- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Aorta
- Blood vessels of head and neck
- Arteries of head and neck
- Veins of head and neck
- Veins of head
- Extracranial veins
- Intracranial veins
- Veins of neck
- Veins of head
- Blood vessels of upper limb
- Blood vessels of thorax
- Blood vessels of abdomen
- Blood vessels of pelvis and lower limb
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
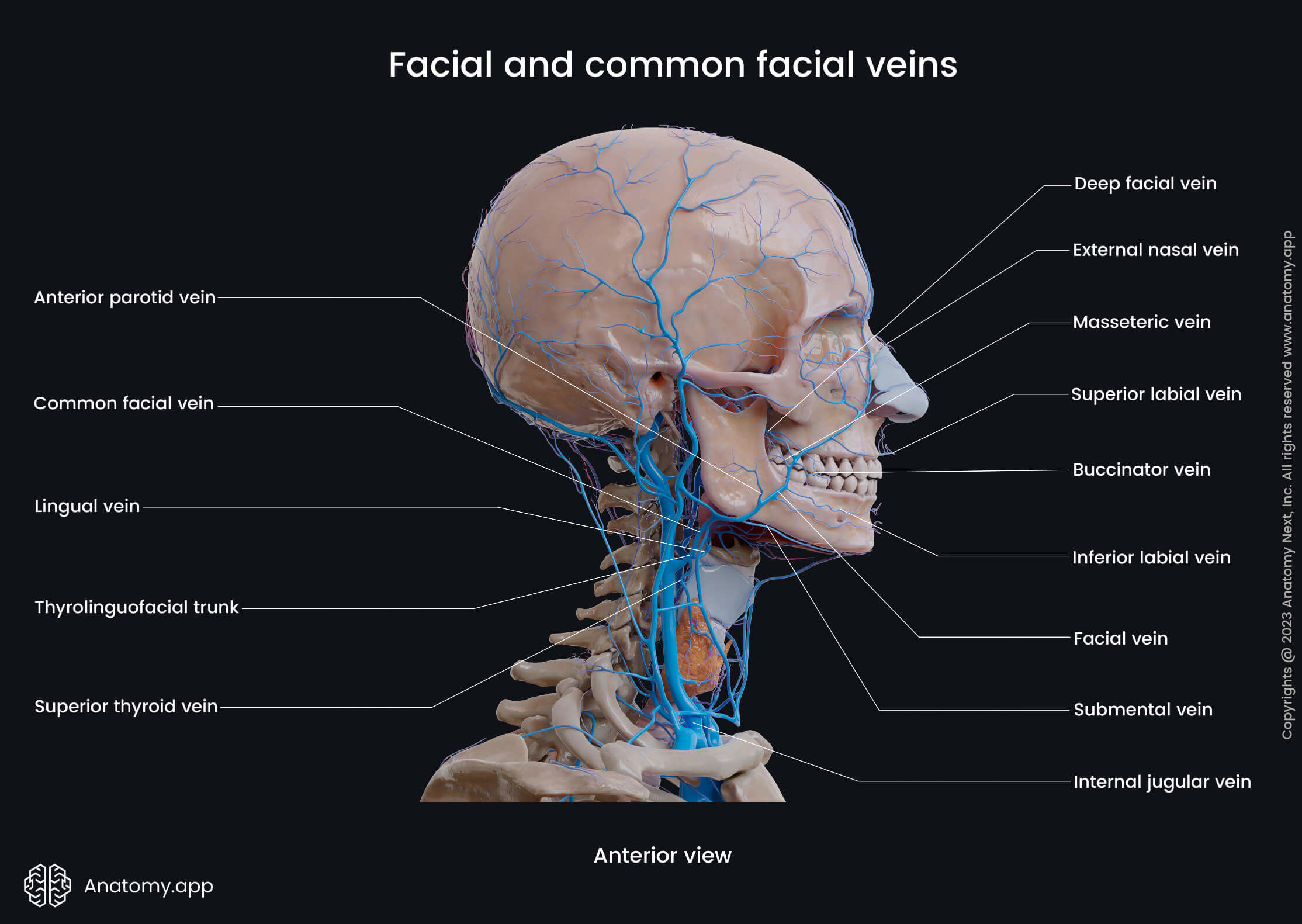
Facial vein
The facial vein (Latin: vena facialis) is a venous blood vessel that is a continuation of the angular vein. The facial vein starts from the medial aspect of the eye as the angular vein reaches the infraorbital margin. It descends posteriorly over the superficial surface of the masseter muscle, crosses the body of the mandible, and passes beneath the platysma, entering the neck.
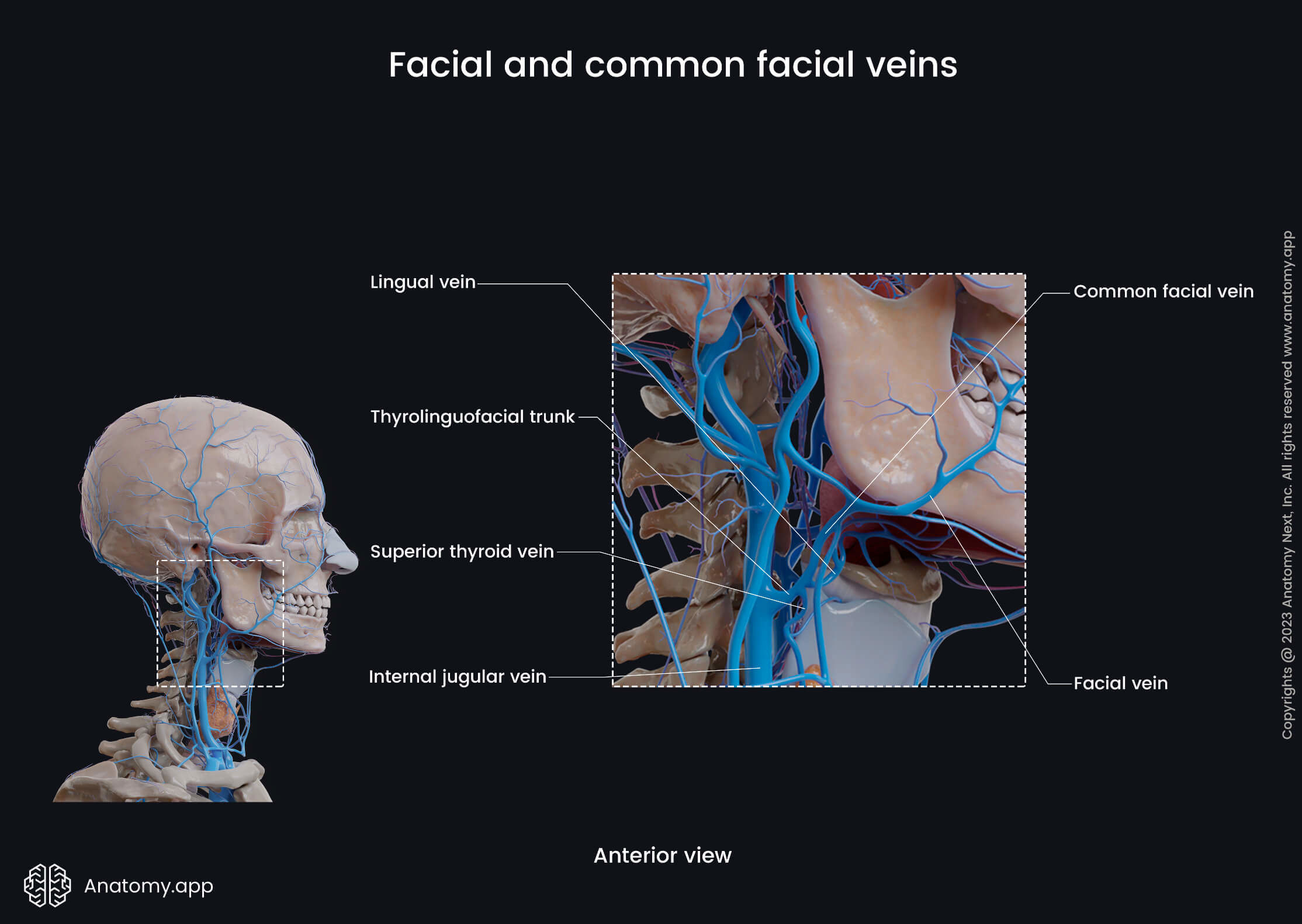
Finally, the facial vein joins with the retromandibular vein to form the common facial vein, which drains into the internal jugular vein. On its way, the facial vein receives the following veins:
- Submental vein
- Tonsillar vein
- External palatine vein
- Submandibular vein
- Pharyngeal vein
- Superior thyroid vein

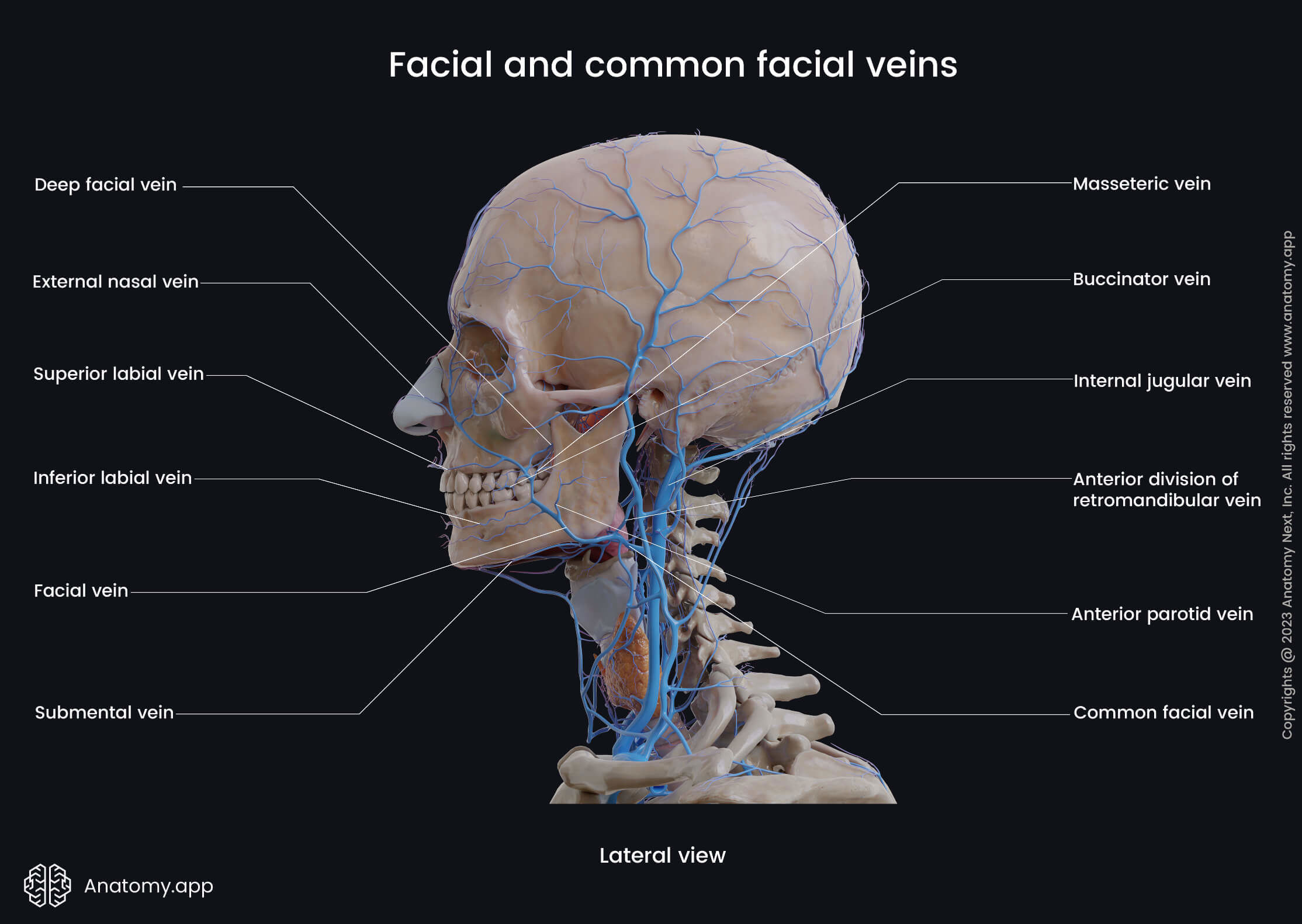
The facial vein collects deoxygenated blood from the forehead, eyelids, outer surface of the nose, lips, submental region, masseter, parotid gland, pterygoid plexus, palatine tonsils, and soft palate.