- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Head muscles
- Neck muscles
- Muscles of upper limb
- Thoracic muscles
- Muscles of back
- Muscles of lower limb
- Pelvic muscles
- Muscles of thigh
- Muscles of leg
- Anterior compartment
- Lateral compartment
- Posterior compartment
- Muscles of foot
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
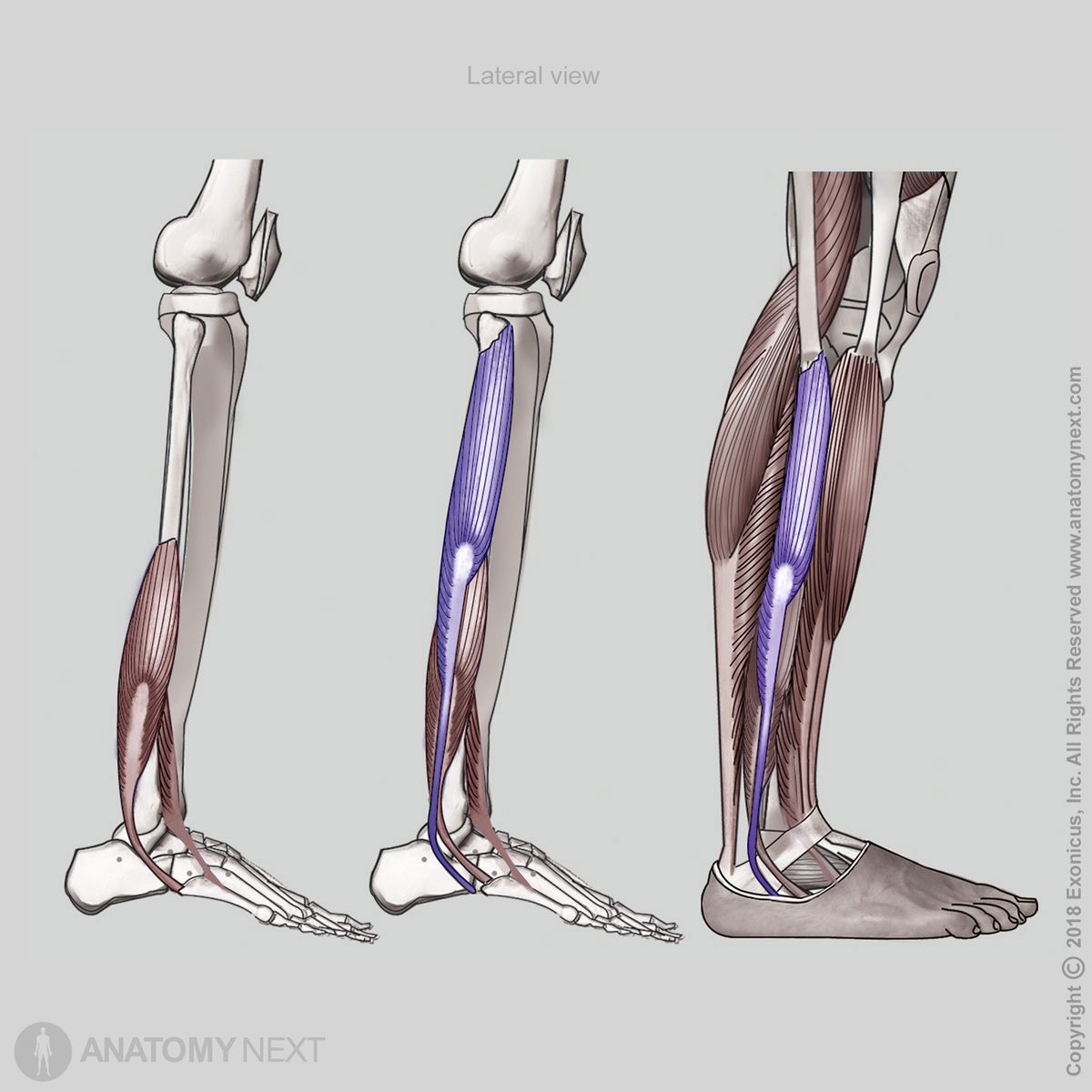
Peroneus longus
The peroneus longus (Latin: musculus peroneus longus; musculus fibularis longus), also known as the fibularis longus, is a superficial muscle located in the lateral compartment of the lower leg together with the peroneus brevis muscle. The peroneus longus stretches between the fibula, medial cuneiform and the first metatarsal bone.
| Peroneus brevis | |
| Origin | Head and upper two-thirds of lateral surface of fibula, intermuscular septa |
| Insertion | Medial cuneiform bone, base of 1st metatarsal bone |
| Action | Foot plantarflexion, foot eversion, supports transverse arch of foot |
| Innervation | Superficial peroneal (fibular) nerve (L5 - S2) |
| Blood supply | Peroneal (fibular) artery, branches of anterior tibial artery |
Origin
The peroneus longus muscle originates from the head and superior two-thirds of the lateral surface of the fibula. Also, it arises from the intermuscular septa.
Insertion
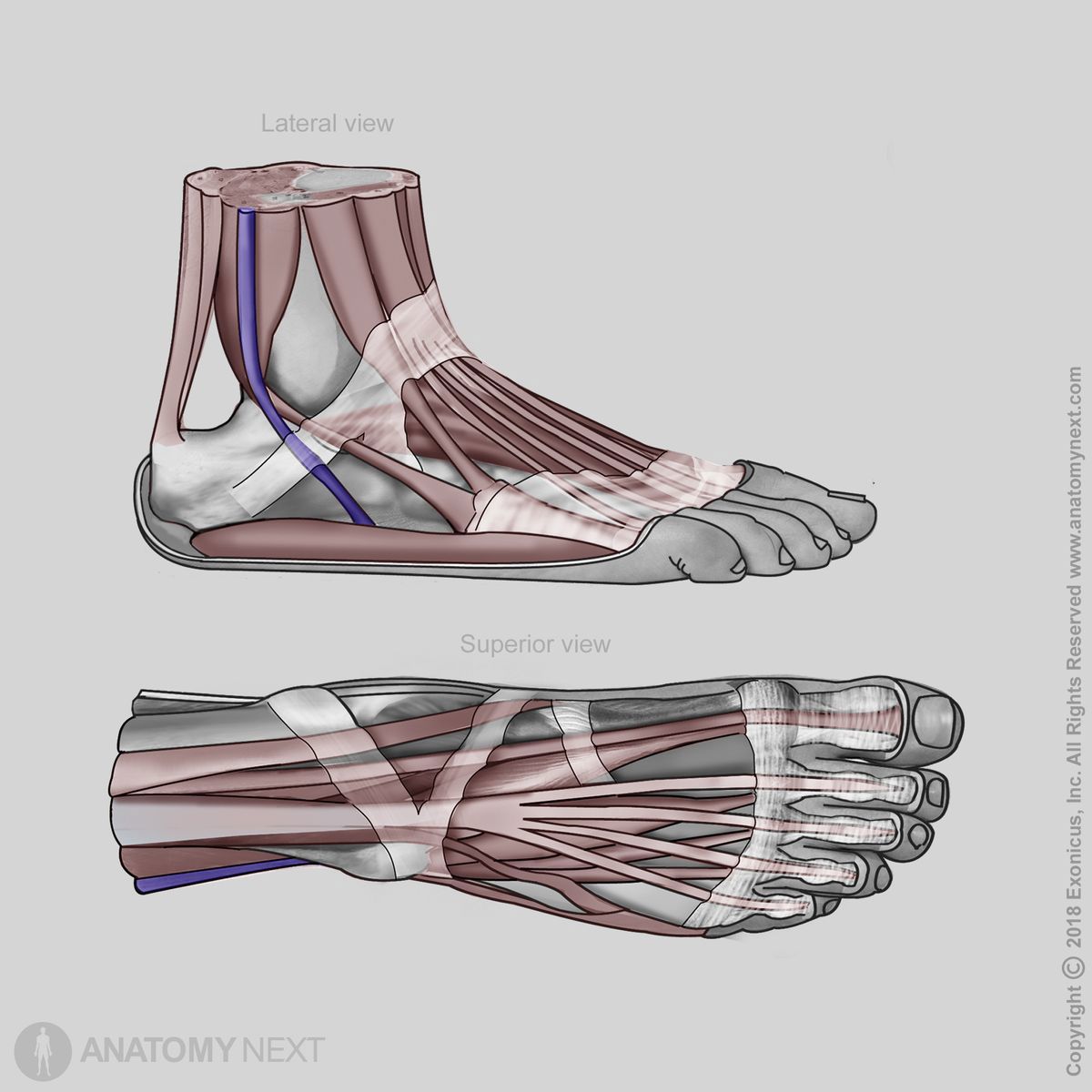
From its origin, the peroneus longus passes downward behind the lateral malleolus and inserts on the medial cuneiform bone and base of the first metatarsal bone.
Action
The peroneus longus provides plantarflexion of the foot at the talocrural (ankle) joint and foot eversion at the subtalar joint. Also, it supports the transverse arch of the foot.
Innervation
The peroneus longus is innervated by the superficial peroneal (fibular) nerve (L5 - S2) - a branch of the common peroneal (fibular) nerve.
Blood supply
The peroneus longus muscle receives arterial blood supply from the peroneal (fibular) artery - a branch of the posterior tibial artery. Additionally, it is supplied by the branches of the anterior tibial artery.