- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Aorta
- Blood vessels of head and neck
- Arteries of head and neck
- Veins of head and neck
- Blood vessels of upper limb
- Blood vessels of thorax
- Blood vessels of abdomen
- Blood vessels of pelvis and lower limb
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
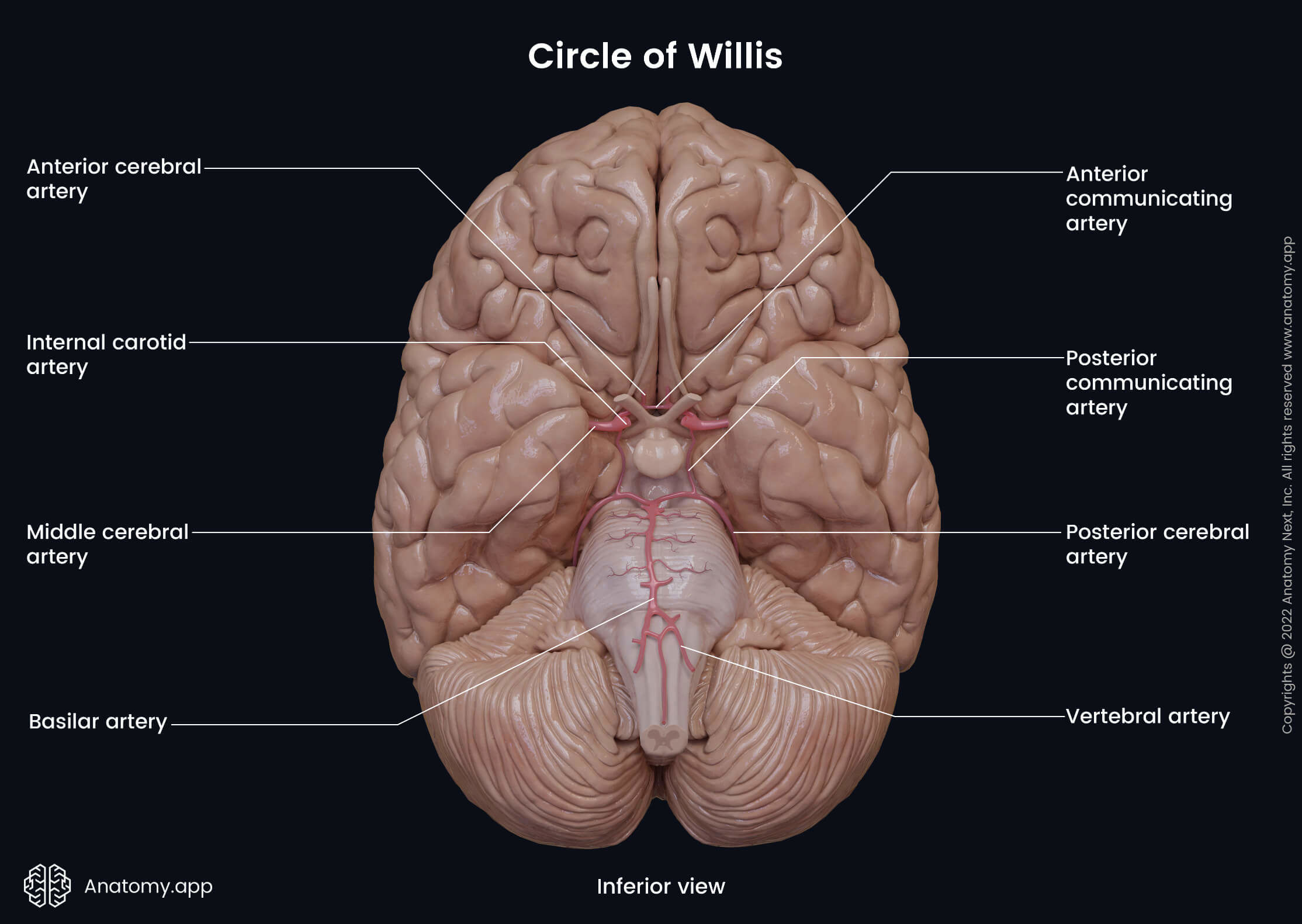
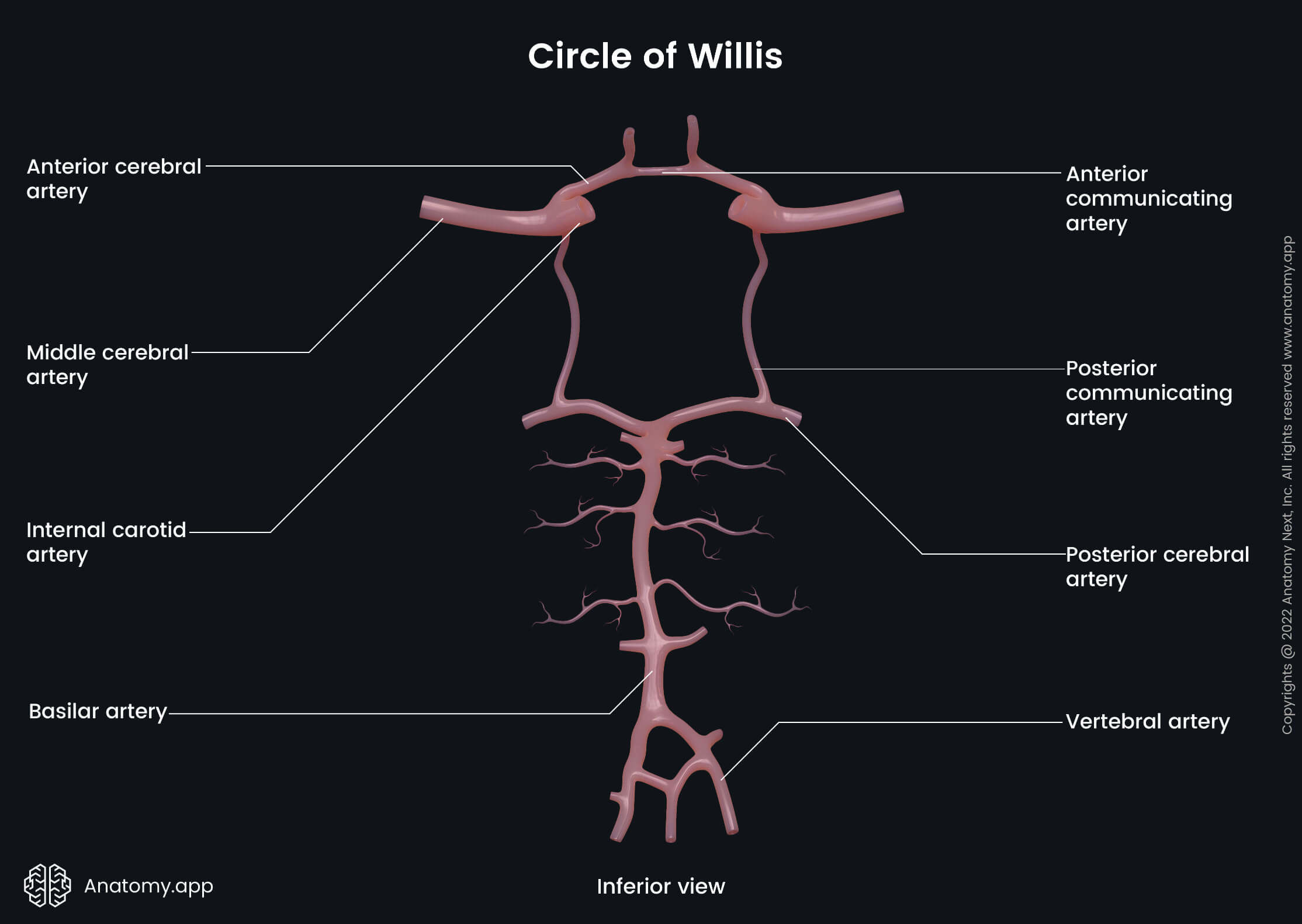
Middle cerebral artery
The middle cerebral artery (MCA, Latin: arteria cerebri media) is one of the terminal branches of the internal carotid artery. It supplies cortical and subcortical regions of the cerebral hemispheres.
Course of MCA
From its origin, the middle cerebral artery continues into the lateral sulcus of the cerebrum. It ascends posteriorly on the insula and divides into branches that project to the lateral aspect of the cerebral cortex.
Branches of MCA
The middle cerebral artery gives off central and cortical branches. The central branches are distributed to subcortical structures of the cerebrum. They include the lenticulostriate arteries that supply such subcortical structures as the lentiform complex, internal capsule, and caudate nucleus.
The cortical branches of the middle cerebral artery supply blood to such cortical structures as the motor and somatosensory cortices, auditory area of the cerebral cortex. The cortical branches of the MCA include the following:
- Orbital branches
- Frontal branches
- Parietal branches
- Temporal branches
The orbital branches of the middle cerebral artery supply the inferior frontal gyrus, as well as the lateral orbital surface of the frontal lobe. The frontal branches supply the precentral, middle, and inferior frontal gyri. The parietal branches supply the postcentral gyrus, inferior parietal lobule, and lower part of the superior parietal lobule. And the temporal branches of the middle cerebral artery are distributed to the lateral surface of the temporal lobe.