- Anatomical terminology
- Skeletal system
- Joints
- Muscles
- Heart
- Blood vessels
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Aorta
- Blood vessels of head and neck
- Blood vessels of upper limb
- Blood vessels of thorax
- Blood vessels of abdomen
- Blood vessels of pelvis and lower limb
- Blood vessels of systemic circulation
- Lymphatic system
- Nervous system
- Respiratory system
- Digestive system
- Urinary system
- Female reproductive system
- Male reproductive system
- Endocrine glands
- Eye
- Ear
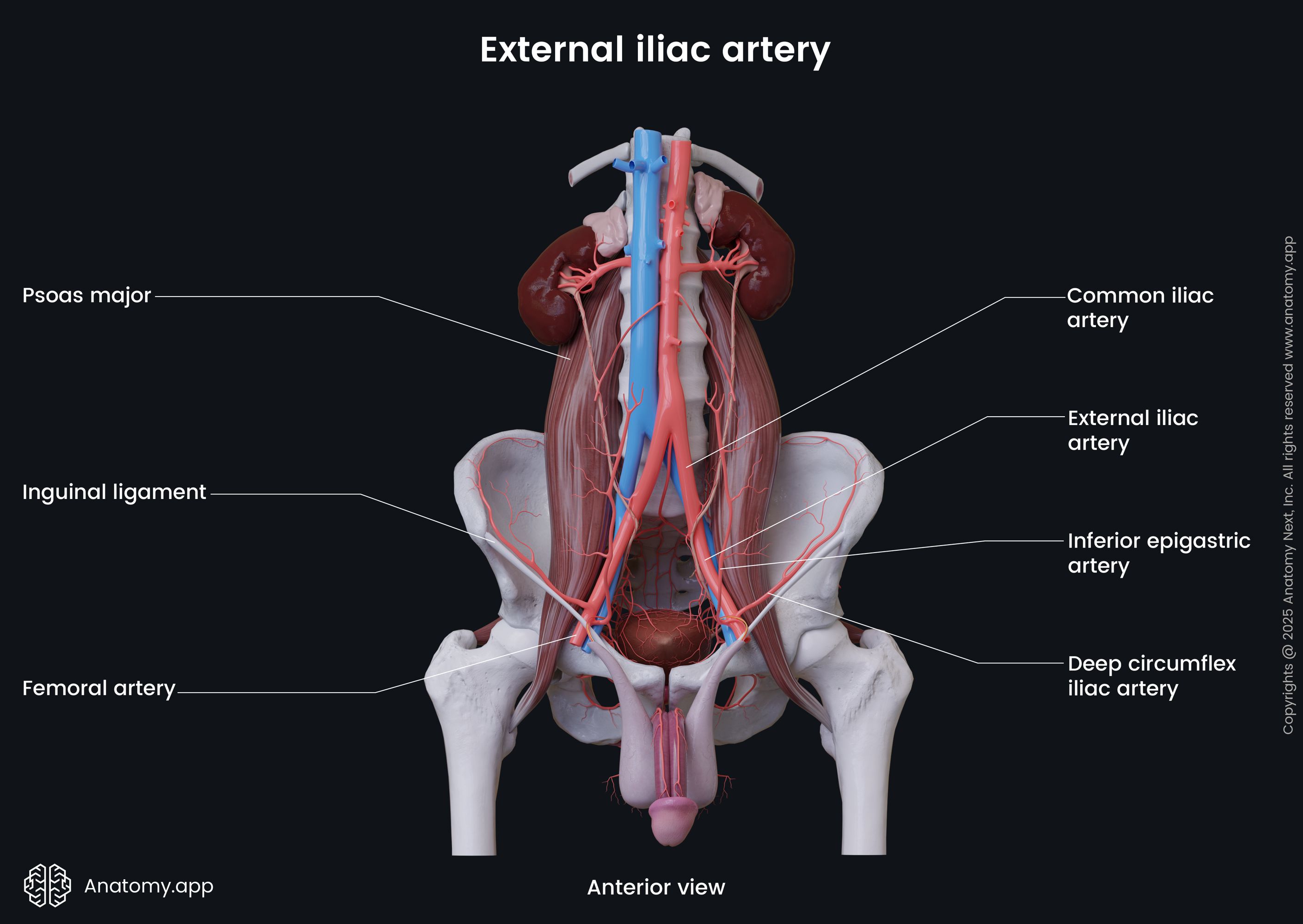
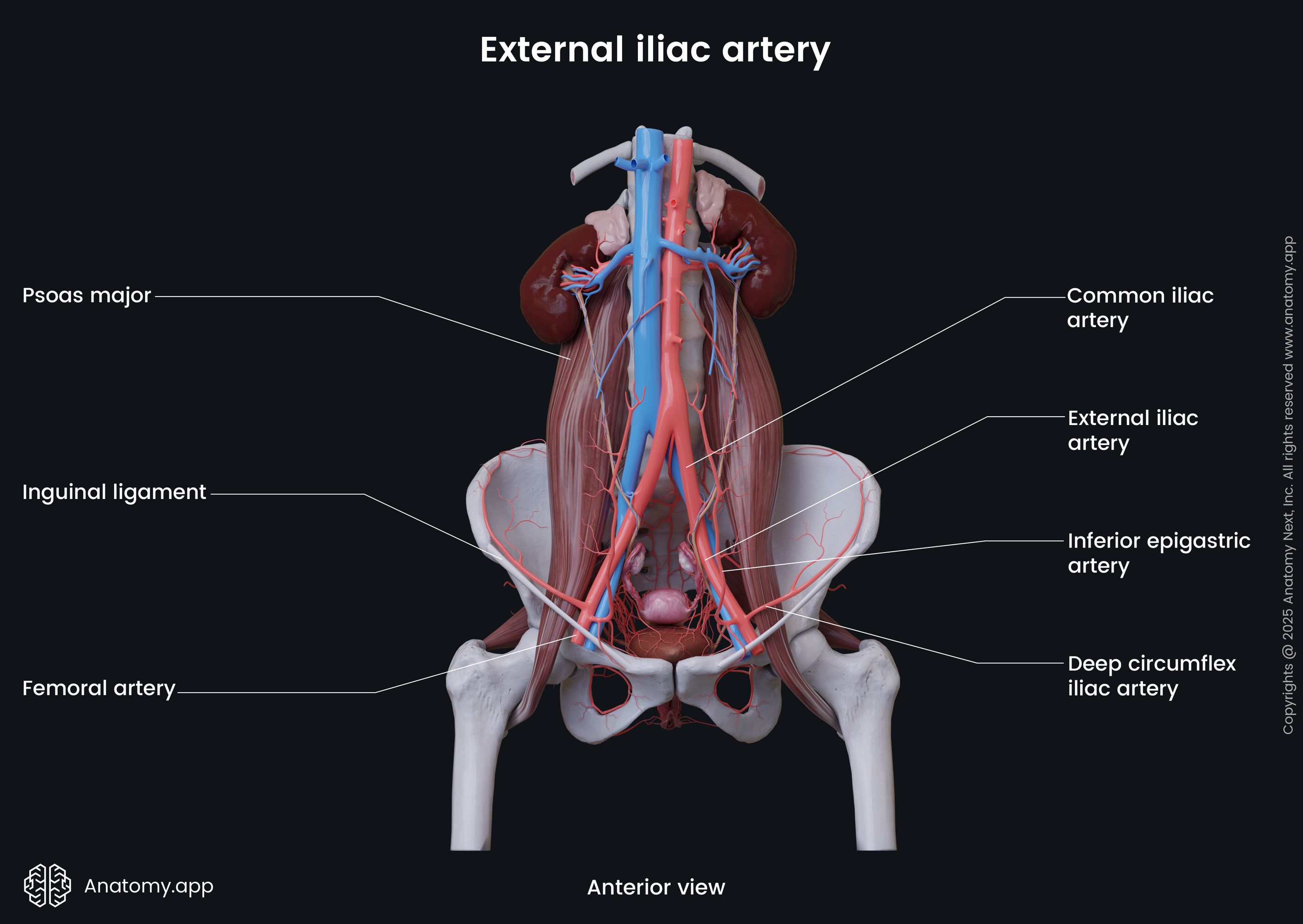
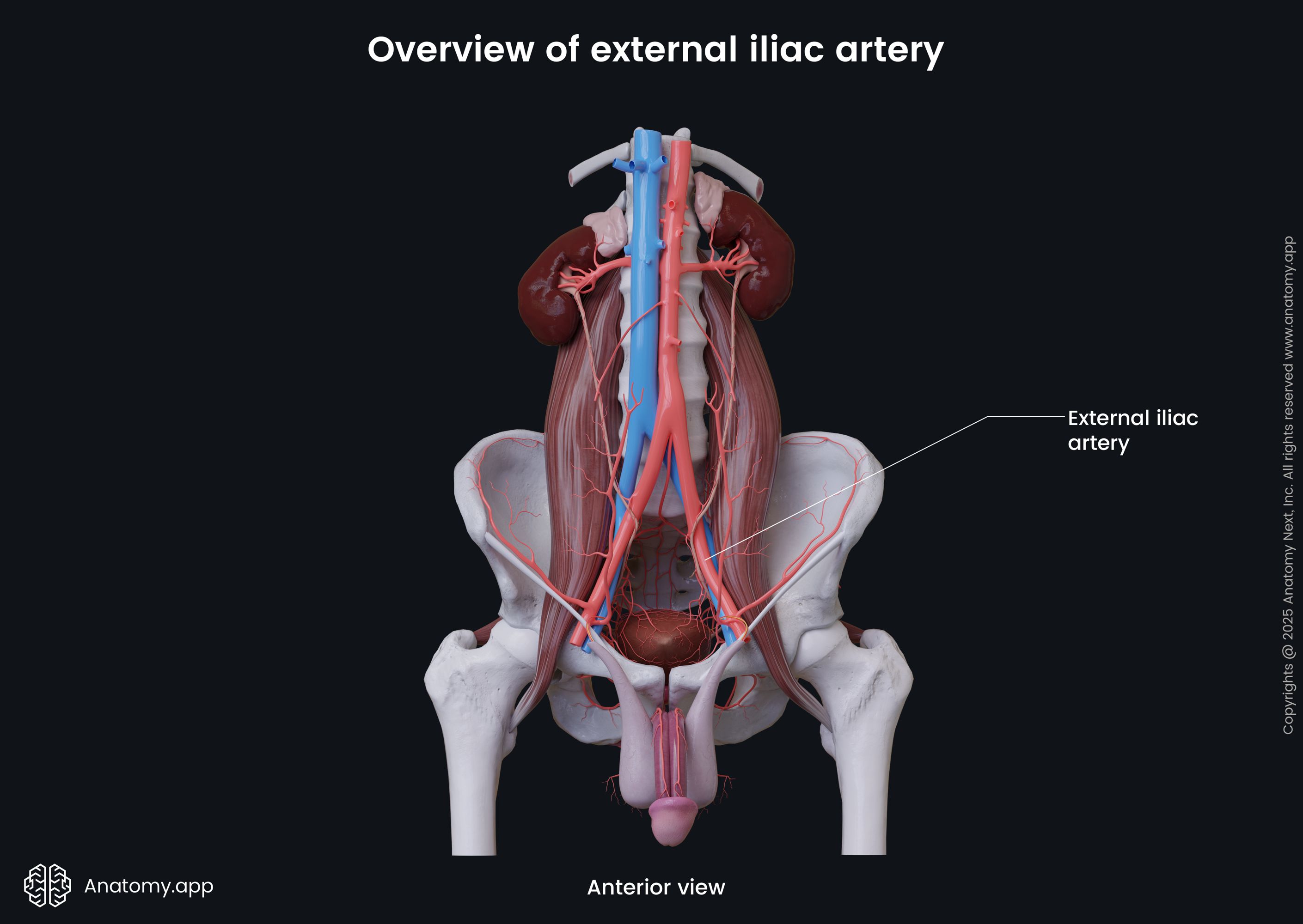
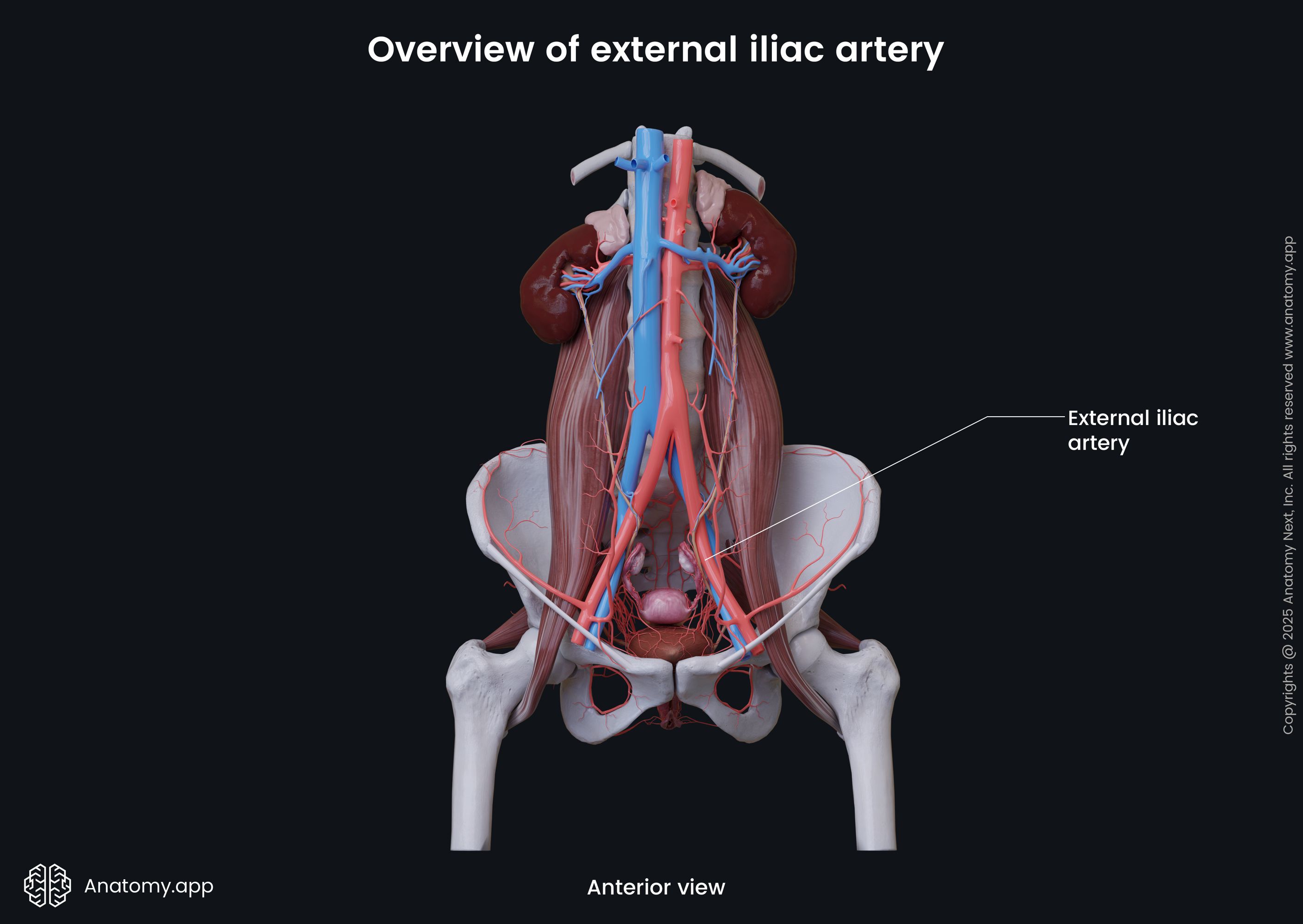
External iliac artery
The external iliac artery (Latin: arteria iliaca externa) is a blood vessel of the pelvis that arises from the common iliac artery after it bifurcates dividing into external and internal iliac arteries. The external iliac arteries are larger than the internal iliac arteries. Branches of the external iliac artery supply blood to the muscles and skin of the lower abdominal wall. Its terminal branch, the femoral artery, descends and provides blood supply to the lower limb.
The external iliac artery runs inferiorly and laterally along the medial border of the psoas major muscle, and at the middle of the inguinal ligament leaves the pelvic cavity via the vascular lacuna. Further, the artery continues as the femoral artery. Thus, the external iliac artery is principally an artery of the lower limb. On its course, it typically gives off only two branches that arise above the inguinal ligament. These are the inferior epigastric artery, and the deep circumflex artery.