- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Head muscles
- Neck muscles
- Muscles of upper limb
- Thoracic muscles
- Muscles of back
- Muscles of lower limb
- Pelvic muscles
- Muscles of thigh
- Anterior compartment
- Medial compartment
- Posterior compartment
- Muscles of leg
- Muscles of foot
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
Gracilis
The gracilis (Latin: musculus gracilis) is a long and slim superficial thigh muscle. It is located in the medial compartment, and together with the pectineus, adductor brevis, adductor magnus and adductor longus, the gracilis is one of the adductor muscles. It overlies all the mentioned muscles as it is the most superficial one of the group. The gracilis descends vertically down the thigh and stretches between the pubis and ischium of the hip bone and the proximal end of the tibia.
| Gracilis | |
| Origin | Ischial ramus, body of pubis, inferior ramus of pubis |
| Insertion | Proximal end of tibia below medial condyle via pes anserinus |
| Action | Thigh flexion, thigh adduction, leg flexion, leg internal rotation |
| Innervation | Obturator nerve (L2 - L4) |
| Blood supply | Branches of deep femoral, medial circumflex femoral, superficial femoral, obturator and descending genicular arteries |
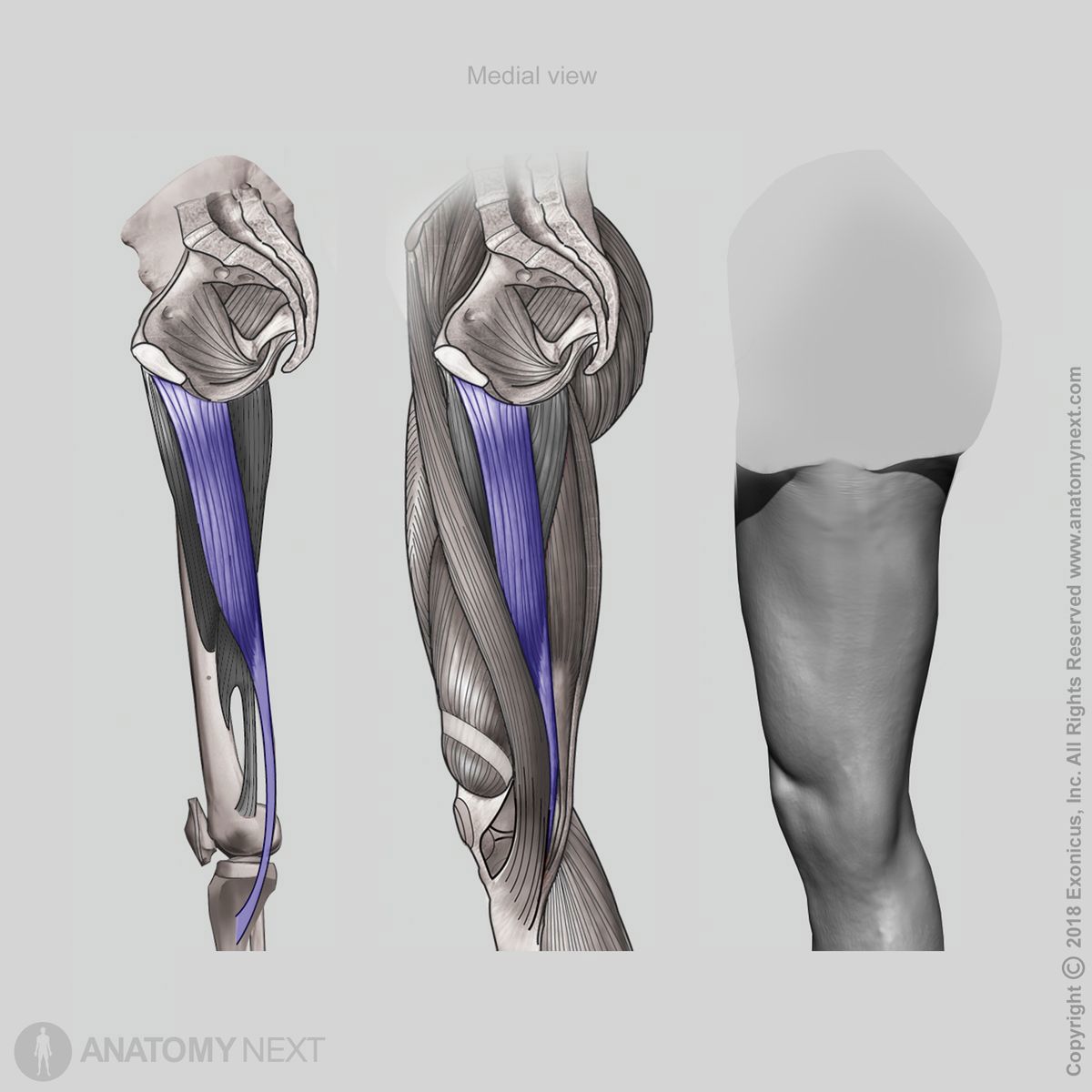
Origin
The gracilis muscle originates from the ischial ramus and the body and inferior ramus of the pubis.
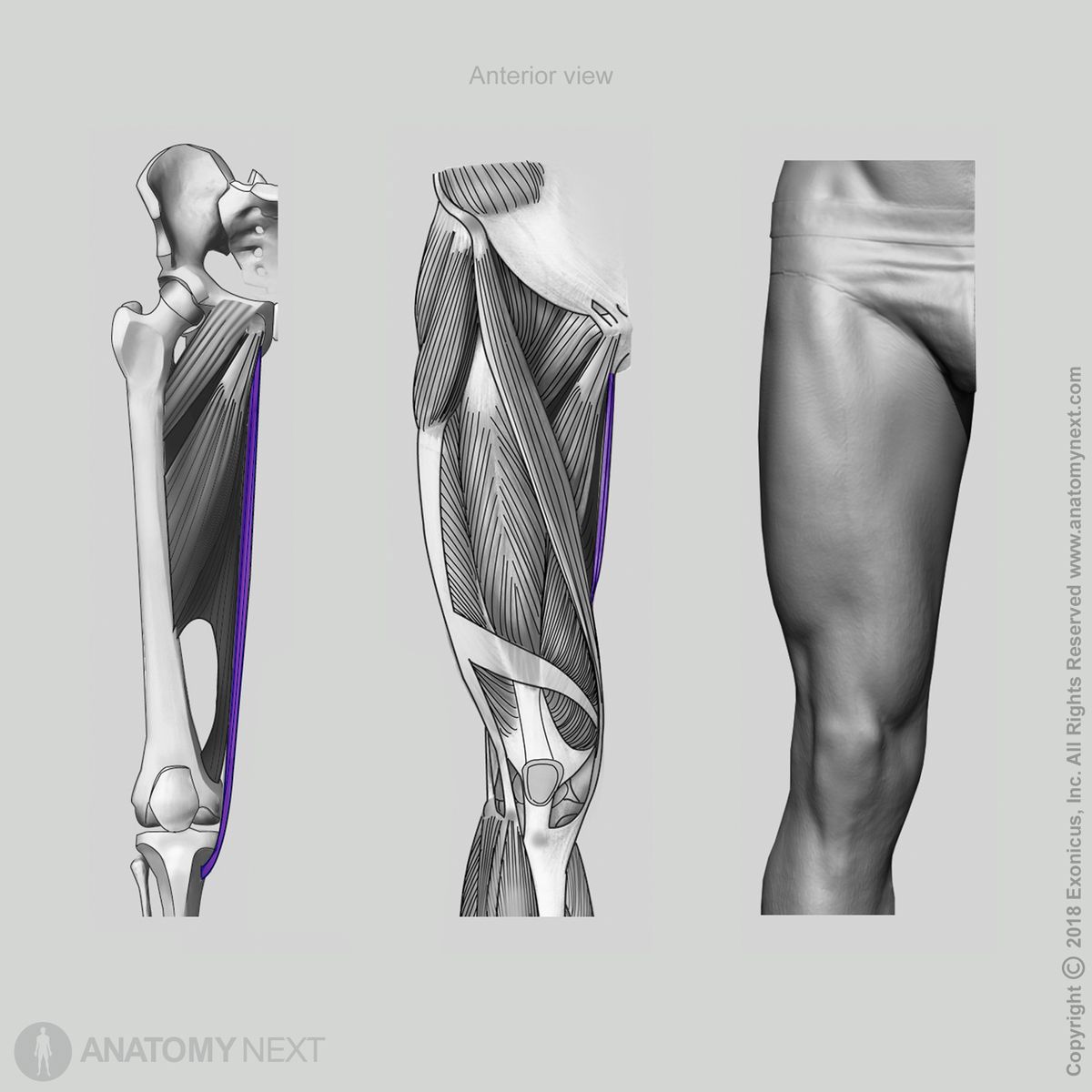
Insertion
The gracilis via the pes anserinus inserts on the proximal end of the tibia below the medial condyle. The distal end of the gracilis tendon blends with tendons of the semitendinosus and sartorius muscles and forms a common tendon called the pes anserinus.
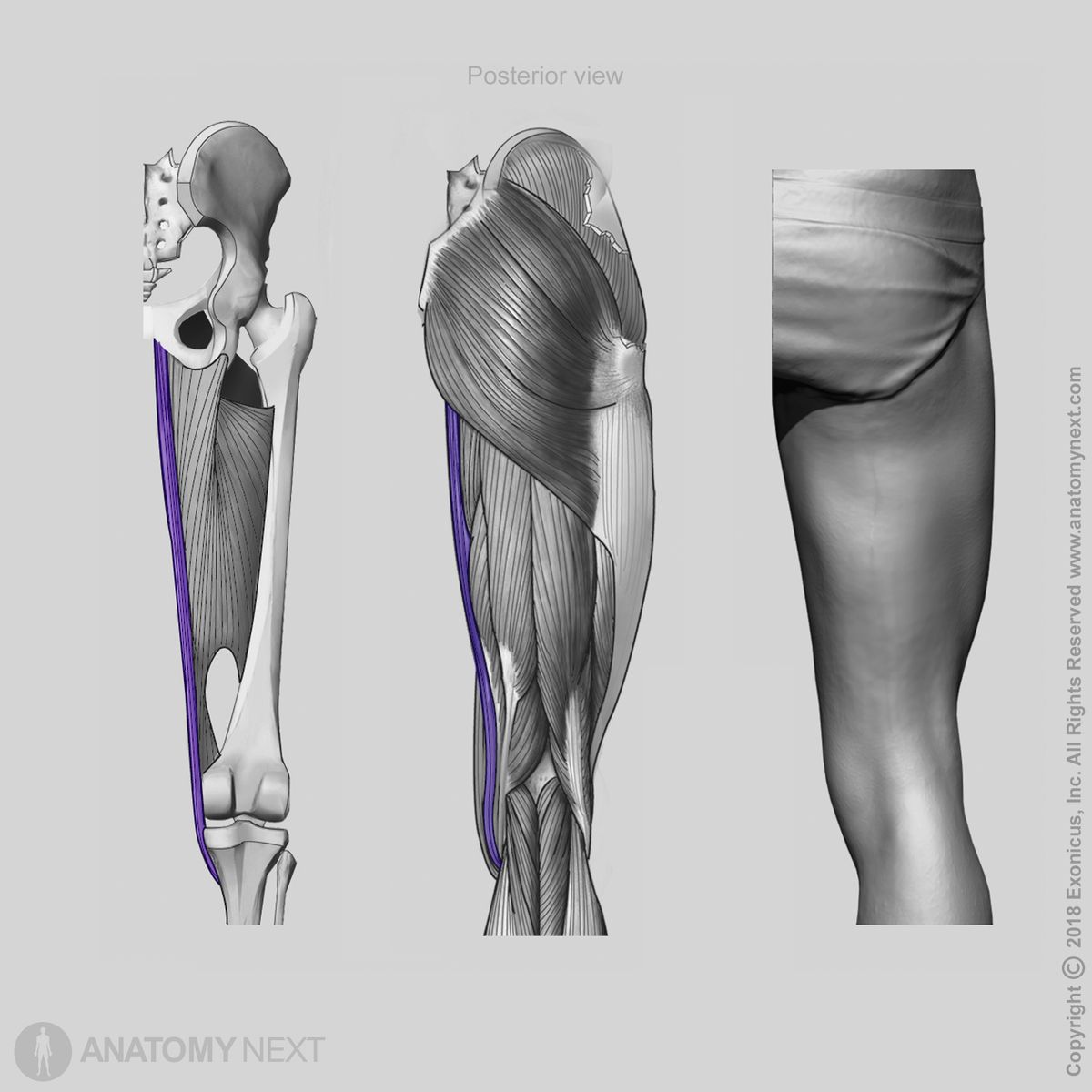
Action
The gracilis muscle provides adduction and flexion of the thigh at the hip joint, as well as flexion and internal rotation of the leg at the knee joint.
Innervation
The gracilis is innervated by the anterior branch of the obturator nerve (L2 - L4) that arises from the lumbar plexus.
Blood supply
The gracilis muscle receives arterial blood supply from the deep femoral, medial circumflex femoral, obturator, and descending genicular arteries.