- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Aorta
- Blood vessels of head and neck
- Arteries of head and neck
- Veins of head and neck
- Veins of head
- Extracranial veins
- Intracranial veins
- Veins of neck
- Veins of head
- Blood vessels of upper limb
- Blood vessels of thorax
- Blood vessels of abdomen
- Blood vessels of pelvis and lower limb
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
Pterygoid venous plexus
The pterygoid venous plexus is an extensive network of veins found in the infratemporal fossa. It forms comprehensive connections with the surrounding veins and other anatomical structures and has clinical significance in transmitting infections.
The pterygoid venous plexus is positioned between the temporalis and lateral pterygoid. In fact, this plexus is located partly between the temporalis and lateral pterygoid and partly between the lateral pterygoid and medial pterygoid.
The pterygoid venous plexus surrounds the pterygoid part of the maxillary artery. Therefore, the tributaries of this plexus go along with the branches of the maxillary artery, and some of their names correspond to the names of the branches of the maxillary artery.
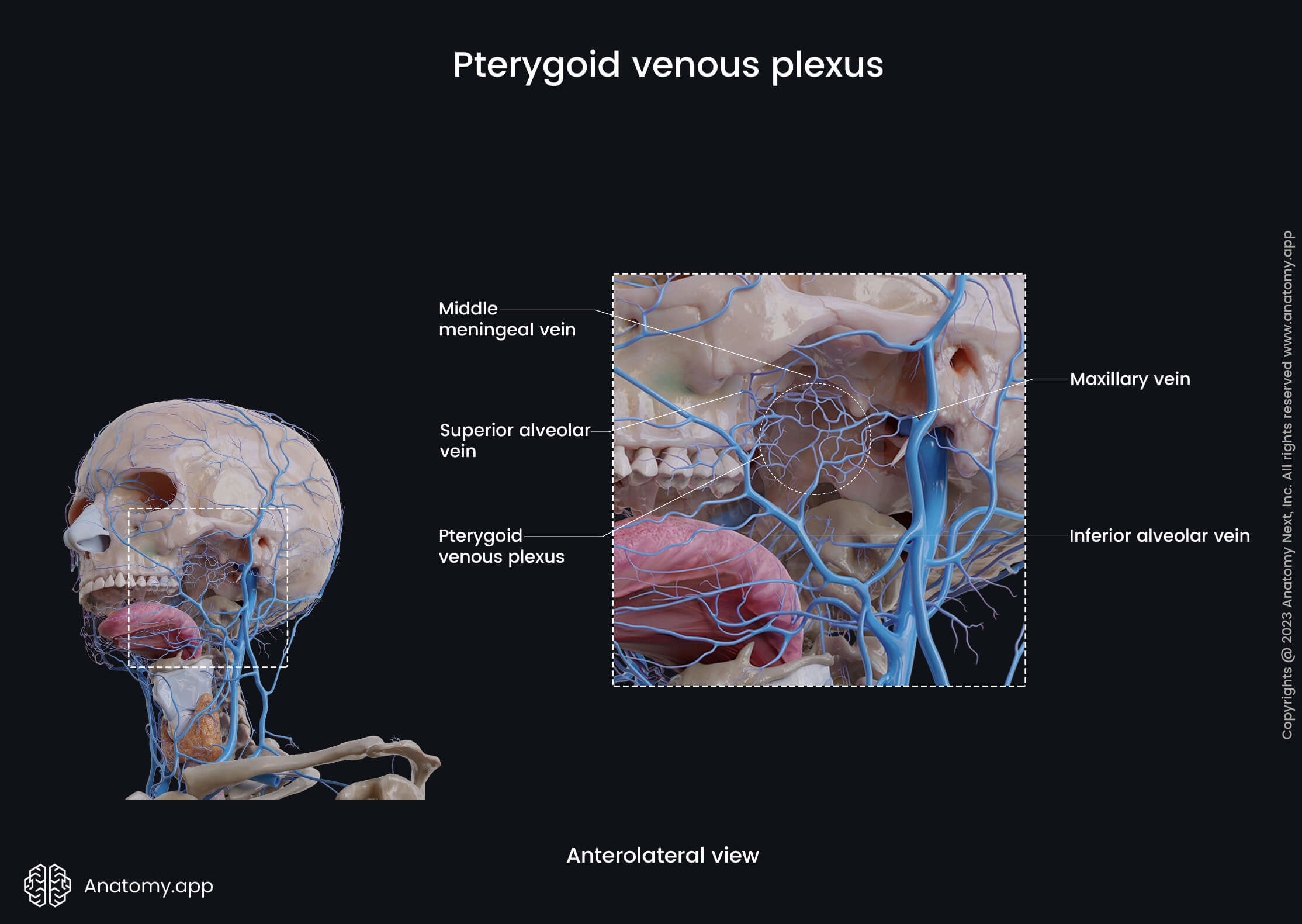
The main tributaries of the pterygoid venous plexus include the following veins:
- Sphenopalatine vein
- Anterior deep temporal and posterior deep temporal veins
- Pterygoid vein
- Masseteric vein
- Buccal vein
- Superior alveolar and inferior alveolar veins
- Infraorbital vein
- Middle meningeal veins
Overall, the veins forming the pterygoid venous plexus collect deoxygenated blood from the palate, nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses, nasopharynx, roof and lateral walls of the oral cavity, teeth, muscles of mastication, temporomandibular joint and the auditory tube.
Posteriorly, the veins of the plexus converge to form the maxillary vein, which further unites with the superficial temporal vein within the tissue of the parotid gland and forms the retromandibular vein.