- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Head muscles
-
Neck muscles
- Superficial neck muscles
- Scalene muscles
- Suprahyoid muscles
- Infrahyoid muscles
- Prevertebral muscles
- Suboccipital muscles
- Muscles of upper limb
- Thoracic muscles
- Muscles of back
- Muscles of lower limb
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
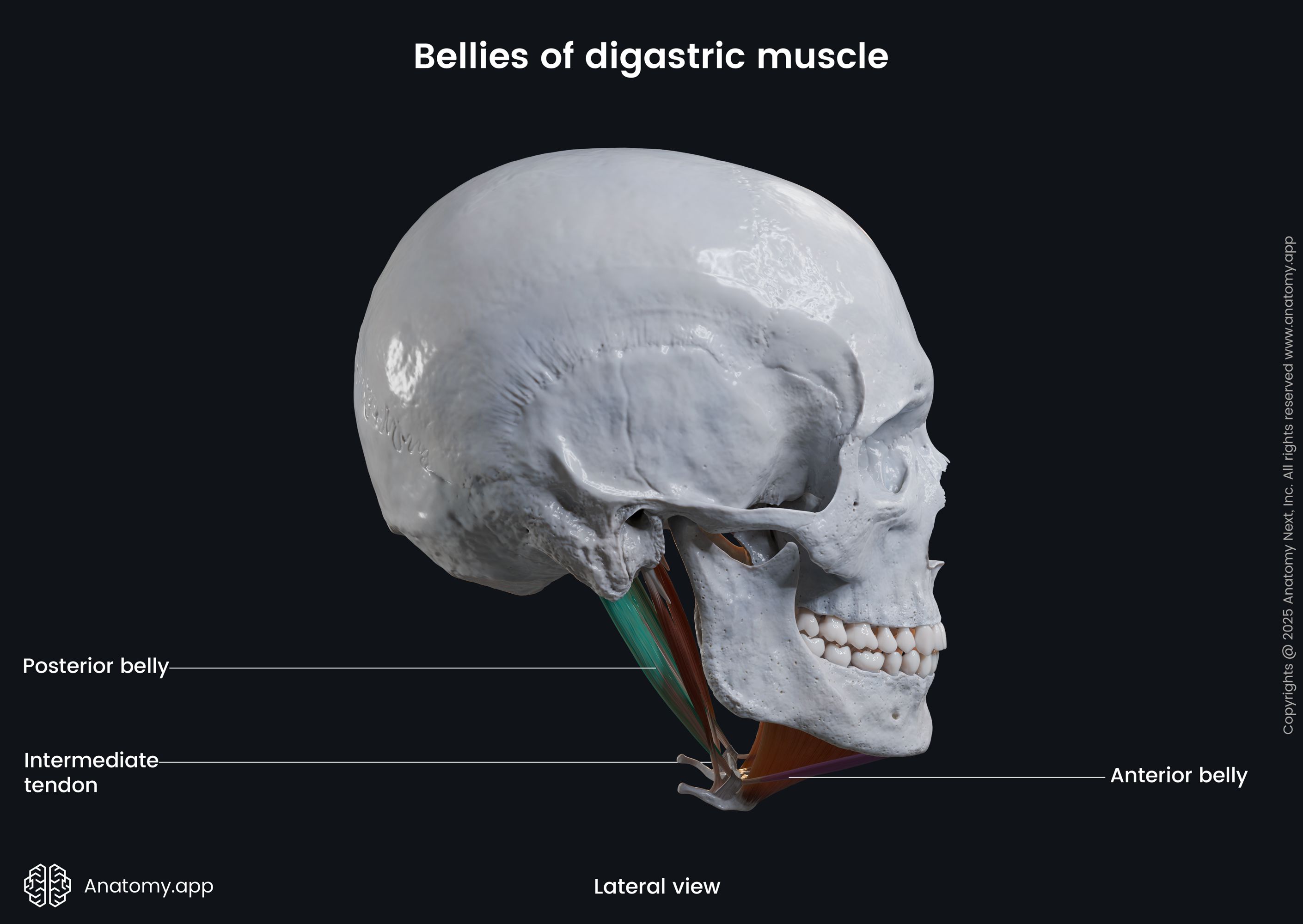
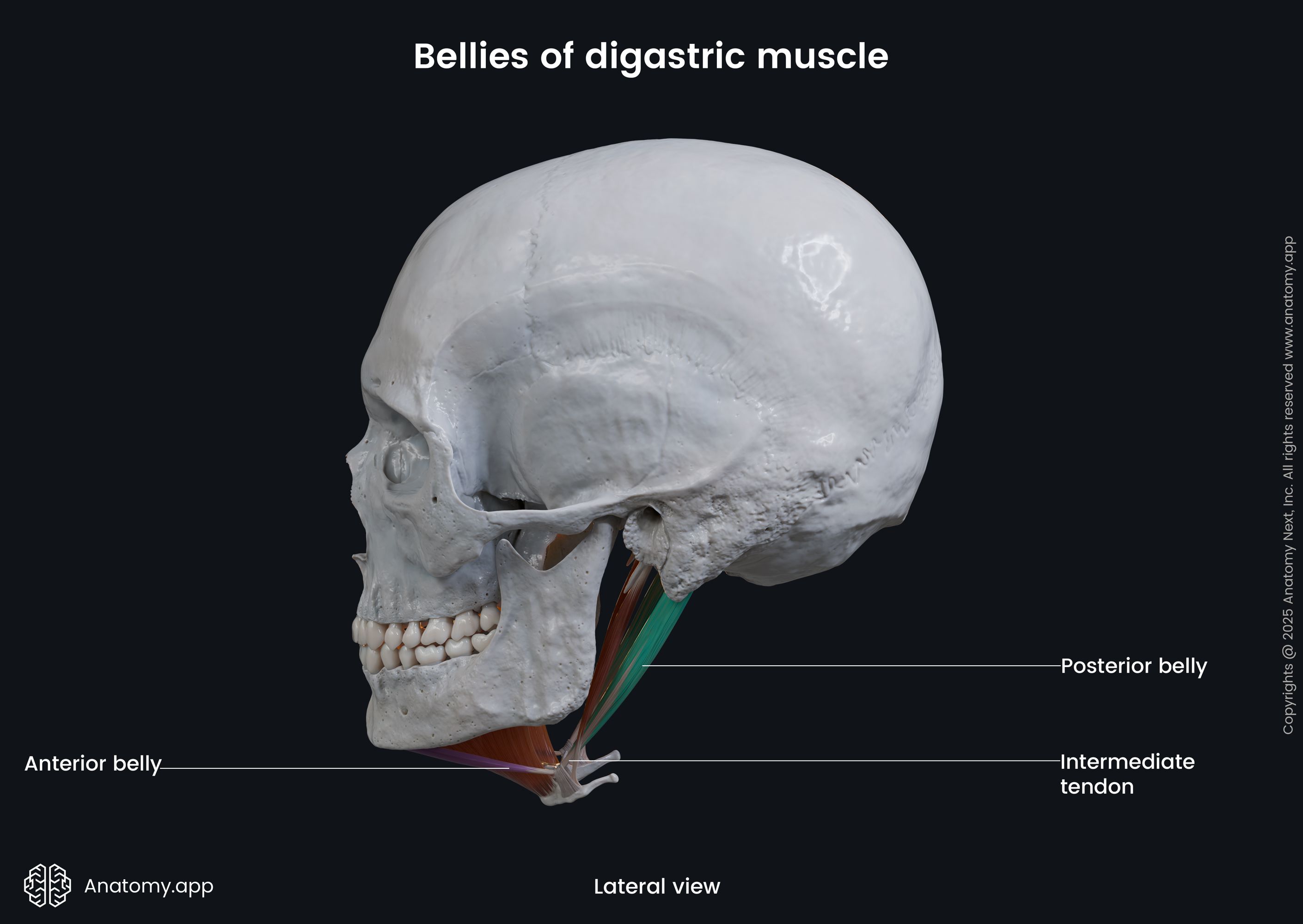
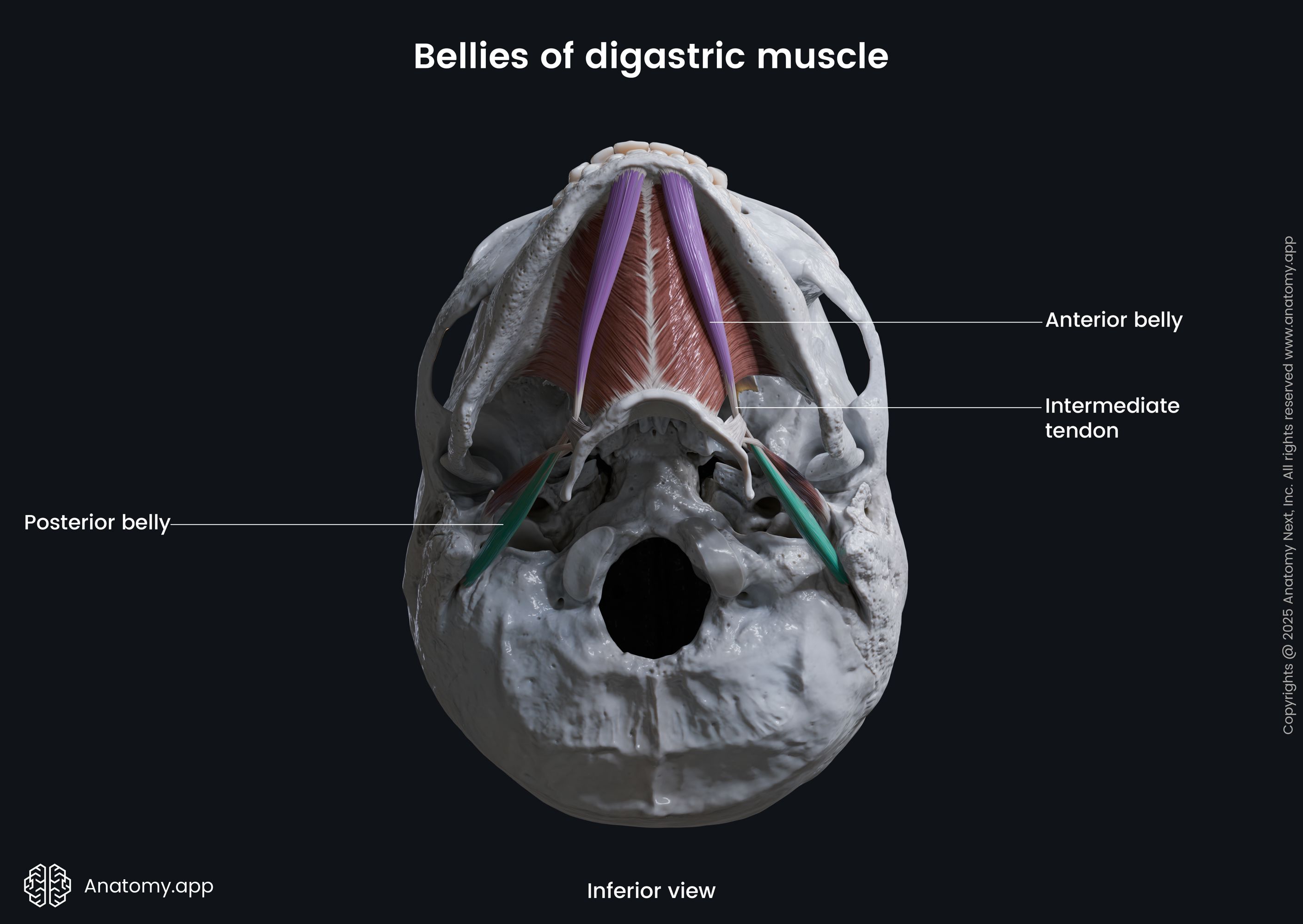
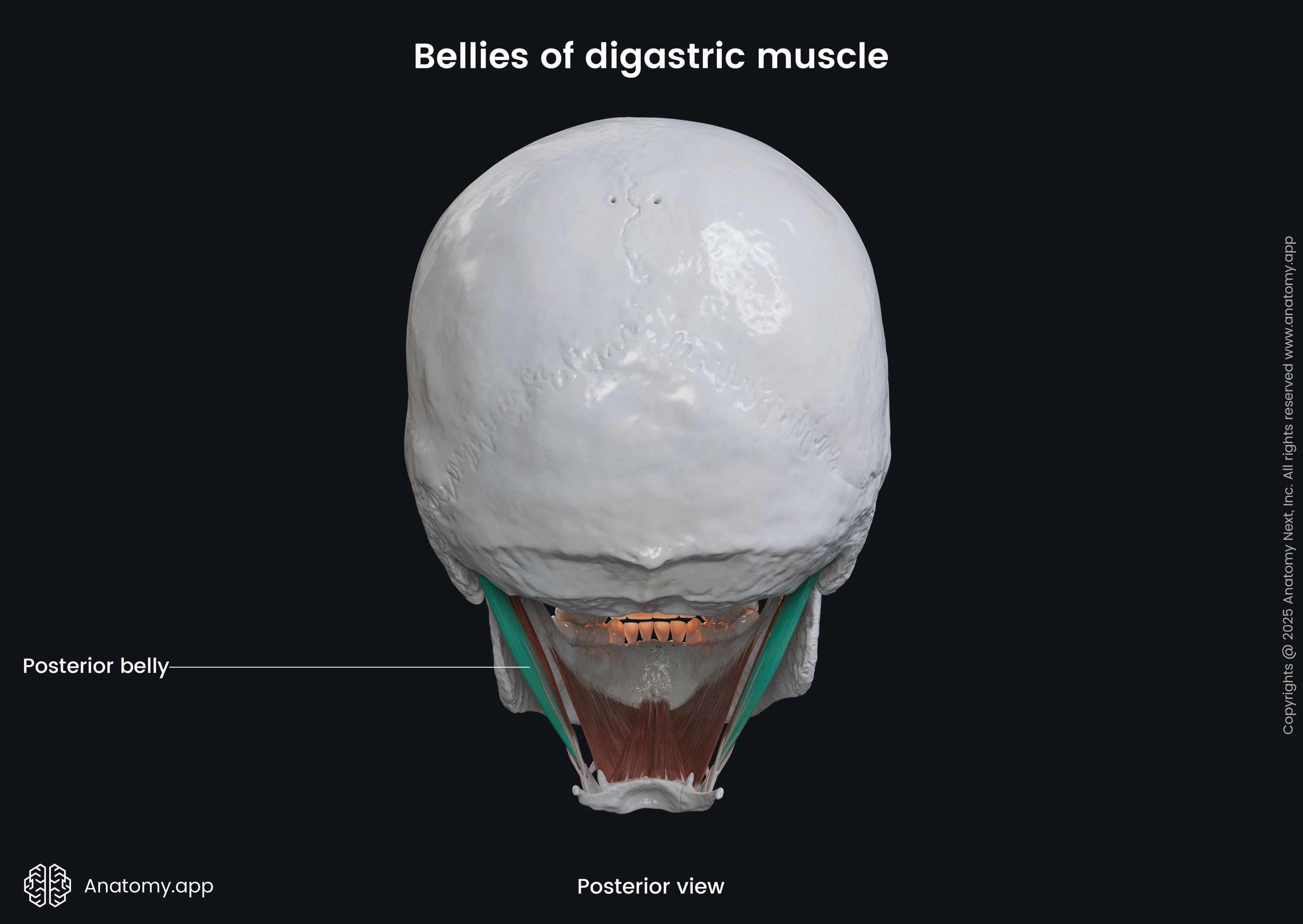
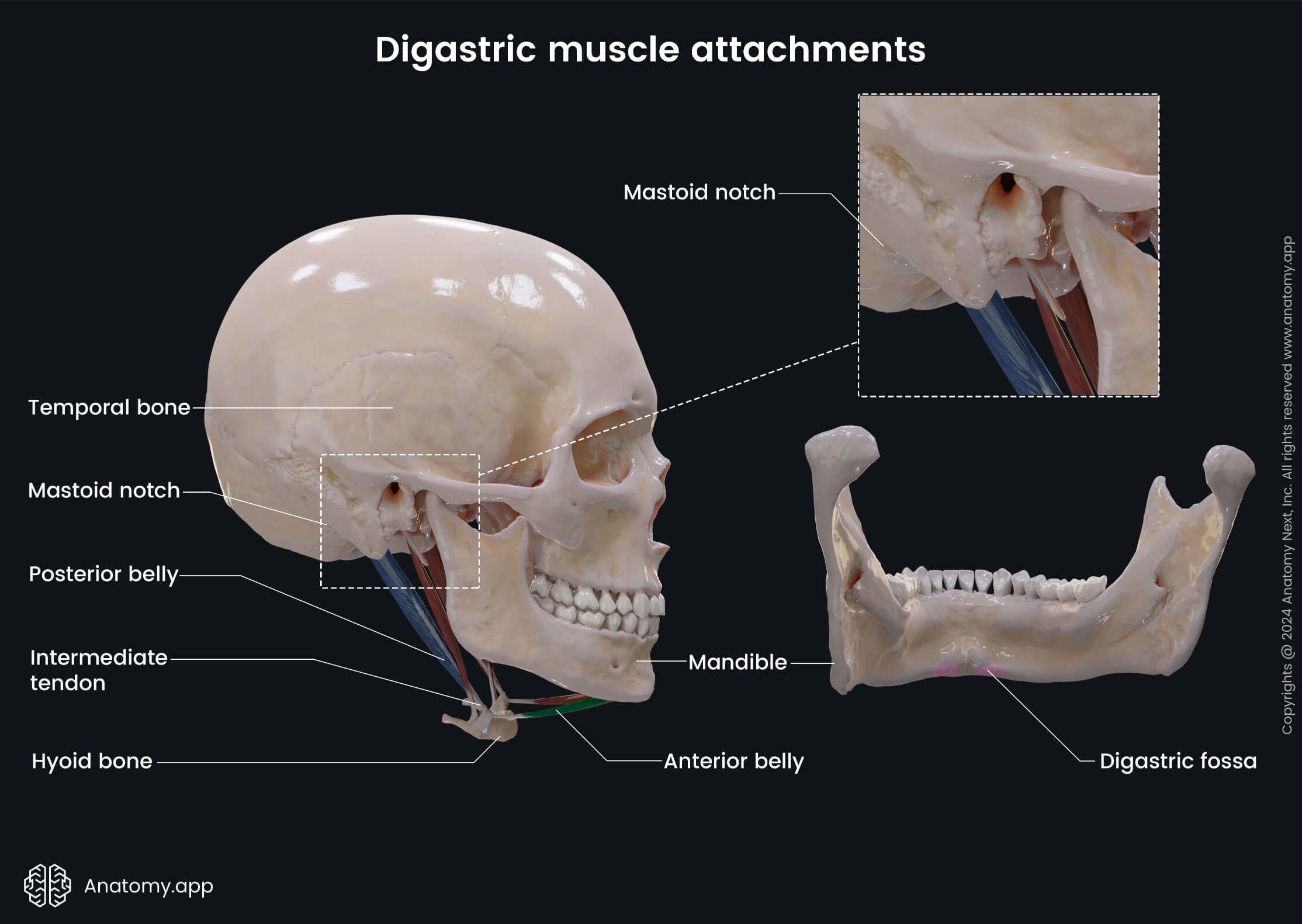
Posterior belly of digastric
The posterior belly of the digastric (Latin: venter posterior musculi digastrici) is one of two bellies composing the digastric muscle. The digastric is one of the muscles of the neck, and its other belly is known as the anterior belly. As the digastric is located above the hyoid bone, it is classified as the suprahyoid neck muscle. It also belongs to the anterior neck muscles. The posterior belly is the largest of both bellies, and it develops from the second pharyngeal arch.
| Posterior belly of digastric | |
| Origin | Mastoid notch of temporal bone |
| Insertion | Hyoid bone via intermediate tendon |
| Action | Elevates hyoid bone, depresses mandible |
| Innervation | Digastric nerve of facial nerve (CN VII) |
| Blood supply | Occipital and posterior auricular arteries |
Origin
The posterior belly originates from the mastoid notch that is located on the temporal bone medial to the mastoid process.
Insertion
From the origin site, the posterior belly of the digastric stretches forward and downward. Fibers of this belly form the intermediate tendon that attaches to the hyoid bone.
Action
Upon activation, the posterior belly of the digastric elevates the hyoid bone or depresses the lower jaw.
Innervation
The posterior belly of the digastric muscle is innervated by the digastric branch of the facial nerve (CN VII).
Blood supply
The posterior belly receives arterial blood supply from the occipital and posterior auricular arteries from the external carotid artery.