- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Aorta
- Blood vessels of head and neck
- Blood vessels of upper limb
- Blood vessels of thorax
- Blood vessels of abdomen
- Blood vessels of pelvis and lower limb
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
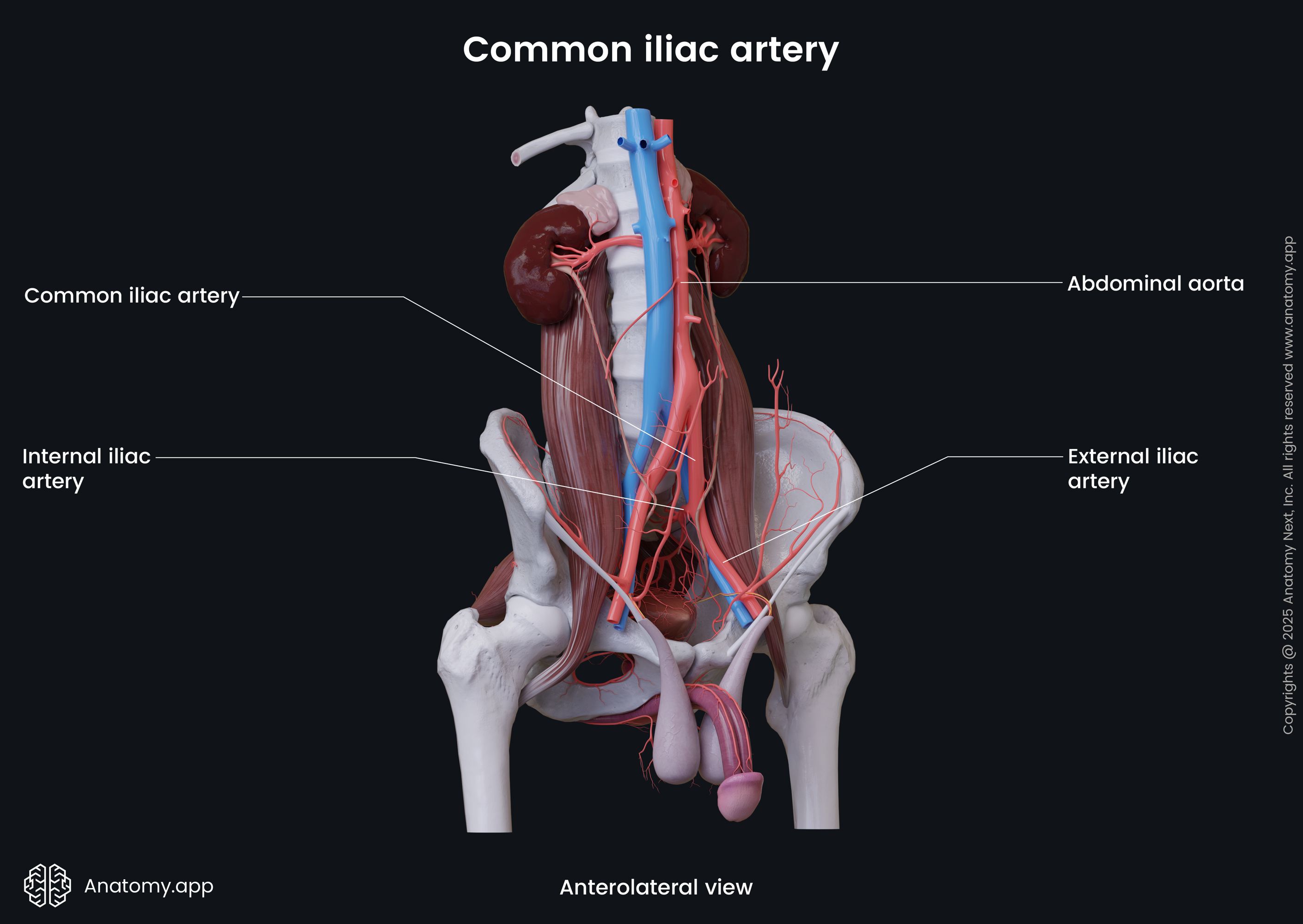
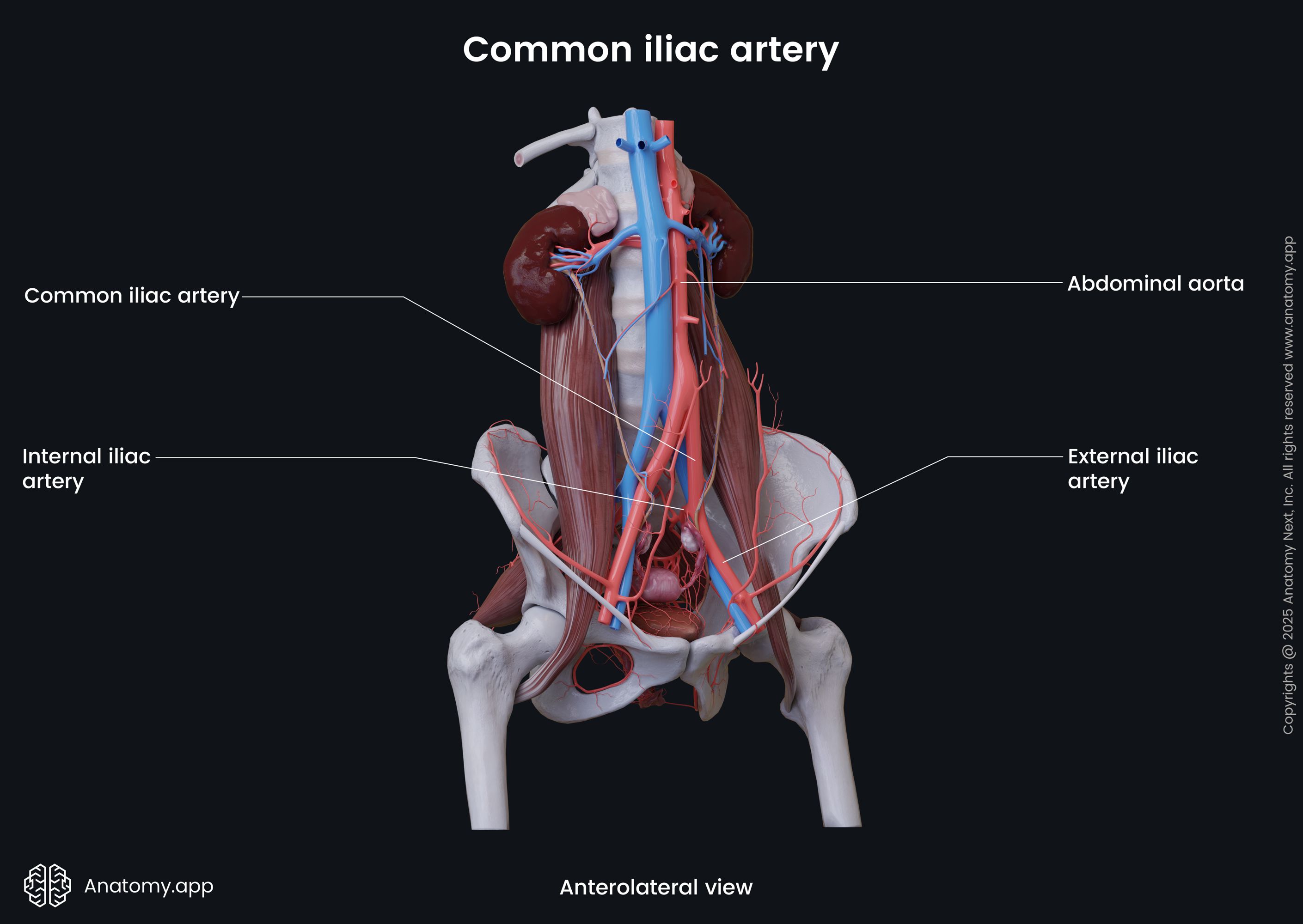
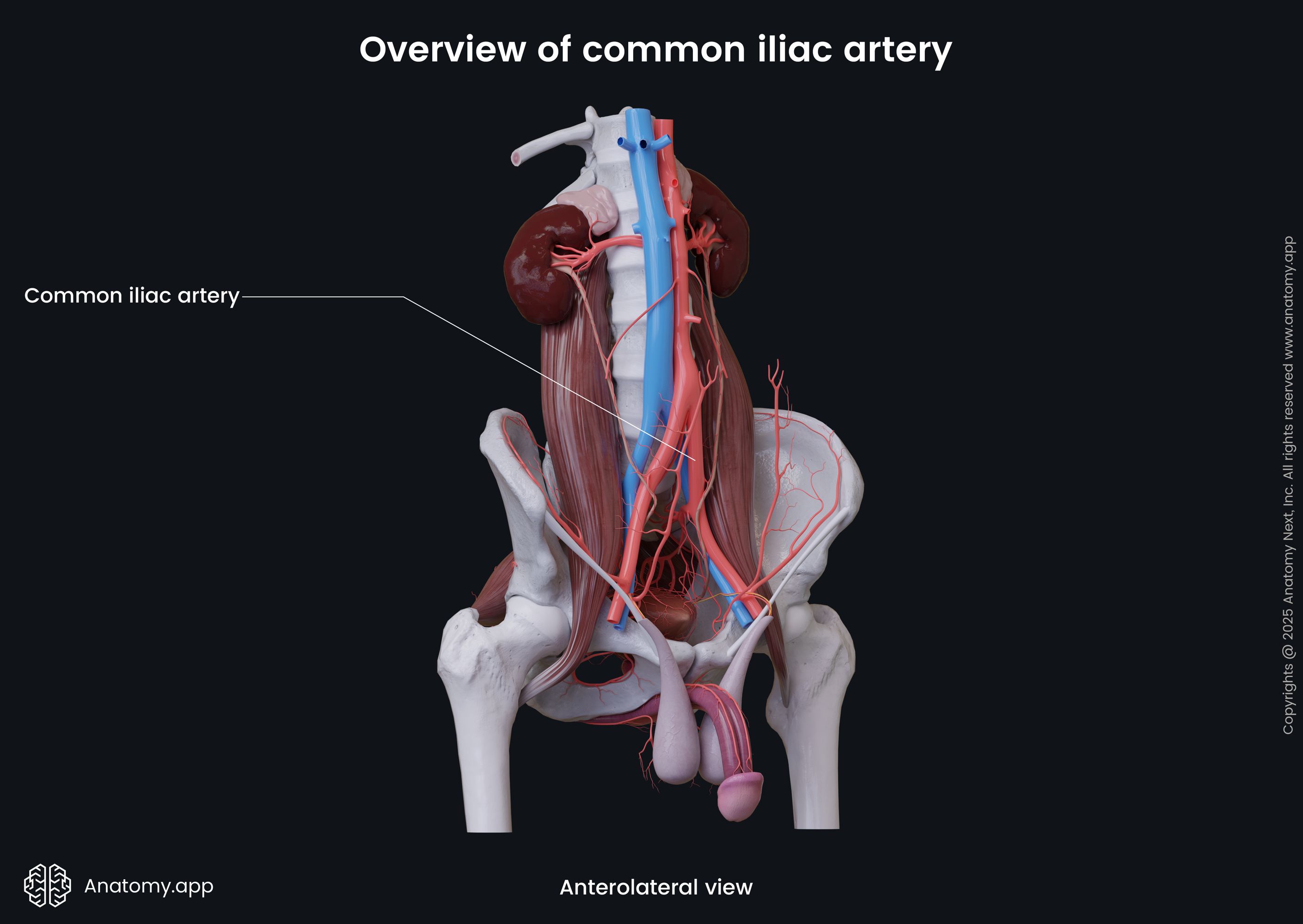
Common iliac artery
The common iliac artery (Latin: arteria iliaca communis) is a paired large elastic artery located on each side of the abdomen in the iliac region. The common iliac arteries arise from the bifurcation of the abdominal aorta, at the level of fourth lumbar vertebra (L4). The artery divides into two large vessels that supply the pelvic region and the lower limb.
Each common iliac artery runs posterolaterally along the medial border of the psoas major muscle. And at the level of the sacroiliac joint this artery divides into two terminal branches: internal iliac artery and external iliac artery. The internal iliac artery supplies the pelvis, while the external iliac artery provides blood supply to the lower extremity. The common iliac artery also gives off small side branches to the peritoneum and surrounding tissues, including the surrounding lymph nodes. On its course, the artery on each side is accompanied by the common iliac vein.