- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Skeleton of trunk
- Skull
-
Skeleton of upper limb
- Bones of shoulder girdle
- Humerus
- Bones of forearm
- Bones of hand
- Skeleton of lower limb
- Joints
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
Radius
The radius (Latin: radius) is one of the long bones located in the forearm. It is also known as the radial bone. The radius extends from the lateral side of the elbow to the thumb side of the wrist. It lies next to the ulna, which is the other bone of the forearm.
The radius has several articulations, and it forms four joints. Two joints are located at the proximal end, including the elbow and proximal radioulnar joints. While two other joints are located at the distal end and they are the wrist and distal radioulnar joints.
The elbow joint is partly formed by an articulation between the head of the radius and the capitulum of the humerus. The proximal radioulnar joint is an articulation between the head of the radius and the radial notch of the ulna.
The distal radioulnar joint is formed by an articulation between the ulnar notch of the radius and the head of the ulna. While the wrist joint is an articulation between the distal end of the radius and the carpal bones.
Like other long bones of the human body, the radius also consists of three main parts: a proximal epiphysis or proximal end, a shaft or diaphysis, and a distal epiphysis or distal end. All parts present with essential anatomical landmarks.
Proximal epiphysis of radius
The proximal epiphysis or end of the radius is the extremity that is located closer to the humerus and faces it. Its significant features include the head of the radius and neck. The proximal extremity participates in the formation of the elbow joint.
The head of the radius is a disc-shaped structure that has a concave surface for articulation with the capitulum of the humerus. The head of the radius also contains an articular circumference for the articulation with the ulna.
The medial part of the head of the radius articulates with the radial notch located on the proximal end of the ulna. This articulation between both bones is known as the proximal radioulnar joint.
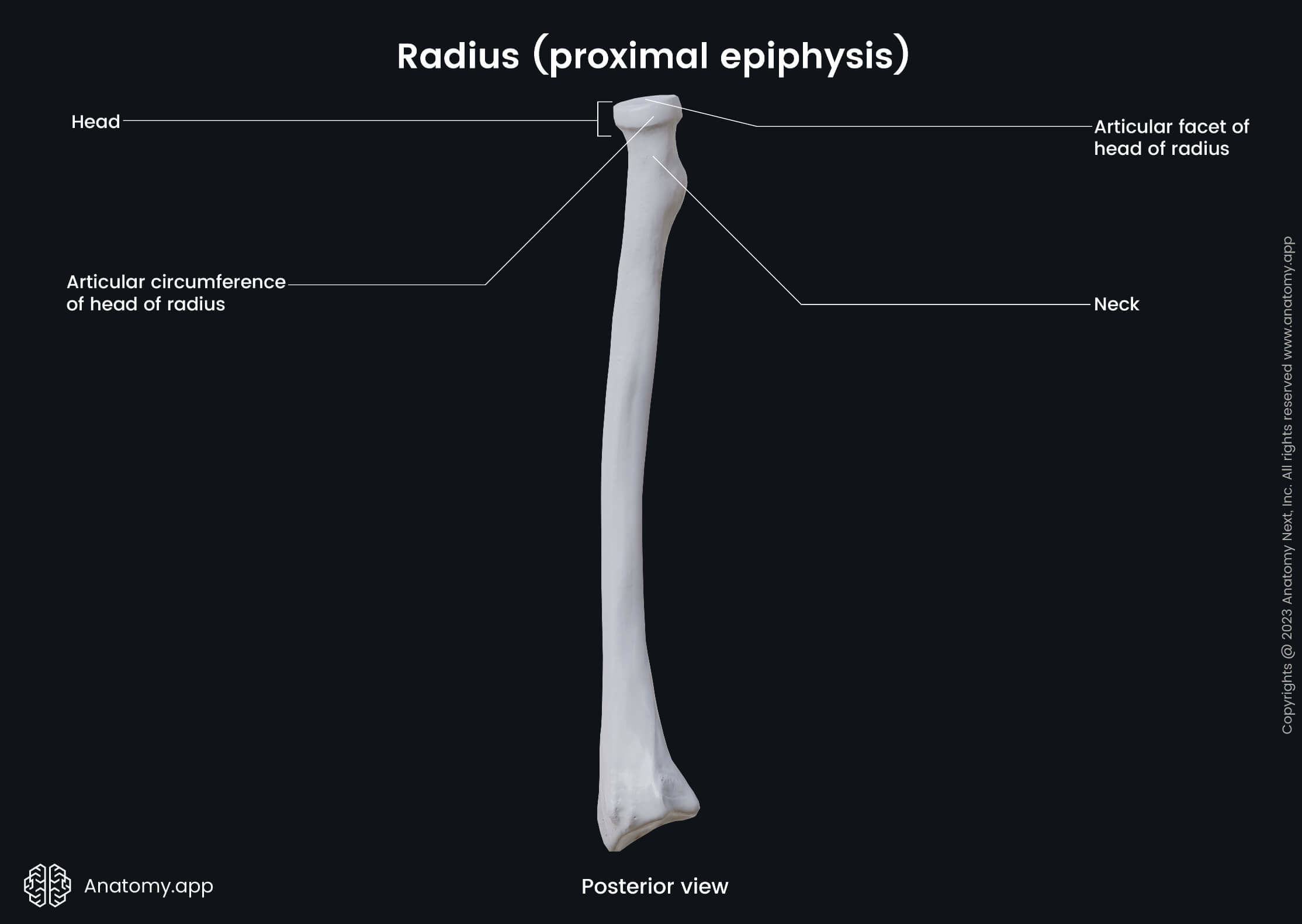
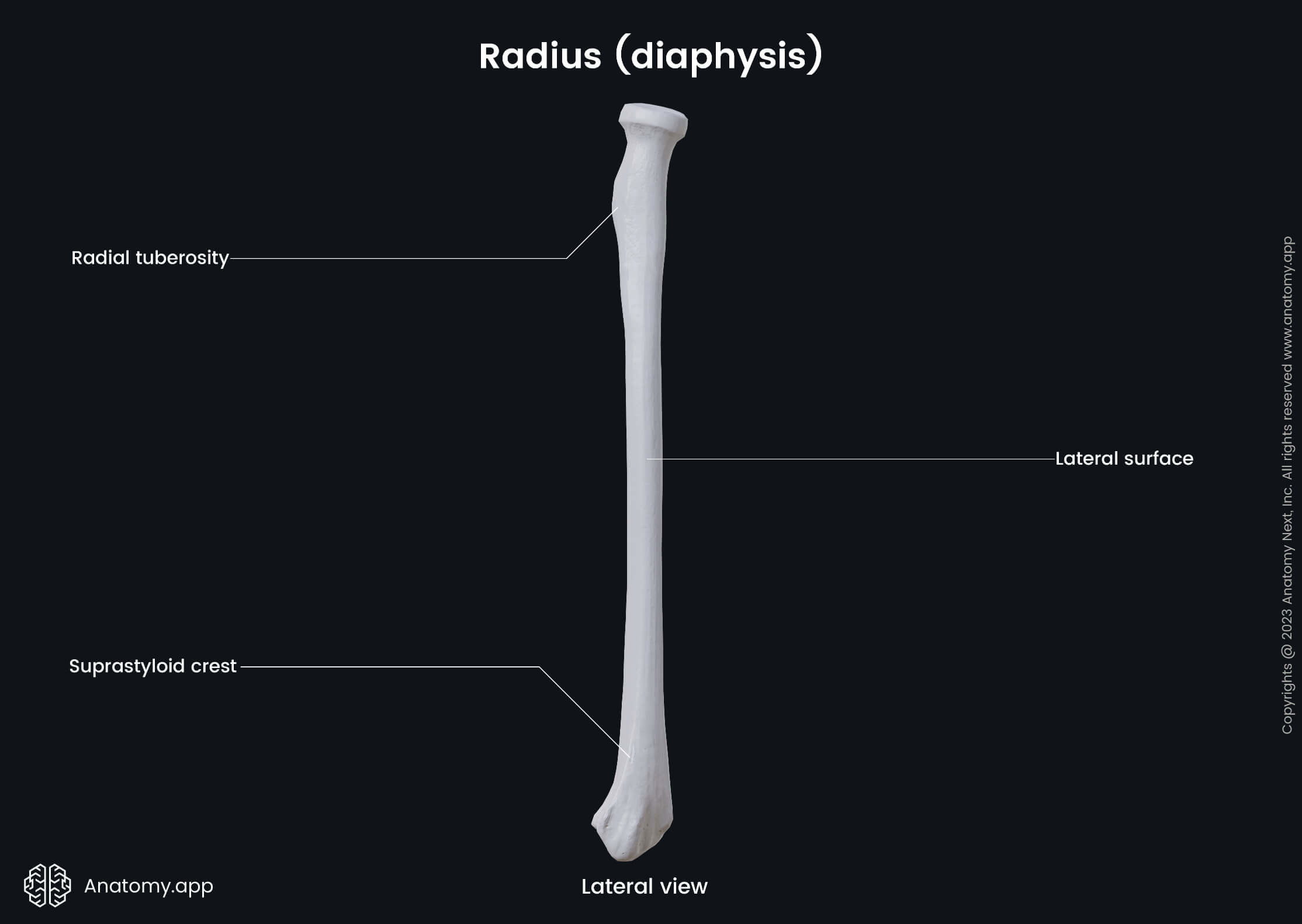
Below the head of the radius is located the neck of the radius. It is a narrow constriction situated distal to the head of the radius between the head and the radial tuberosity of the radius.
The radial tuberosity is also referred to as the bicipital tuberosity. It is an oval and convex bony eminence located just below the neck of the radius on its medial aspect. The biceps brachii muscle inserts here.
Diaphysis of radius
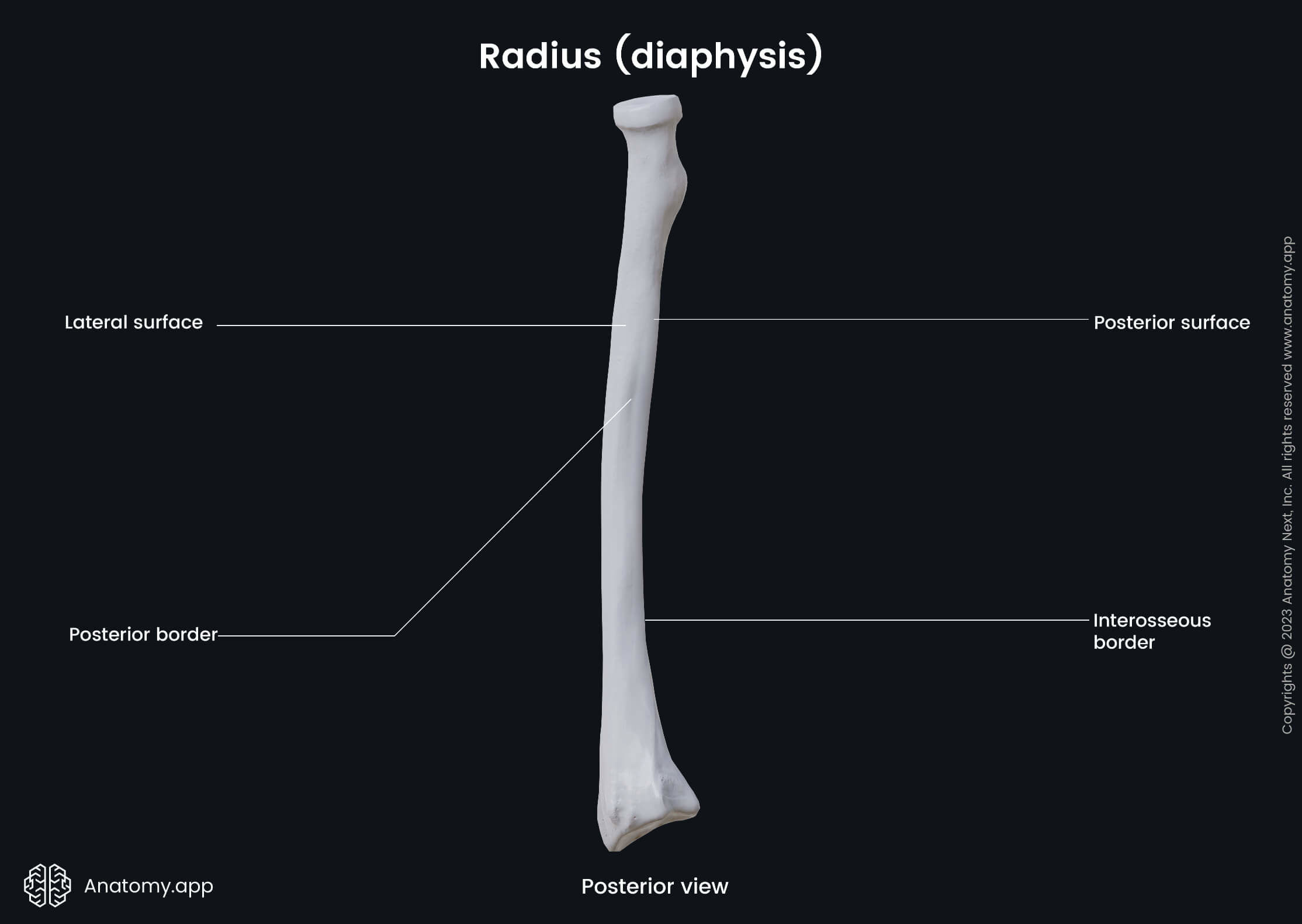
The diaphysis or the shaft of the radius is the long middle part of the bone, and it has the shape of a triangular prism. The radial shaft is convex on the lateral side, and it enlarges and expands in diameter towards the wrist.
The radial shaft presents with three borders - anterior, posterior and interosseous borders. It also has three surfaces - anterior, posterior and lateral surfaces. Several important anatomical landmarks are found on the radial shaft, and on these landmarks originate and insert muscle tendons.
Laterally two muscles of the forearm are attached to the radial shaft, and these muscles are:
- Supinator - attaches to the lateral aspect of the shaft, covering a significant part of it;
- Pronator teres - attaches below the attachment of the supinator; it inserts on the pronator tuberosity that is a rough area located in the middle of the lateral surface.
The posterior surface of the radial shaft serves as an origin site for two muscles:
- Abductor pollicis longus - originates just below the posterior margin of the attachment of the supinator muscle;
- Extensor pollicis longus - originates more distally from the previous muscle.
Two muscles are found anteriorly, and they include:
- Flexor digitorum superficialis - origins from the proximal half of the anterior border;
- Flexor pollicis longus - originates just below the origin site of the flexor digitorum superficialis.
Muscles that insert on the lateral surface of the radial shaft are as follows:
- Pronator quadratus - covers the distal end of the lateral surface of the shaft;
- Brachioradialis - inserts slightly inferior to the pronator quadratus and on the opposite side of it.
Distal end of radius
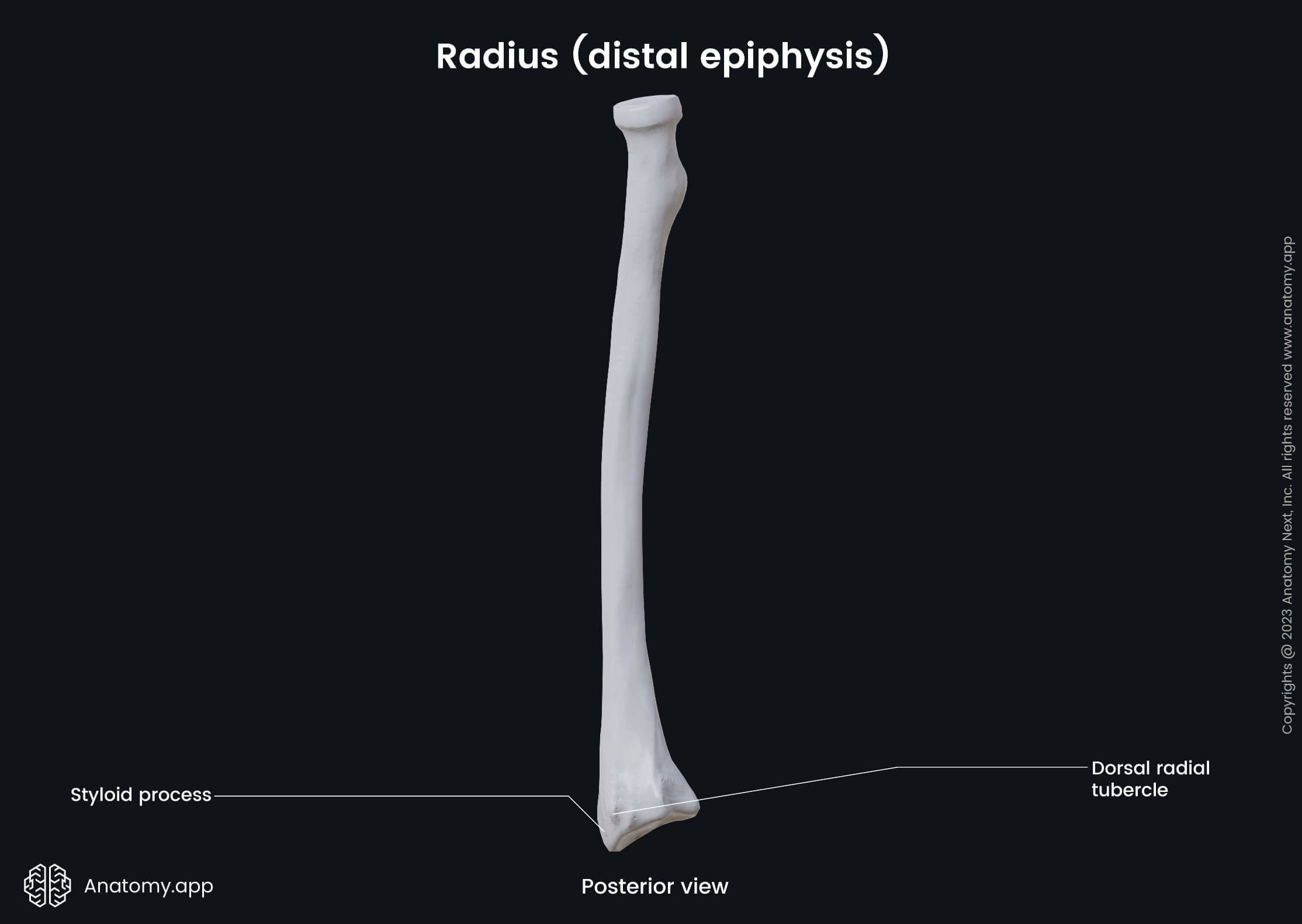
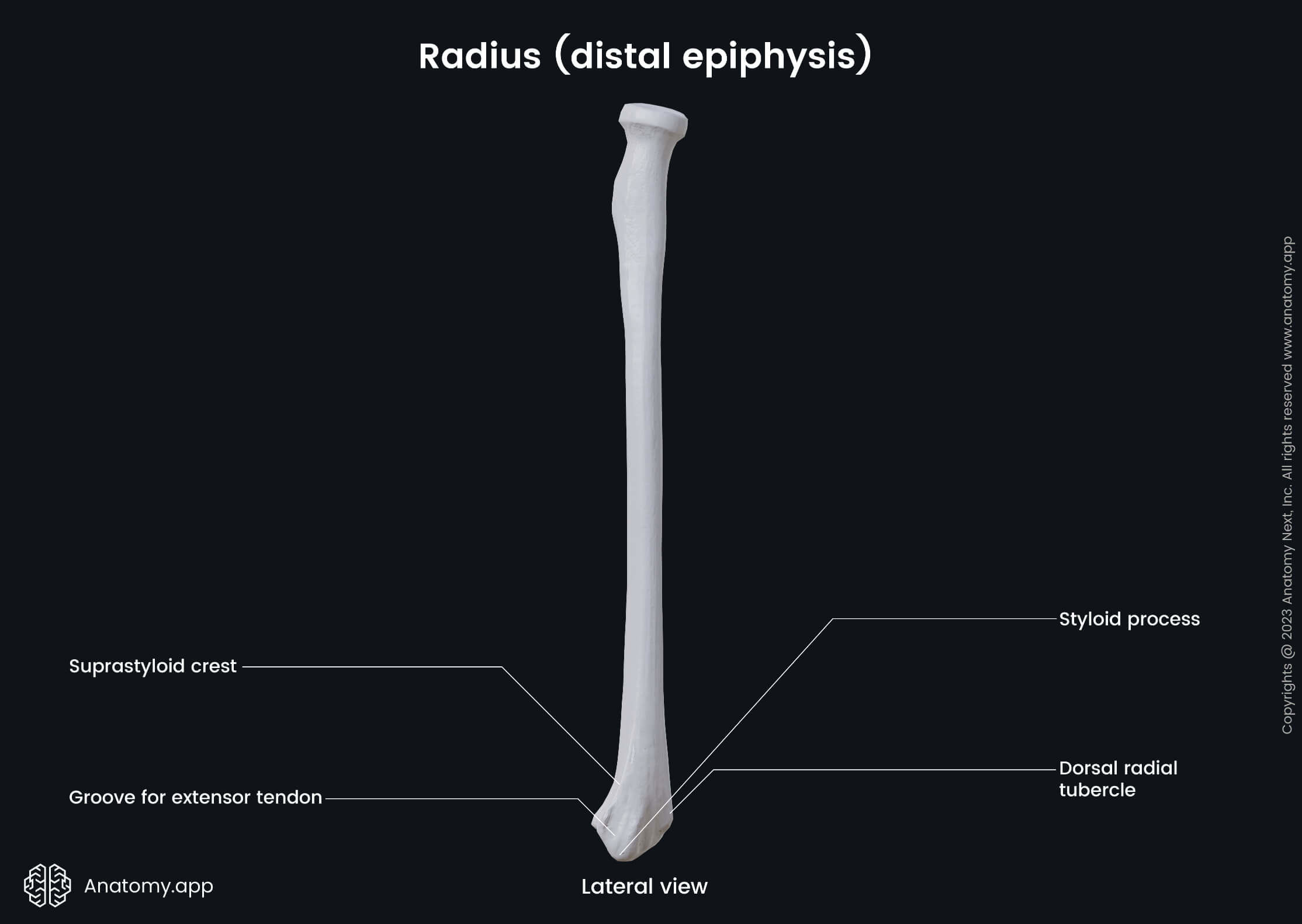
The distal epiphysis or distal end of the radius is located closer to the wrist. Like other parts of the radius, it also contains several essential landmarks, including the dorsal tubercle and ulnar notch.
The dorsal tubercle is a bony projection on the posterior aspect of the distal end. It lies between the grooves for the tendons of the extensor carpi radialis longus and brevis, and the tendon of the extensor pollicis longus muscle.
The ulnar notch is a narrow concavity found on the medial aspect of the distal end of the radius. It articulates with the head of the ulna, and both bones together form the distal radioulnar joint.
The lateral side of the distal end is prolonged downward as a projection that is known as the radial styloid process. It serves as an attachment site for the tendon of the brachioradialis muscle.