- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Head muscles
-
Neck muscles
- Superficial neck muscles
- Scalene muscles
- Suprahyoid muscles
- Infrahyoid muscles
- Prevertebral muscles
- Suboccipital muscles
- Muscles of upper limb
- Thoracic muscles
- Muscles of back
- Muscles of lower limb
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
Rectus capitis anterior
The rectus capitis anterior (Latin: musculus rectus capitis anterior) is a short muscle located anterior to the vertebral column. It stretches between the atlas and the base of the skull. The rectus capitis anterior is known as one of the prevertebral neck muscles. This muscle also belongs to the anterior neck muscles. The rectus capitis anterior provides the flexion of the head.
| Rectus capitis anterior | |
| Origin | Lateral mass and transverse process of atlas (C1) |
| Insertion | Basilar part of occipital bone |
| Action | Flexion of head at atlanto-occipital joint |
| Innervation | Anterior rami of 1st and 2nd cervical spinal nerves (C1 - C2) |
| Blood supply | Branches of vertebral and ascending pharyngeal arteries |
Origin
The rectus capitis anterior muscle originates from the anterior surface of the lateral mass and transverse process of the atlas (C1).
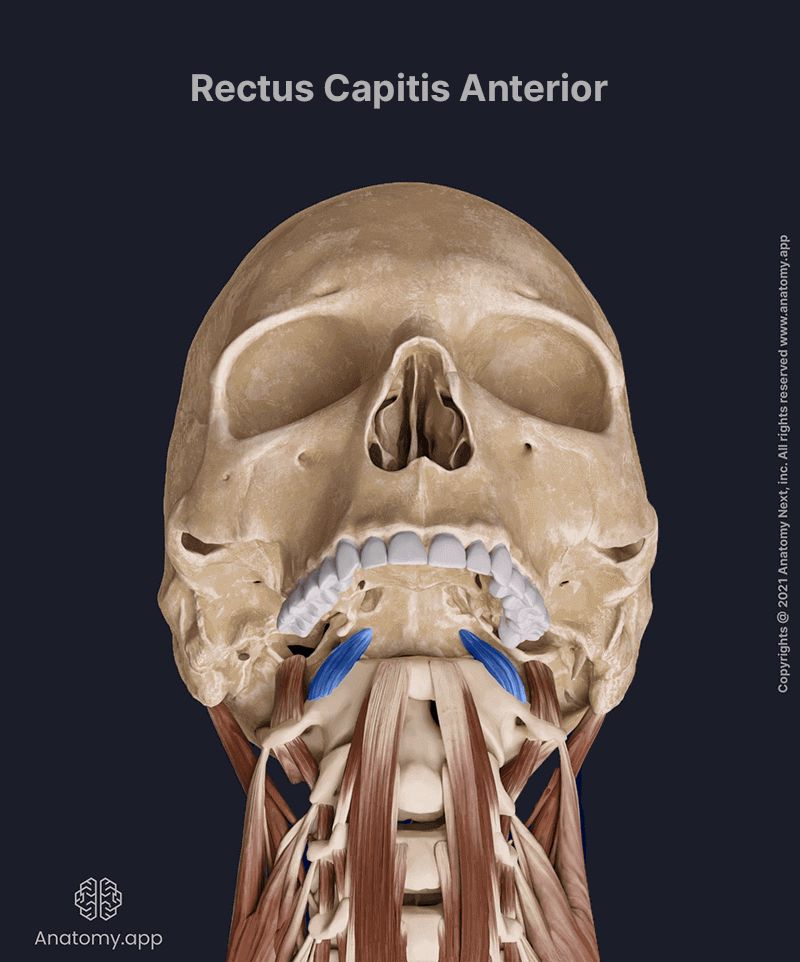
Insertion
The fibers of the rectus capitis anterior insert on the inferior surface of the basilar part of the occipital bone.
Action
Upon contraction, the rectus capitis anterior muscle aids in flexion of the head at the atlanto-occipital joint.
Innervation
The rectus capitis anterior is innervated by the branches arising from the loop between the anterior rami of the 1st and 2nd cervical spinal nerves (C1 - C2).
Blood supply
The rectus capitis anterior muscle receives arterial blood supply from the branches of the vertebral and ascending pharyngeal arteries. The first one is a branch of the subclavian artery, while the latter is a branch of the external carotid artery.