- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Aorta
- Blood vessels of head and neck
- Arteries of head and neck
- Veins of head and neck
- Blood vessels of upper limb
- Blood vessels of thorax
- Blood vessels of abdomen
- Blood vessels of pelvis and lower limb
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
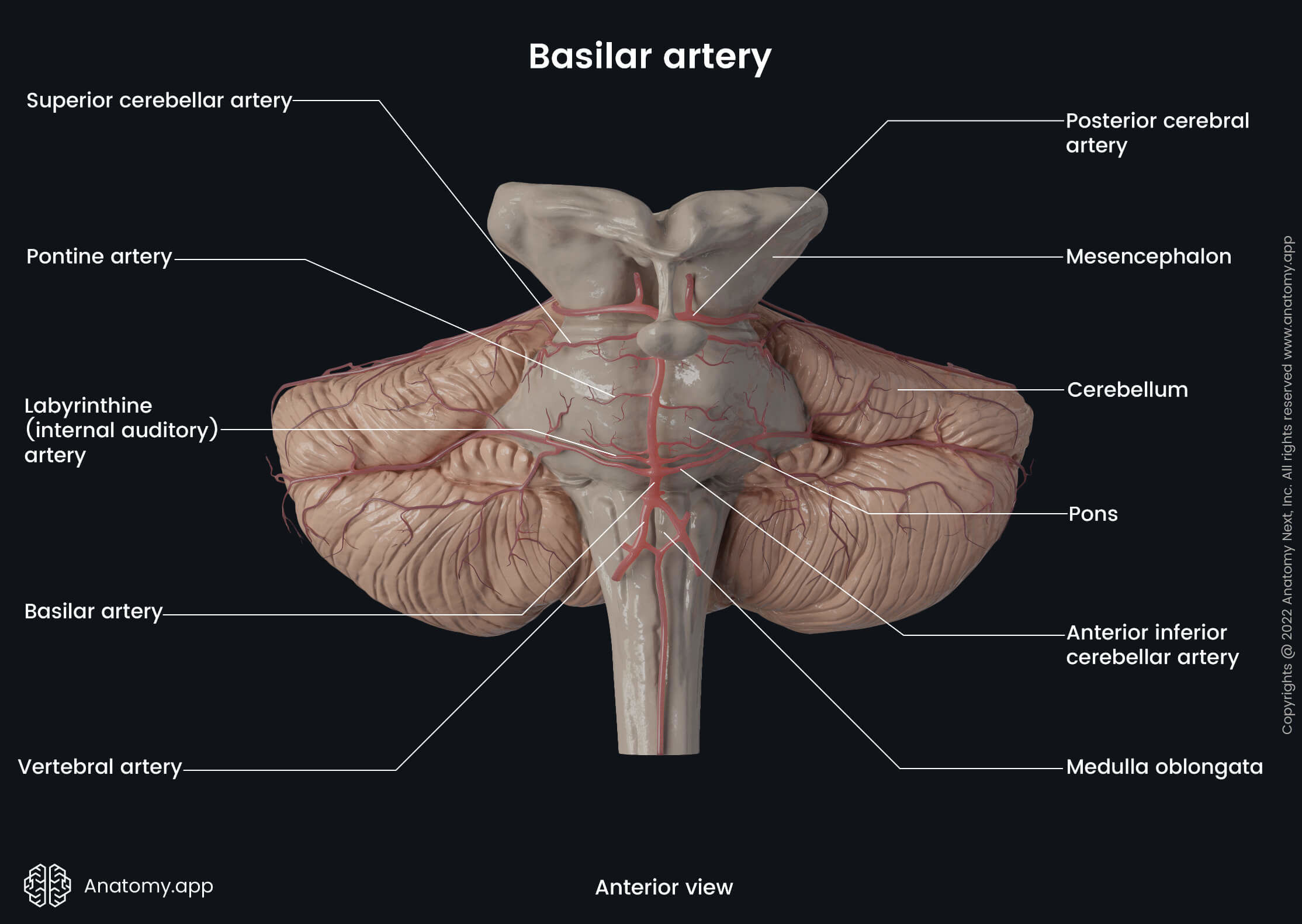
Posterior cerebral artery
The posterior cerebral artery (PCA, Latin: arteria cerebri posterior) is the terminal branch of the basilar artery. It supplies arterial blood to the occipital, temporal lobes of the brain and visual areas of the cerebral cortex. The artery also provides blood supply to several subcortical structures of the cerebrum.
From its origin, the posterior cerebral artery curves laterally receiving the posterior communicating artery. Then the vessel passes posteriorly around the cerebral peduncle of the midbrain to reach the tentorial cerebral surface, where it supplies the temporal and occipital lobes. The PCA has cortical and central branches. The cortical branches of the posterior cerebral artery are as follows:
- Temporal branches
- Occipital branches
- Parieto-occipital branches
The temporal branches of the PCA supply the following areas of the brain: uncus, parahippocampal, medial and lateral occipitotemporal gyri. The occipital branches supply the cuneus, lingual gyrus, and posterolateral surface of the occipital lobe. And the parieto-occipital branches supply the cuneus and precuneus.
The central branches of the PCA include the following:
- Posteromedial central branches
- Posterior choroidal branches
- Posterolateral central branches
The posteromedial central branches of the posterior cerebral artery supply the anterior thalamus, subthalamus, lateral wall of the third ventricle, and globus pallidus. The posterior choroidal branches supply the lateral geniculate body, choroid plexuses of the third and lateral ventricles, and the fornix. And the posterolateral central branches supply the cerebellar peduncles, posterior thalamus, superior and inferior colliculi of the midbrain, pineal gland, and medial geniculate body.