- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Aorta
- Blood vessels of head and neck
- Arteries of head and neck
- Veins of head and neck
- Blood vessels of upper limb
- Blood vessels of thorax
- Blood vessels of abdomen
- Blood vessels of pelvis and lower limb
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
Posterior communicating artery
The posterior communicating artery (Latin: arteria communicans posterior) is a branch of the internal carotid artery that supplies several brain regions. This artery participates in forming the circle of Willis.
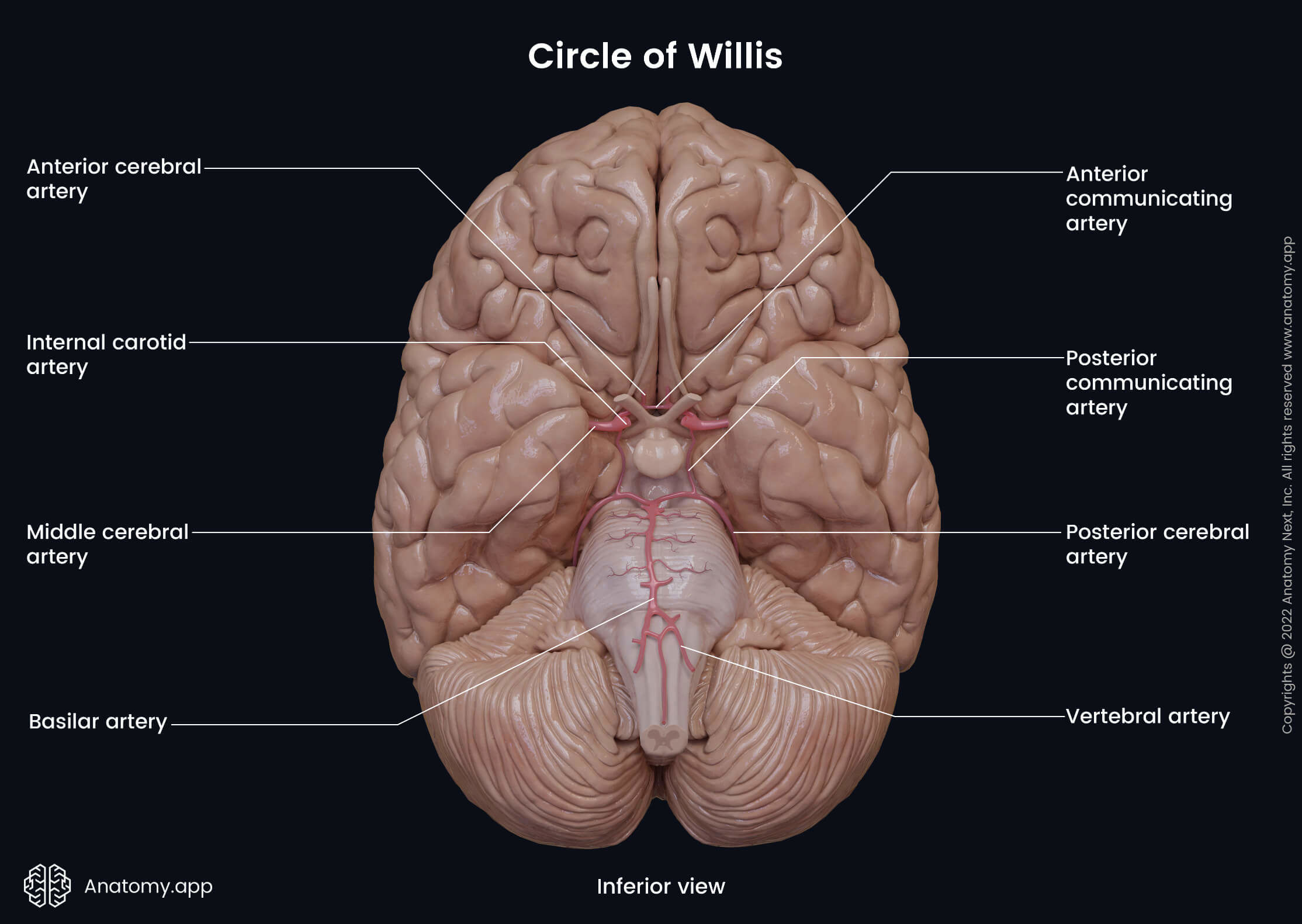
The posterior communicating artery arises from the posterior aspect of the internal carotid artery. It passes backward above the oculomotor nerve (CN III) and anastomoses with the posterior cerebral artery, forming the circulus arteriosus or the circle of Willis around the interpeduncular fossa. The posterior communicating artery connects the internal carotid artery, anterior cerebral and middle cerebral arteries, and the posterior cerebral artery with each other.
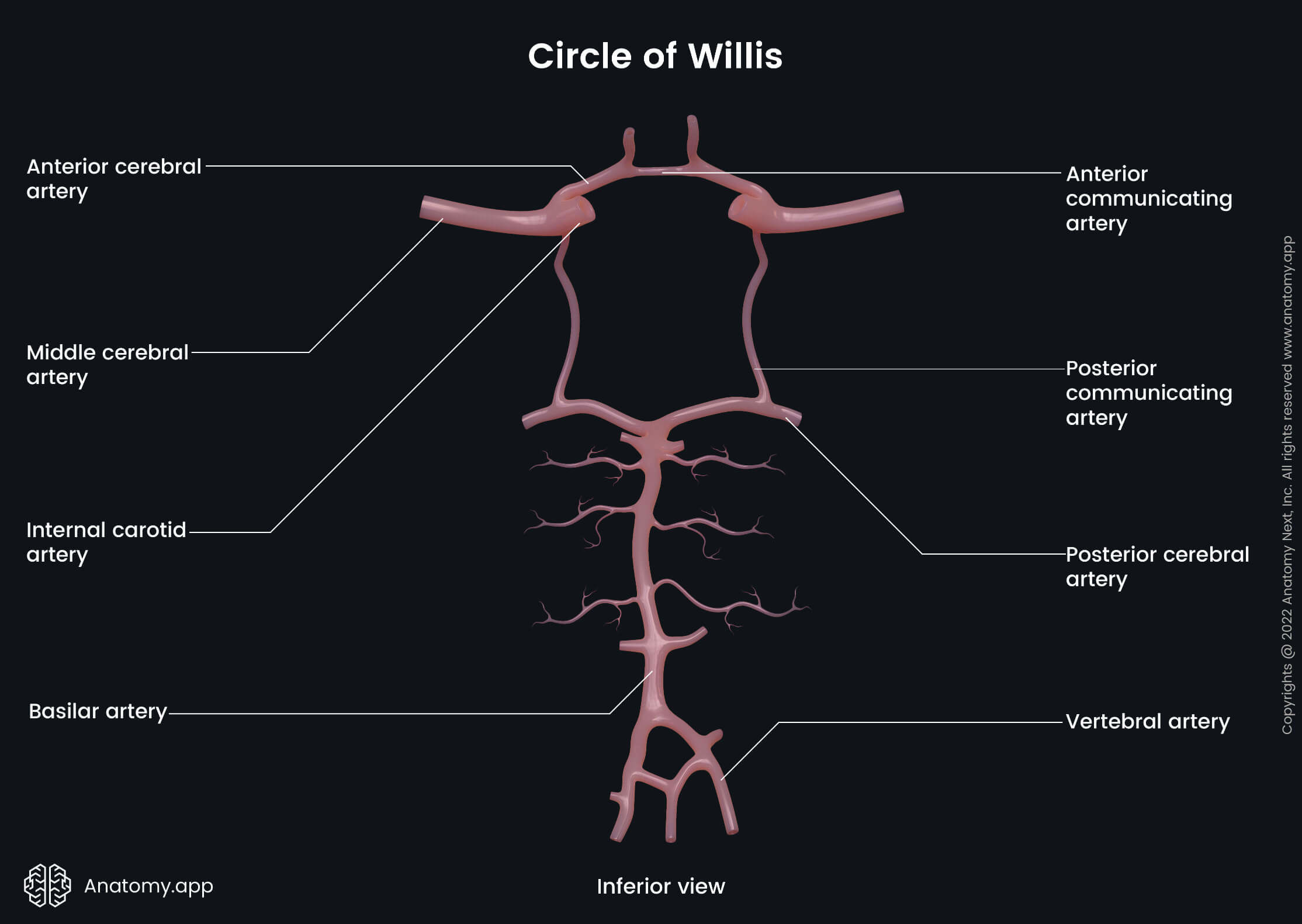
The posterior communicating artery provides blood supply to the medial thalamic surface and the walls of the third ventricle. Small side branches arise from the artery to supply the posterior perforated substance.