- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Head muscles
-
Neck muscles
- Superficial neck muscles
- Scalene muscles
- Suprahyoid muscles
- Infrahyoid muscles
- Prevertebral muscles
- Suboccipital muscles
- Muscles of upper limb
- Thoracic muscles
- Muscles of back
- Muscles of lower limb
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Lymphatic system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
Digastric
The digastric muscle (Latin: musculus digastricus) is a small paired muscle of the neck that stretches between the mandible and hyoid bone. It is located in the anterior compartment of the neck. Therefore, the digastric belongs to the anterior neck muscles. Also, as it is located above the hyoid bone, the digastric is classified as the suprahyoid muscle. Other suprahyoid muscles include the geniohyoid, stylohyoid and mylohyoid muscles.
The digastric muscle is composed of two muscular bellies - anterior and posterior. Both bellies are connected by an intermediate tendon. The tendon attaches to the superior surface of the hyoid bone as a fibrous connective tissue band. The posterior belly passes from the temporal bone to the intermediate tendon, while the anterior belly extends from the mandible to the intermediate tendon.
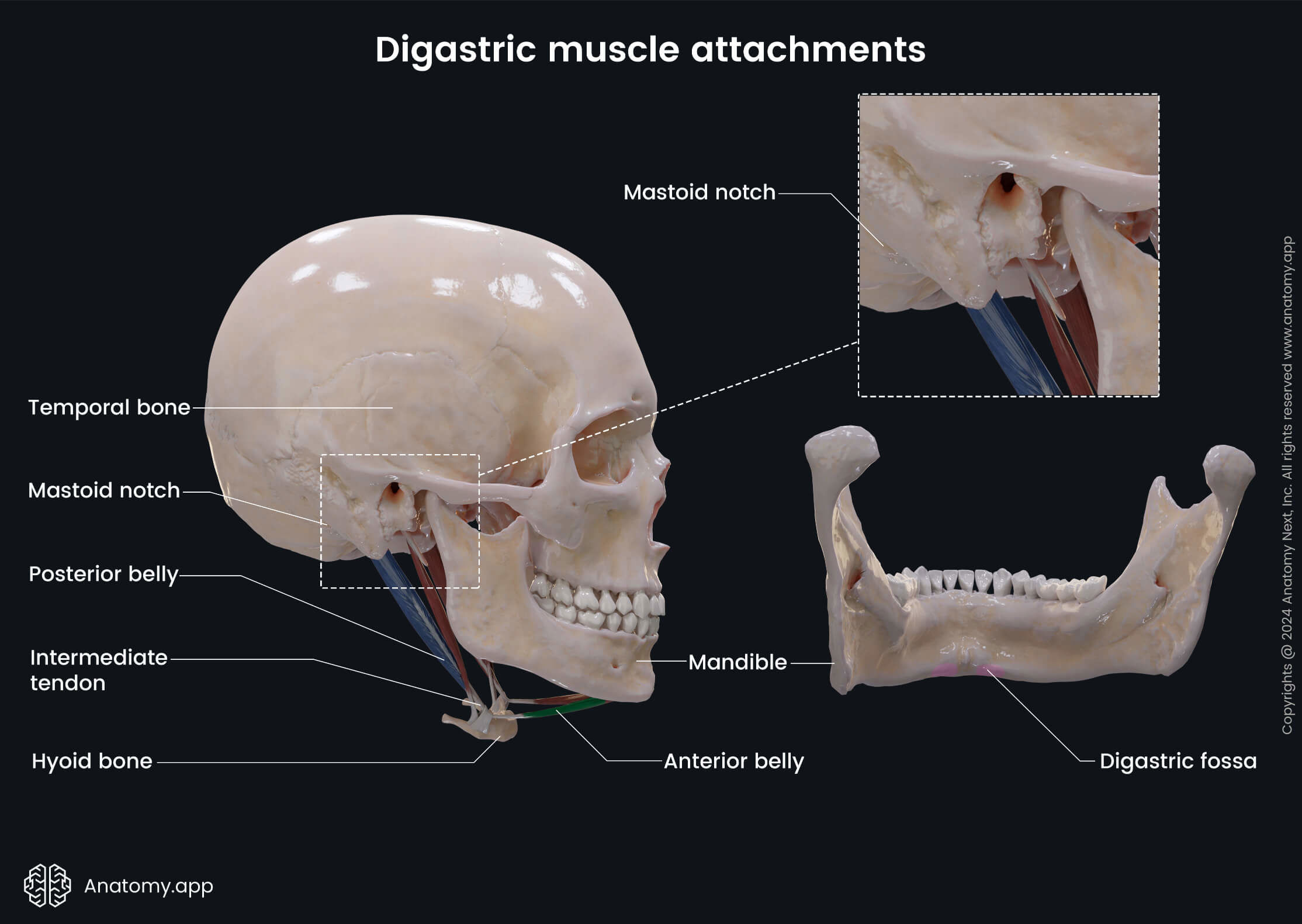
To be more precise, the origin site of the anterior belly is the digastric fossa of the mandible, but the posterior belly originates from the mastoid notch of the temporal bone. Both bellies of the digastric muscle insert on the hyoid bone via the intermediate tendon. The digastric muscle depresses the mandible (opens the jaw) when the masseter and temporalis are relaxed.
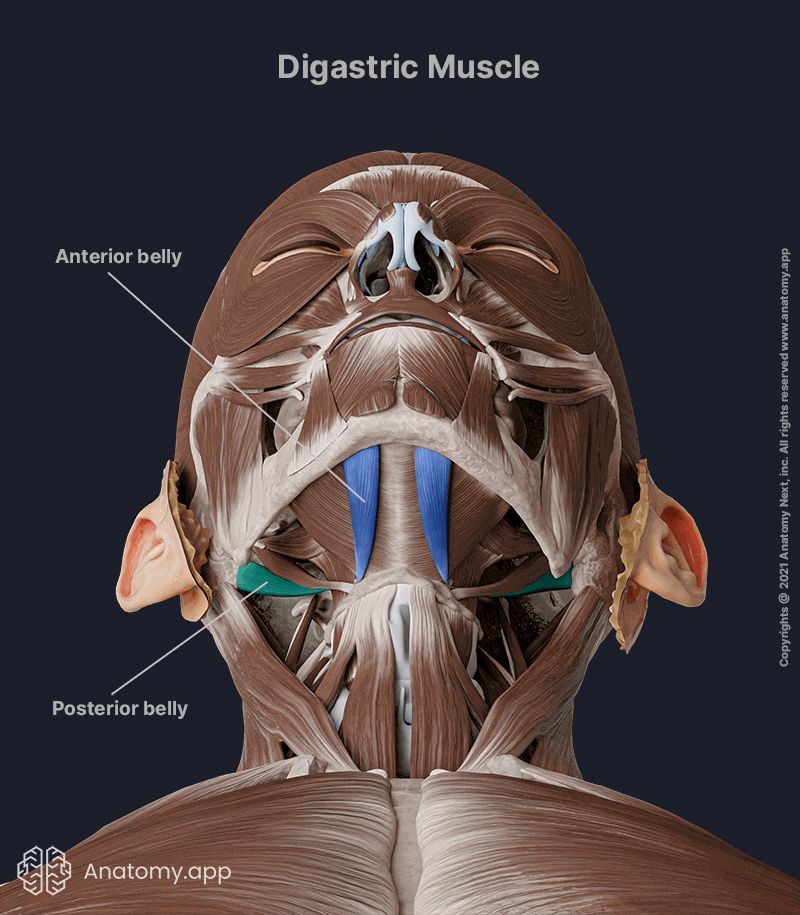
Each belly has a different embryological origin, so they do not have a common nerve supply. The nerve supply for the digastric muscle is provided by two cranial nerves. The digastric branch of the facial nerve (CN VII) innervates the posterior belly. In contrast, the mylohyoid nerve, a branch coming from the inferior alveolar nerve of the mandibular nerve (CN V3), supplies the anterior belly.