- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Head muscles
- Neck muscles
- Muscles of upper limb
- Thoracic muscles
- Muscles of back
- Superficial back muscles
- Intermediate back muscles
- Deep back muscles
- Superficial layer
- Intermediate layer (Erector Spinae)
- Deep layer (Transversospinales)
- Deepest layer
- Muscles of lower limb
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
Splenius capitis
The splenius capitis (Latin: musculus splenius capitis) is a broad strap-like deep back muscle located in the back of the neck. It stretches between the spinous processes of the cervical and thoracic vertebrae and the temporal and occipital bones of the skull. Together with the splenius cervicis, the splenius capitis forms the superficial layer of the deep or intrinsic muscles of the back. The upper part of the muscle lies deep below the sternocleidomastoid, and it participates in forming the floor of the posterior (lateral) neck triangle. The lower part of the muscle is covered by the trapezius. The splenius capitis lies superior to the semispinalis capitis and longissimus capitis muscles.
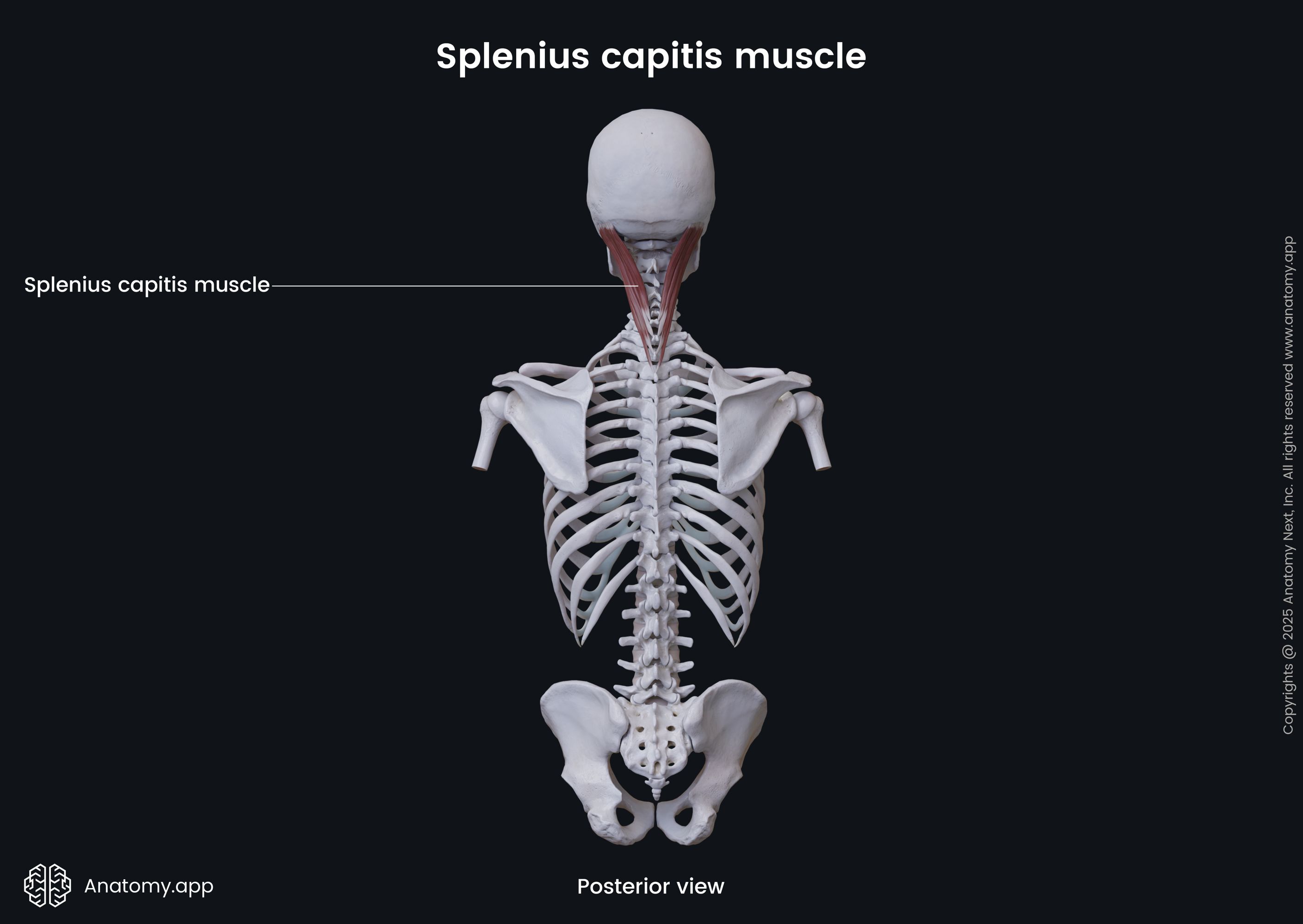
| Splenius capitis | |
|---|---|
| Origin | Lower half of nuchal ligament, spinous processes of C7 - T3 vertebrae |
| Insertion | Mastoid process of temporal bone, external surface of occipital bone below lateral aspect of superior nuchal line |
| Action | Bilateral contractions - extension of head and neck Unilateral contractions - ipsilateral rotation and lateral flexion of head and neck |
| Innervation | Lateral branches of dorsal rami of C2 - C3 spinal nerves |
| Blood supply | Branches of occipital artery |
Origin
The splenius capitis muscle originates from the lower half of the nuchal ligament and the spinous processes of the seventh cervical to third thoracic vertebrae (C7 - T3).
Insertion
The fibers of the splenius capitis insert on the mastoid process of the temporal bone and the adjacent occipital bone - on its external surface just below the lateral aspect of the superior nuchal line.
Action
Muscle contractions on both sides (bilateral contractions) extend the head and neck. Contractions on one side (unilateral contractions) rotate and lateral flex the head and neck to the same side (ipsilateral).
Innervation
The splenius capitis is innervated by the lateral branches of the dorsal rami of the second to third cervical spinal nerves (C2 - C3).
Blood supply
The splenius capitis muscle receives arterial blood supply from the branches of the occipital artery that arises from the external carotid artery.