- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Aorta
- Blood vessels of head and neck
- Blood vessels of upper limb
- Blood vessels of thorax
- Blood vessels of abdomen
- Blood vessels of pelvis and lower limb
- Arteries of pelvis and lower limb
- Veins of pelvis and lower limb
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
Uterine artery
The uterine artery (Latin: arteria uterina) is a branch of the anterior trunk of the internal iliac artery. It provides arterial blood supply to the uterus and cervix among other female reproductive organs, including the vagina, ovaries, Fallopian tubes. This artery also supplies the lower third of the ureter.
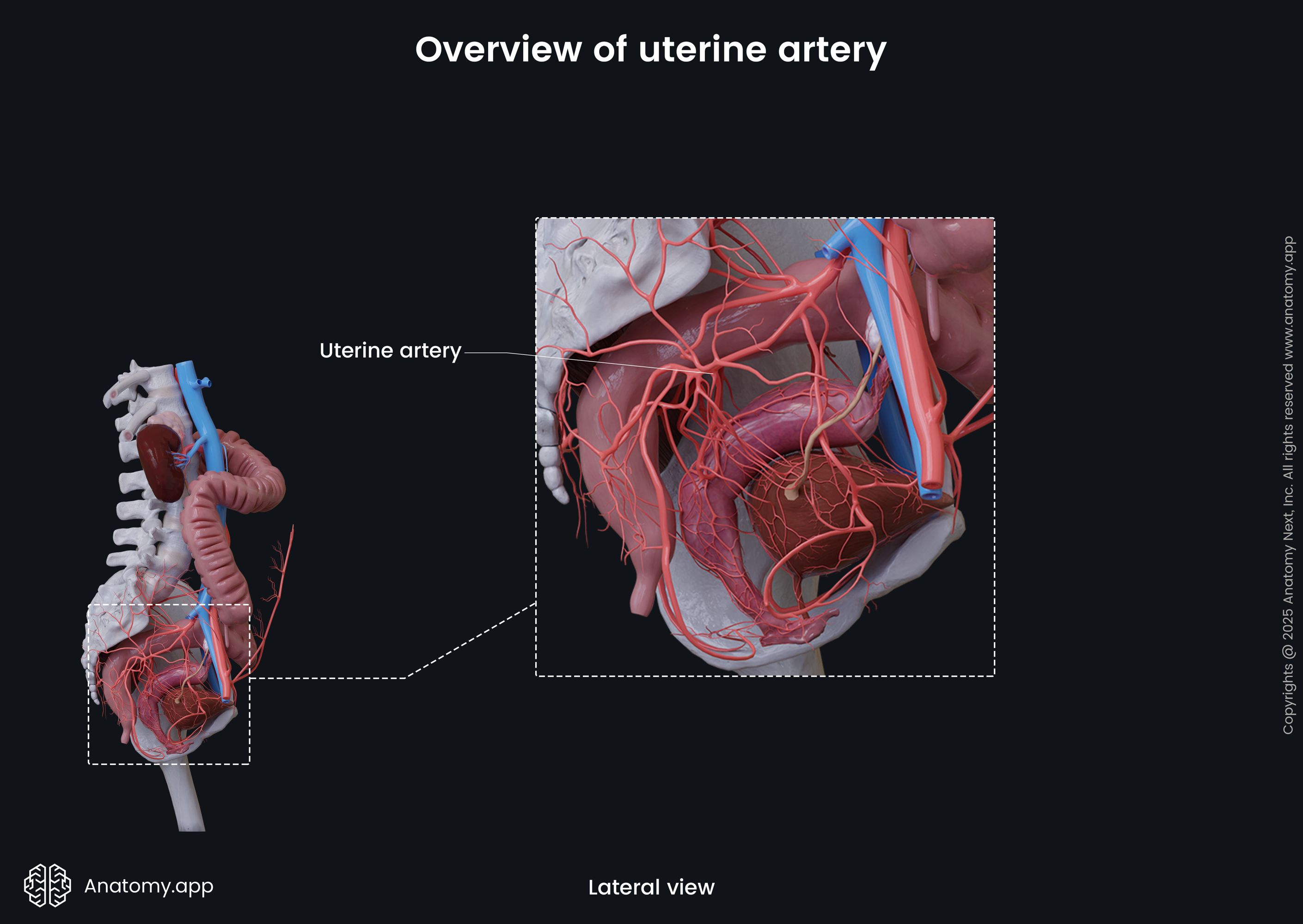
The uterine artery passes inferiorly along the lateral wall of the lesser pelvis, then it goes within the broad ligament of the uterus and within the cardinal ligament to reach the cervix uteri. Then the artery travels through the parametrium to the fundus of the uterus. The uterine artery gives off several branches, including the following:
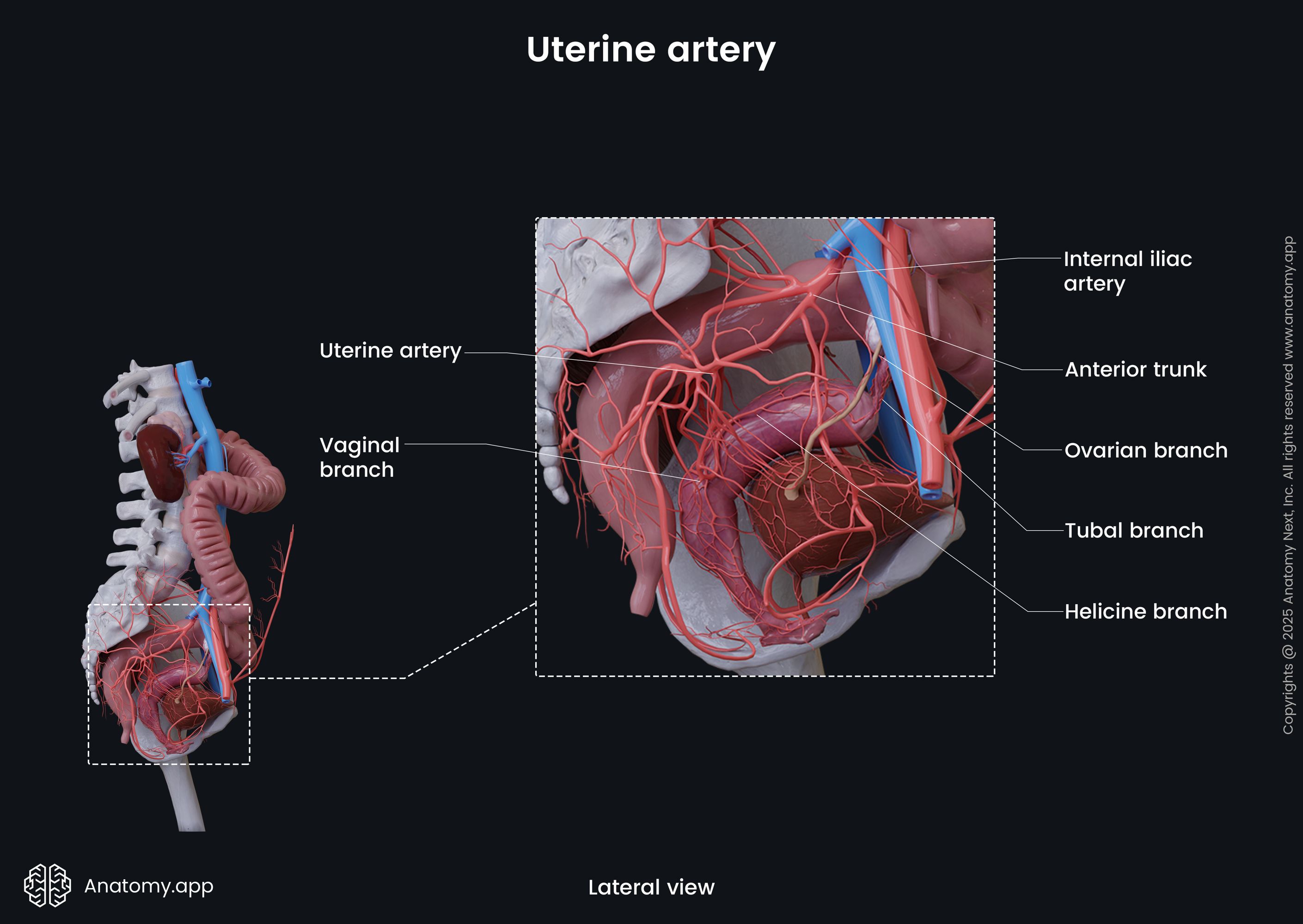
The vaginal artery arises from the uterine artery at the cervix uteri and descends along the lateral wall of the vagina. The ovarian branch of the uterine artery arises at the level of the cornu of the uterus, passes along the ovarian ligament and reach the ovaries to supply them. The tubal branch travels within the mesosalpinx to the Fallopian (uterine) tube.