- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Head muscles
- Neck muscles
- Muscles of upper limb
- Thoracic muscles
- Muscles of back
- Muscles of lower limb
- Pelvic muscles
- Muscles of thigh
- Muscles of leg
- Anterior compartment
- Lateral compartment
- Posterior compartment
- Muscles of foot
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
Extensor digitorum longus
The extensor digitorum longus (Latin: musculus extensor digitorum longus) is a long, thin muscle located in the anterior compartment of the leg, just behind the tibialis anterior. Like the tibialis anterior and extensor hallucis longus, the extensor digitorum longus is also known as one of the extensors. It stretches between the fibula, tibia and phalanges.
| Extensor digitorum longus | |
| Origin | Anteromedial aspect of proximal fibula, lateral condyle of tibia, upper anterior surface of interosseous membrane of leg |
| Insertion | Distal and middle phalanges of 2nd to 5th fingers |
| Action | Extension of 2nd to 5th toes, foot dorsiflexion |
| Innervation | Deep peroneal (fibular) nerve (L4 - S1) |
| Blood supply | Branches of anterior tibial artery |
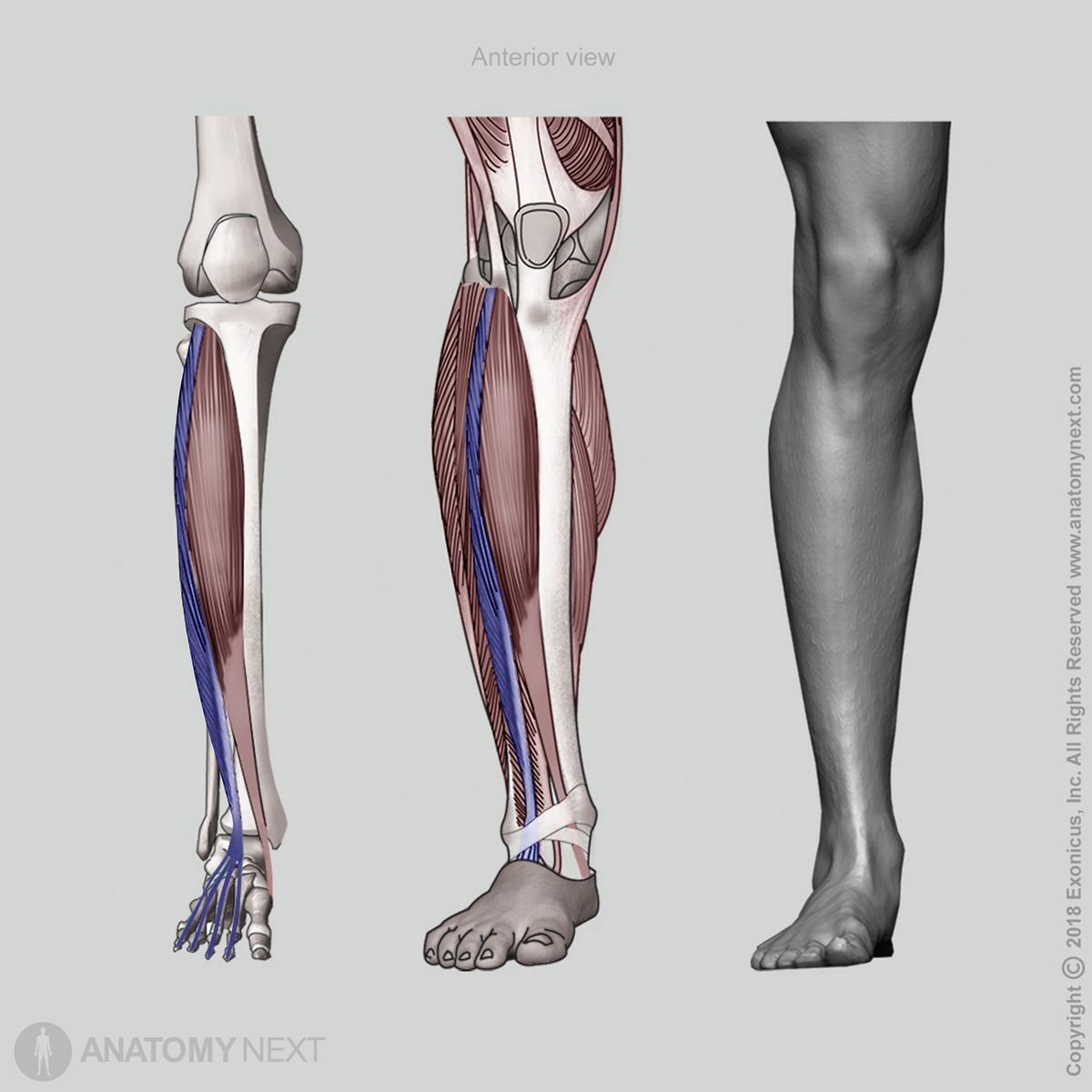
Origin
The extensor digitorum longus muscle originates from the lateral condyle of the tibia and the anteromedial aspect of the proximal fibula. Also, it arises from the upper anterior surface of the interosseous membrane of the leg.
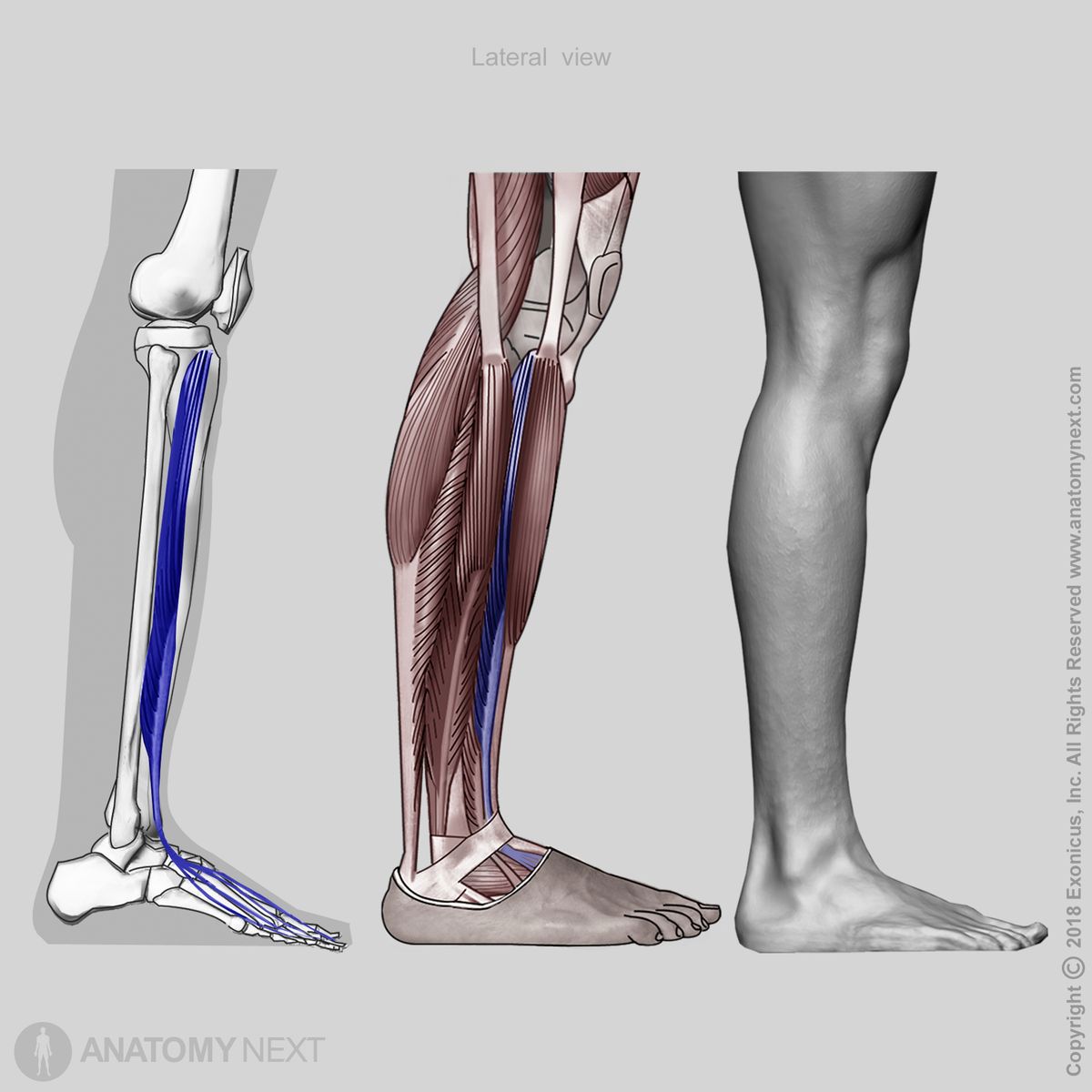
Insertion
The extensor digitorum longus goes down the leg. Above the ankle, it forms a tendon that passes below the superior extensor retinaculum and goes through the inferior extensor retinaculum. Within the inferior extensor retinaculum, the tendon divides into four tendon slips that insert on the distal and middle phalanges of the second to fifth fingers as part of the extensor expansion complex.
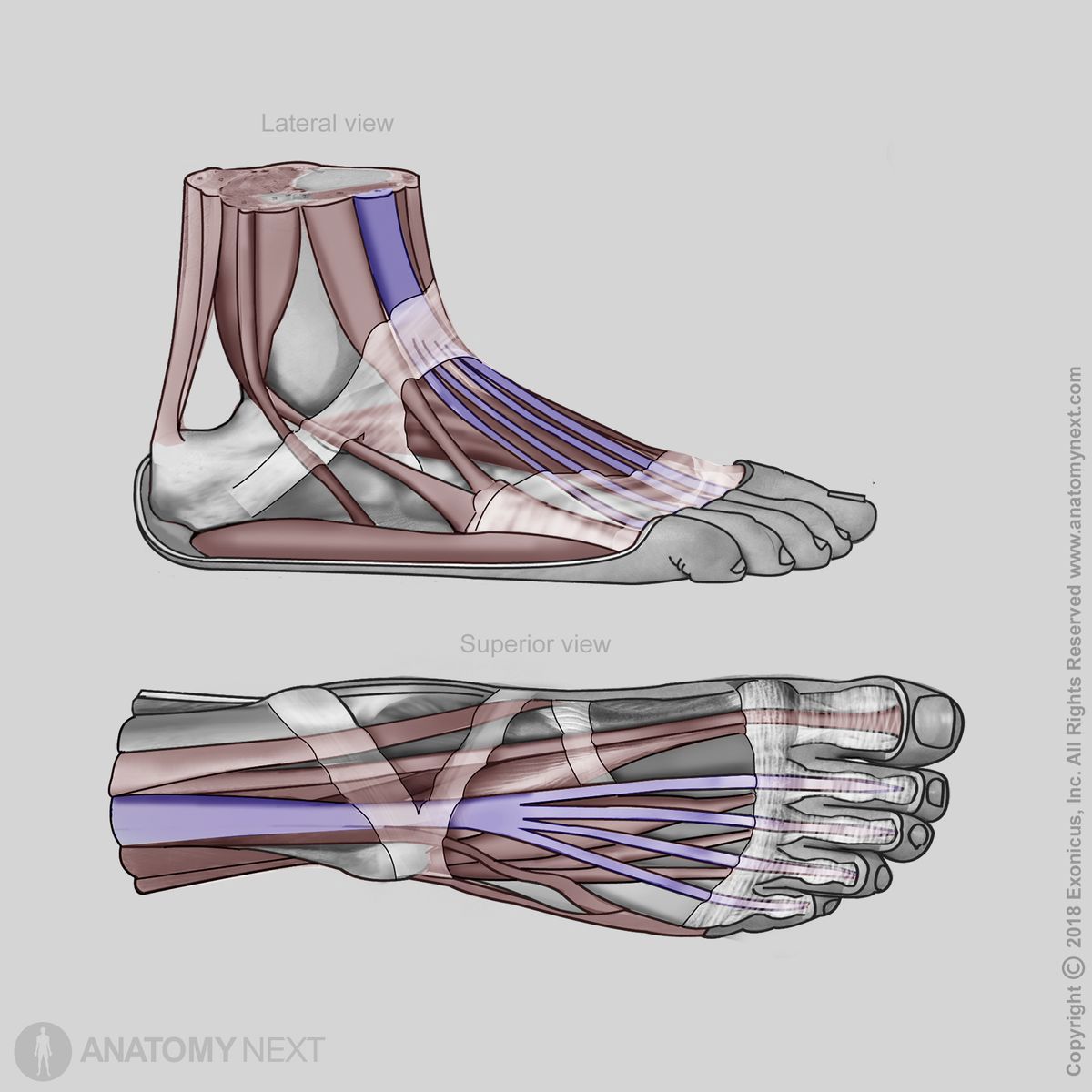
Action
The extensor digitorum longus muscle provides foot dorsiflexion at the talocrural (ankle) joint and extension of the toes at the second to fifth metatarsophalangeal and interphalangeal joints.
Innervation
The extensor digitorum longus is innervated by the deep peroneal (fibular) nerve (L4 - S1) - a branch of the common peroneal (fibular) nerve.
Blood supply
The extensor digitorum longus muscle receives arterial blood supply from the branches of the anterior tibial artery.