- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Head muscles
- Neck muscles
- Muscles of upper limb
- Thoracic muscles
- Muscles of back
- Superficial back muscles
- Intermediate back muscles
- Deep back muscles
- Superficial layer
- Intermediate layer (Erector Spinae)
- Deep layer (Transversospinales)
- Deepest layer
- Muscles of lower limb
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
Splenius cervicis
The splenius cervicis (Latin: musculus splenius cervicis), also known as the splenius colli, is a paired long and relatively thin deep muscle of the back that is located in the back of the neck. It stretches between the spinous processes of the thoracic vertebrae and transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae. Together with the splenius capitis, the splenius cervicis lie in the superficial layer of the deep back muscles.
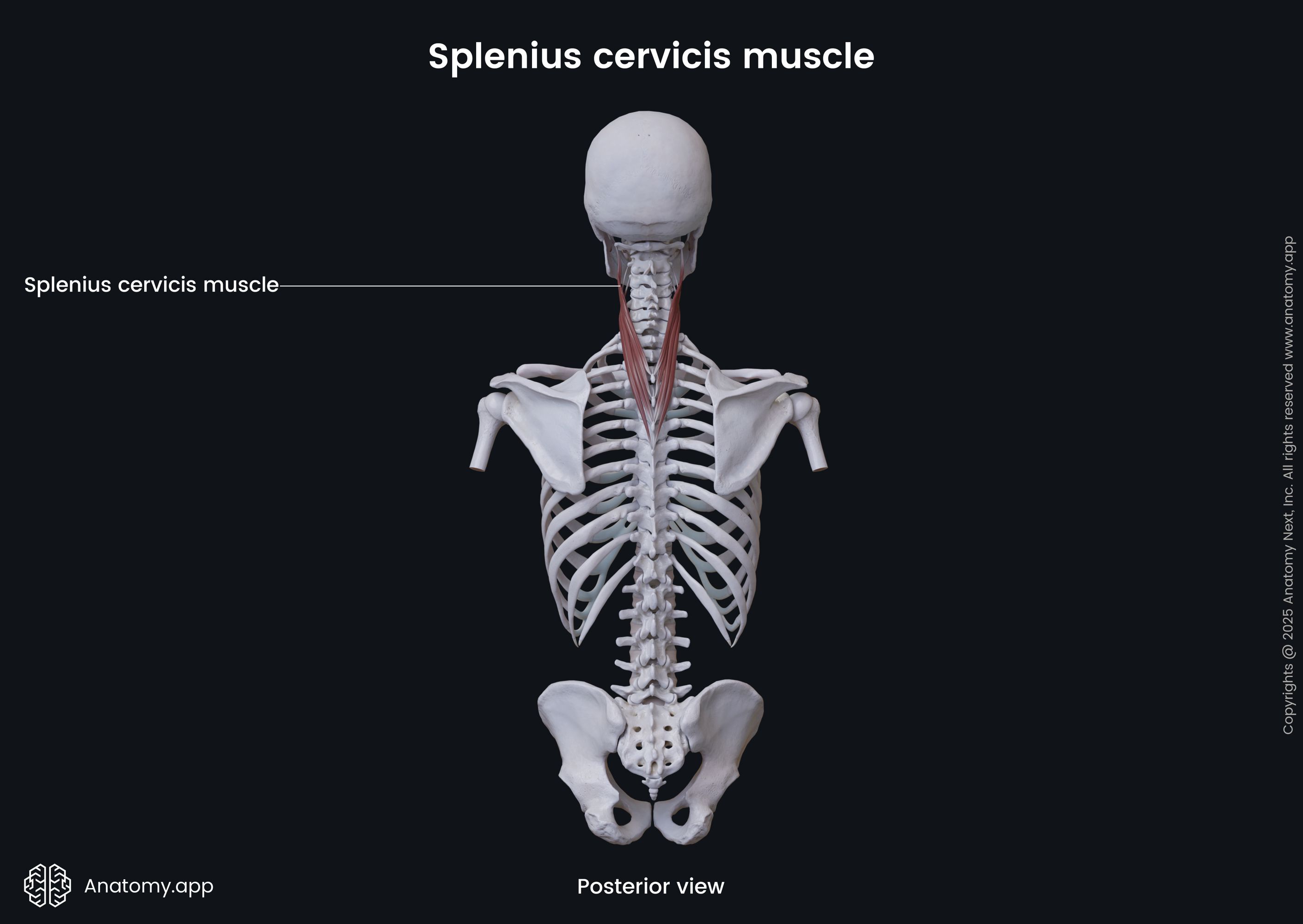
| Splenius cervicis | |
|---|---|
| Origin | Spinous processes of T3 - T6 vertebrae |
| Insertion | Transverse processes of C1 - C3 vertebrae |
| Action | Bilateral contractions - extension of neck Unilateral contractions - ipsilateral rotation and lateral flexion of neck |
| Innervation | Dorsal rami of lower cervical spinal nerves |
| Blood supply | Occipital, transverse cervical and deep cervical arteries |
Origin
The splenius cervicis muscle originates from the spinous processes of the third to sixth thoracic vertebrae (T3 - T6).
Insertion
The fibers of the splenius cervicis insert on the posterior tubercles of the transverse process of the first to third cervical vertebrae (C1 - C3).
Action
Muscle contractions on both sides (bilateral contractions) extend the neck. Muscle contractions on one side (unilateral contractions) rotate and lateral flex the neck to the same side (ipsilateral).
Innervation
The splenius cervicis is innervated by the dorsal rami of the lower cervical spinal nerves that arise from the cervical plexus.
Blood supply
The splenius cervicis muscle receives arterial blood supply mainly from the occipital, transverse cervical and deep cervical arteries. The occipital artery arises from the external carotid artery, the transverse cervical artery is a branch of the thyrocervical trunk, while the deep cervical artery originates from the costocervical trunk.