- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Head muscles
- Neck muscles
- Muscles of upper limb
- Muscles of pectoral girdle
- Muscles of shoulder region
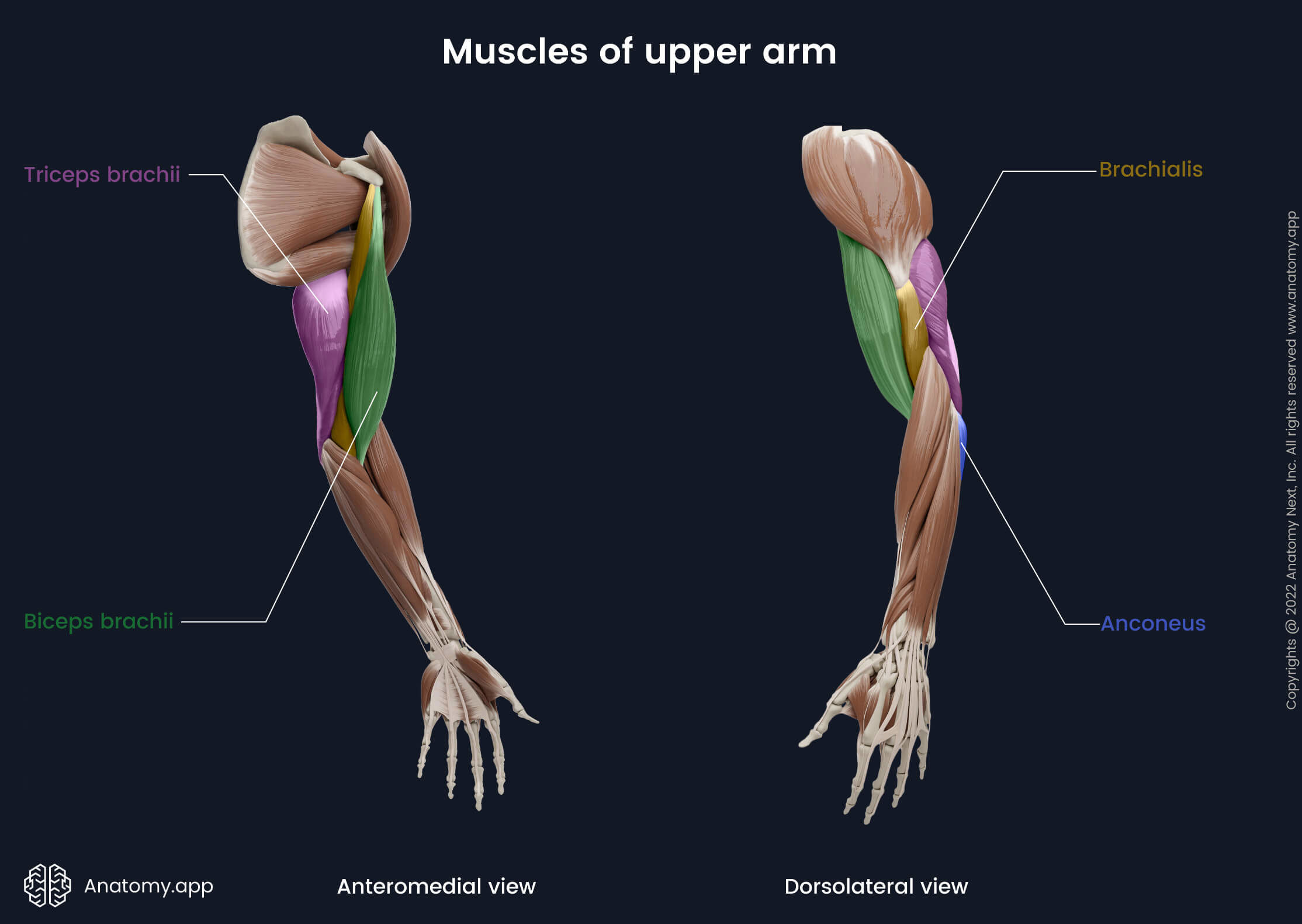
- Muscles of upper arm
- Anterior compartment
- Posterior compartment
- Muscles of forearm
- Muscles of hand
- Thoracic muscles
- Muscles of back
- Muscles of lower limb
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
Biceps brachii
The biceps brachii (Latin: musculus biceps brachii) is a sizable two-headed muscle of the upper limb. It is located in the anterior compartment of the upper arm together with the brachialis and coracobrachialis muscles. The biceps brachii stretches between the scapula and radius and acts at the shoulder and elbow joints. It is the most prominent and essential muscle of the anterior upper arm. The biceps brachii is composed of two heads, named the long and short heads.
| Biceps brachii | |
| Origin | Long head - supraglenoid tubercle of scapula Short head - coracoid process of scapula |
| Insertion | Radial tuberosity of radius Deep fascia of forearm (bicipital aponeurosis) |
| Action | Entire muscle - flexion and supination of forearm Long head - abduction of arm Short head - flexion of arm |
| Innervation | Musculocutaneous nerve (C5 - C6) |
| Blood supply | Brachial artery |
Origin
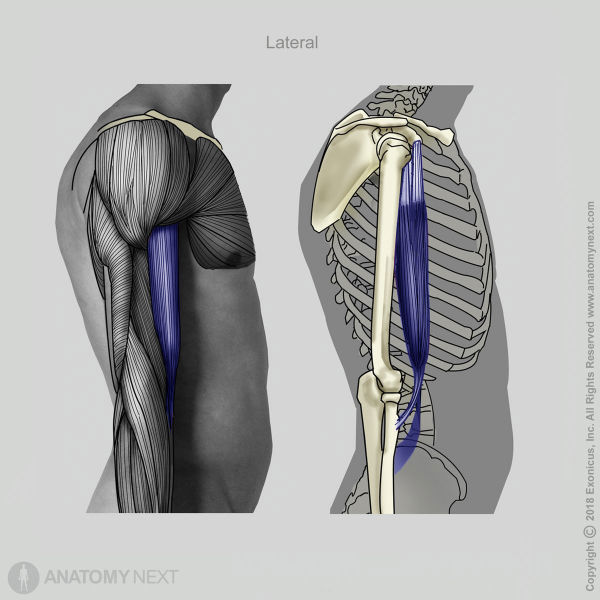
The long head of the biceps brachii originates from the supraglenoid tubercle of the scapula, while the short head arises from the coracoid process of the scapula.
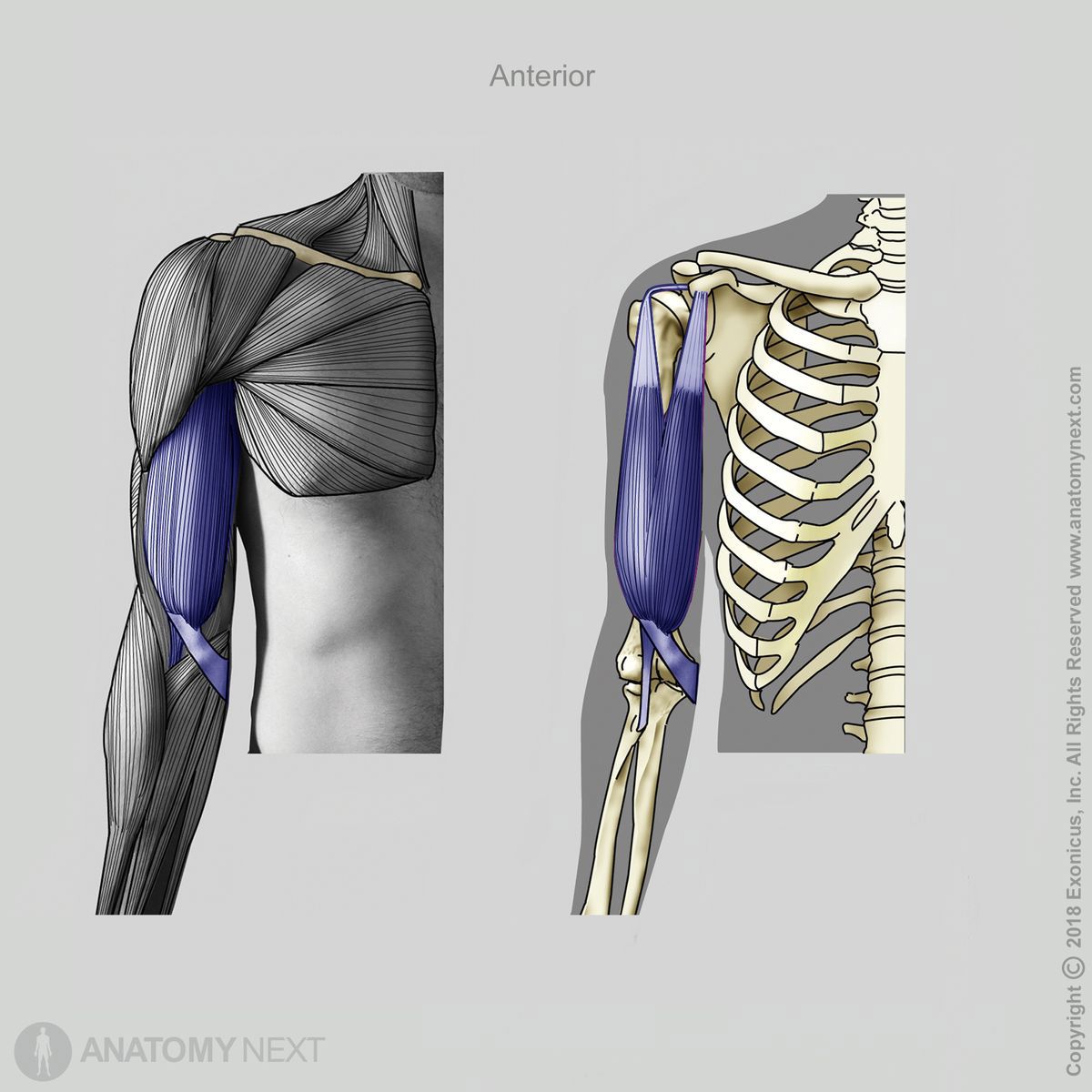
Insertion
Fibers of both heads merge at the anterior middle aspect of the humerus and insert on the radial tuberosity of the radius. The bicipital aponeurosis - connective tissue membrane - arises from the distal portion of the muscle and inserts into the deep fascia of the forearm.
Action
The primary functions of the biceps brachii muscle are flexion and supination of the forearm at the elbow joint. Fibers of the short head provide flexion of the arm, while fibers of the long head are responsible for abduction of the arm.
Innervation
The biceps brachii is innervated by the musculocutaneous nerve (C5 - C6) that is a branch of the brachial plexus.
Blood supply
The biceps brachii muscle receives arterial blood supply from various branches of the brachial artery.