- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Aorta
- Blood vessels of head and neck
- Arteries of head and neck
- Veins of head and neck
- Veins of head
- Extracranial veins
- Intracranial veins
- Veins of neck
- Veins of head
- Blood vessels of upper limb
- Blood vessels of thorax
- Blood vessels of abdomen
- Blood vessels of pelvis and lower limb
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
Lingual vein
The lingual vein (Latin: vena lingualis) is a blood vessel that drains the tongue and is formed by the union of sublingual, deep lingual, and dorsal lingual veins. The lingual vein accompanies the lingual artery, passes adjacent to the hyoglossus muscle and near the greater horn of the hyoid bone drains into the internal jugular vein.
The dorsal lingual vein collects venous blood from the sides and dorsum of the tongue. The sublingual vein drains the floor of the oral cavity and the sublingual gland. And the deep lingual vein arises near the tip of the tongue, passes posteriorly below the mucous membrane on the inferior surface of the tongue.
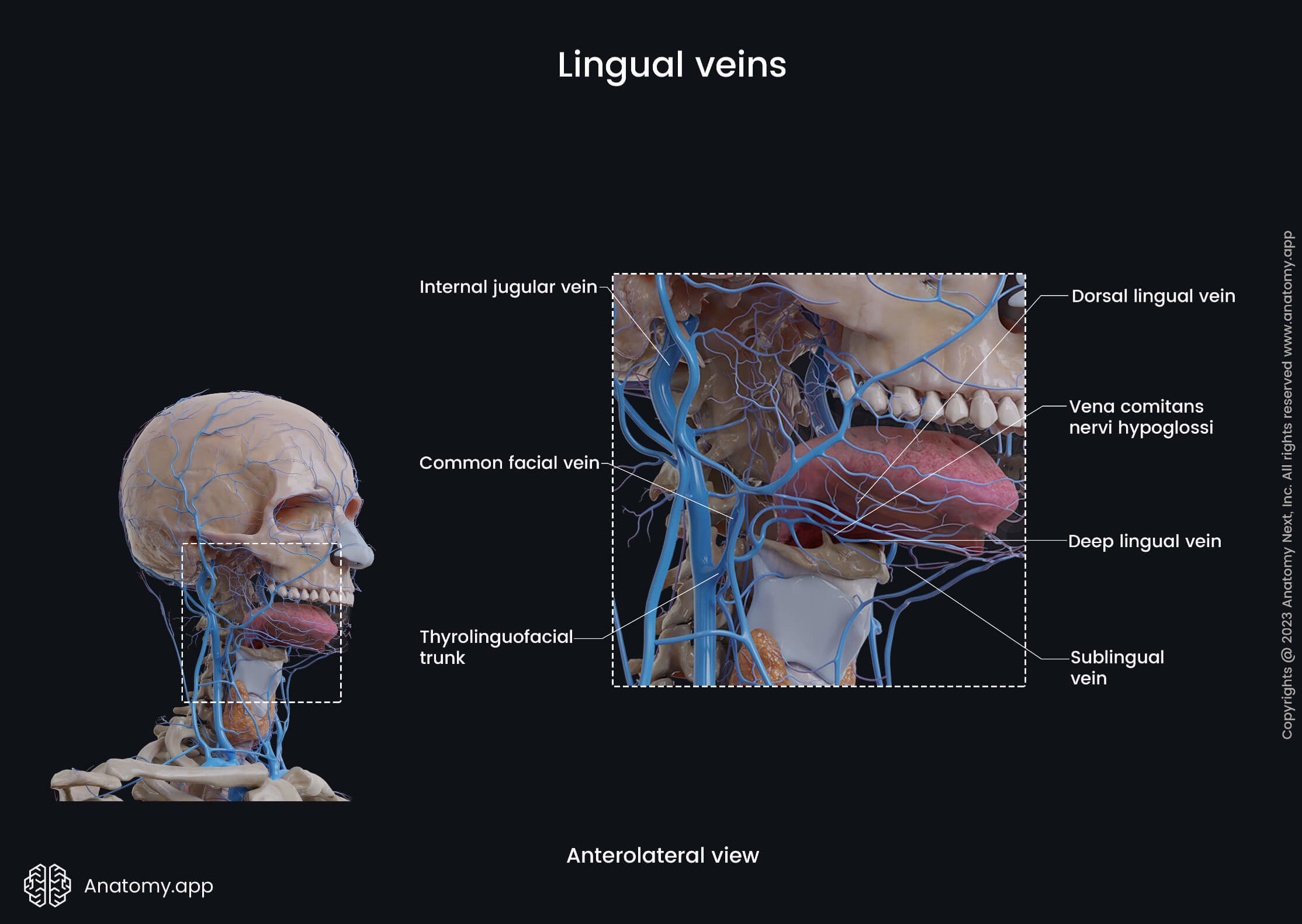
Near the anterior border of the hyoglossus, the deep lingual vein unites with the sublingual vein forming the vena comitans of the hypoglossal nerve (vena comitans nervi hypoglossi), which variably joins the lingual vein. This vein passes backwards and flows into one of the following veins: lingual vein, facial vein, or internal jugular vein.
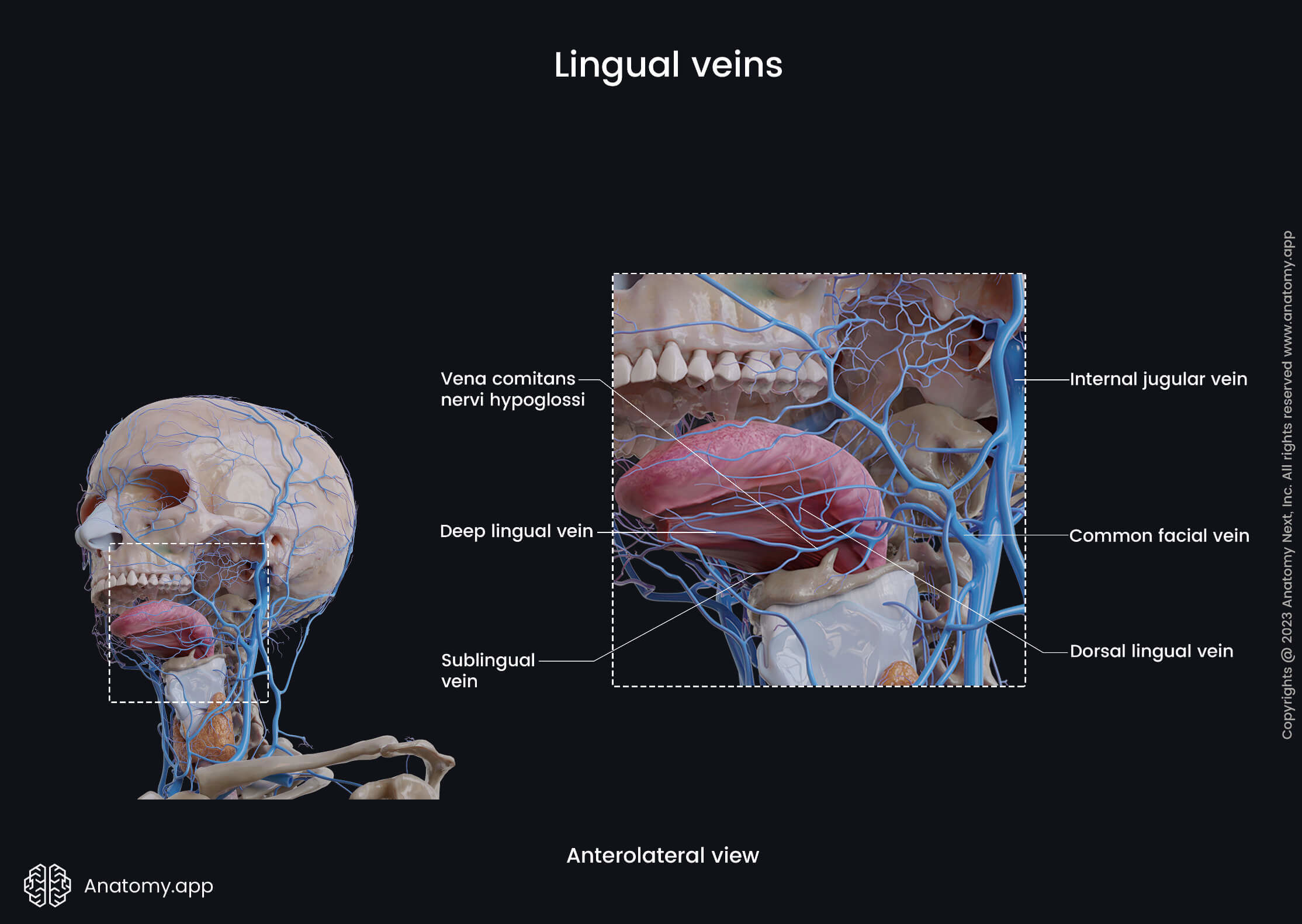
To sum up, the lingual vein collects venous blood from the muscles and mucosa of the tongue, floor of the oral cavity, and from salivary glands.