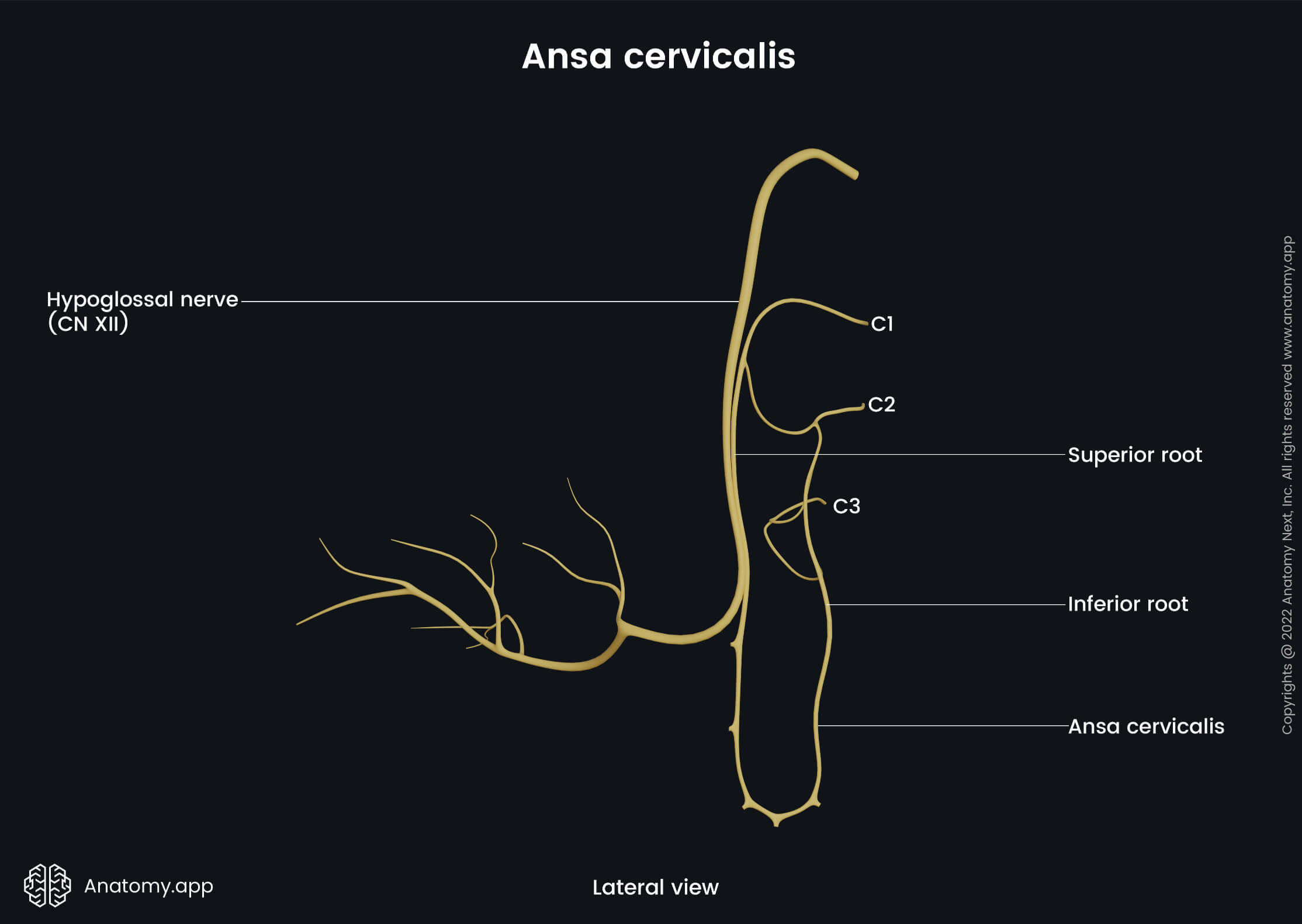
The superior root originates from the ventral ramus of the first cervical spinal nerve (C1). However, sometimes fibers from the ventral ramus of the second cervical spinal nerve (C2) also contribute. They pass posterior to the posterior belly of the digastric muscle together with the fibers of the hypoglossal nerve (CN XII). Eventually, these motor fibers branch off the hypoglossal nerve in the carotid triangle, creating the superior root of the ansa cervicalis. It should be noted that the superior root does not contain fibers from the hypoglossal nerve!
The superior root of the ansa cervicalis is sometimes also referred to as the ramus descendens hypoglossi. It branches off the hypoglossal nerve when it curves around the occipital artery. The superior root descends further anterior to the carotid sheath or as a part of it. After giving a branch to the superior belly of the omohyoid and branches to the upper aspects of the sternohyoid and sternothyroid muscles, the superior root unites with the inferior root of the ansa cervicalis.
The inferior root of the ansa cervicalis is formed by the ventral rami of the C2 and C3 spinal nerves. It provides branches to the inferior belly of the omohyoid muscle and lower aspects of the sternothyroid and sternohyoid muscles.
The inferior root is sometimes called the ramus descendens cervicalis. It passes inferiorly along the internal jugular vein on its anterolateral side. After crossing the vein roughly midway, the inferior root further goes anterior to it. Finally, it unites with the superior root of the ansa cervicalis anterior to the common carotid artery. Occasionally, the inferior root may travel between the common carotid artery and the internal jugular vein.
References:
- Gray, H., & Carter, H. (2021). Gray’s Anatomy (Leatherbound Classics) (Leatherbound Classic Collection) by F.R.S. Henry Gray (2011) Leather Bound (2010th Edition). Barnes & Noble.
- Tubbs, S. R., Rizk, E., Shoja, M., Loukas, M., Barbaro, N., & Spinner, R. J. (2015). Nerves and Nerve Injuries: Vol 1: History, Embryology, Anatomy, Imaging, and Diagnostics (1st ed.). Academic Press.
- Rea, P. (2016). Essential Clinically Applied Anatomy of the Peripheral Nervous System in the Head and Neck (1st ed.). Academic Press.